My Photo-See camera, developing tank and instruction manual.
Almost 20 years before Dr. Land and Polaroid made instant photography world famous, a camera called the Photo-See was introduced in 1936. This company brought a very short-lived and straightforward box camera, along with a pocket-sized developing tank, to the market. These two items enable the photographer to take a photo and develop it without needing to send the film to be processed and printed.
I don't remember when I purchased the Photo-See camera. I know it was well over 20 years ago. When I bought the photo see cameras, there were at least two, possibly three, of the same camera purchased in a lot of cameras purchased.
Several years ago, I recall selling one or two of the cameras on eBay. It wasn't until recently that I understood that there are two parts to this camera. The camera itself, and the developing tank in which the film for the camera was placed and processed.
Initially, I thought the developing tank fit onto the back of the camera, but I was wrong. The developing tank is actually a separate part that the film from the photo camera fits into, allowing the photographer to process the film at any time they want to. The idea was that the photographer could take the photo, then have the print ready within a few minutes.
The History:
The Photo-See camera was the brainchild of Herman Casler, who was born in 1867 in Sandwich, IL, and raised in Fort Plain, NY. Over his lifetime, Casler invented and patented several different products and was also a partner in K.M.C.D. Syndicate, this was along with W.K.-L. Dickson, Elias Koopman, and Henry N. "Harry" Marvin.
American Mutoscope and Biograph Founders, 1895. Casler upper right.
Casler, Dickson, and Marvin collaborated in 1893 on a detective camera, the size of a watch, called the Photoret. The Photoret was a watch based on a pocket watch, similar to the Expo camera.
Casler started his career as a Draftsman for General Electric Co., designing electric rock drills. He became the superintendent of Marvin Drill Company in 1895, which Harry Marvin owned.
Casler, following Dickson's proposal, invented the Mutoscope, which displayed short films through flip-cards rotated by a hand crank that could be slowed down or sped up at the operator's will by turning the crank faster or slower. The prototype of the Mutograph camera was completed in November 1894, first tested with film in June 1895, and the first official Mutoscope films were made in August 1895.
Patent for Photo-See camera
Marvin & Casler Co. was formed in 1896, where they manufactured the Mutoscope, which was very popular in nickelodeons during this time. The Mutoscope and Thomas Edison's Kinetoscope are the beginning of the motion picture business as we know it.
His work in inventing motion picture cameras, projectors, and other motion picture equipment extended well beyond the 1920s, where he helped develop a more miniature hand-cranked motion picture camera and a three-pronged shutter that helped reduce flicker during projection.
Herman Casler is also the inventor of the Photo-See camera, which was patented in 1937. The company was short-lived, as Casler passed away in 1939, and I don't see production of the camera continuing much after his death.
The Camera & Developing Tank:
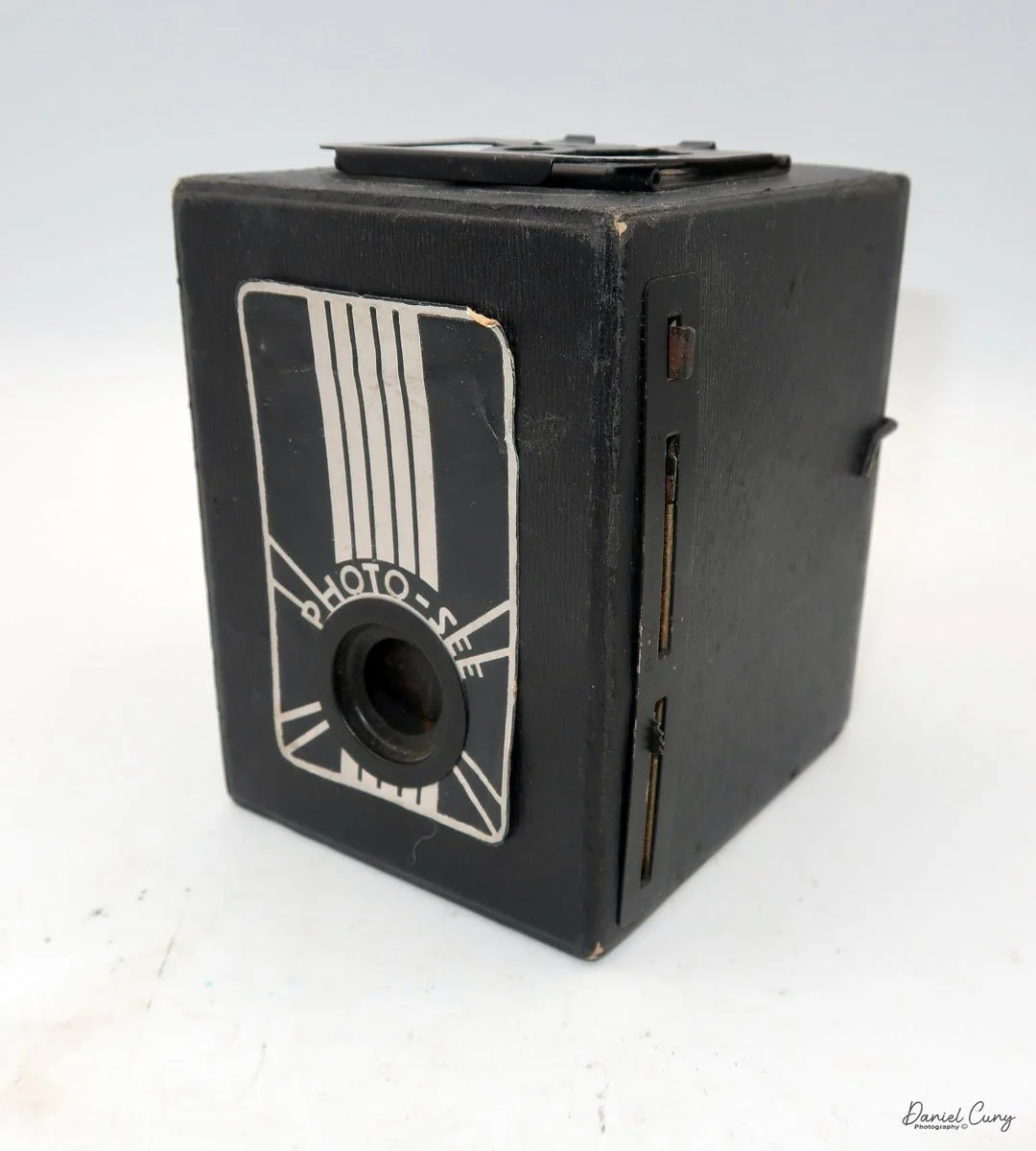
The Photo-See camera is a straightforward box camera design with a few differences, which I'll explain. The camera is 4" tall by 3 "wide by 4.5" deep, including the focusing device, and weighs 12.3 ounces.
The front of the camera features a distinctive Art Deco design, which is enhanced by a sticker applied to the front of the camera. The camera is made from a thicker cardboard material, featuring a two-part, fold-up viewfinder on top. It's said the viewfinder is put on backwards, but that's not the case, as I find it to work better than the other way.
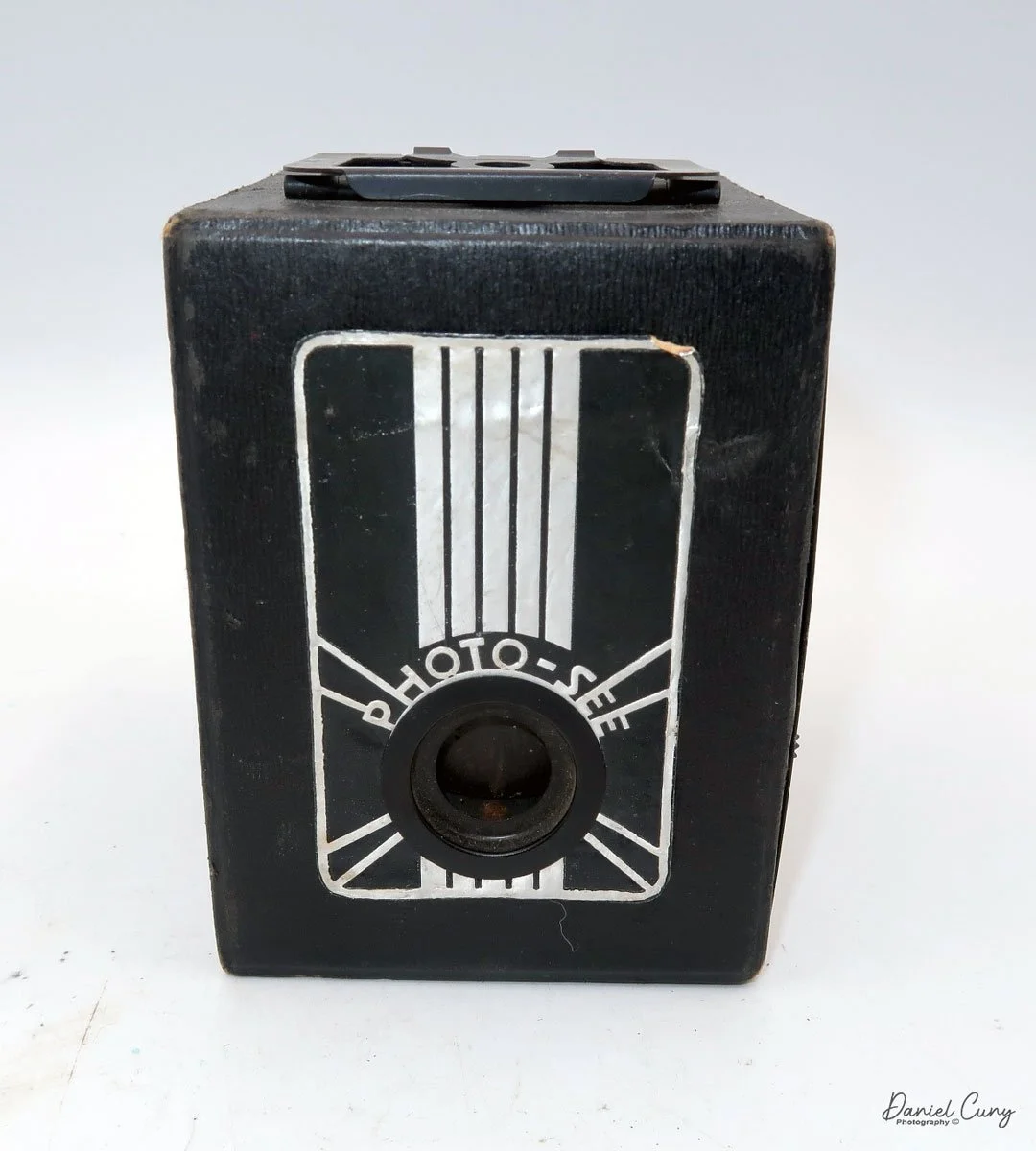
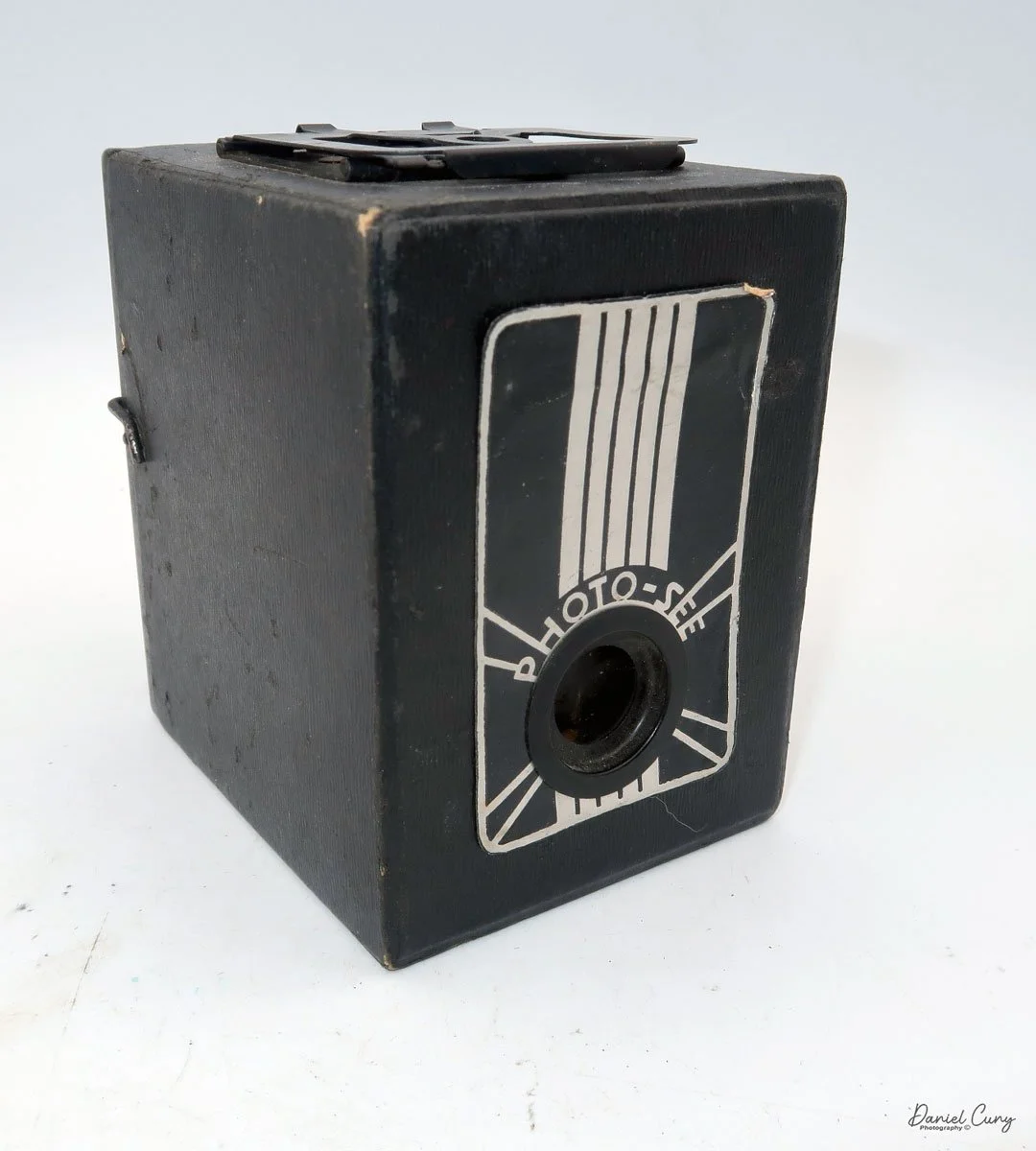
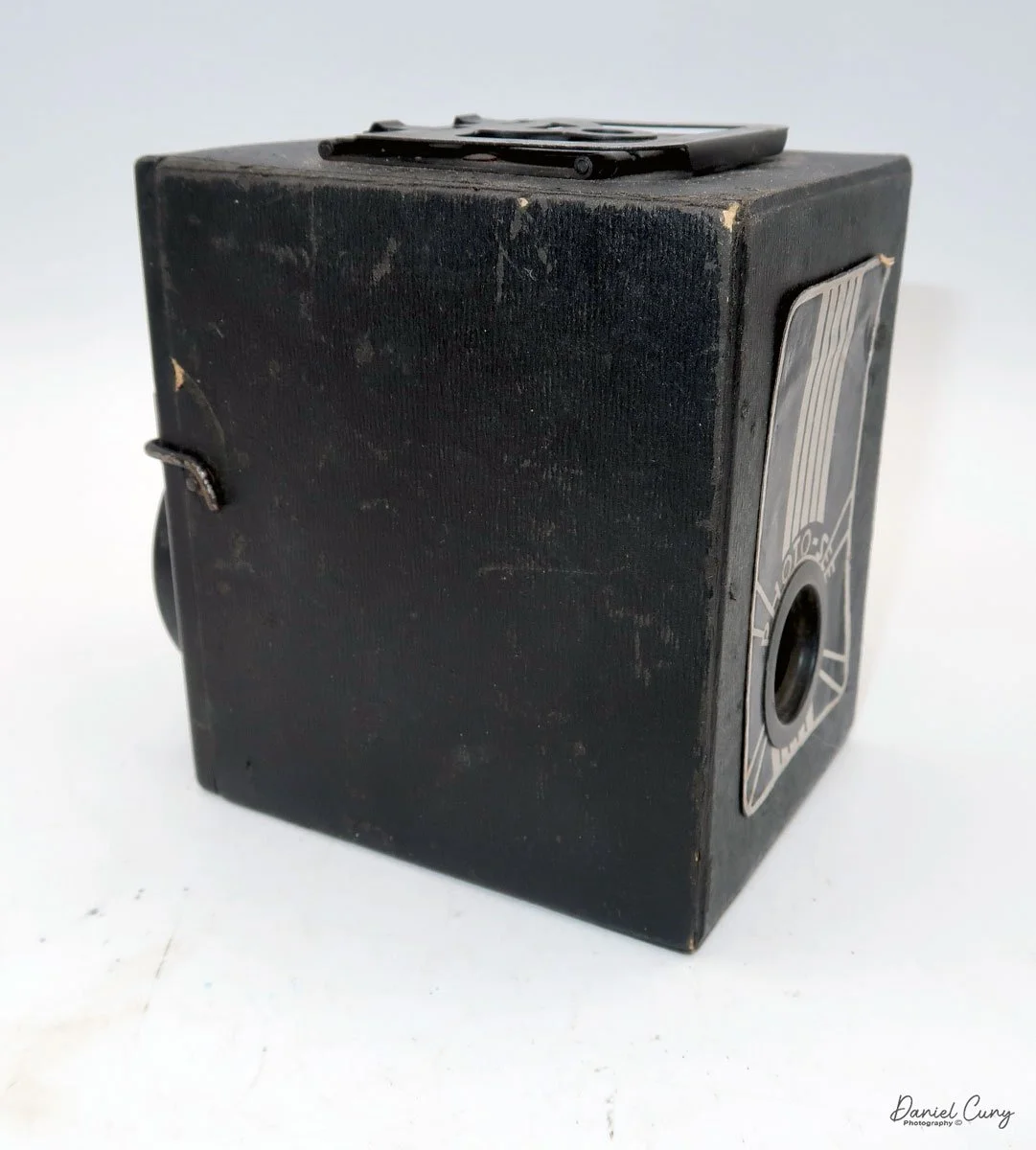
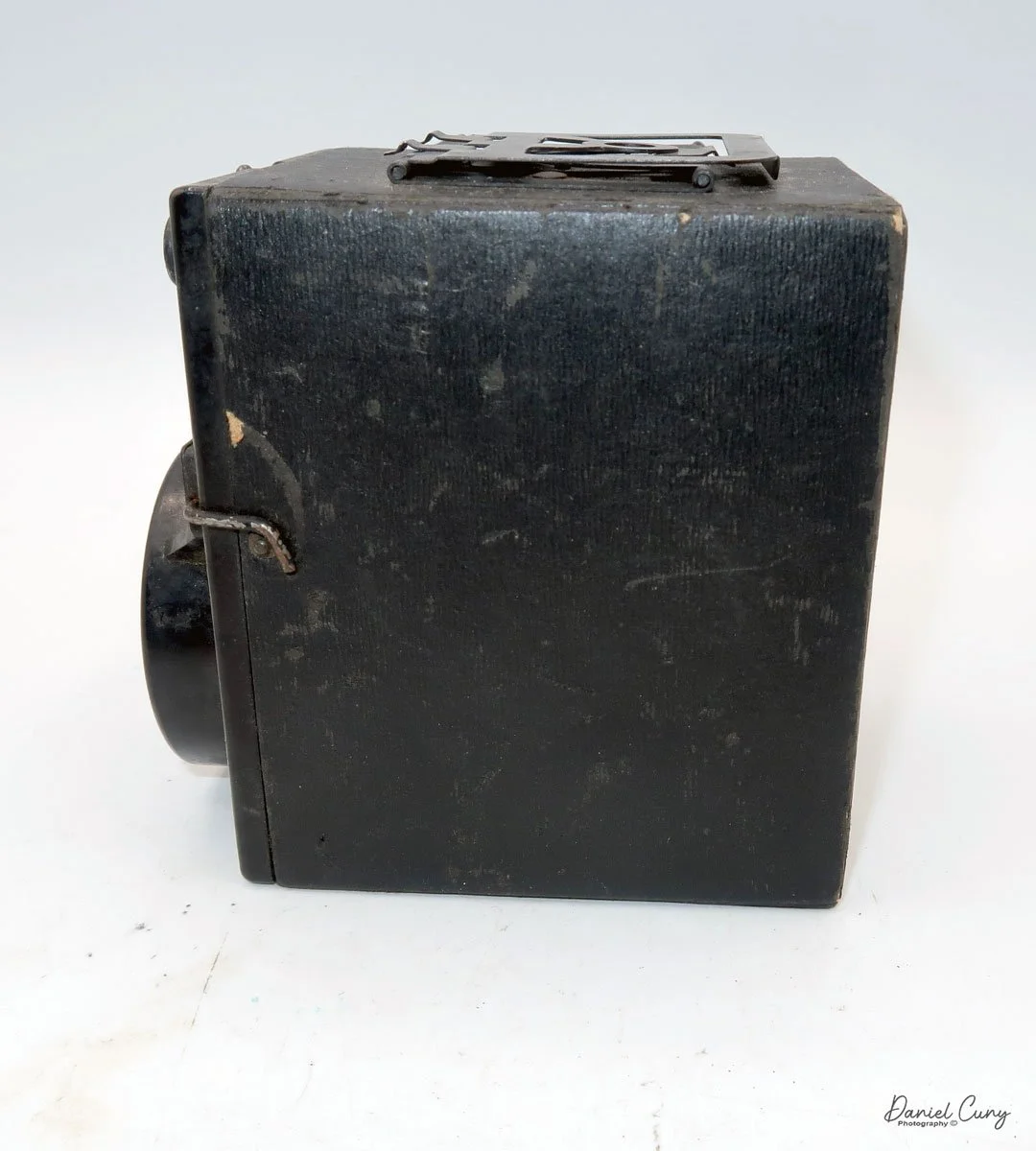
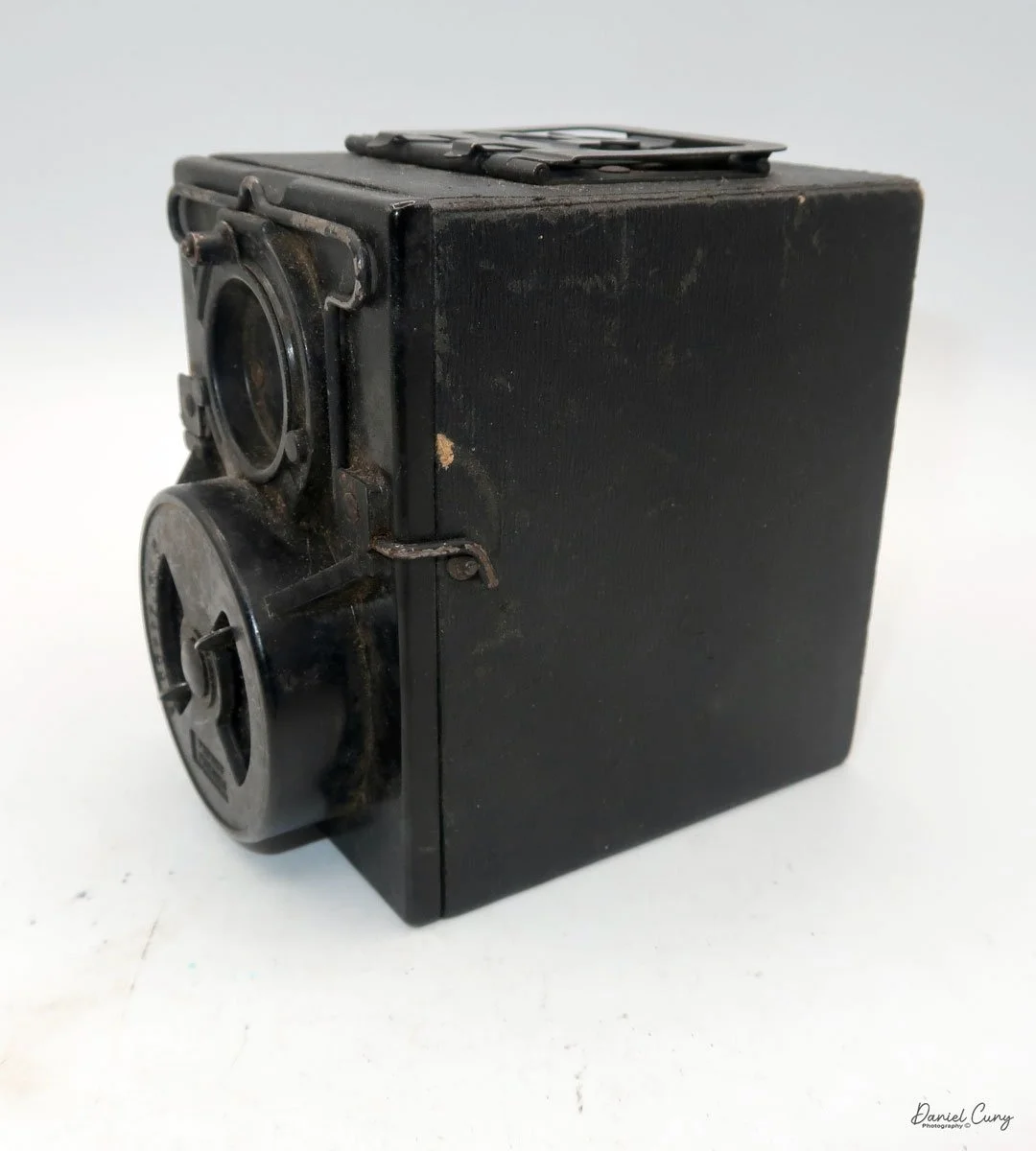
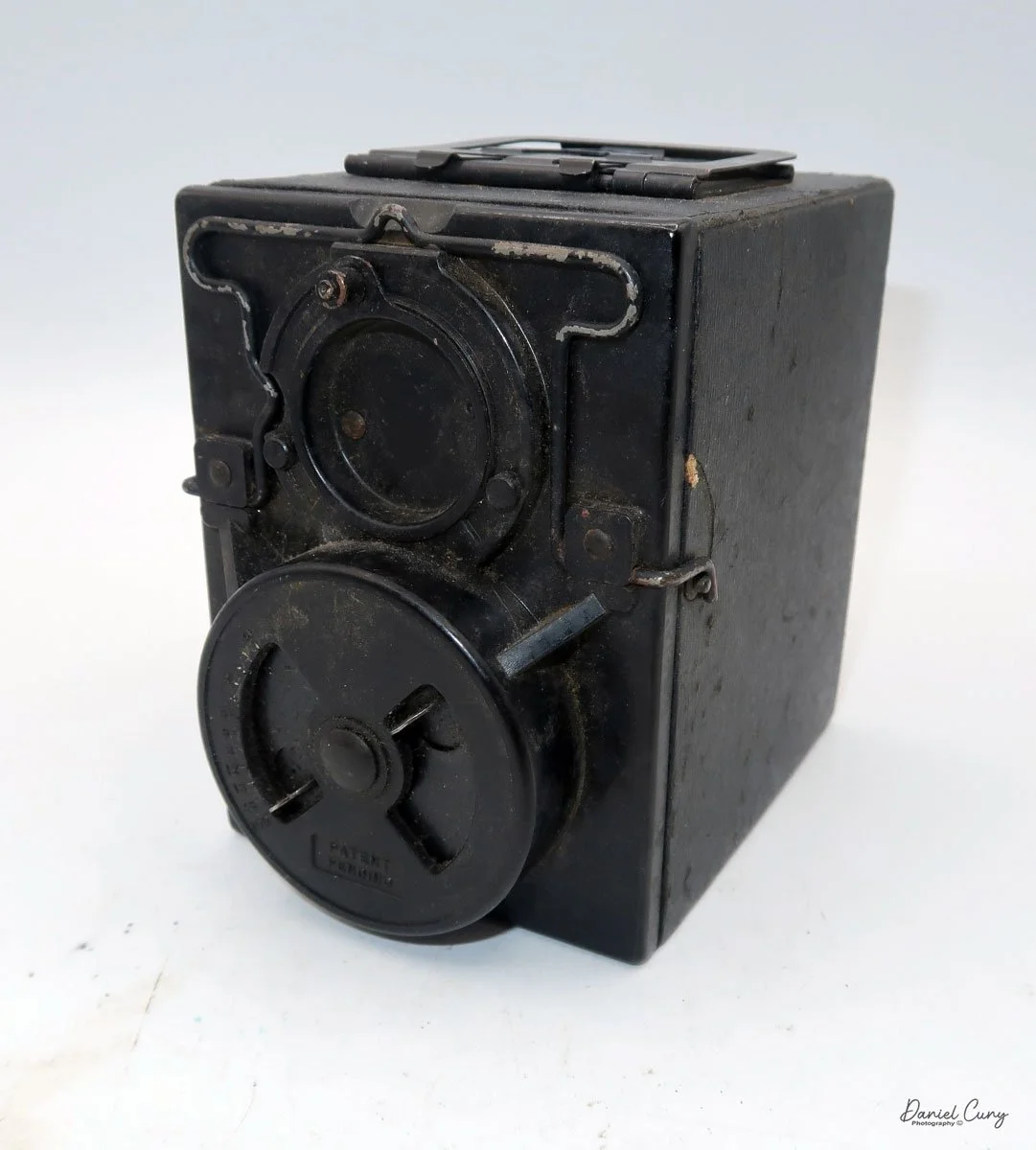
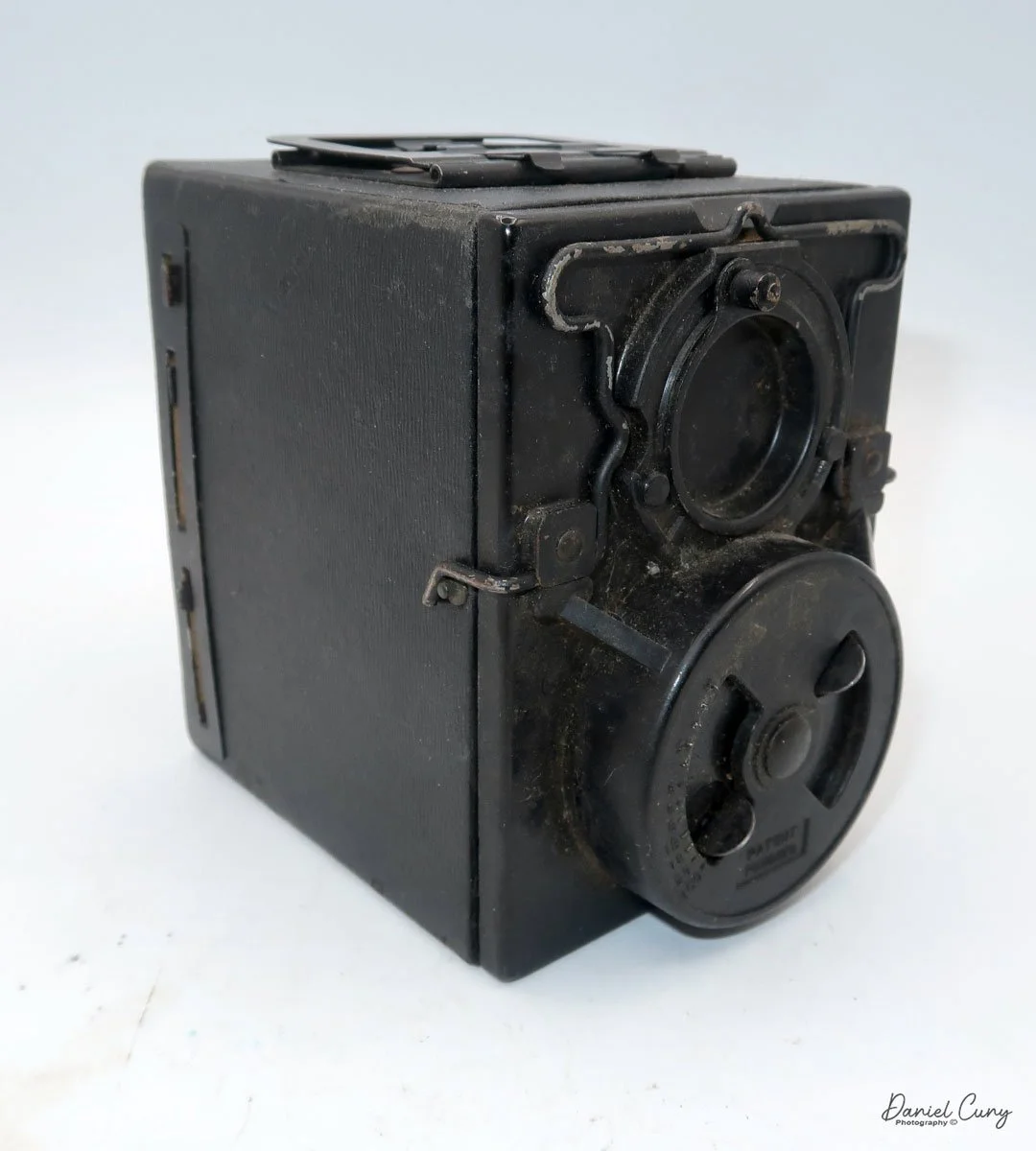
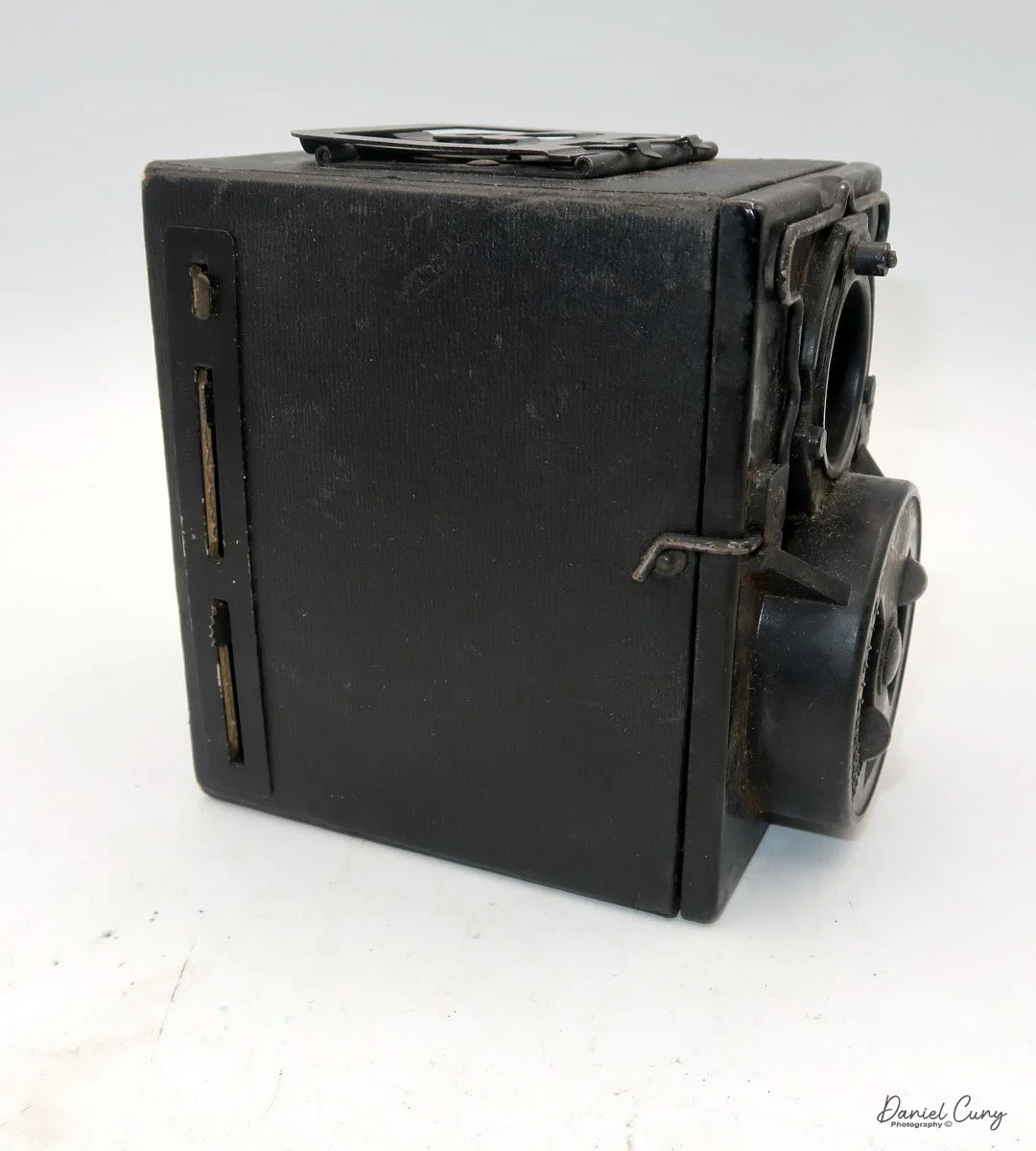
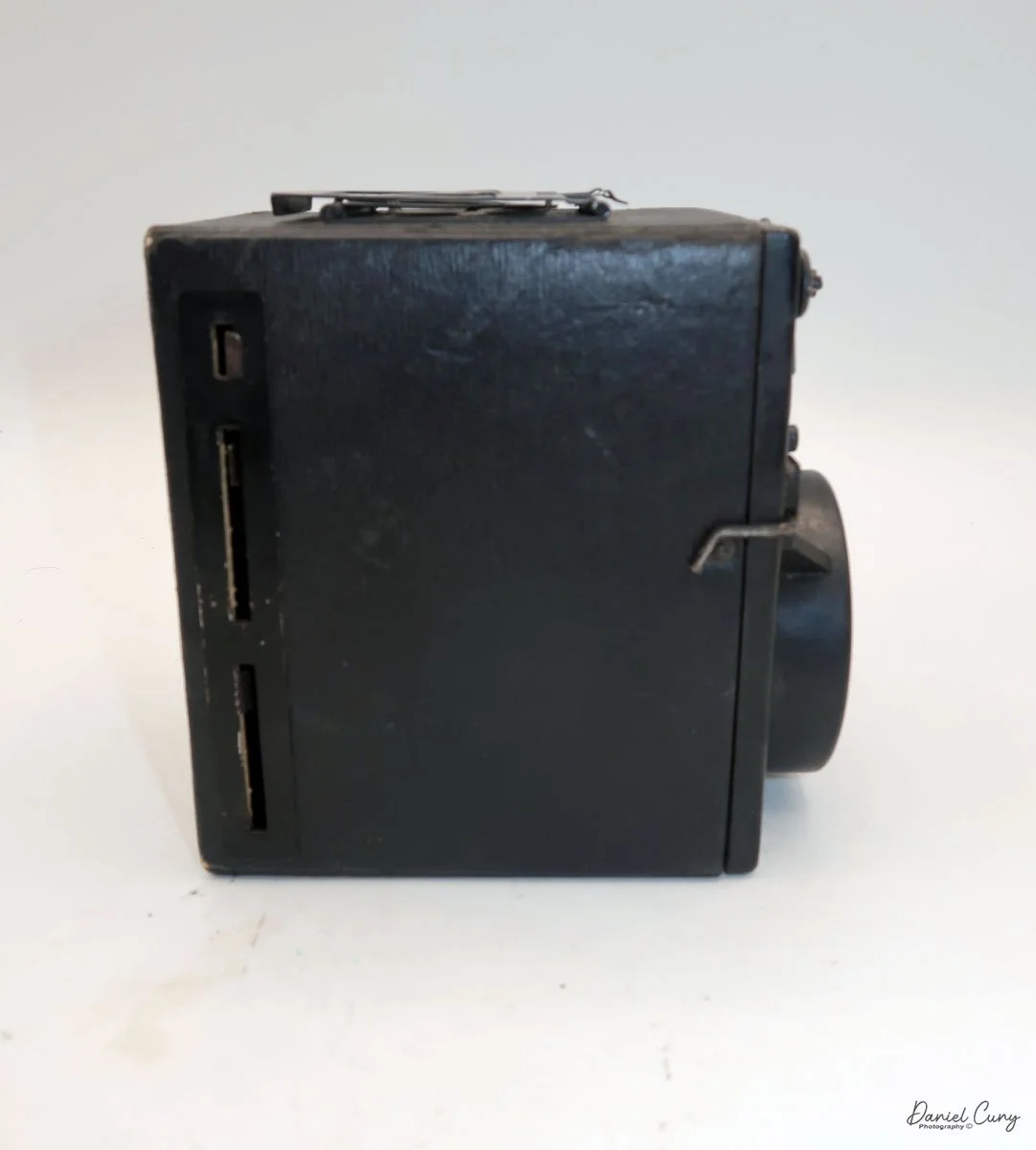
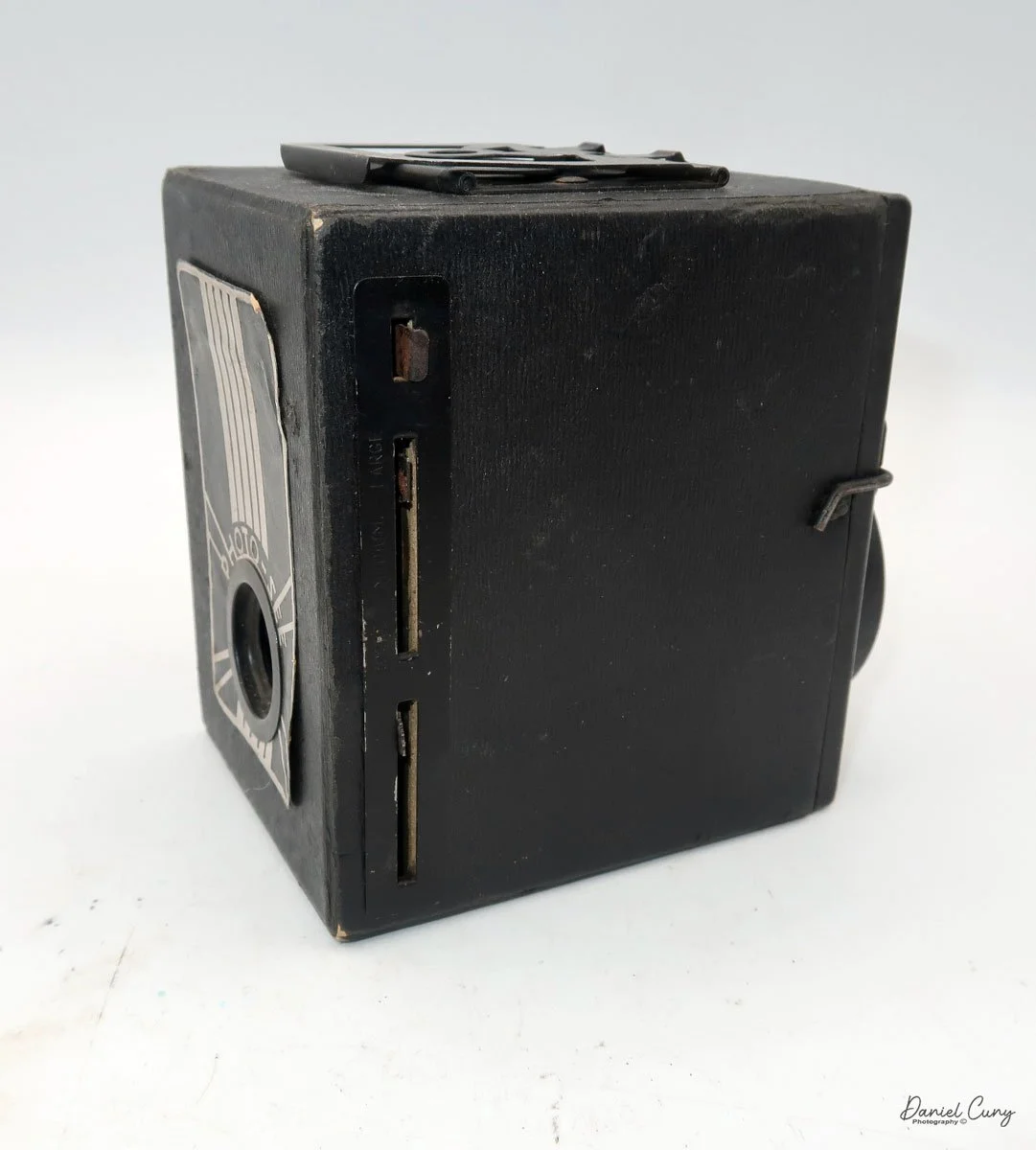












On the left side of the camera are three controls; on top is the shutter control. When the bar is "in," the camera takes a regular snapshot, and when it's "out", the shutter stays open for a more prolonged exposure. This is similar to other box cameras from the same time period. The middle slider controls the aperture setting. They are Small, Medium, and Large. The bottom lever is the shutter release.
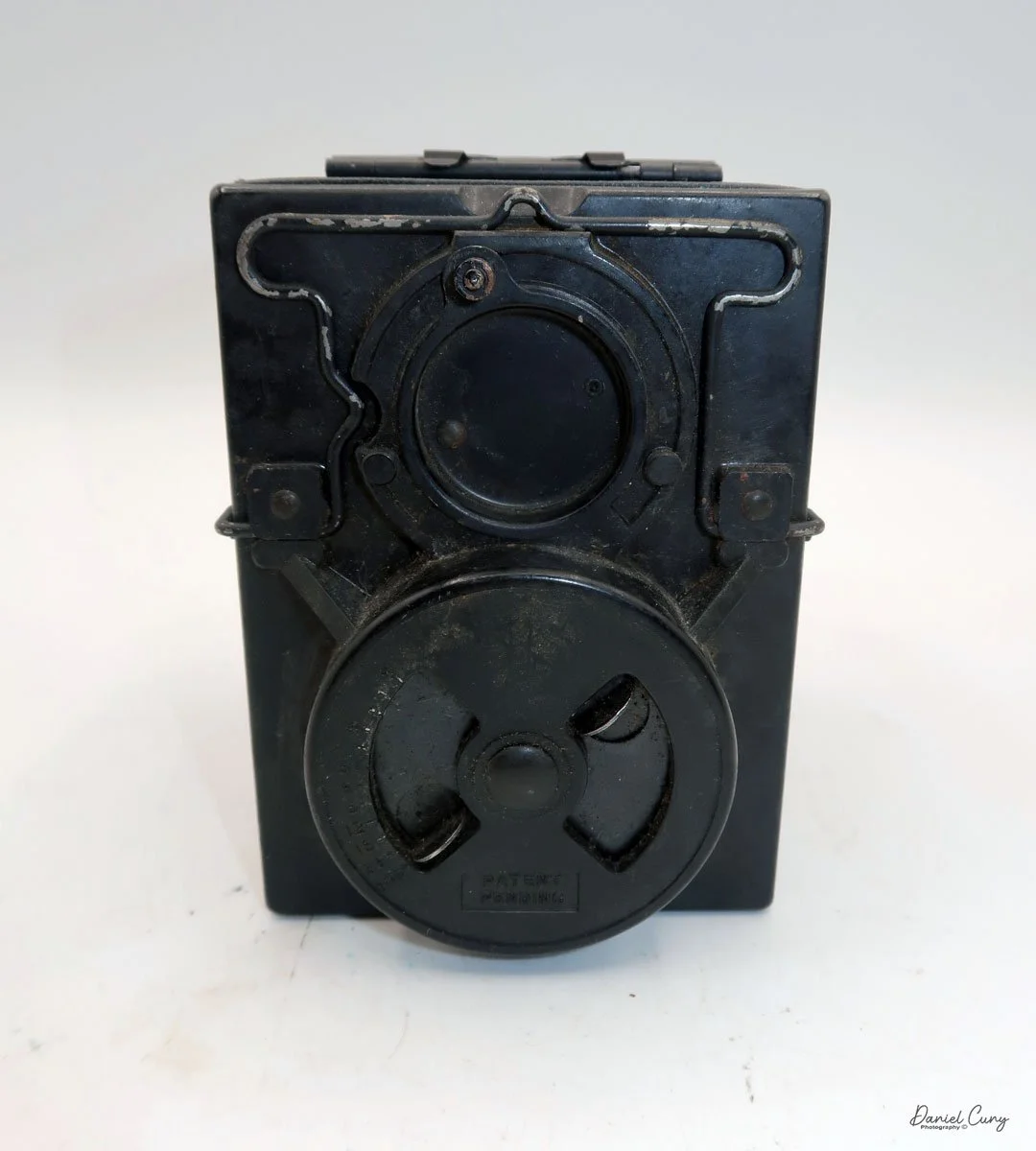
On the back of the camera, there are three main controls. The bar at the top is pulled down to remove the film from the camera. The smaller round disk on top is turned from the 3:00 to the 9:00 position to expose the film when you're ready to take a photograph. Then the disk is in the 9:00 position, which also locks the top bar, so you cannot take the back off when the film is ready to be exposed. Under the small disk is a larger disk, known as the focusing disk, which is turned to the desired distance from your subject. This is achieved by adjusting the internal focus of the film, moving it back, in, or out, which enables the film to shift its focus from 3 feet to infinity.
When you remove the film back and look inside, you'll see that it's spring-loaded, where you would load the film pack into the camera. The motion of the smaller disk on the outside of the back moved a pin on the inside up and down, which would open a dark slide, allowing light to hit the film once the shutter release was flipped. Moving the disk back to the original position closes the dark slide.
The Photo-See camera, when used in the vertical position, takes a horizontal image, and to take a vertical photo, you turn the camera to the horizontal position. Very similar to how half-frame cameras work.
The Developing tank is 4.5" long by 3.75" wide by 2.5" deep, and weighs 9.4 ounces. The tank is composed of two parts and held together by a locking arm and a clip that wraps around the tank. Unlocking the arm swings the bar out of the way. On the back side are two spring-loaded clips that need to be squeezed to disassemble the tank.
Once apart, you slide the locking lever away and turn the disk on the tank to the "up" position. This allows the film to be loaded into the tank. Put the back onto the tank, and turn the disk to the "down position, which exposes the film to the chemicals. Once the film is in the tank, you assemble the two pieces and lock them together to initiate the processing.
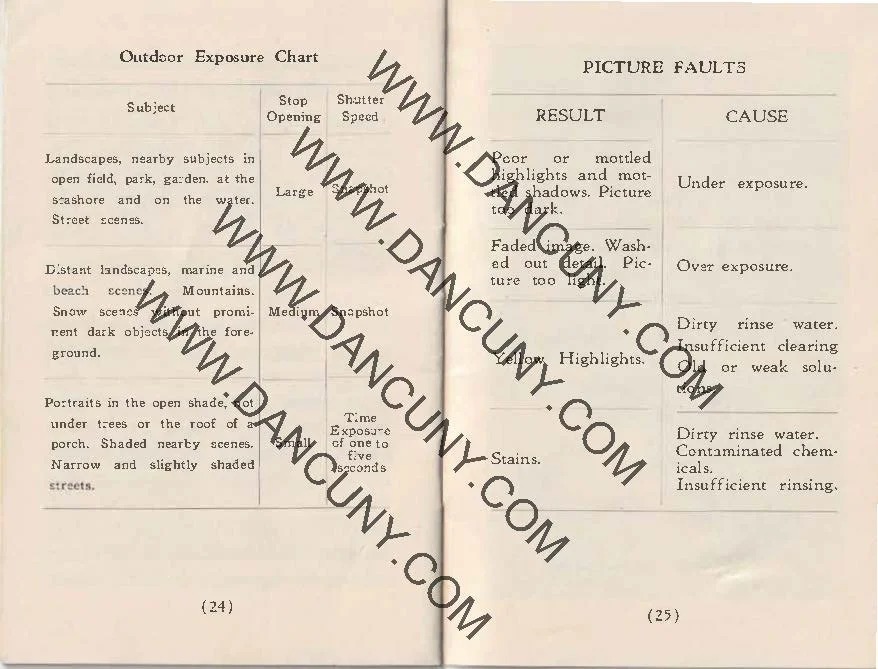
According to the manual, four bottles and four packets of chemicals are needed for developing your image. #1 is the developer, #2 is the bleacher, #3 is the clearer, and #4 is the toner. Pour the packets into the numbered bottles, fill them with water, and mix. Pour the contents into the larger opening for developing. This camera produces photos and not negatives. Once developed, the final image size is 1 11/16 x 1 1/8 inches.















Results:
Unfortunately, the film for this camera isn't available, so I have no images to show from it. Heck, I've been looking for film for this for many years and have not seen one for sale anywhere.
Conclusion:
This camera is such an oddball, I couldn't resist writing about it, especially since it was many years ahead of its time. I understand that the process is lengthy, that you need to carry chemicals, and that the image size is small. These factors were the reason why this didn't gain popularity.
It's nice to have an almost complete system in the collection. A film pack and the box would be nice, but having the camera, developing tank, and manual is good.
Thank you for taking a few minutes to read about this odd and unusual camera from almost 90 years ago.
Click on the link to see my other camera reviews.
Cuny's Camera & Photo is my eBay store, where I sell some of the cameras I've reviewed, along with other camera-related items.
Until next week, please be safe.






















































