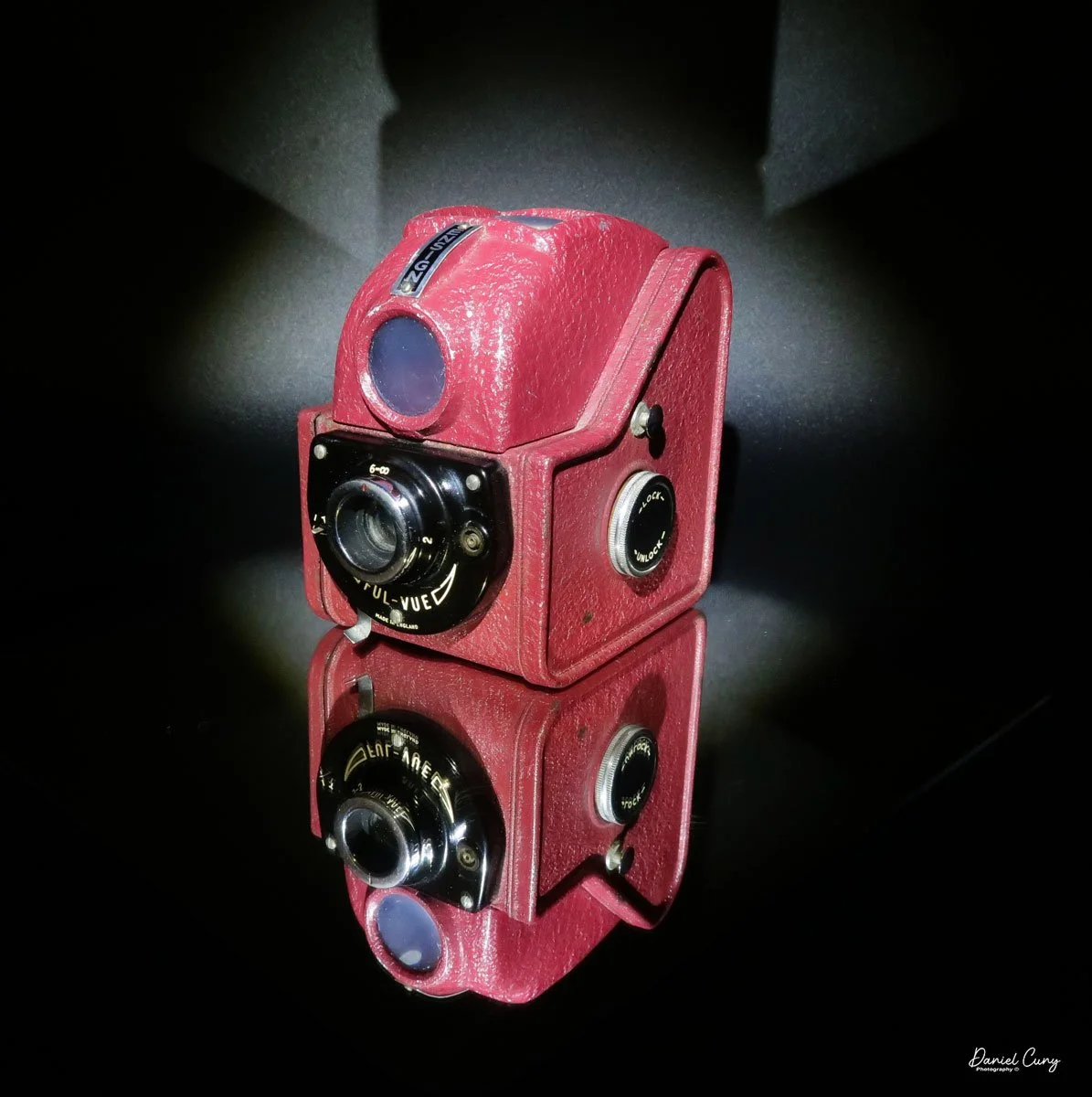
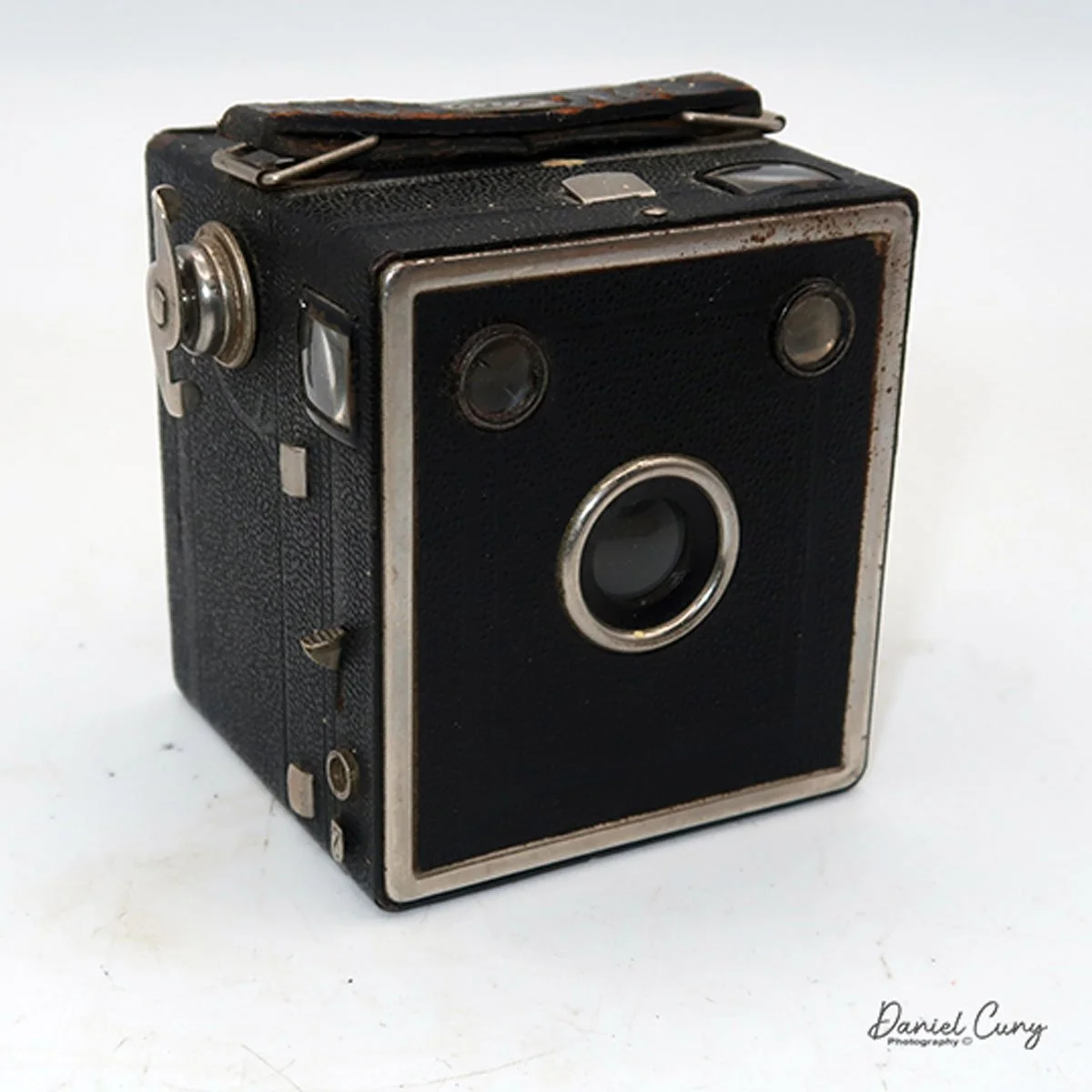
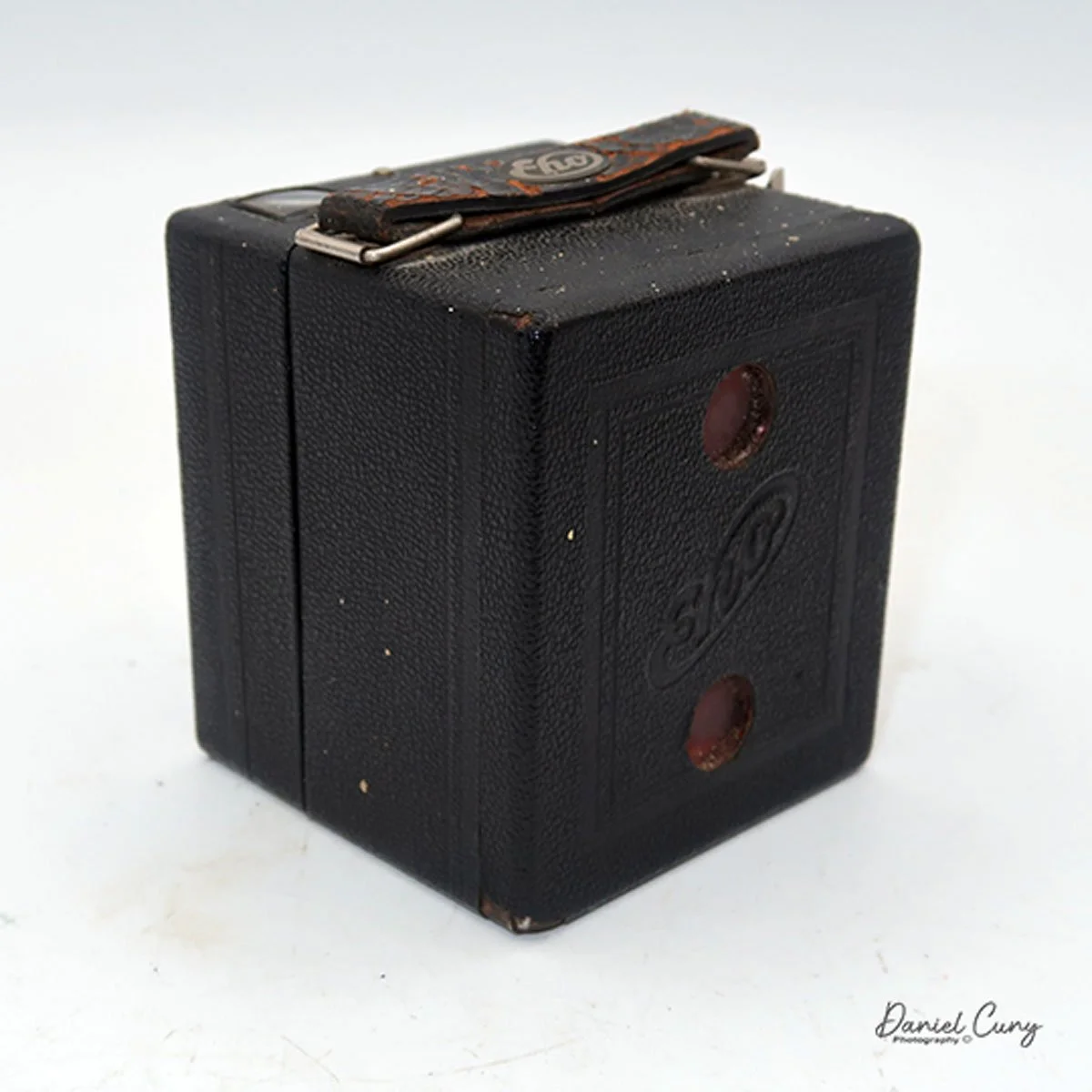
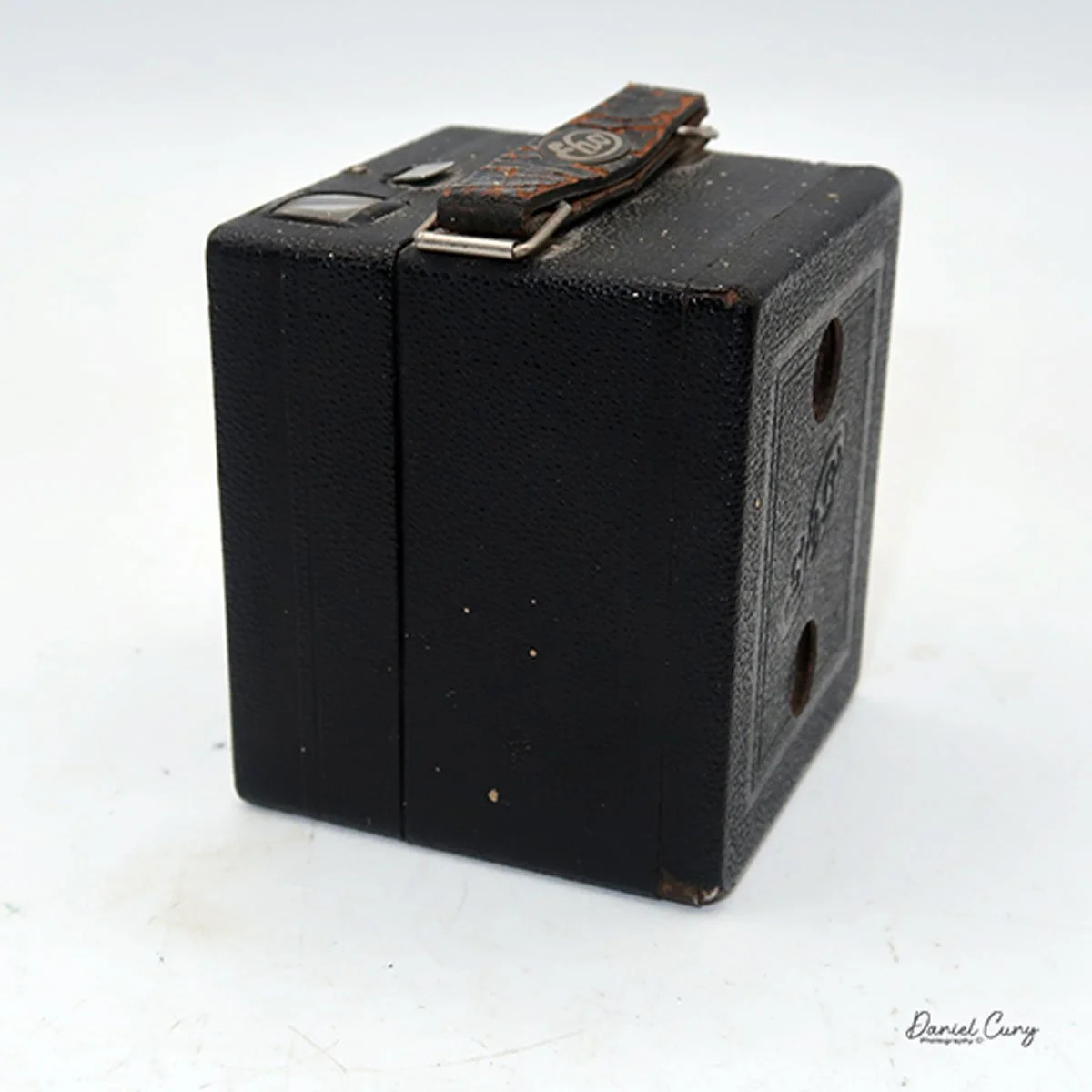
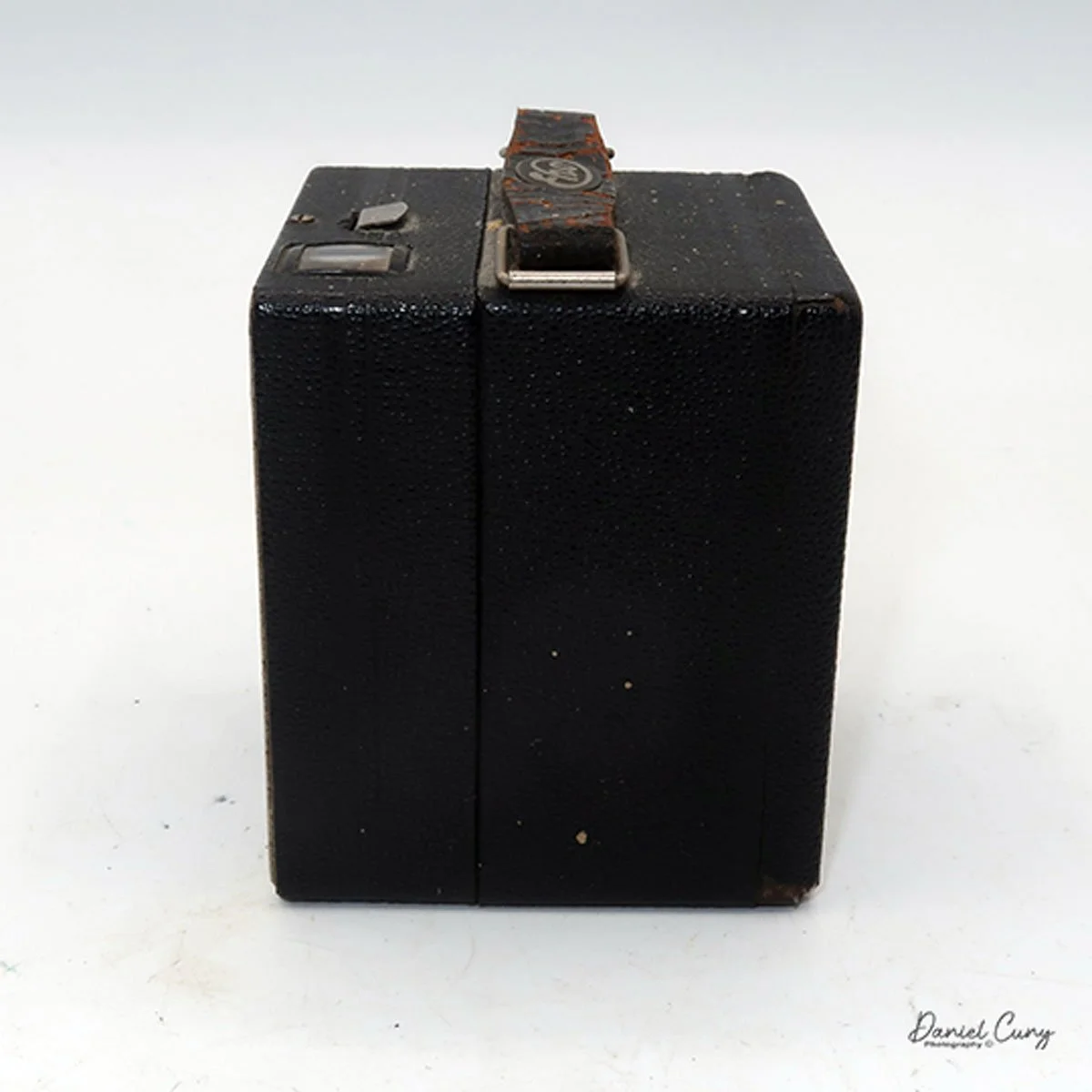
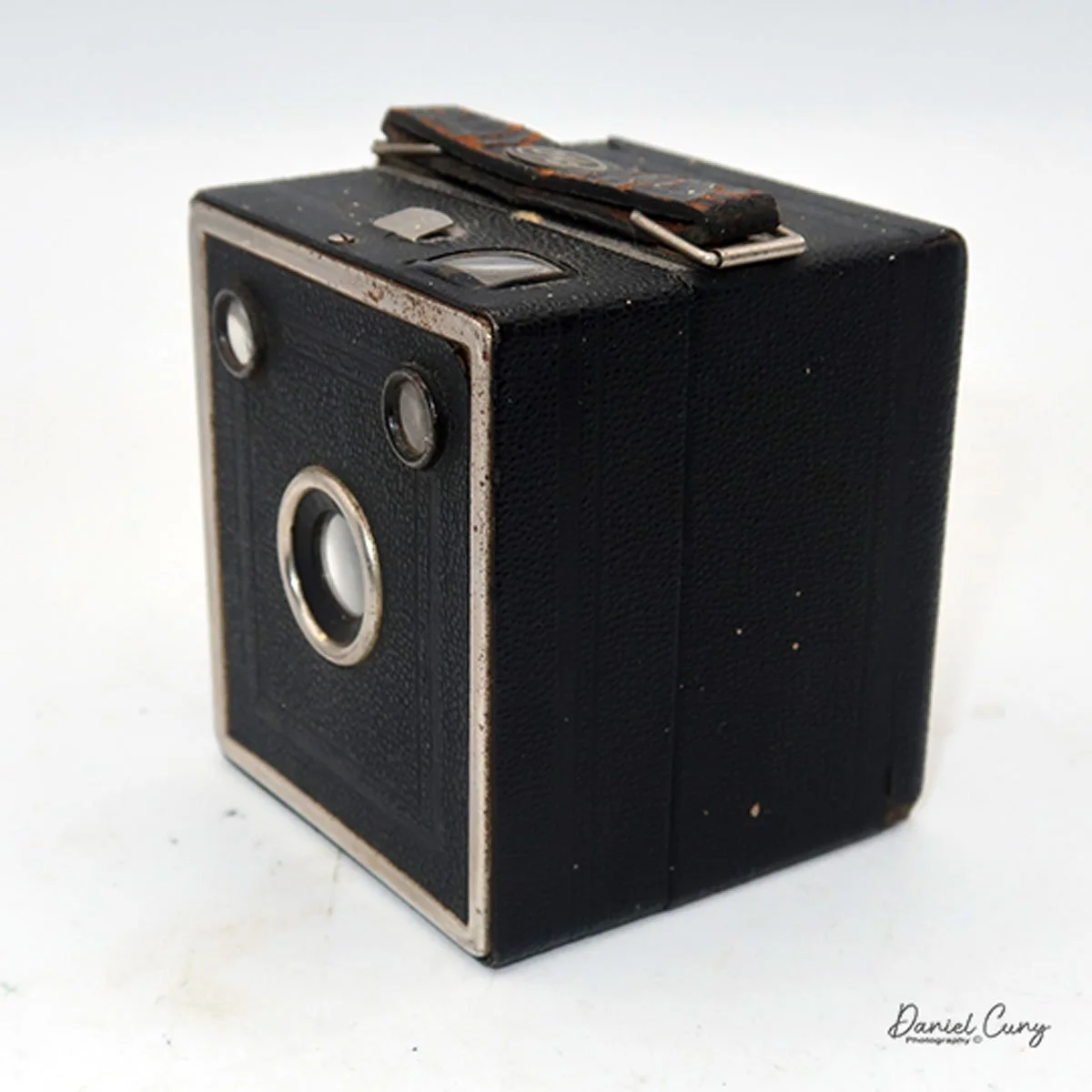
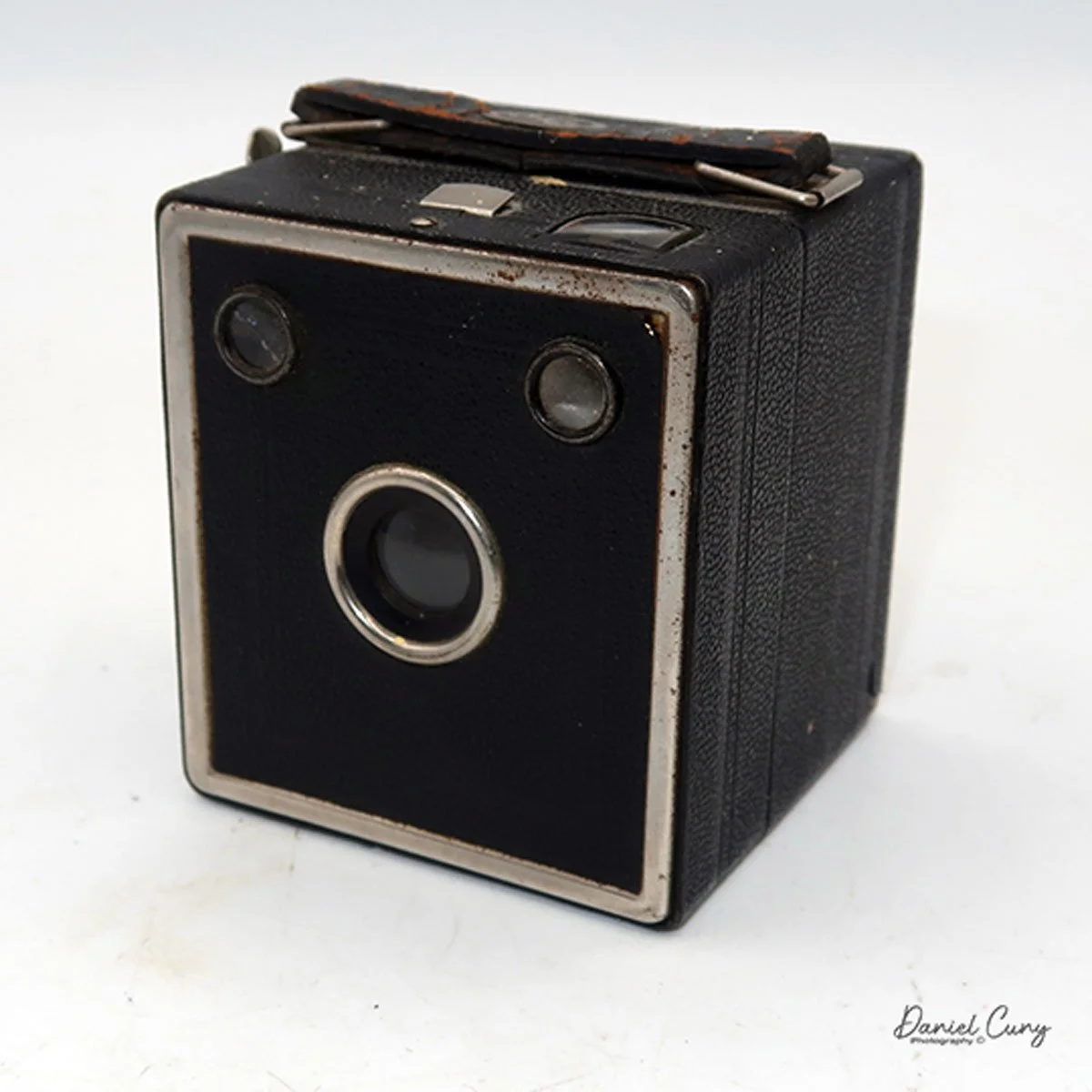
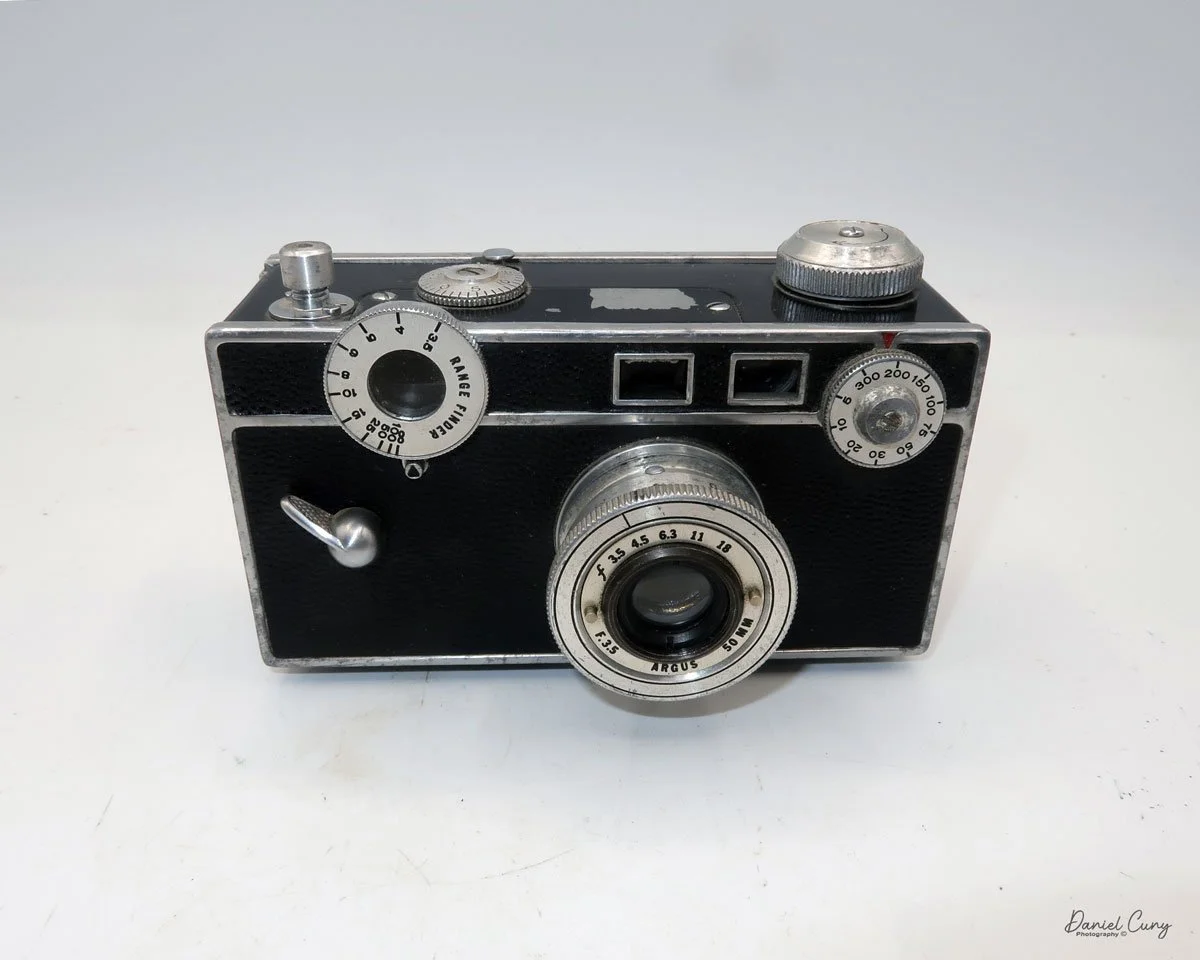
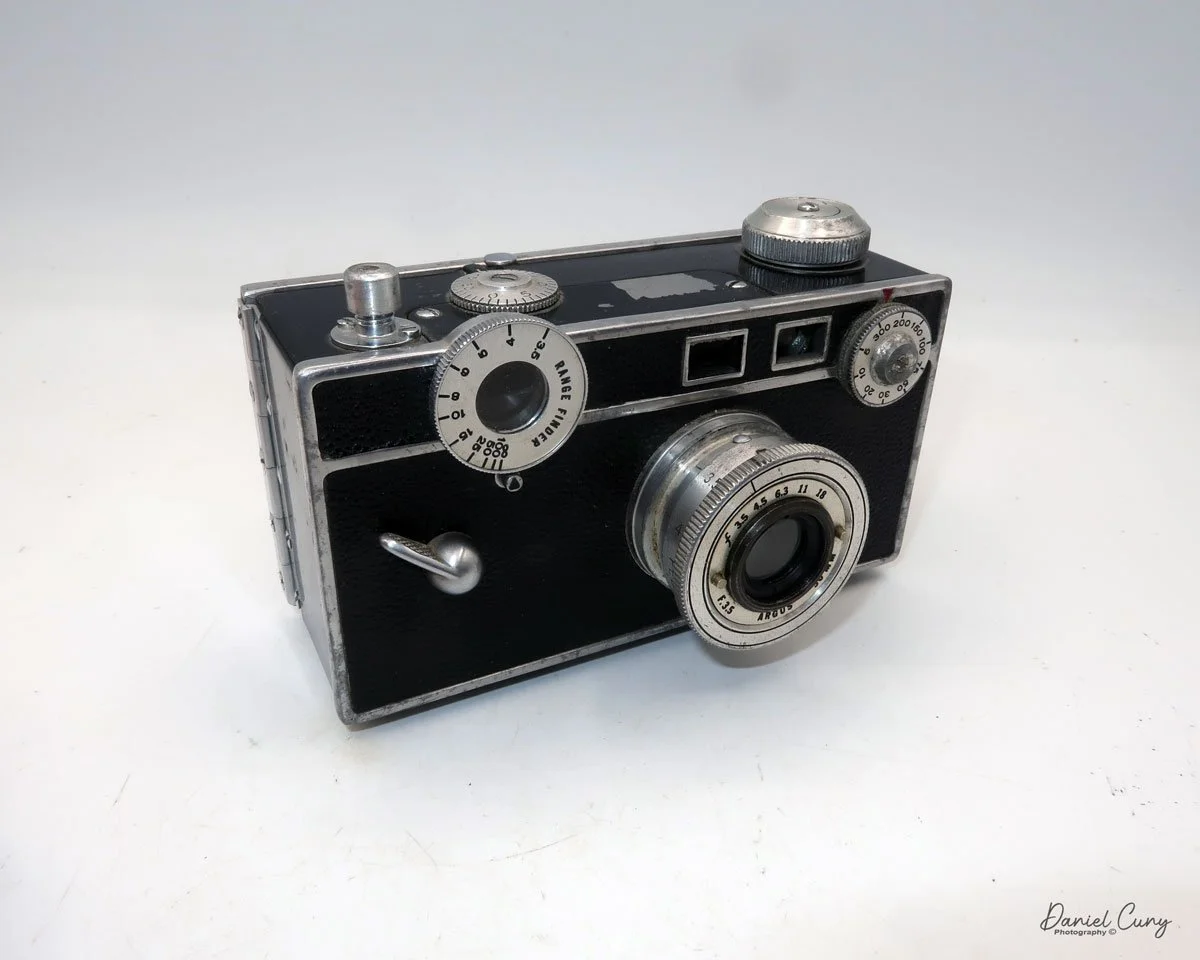
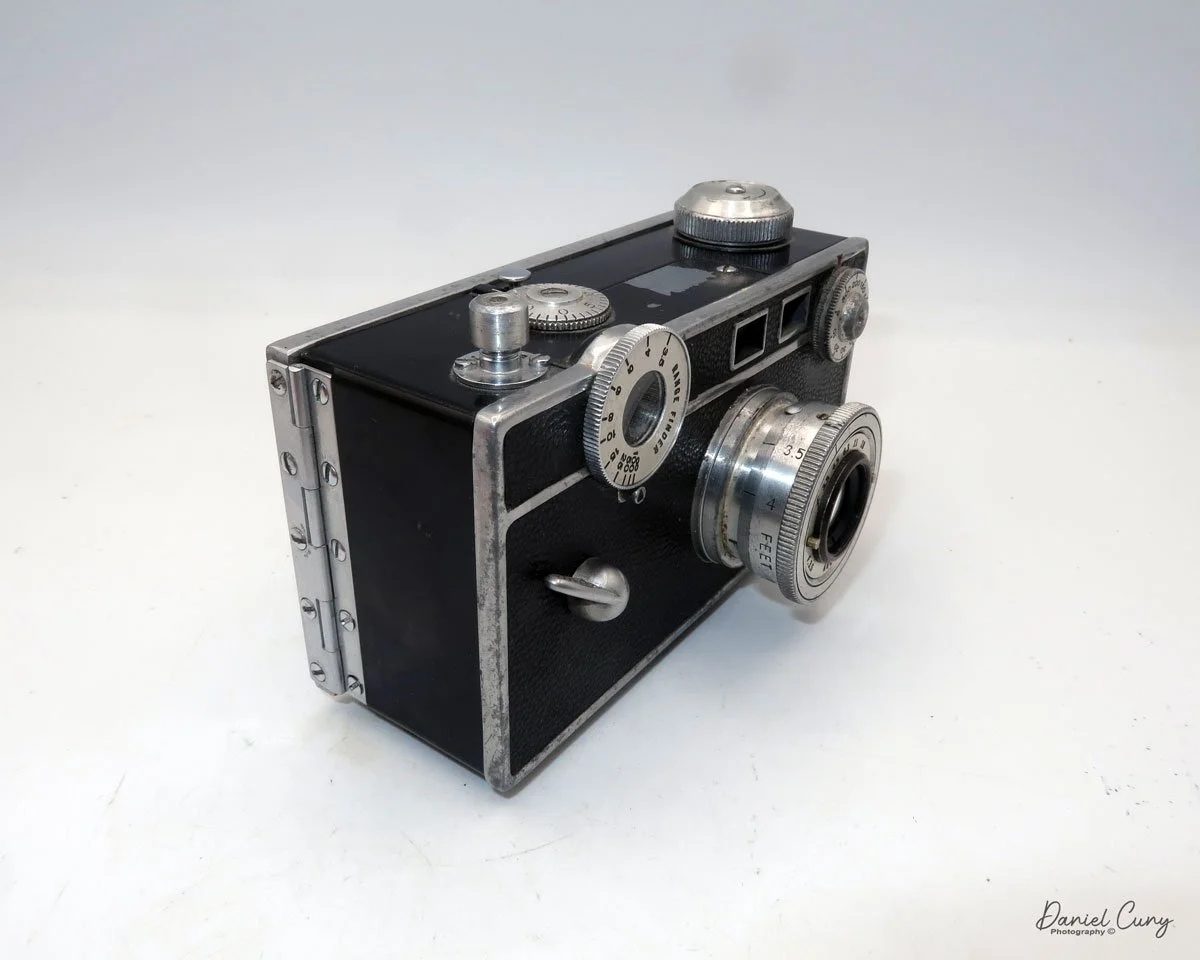
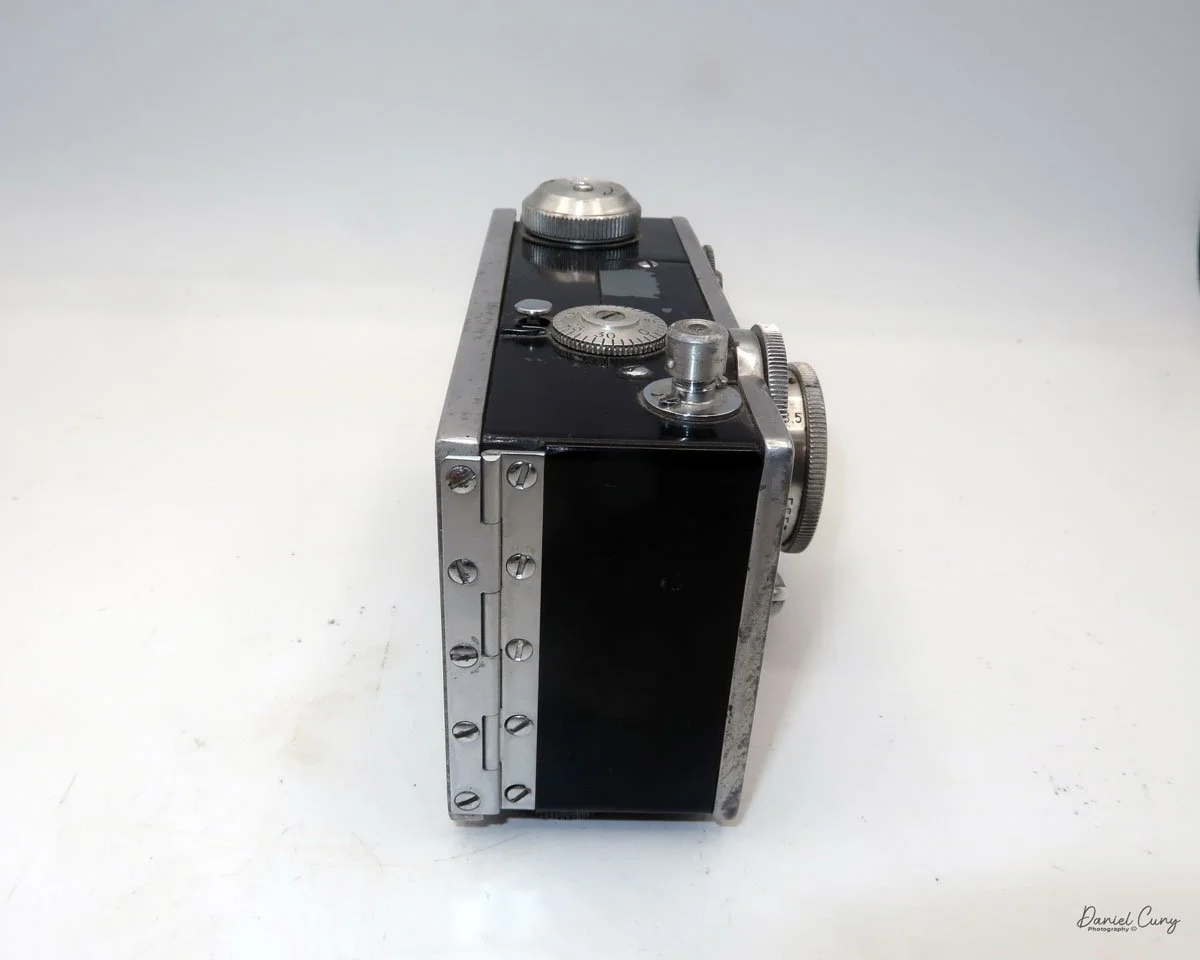
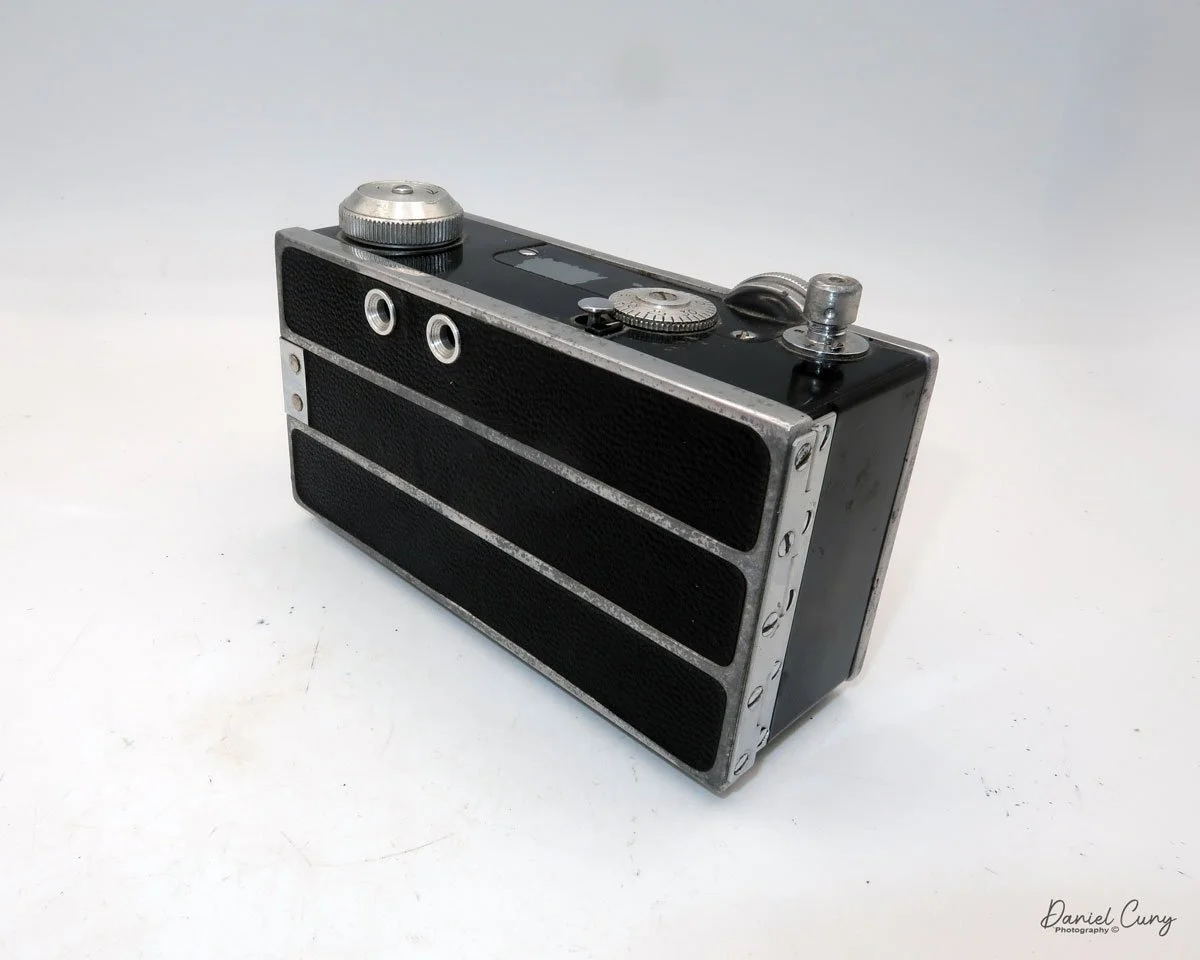
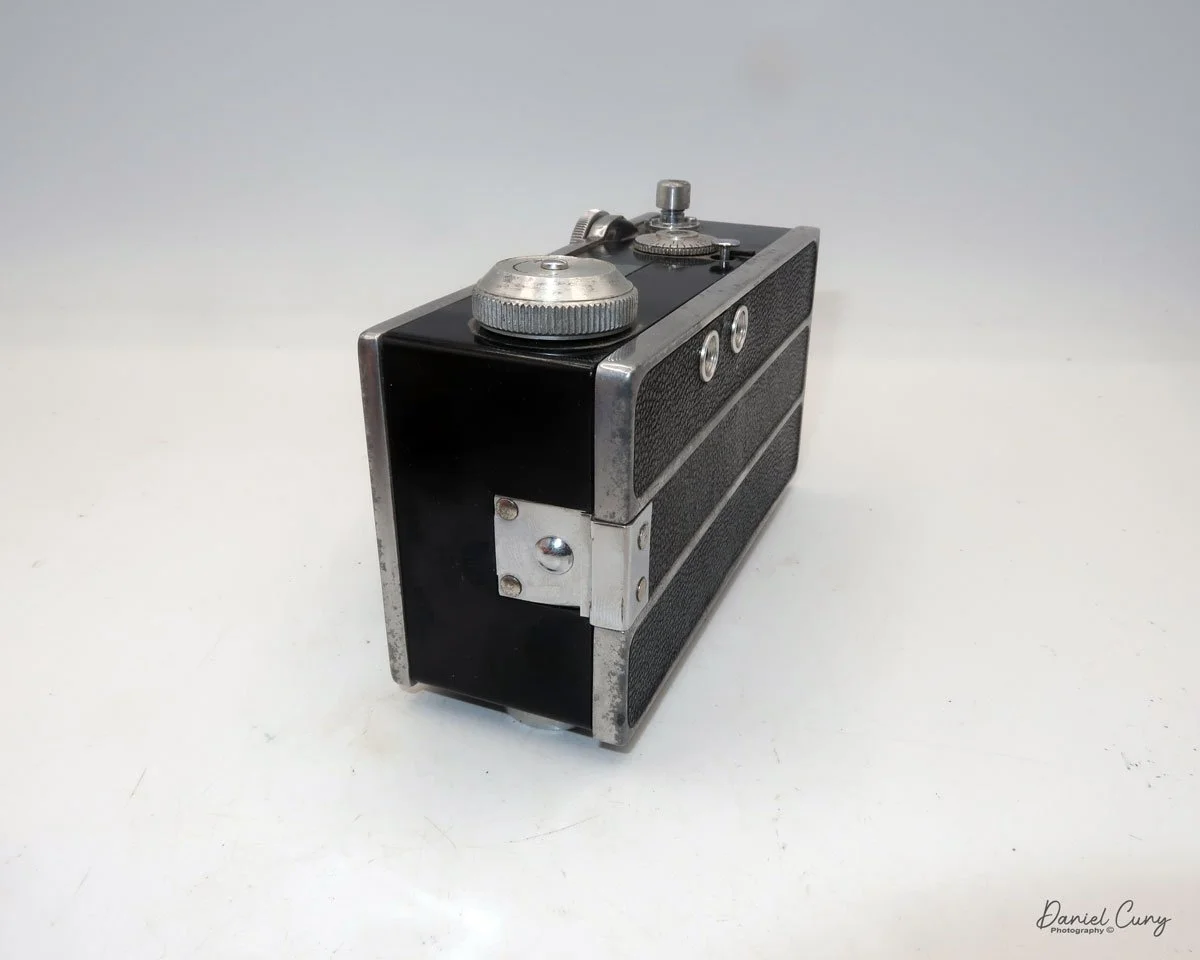
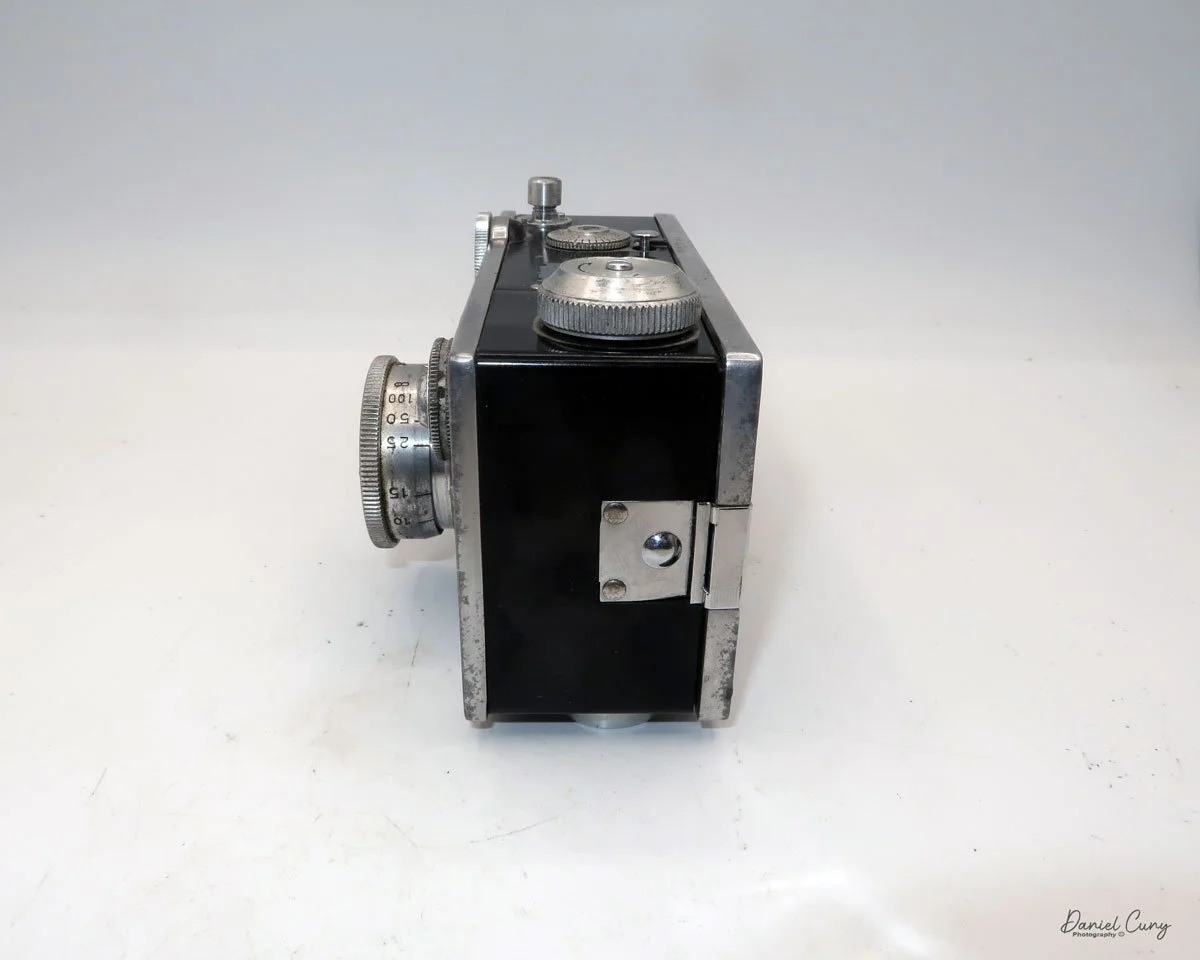
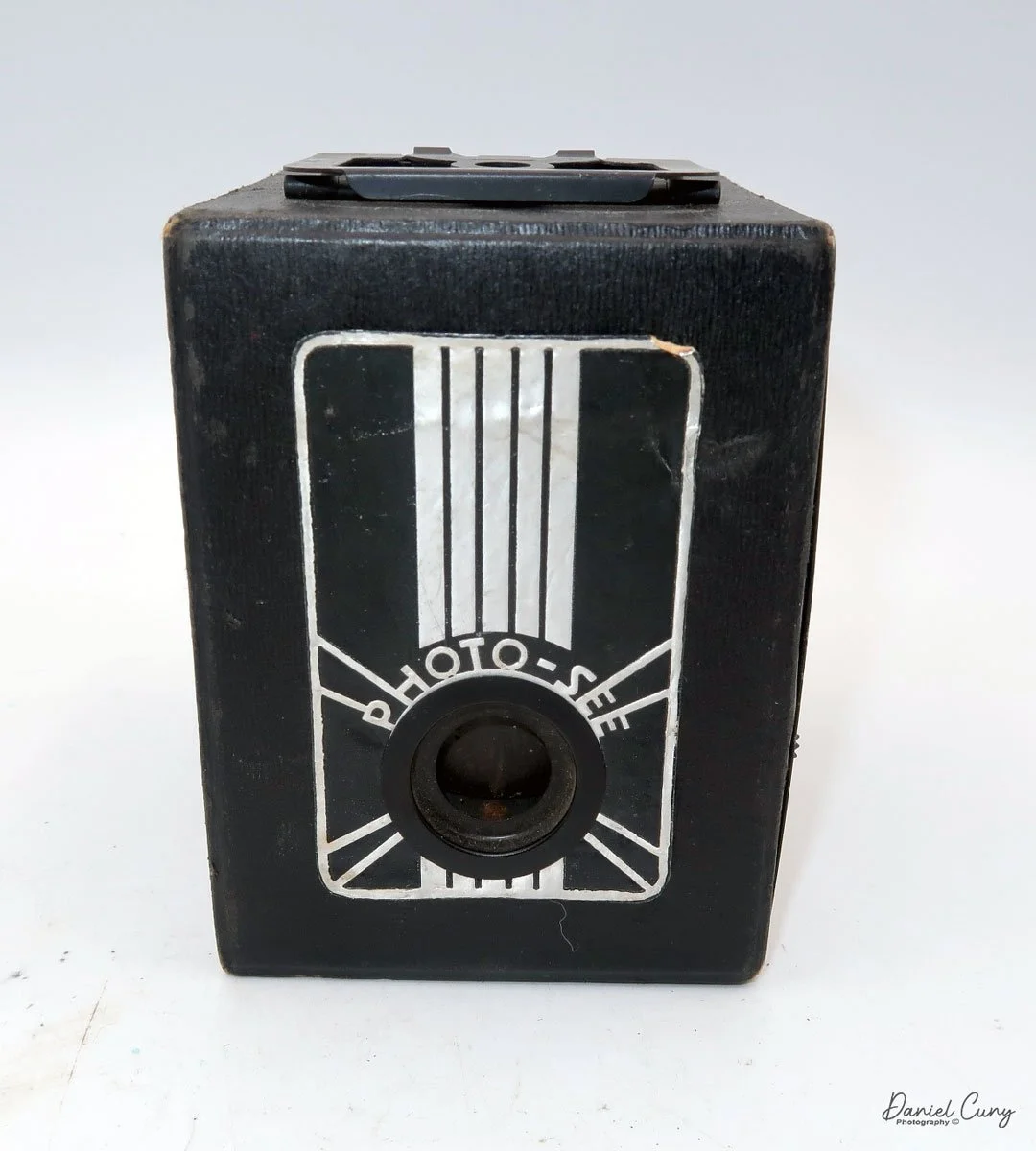
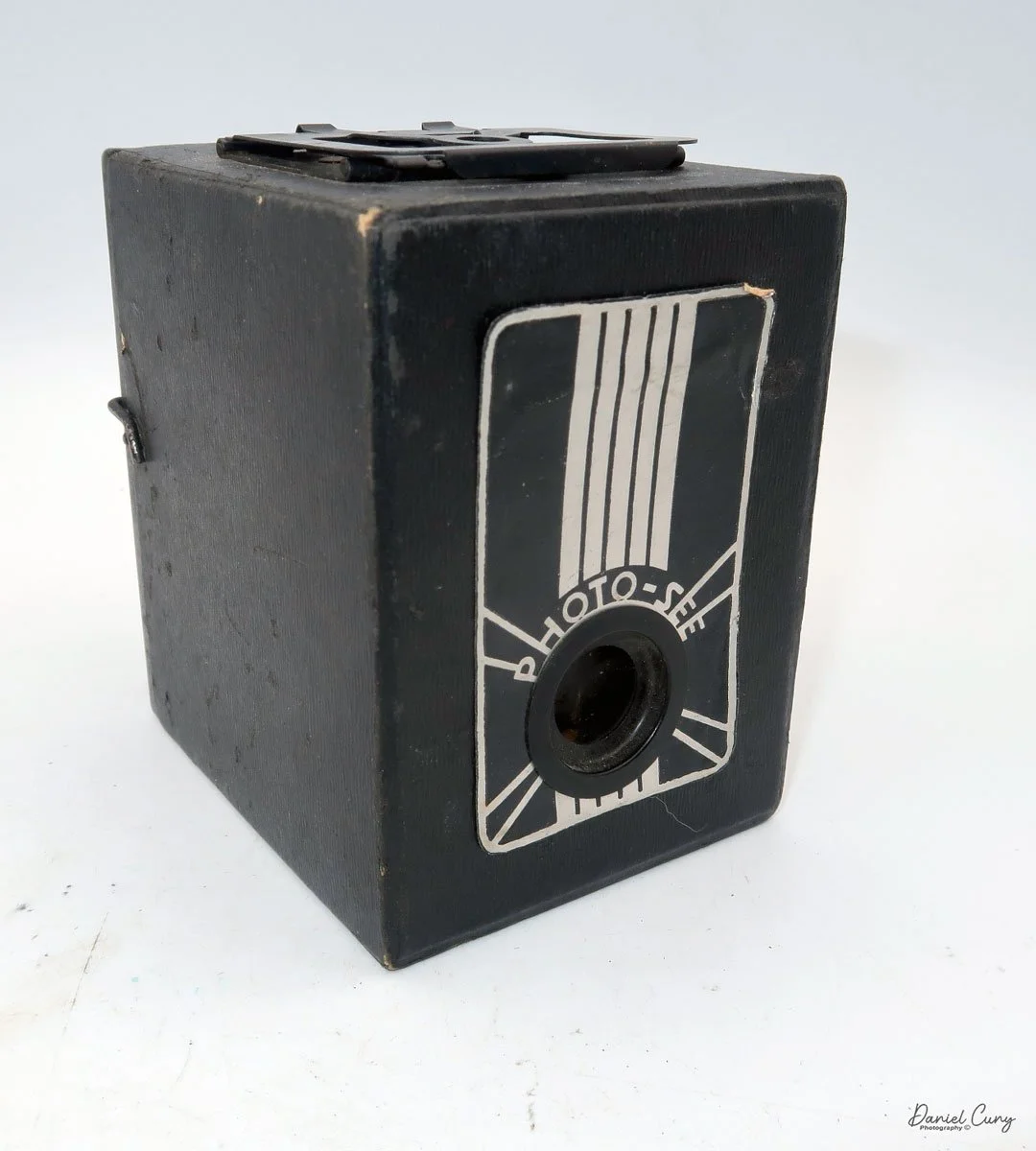
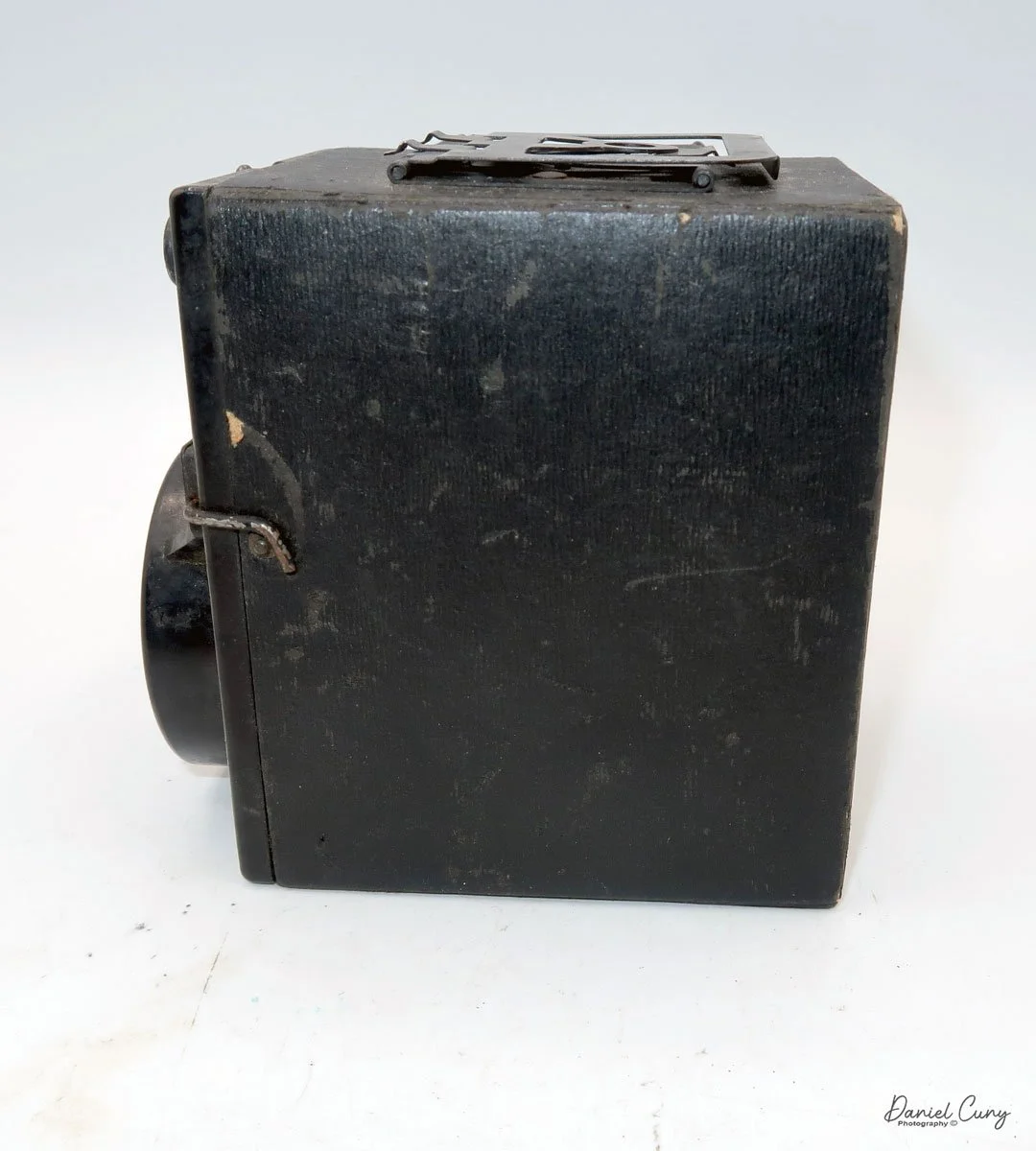
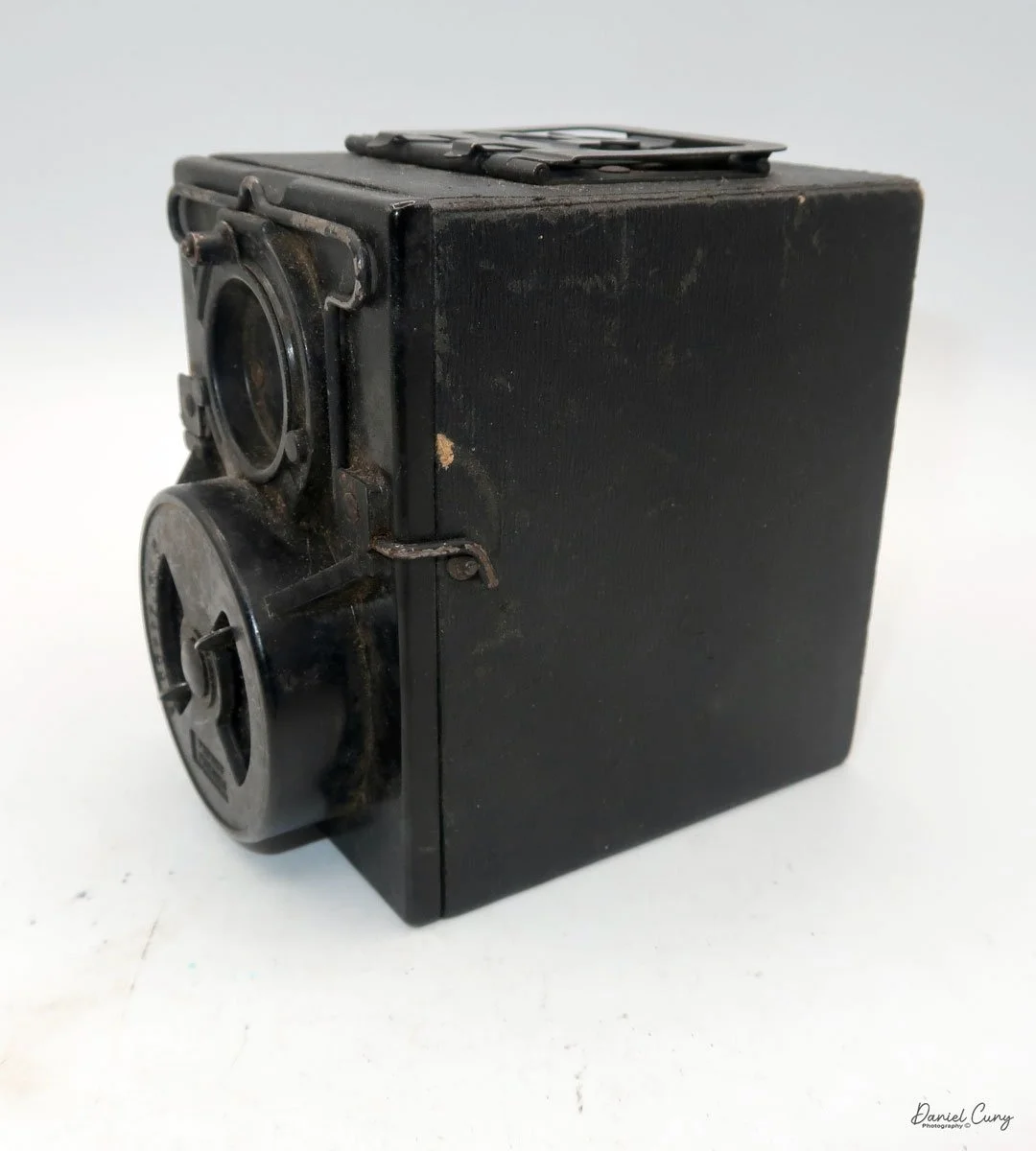
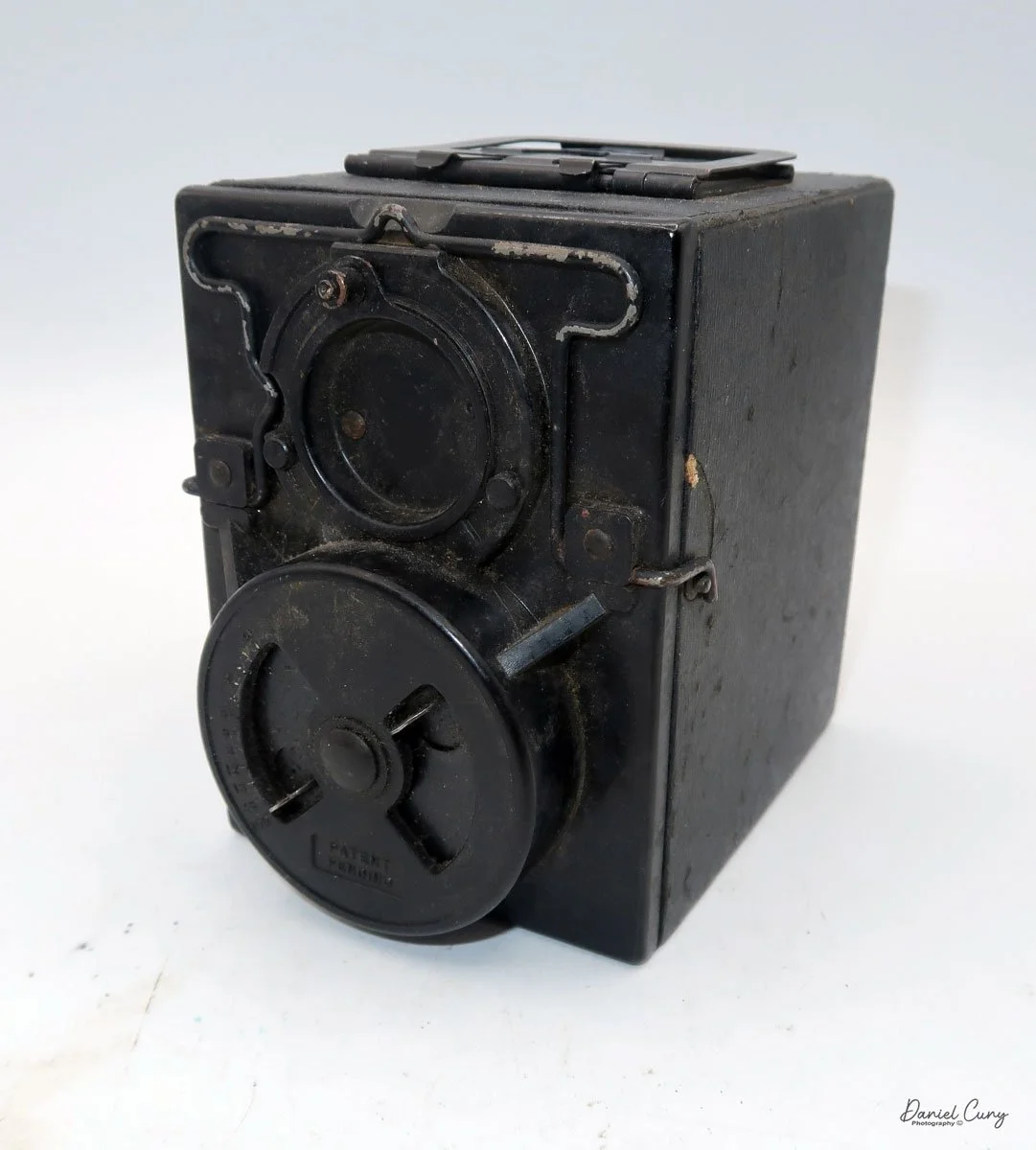
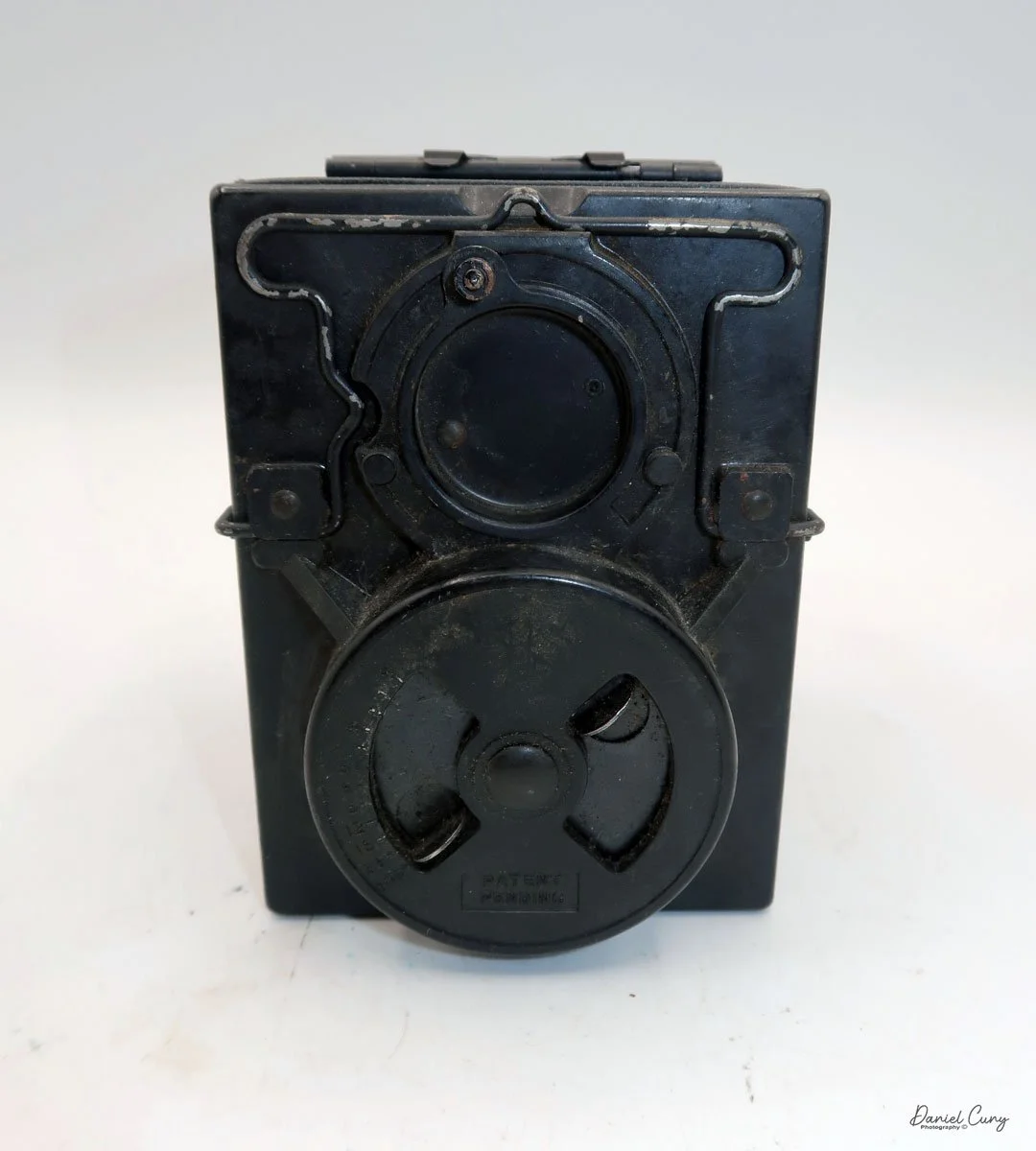
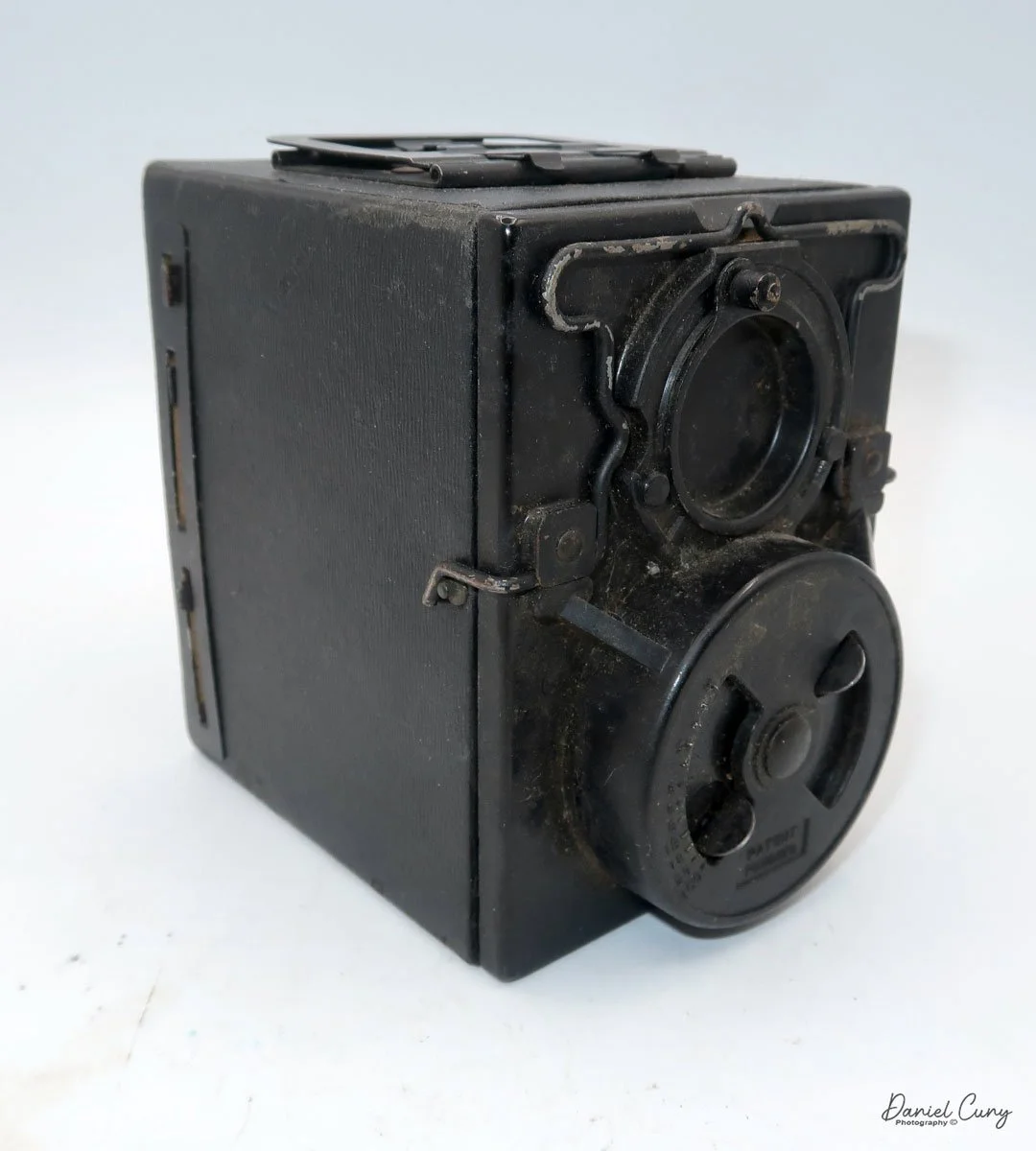
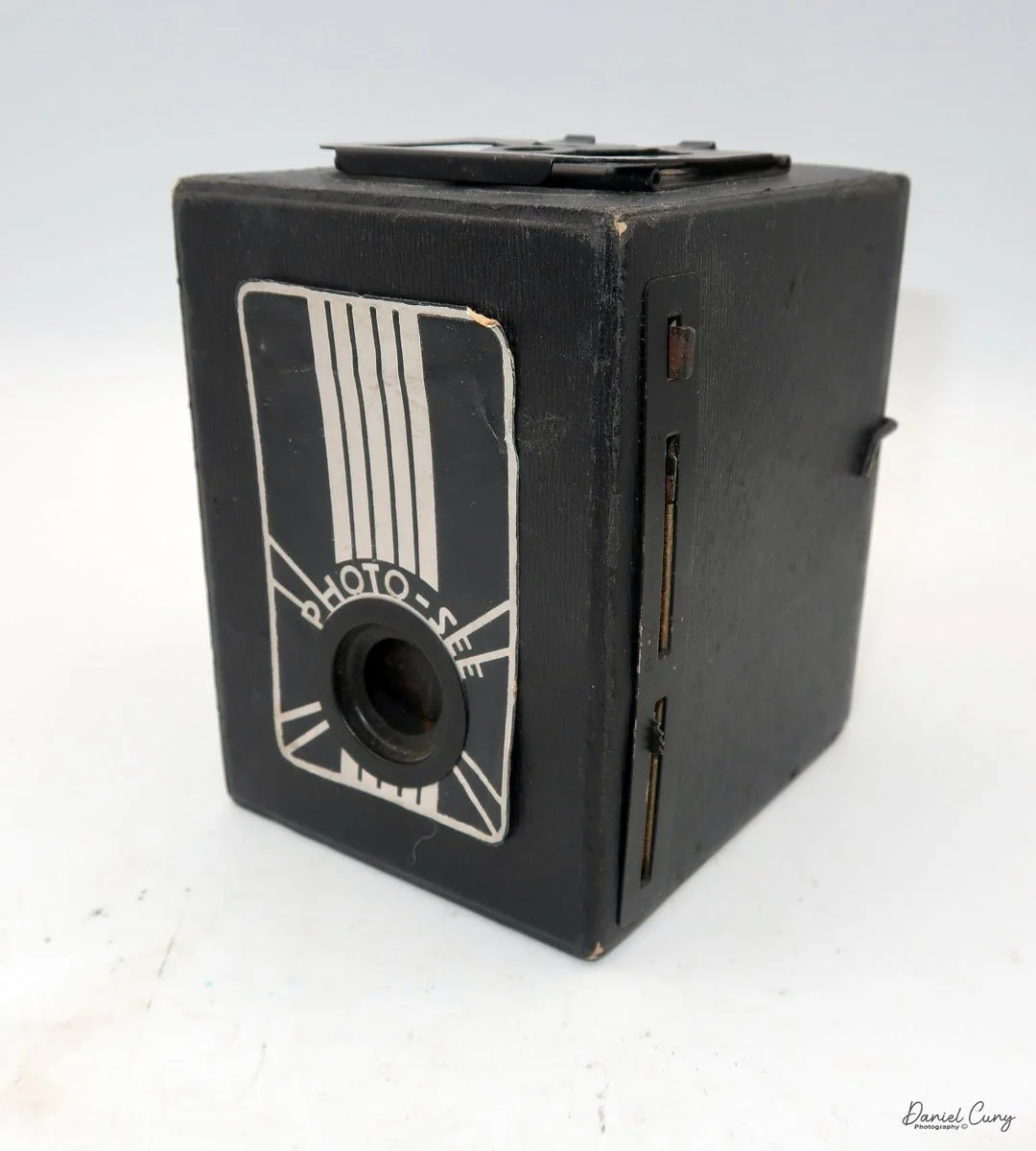
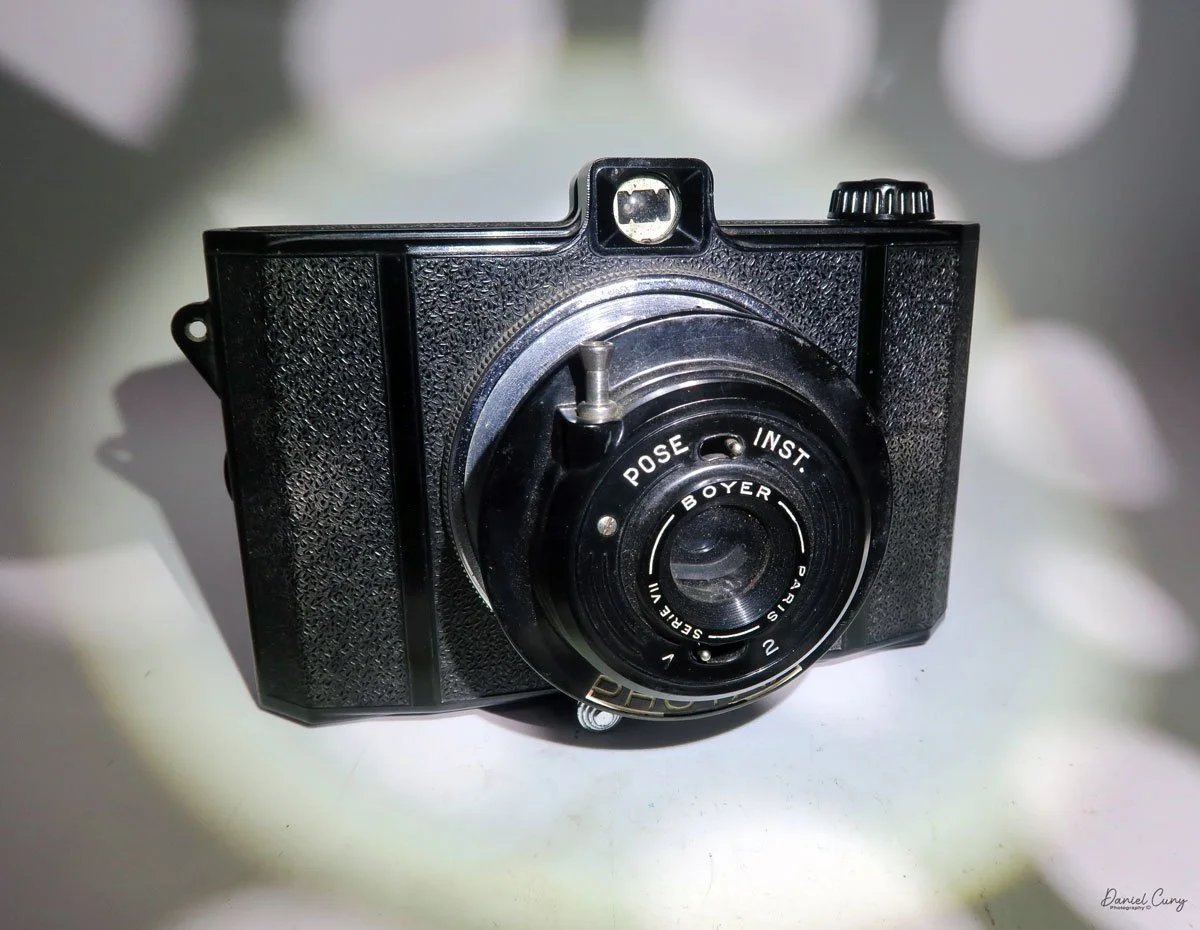
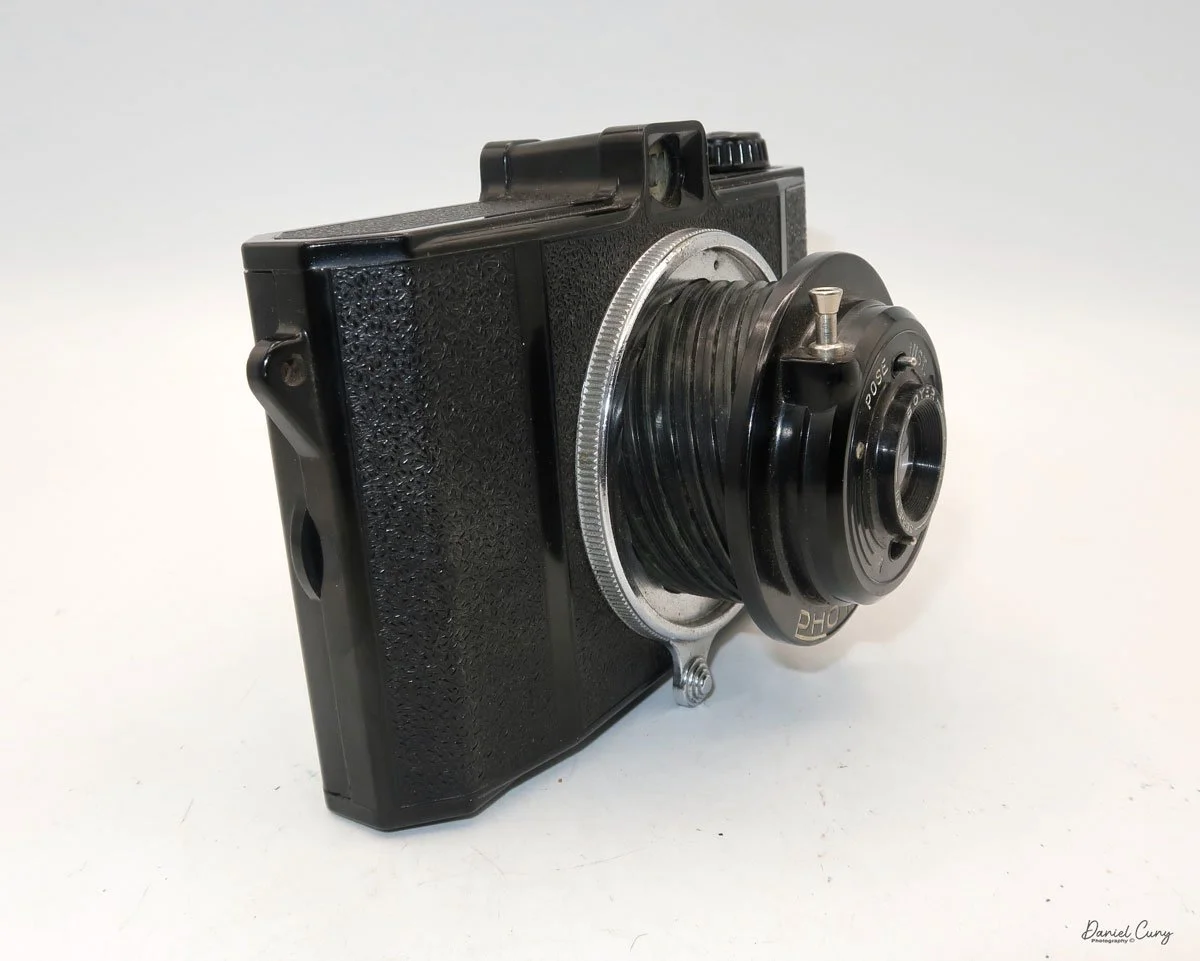
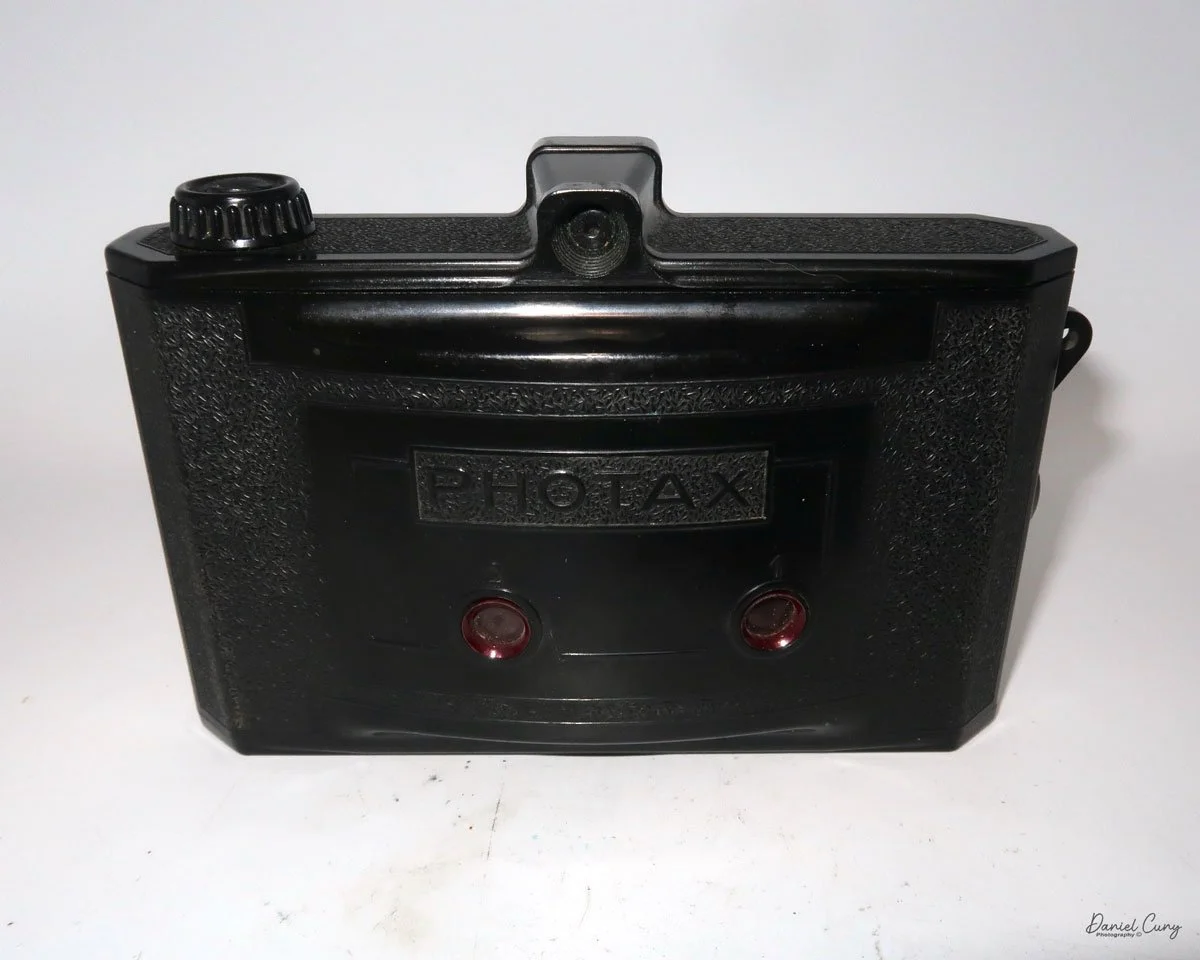
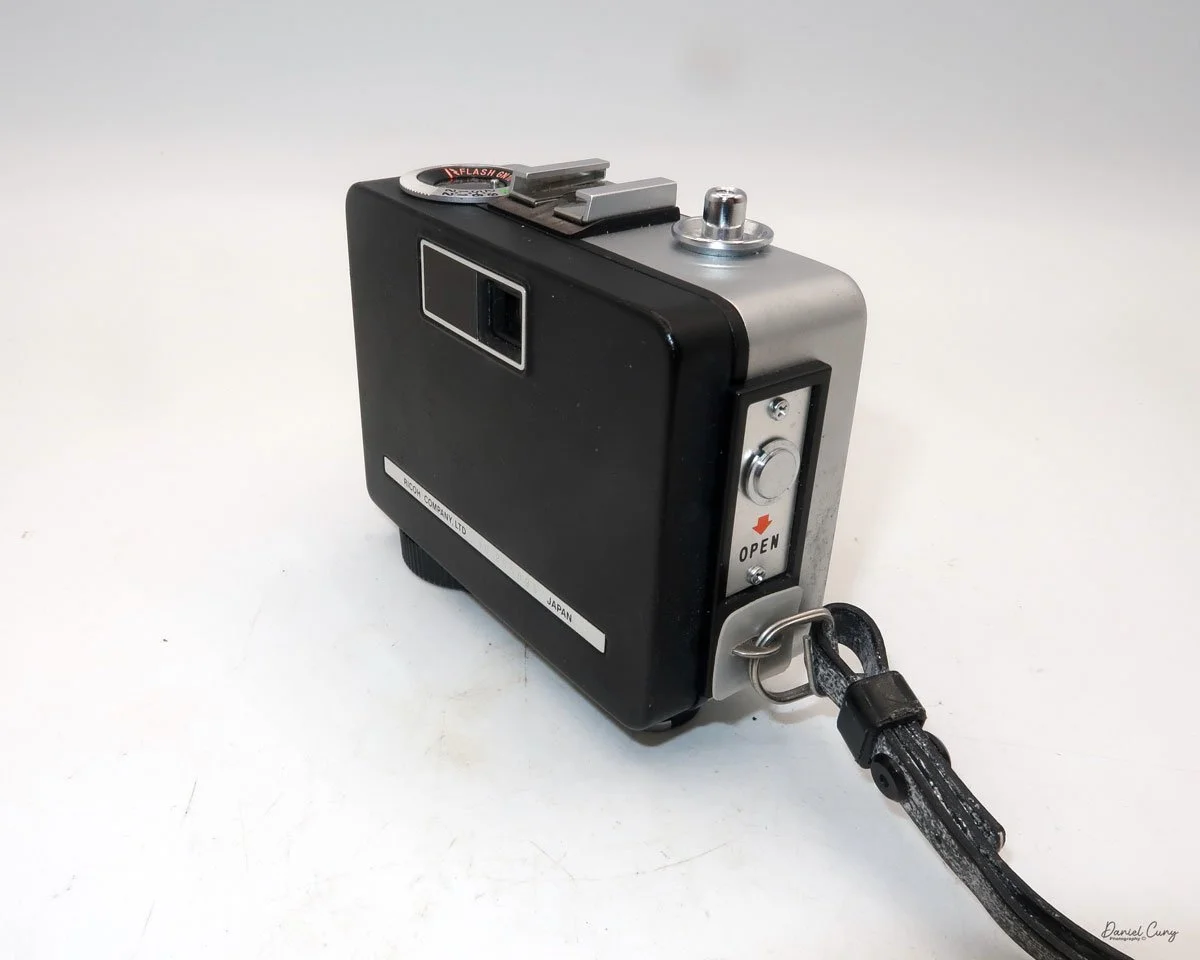
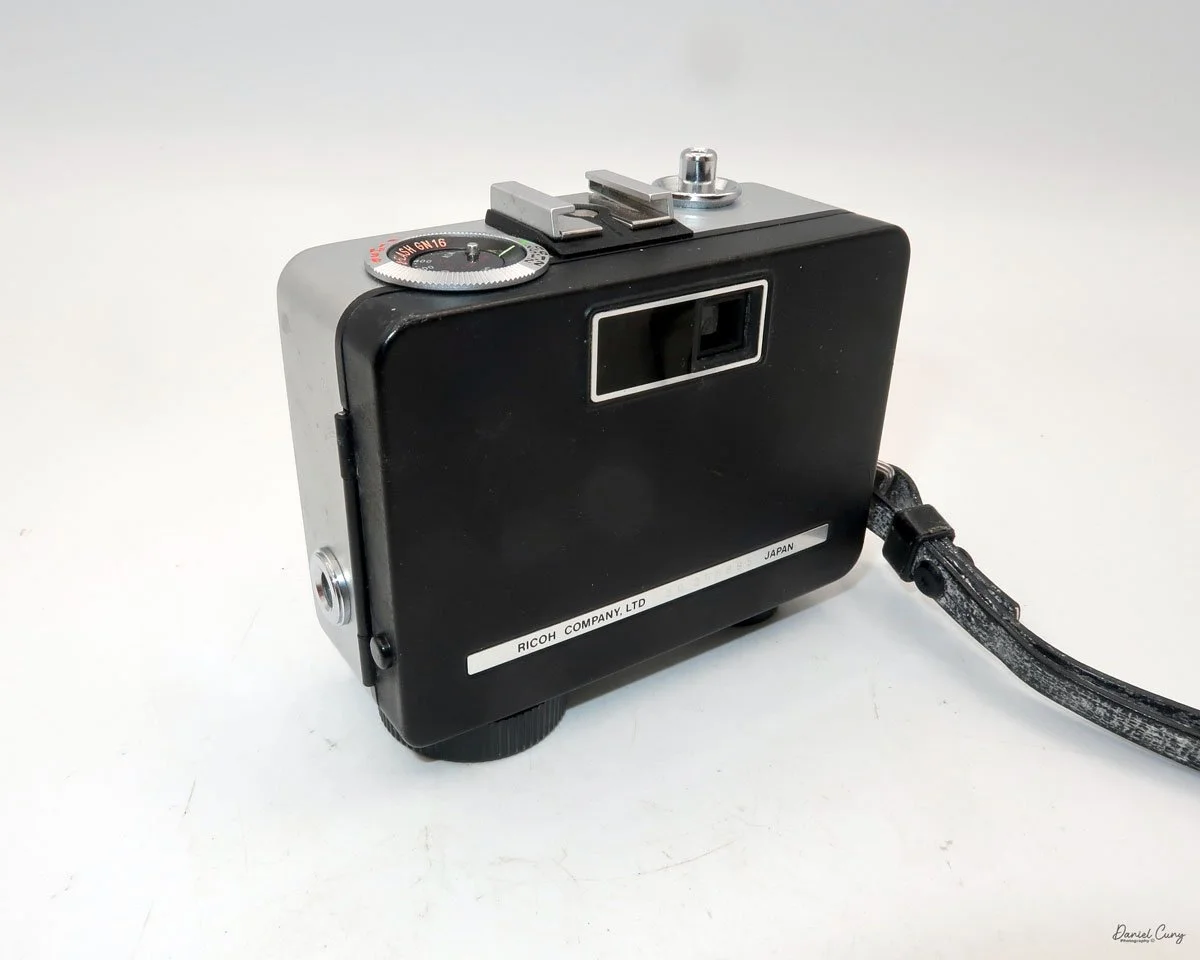
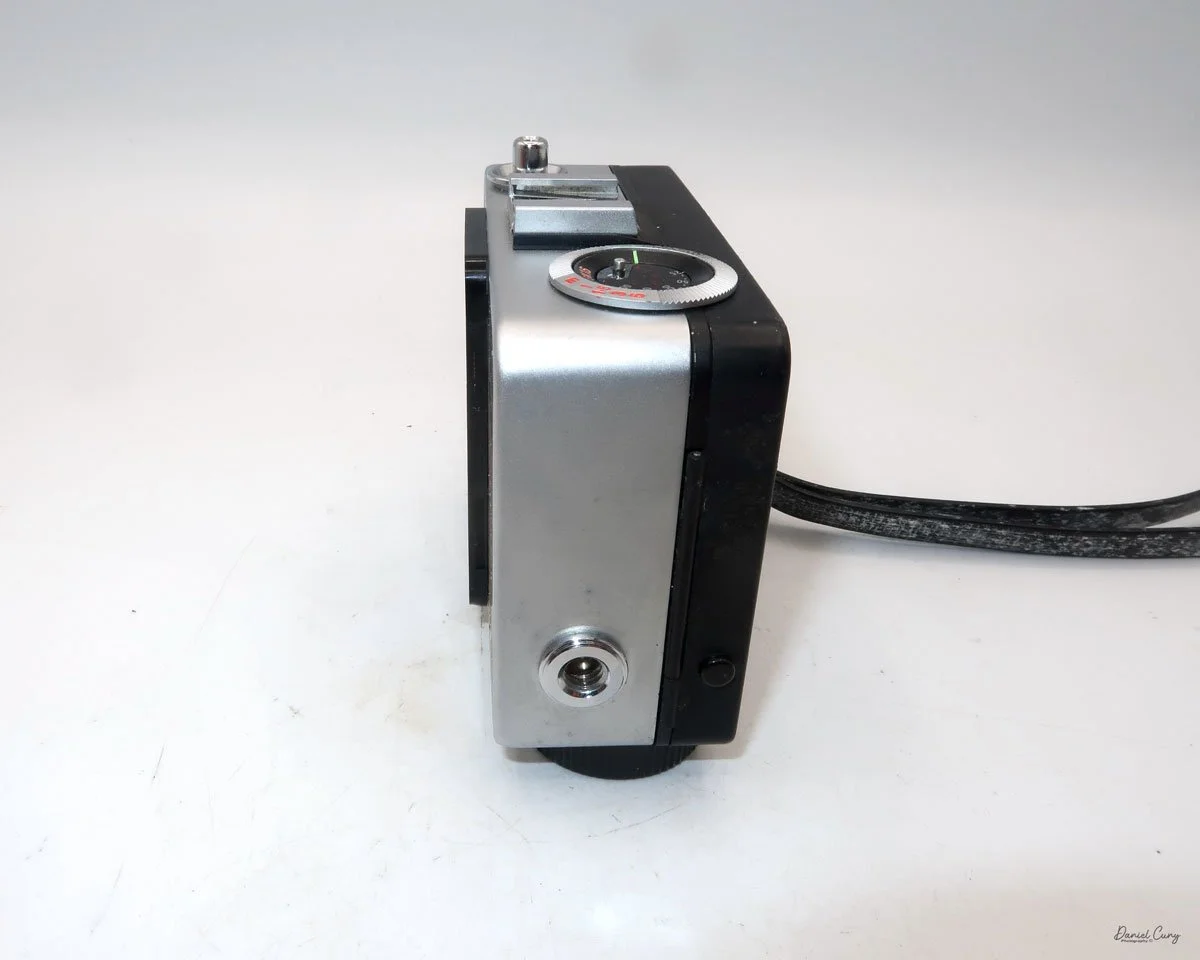
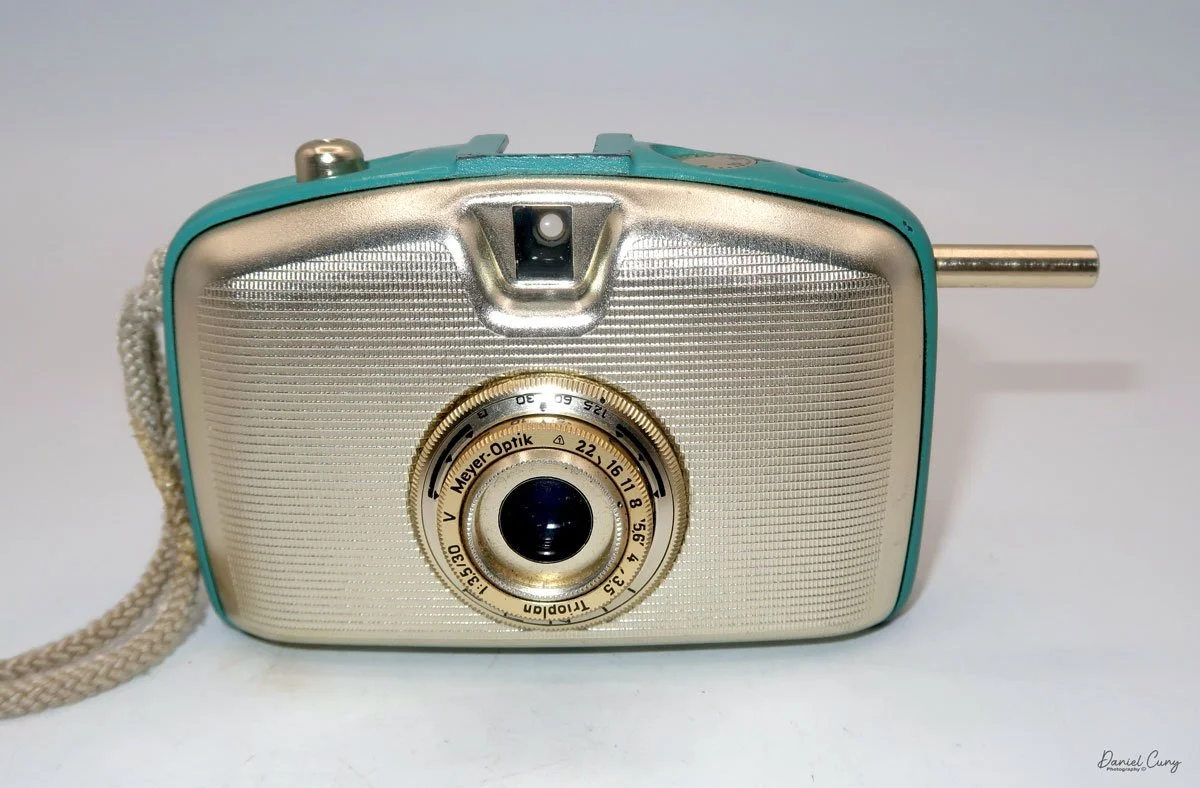
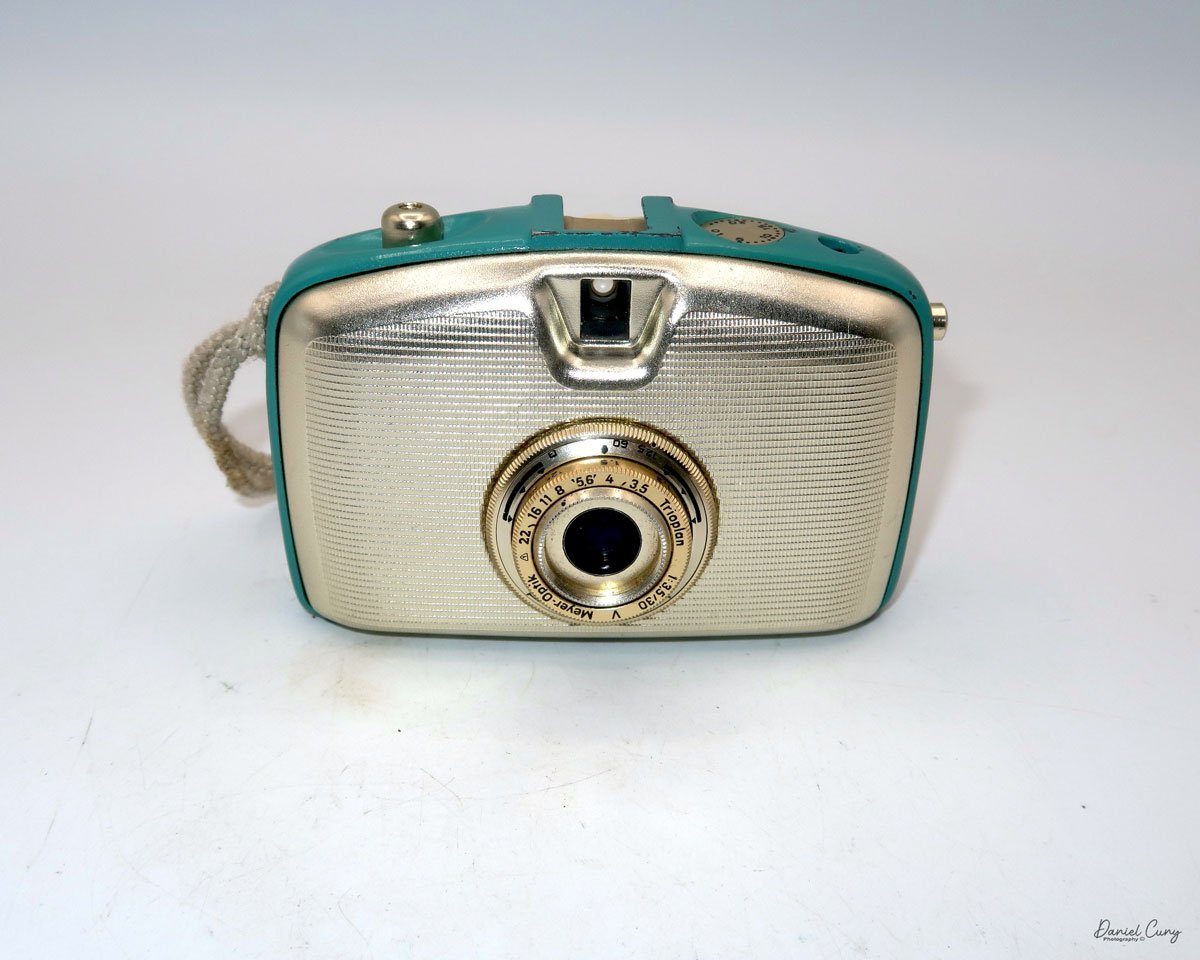
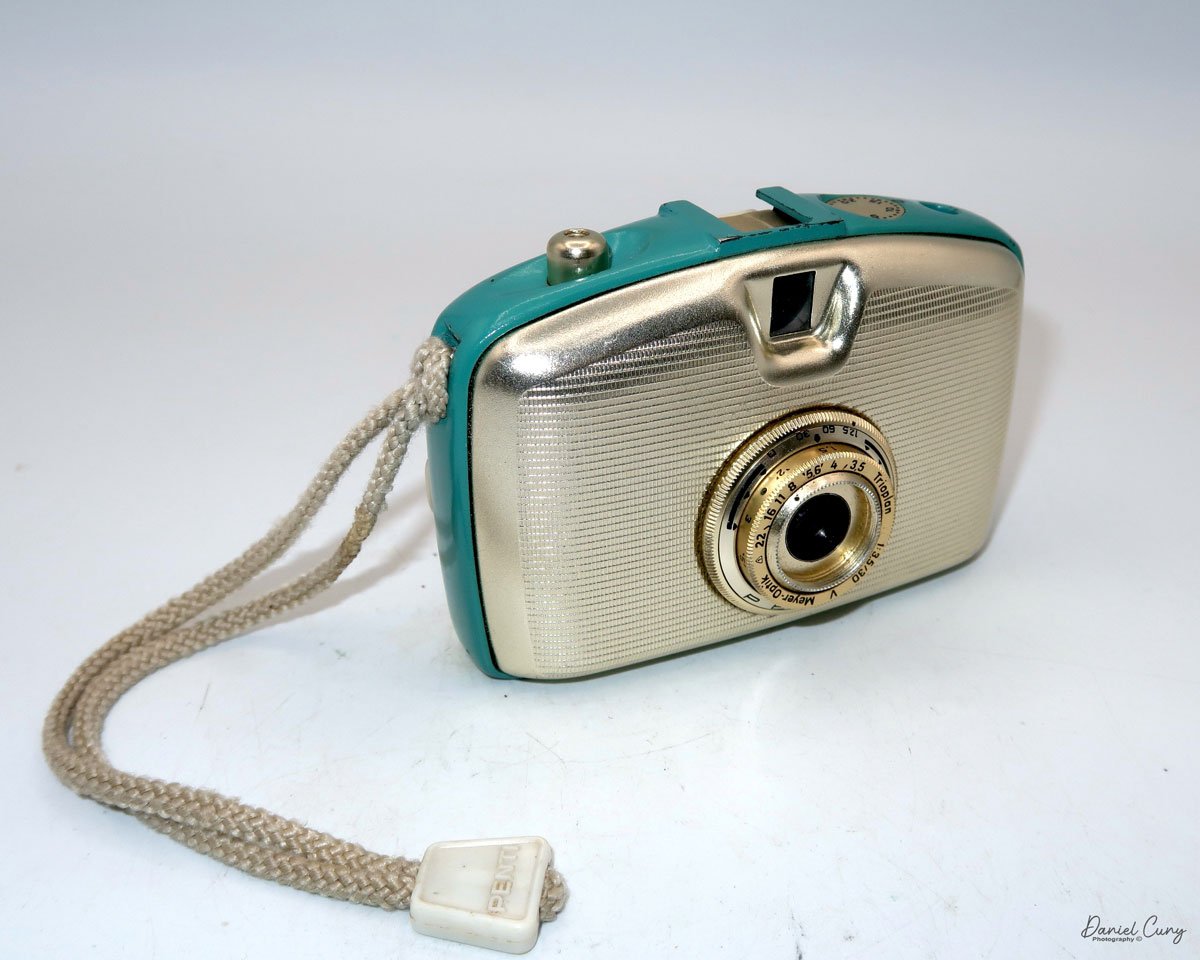
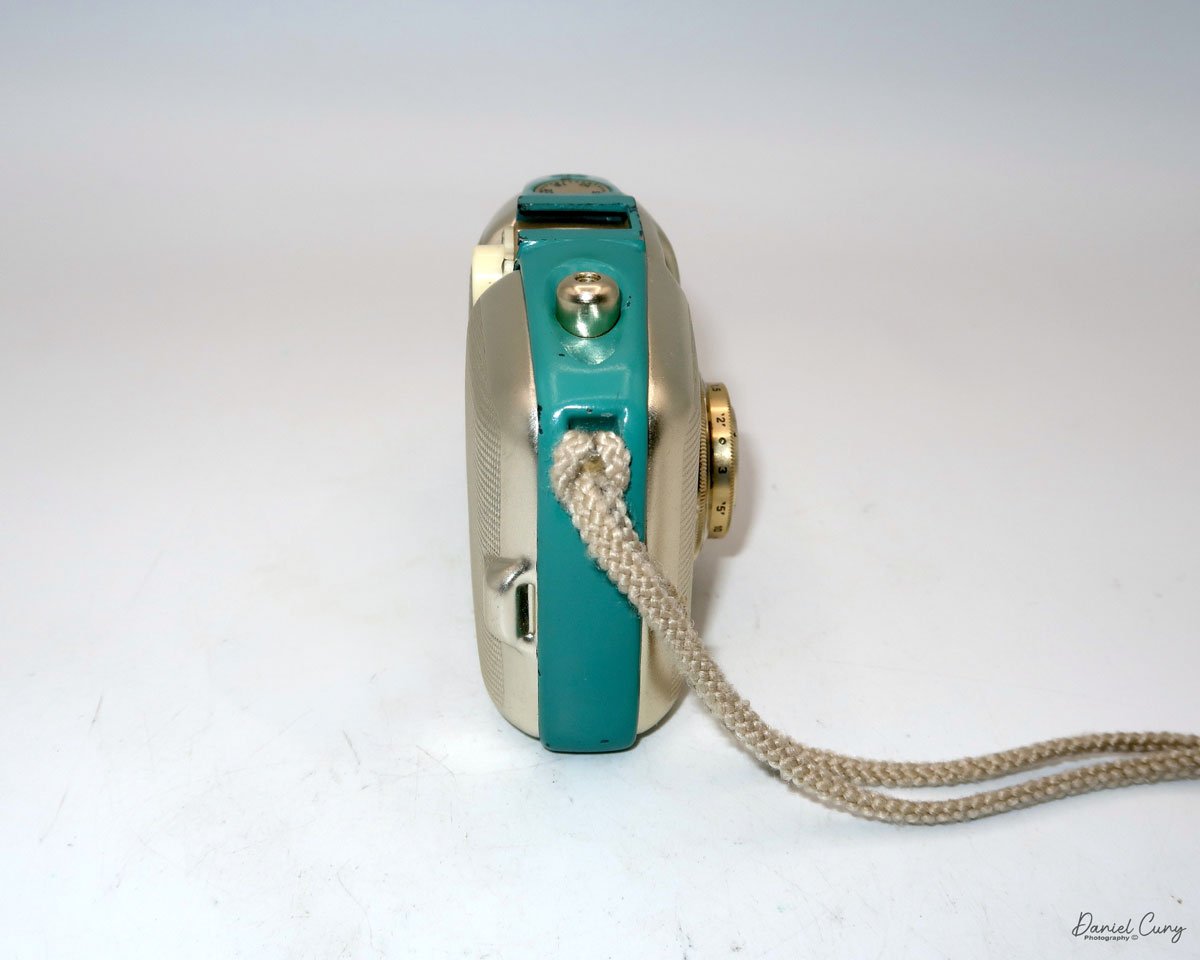
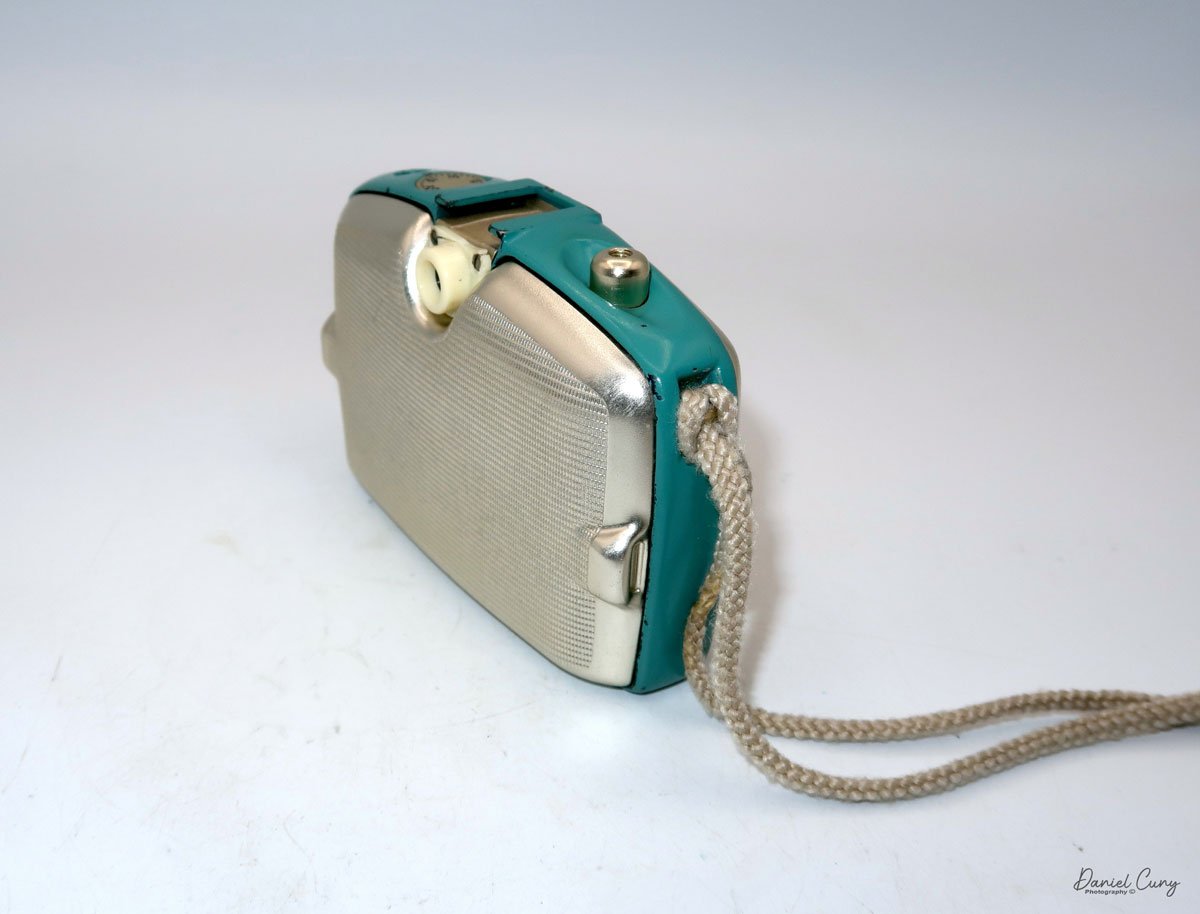
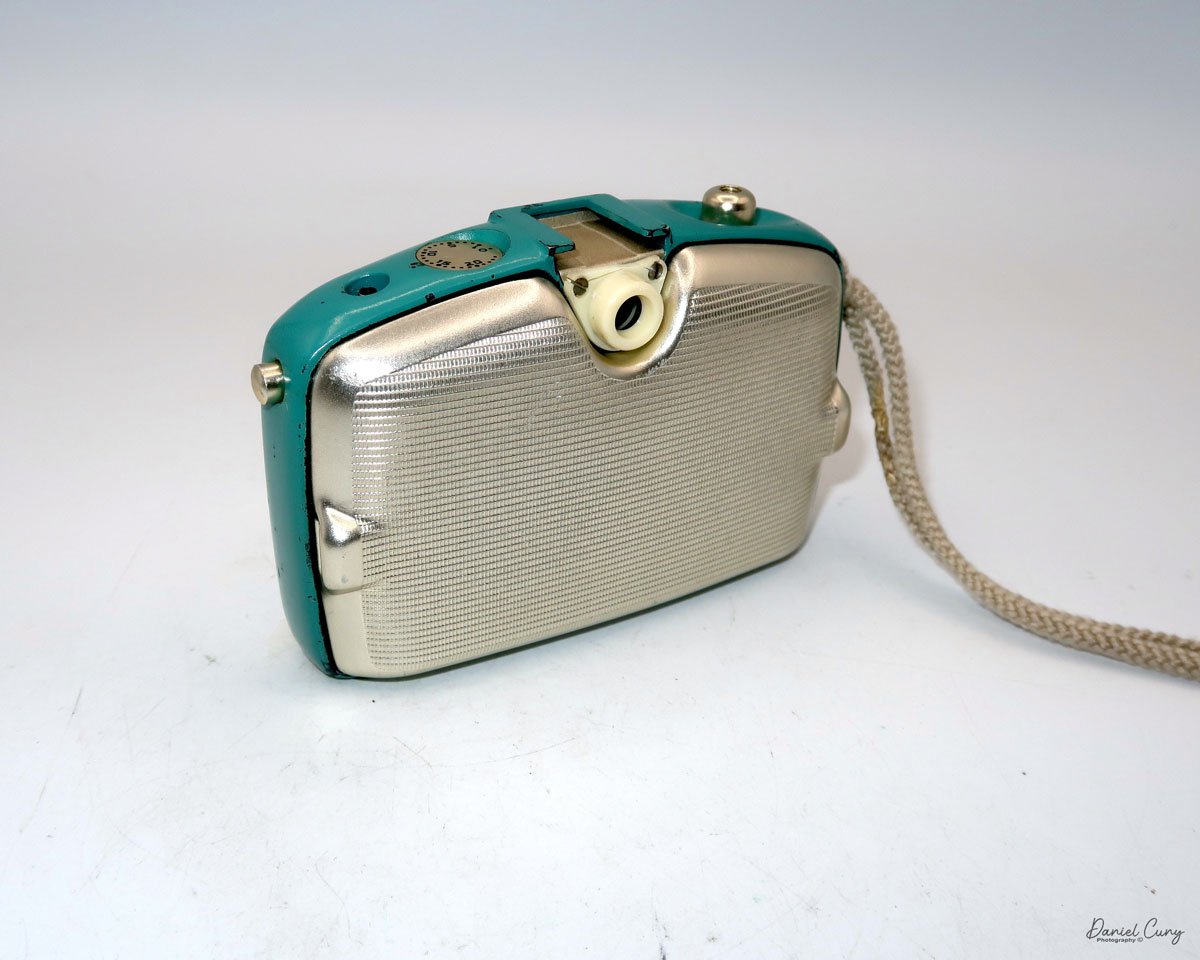
My GOMZ Malyutka camera
It wasn't until later in my camera-collecting career that I developed an interest in miniature and subminiature cameras. It was the more unusual or the odder looking camera items like the pen-shaped Stylophot, or the round Petal camera, the Twin Lens style miniature cameras like the Gemflex camera, or the miniature cameras which resemble small rangefinder or SLR cameras like the Golden Ricoh 16, where I really enjoyed having them in my collection. They are very unique cameras and items that stand out because they are so different from the larger box, folding, or view cameras. A real advantage of having miniature and subminiature cameras in your collection is the amount of display space they save. You can display many more items and accessories in a much smaller area.
The GOMZ Malyutka is a camera I purchased around 10 years ago, and I didn't start researching it until about a year ago, when I found out it was pretty rare. I didn't even have it in my display of miniature or subminiature cameras until that time.
This is another camera I purchase in a group or "lot" of camera in a fairly unknown auction of camera. My real prize and the main item I was bidding on was an early Nikon F body, and tucked in the background was an early Nikon 5cm f2 tick mark lens, which, due to the angle of the lens and the low visibility of people looking, not many people bid on the "Lot", so luckily it was one that I won. There were also other items within the "lot" that I had minimal interest in, but the Tick Mark lens and early Nikon F body were the prize.
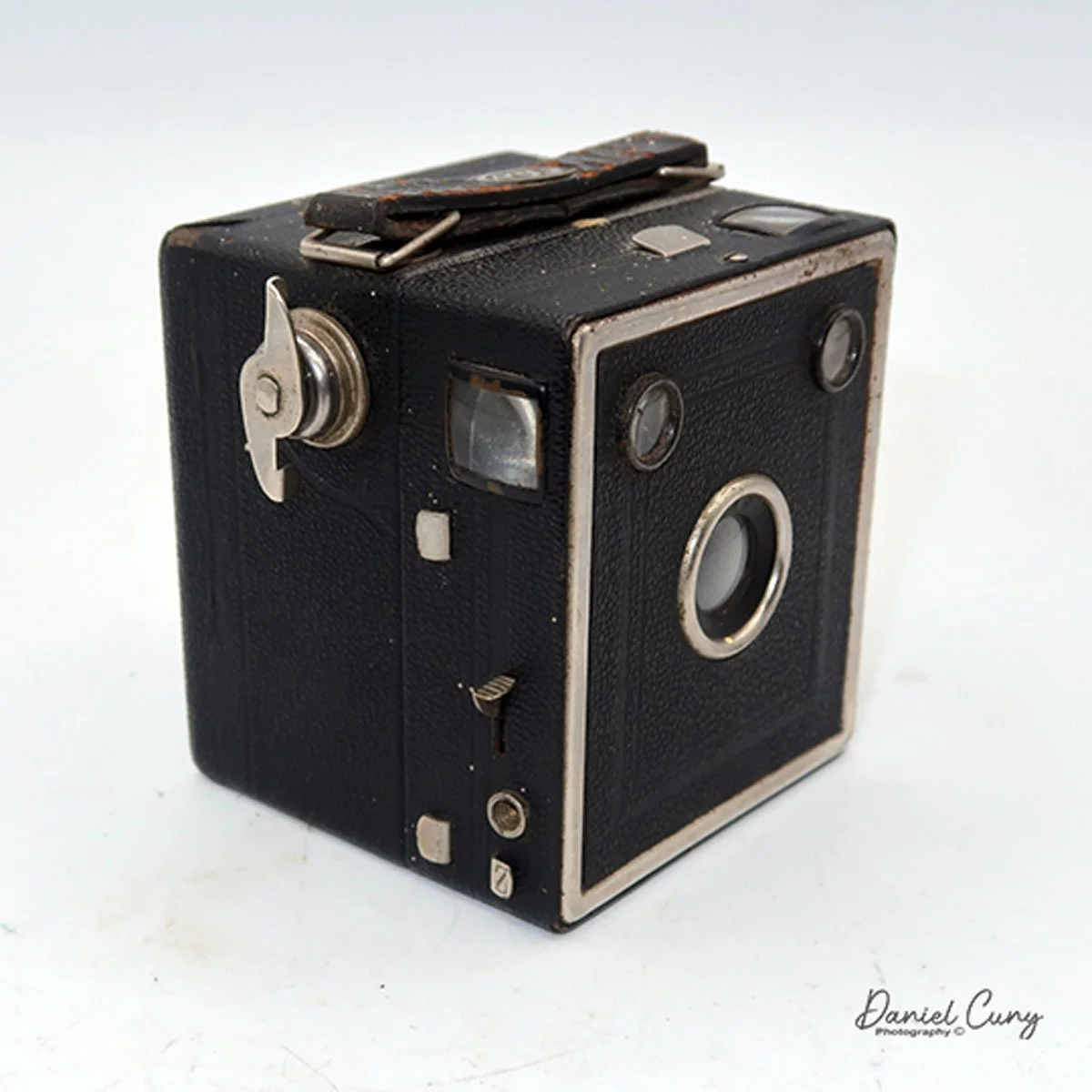
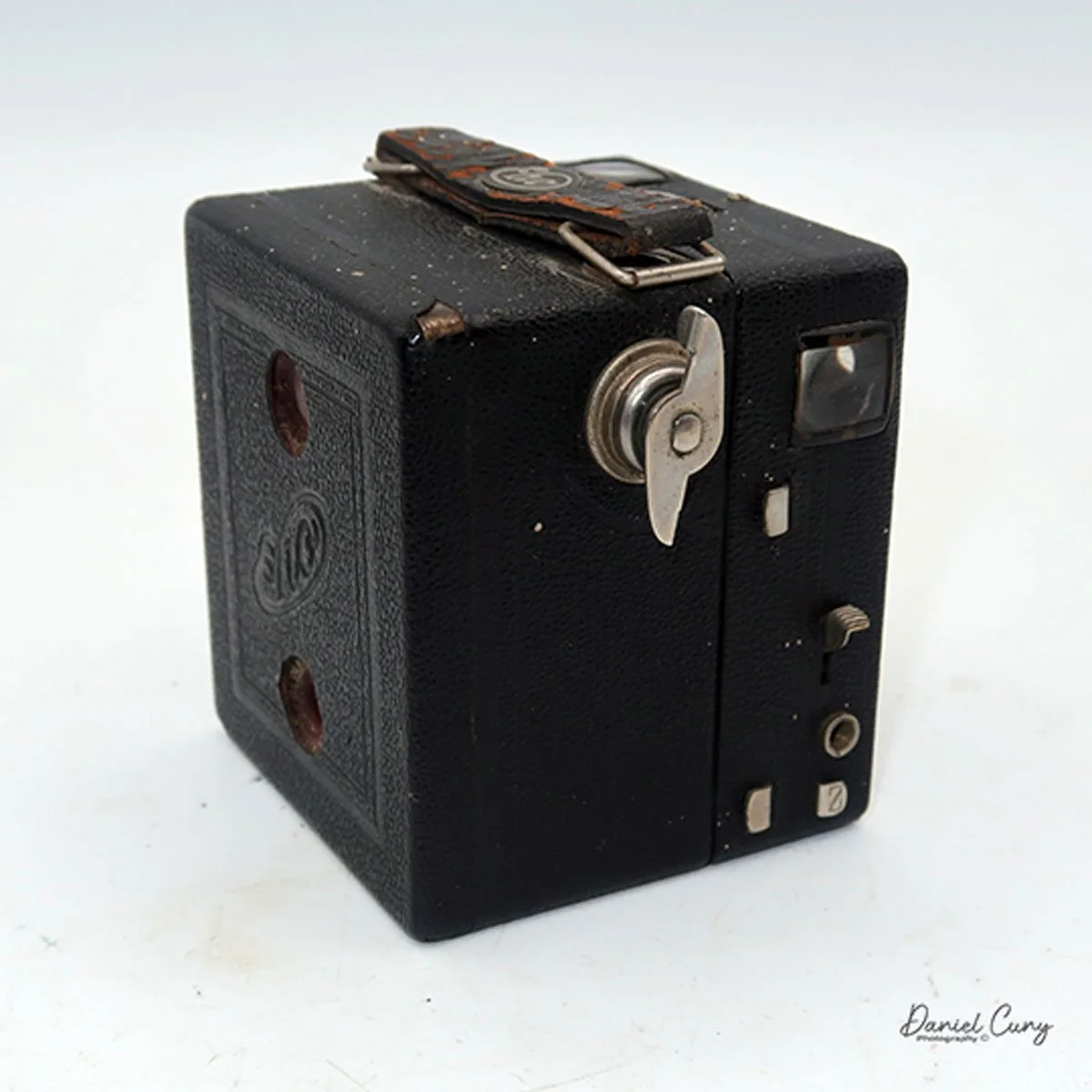
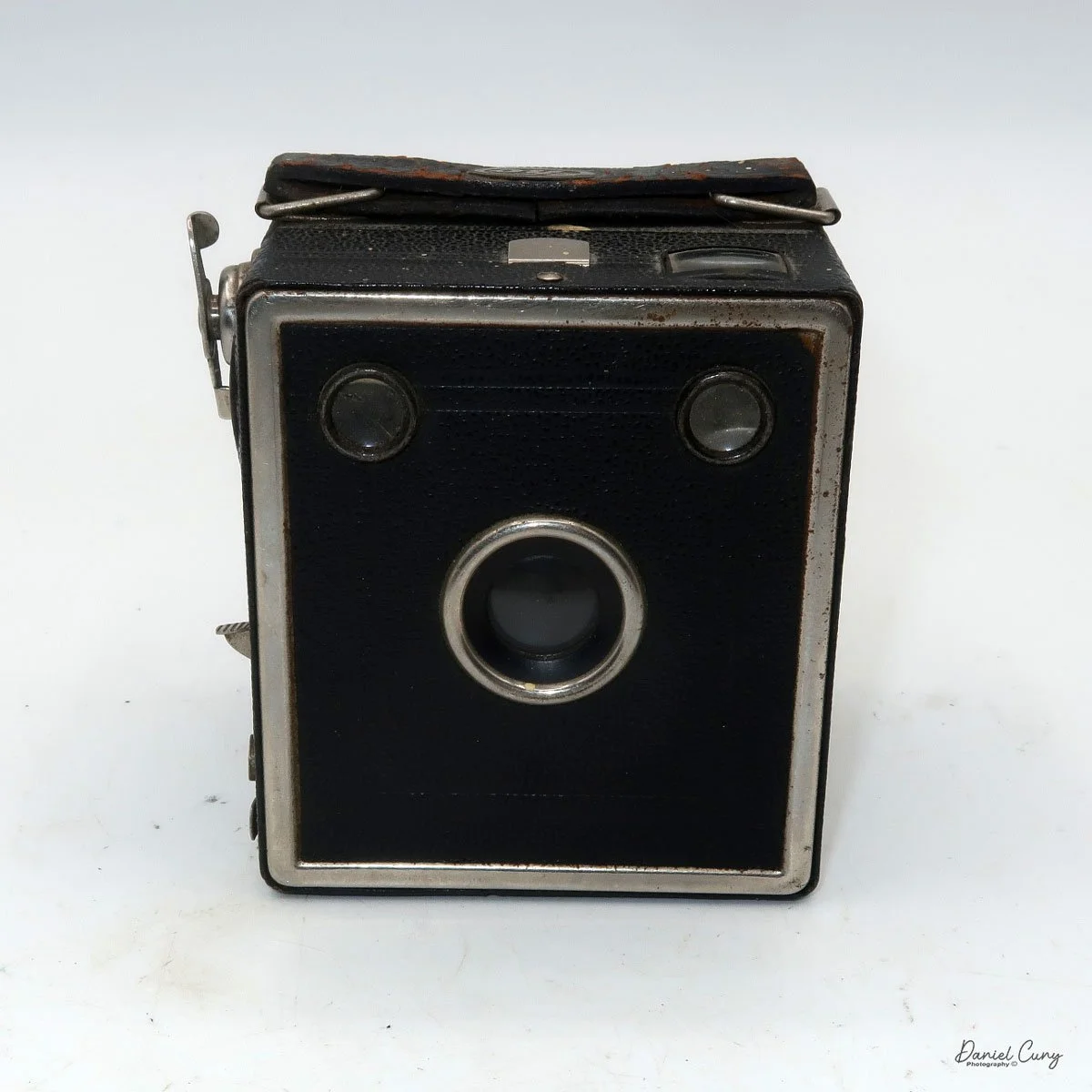
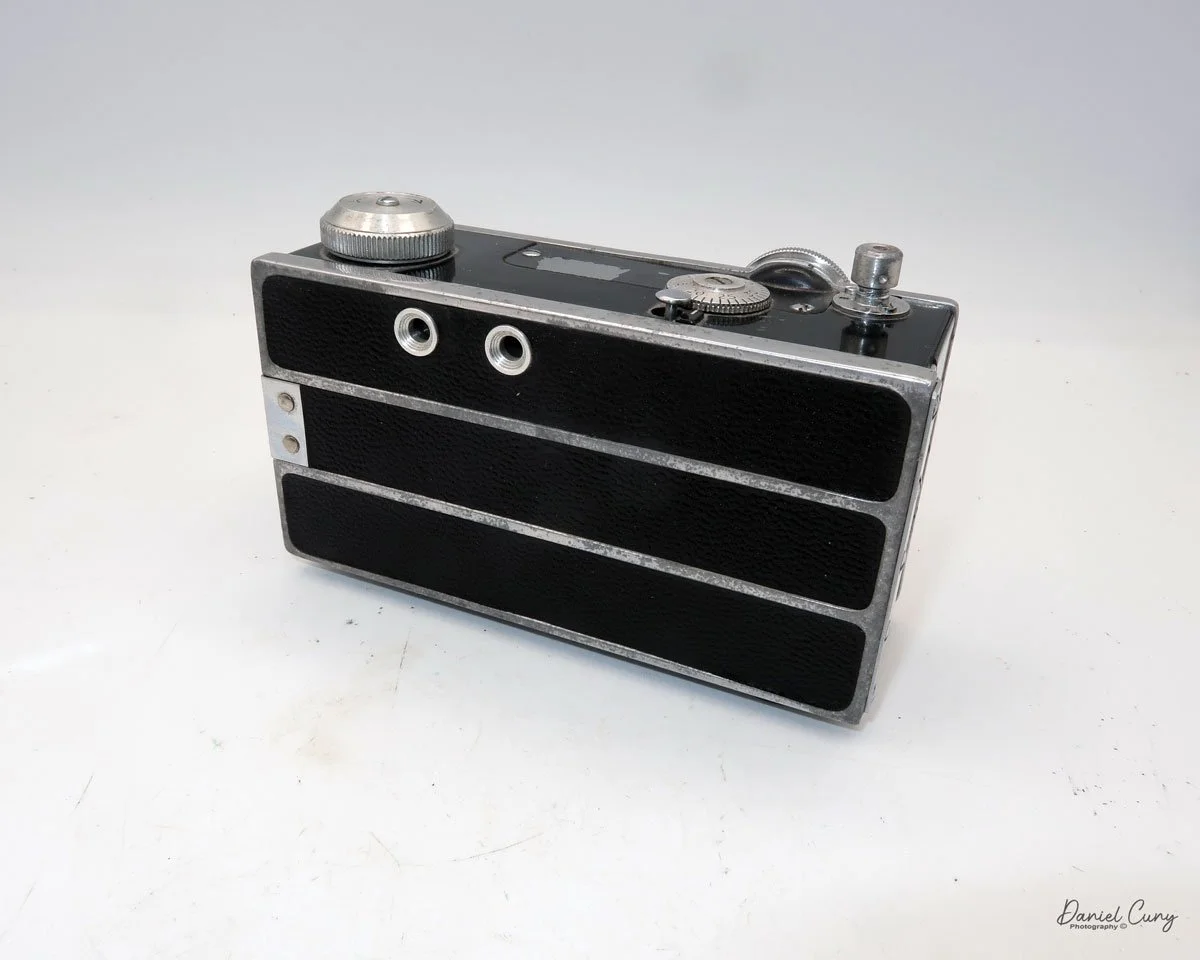
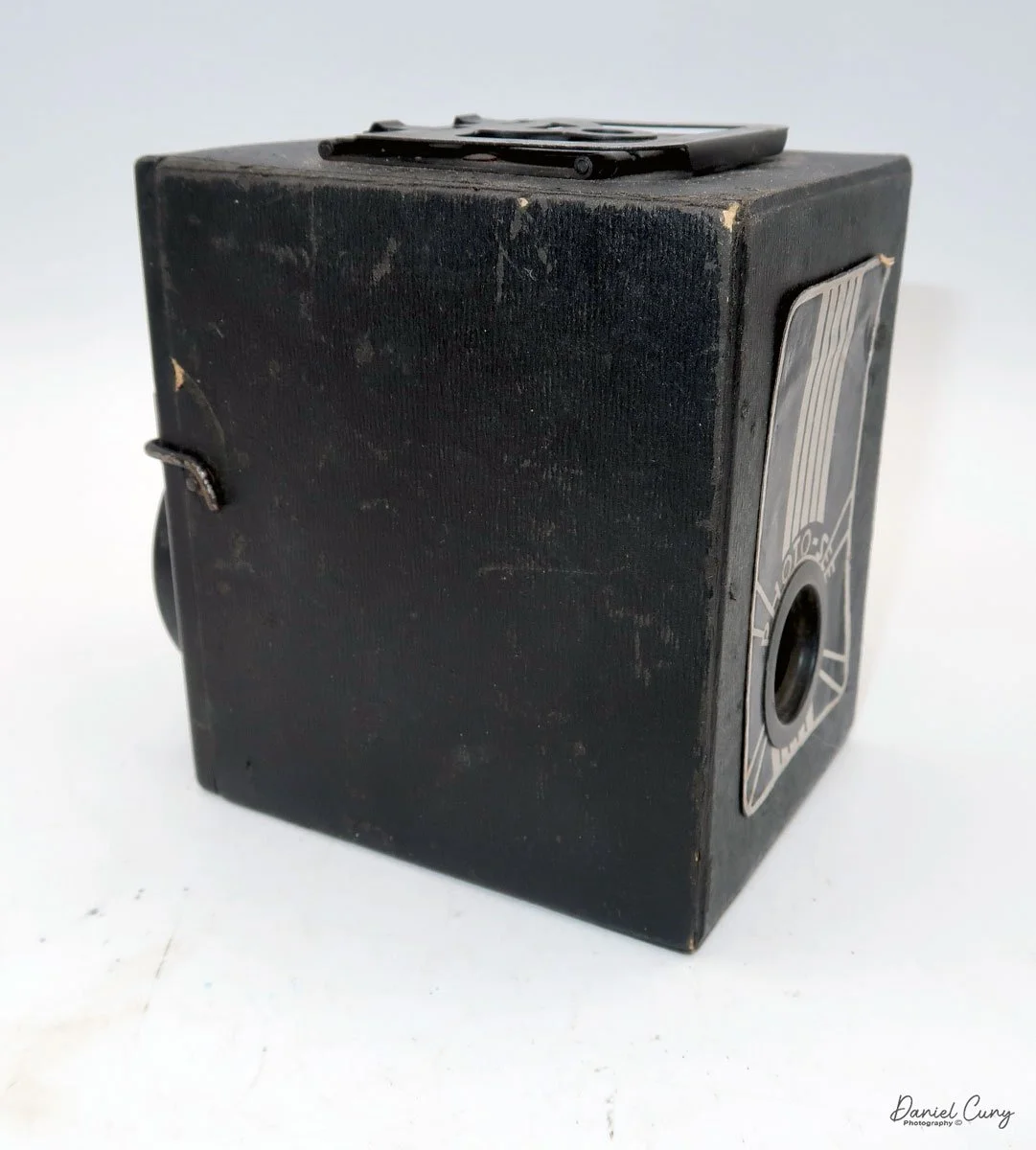
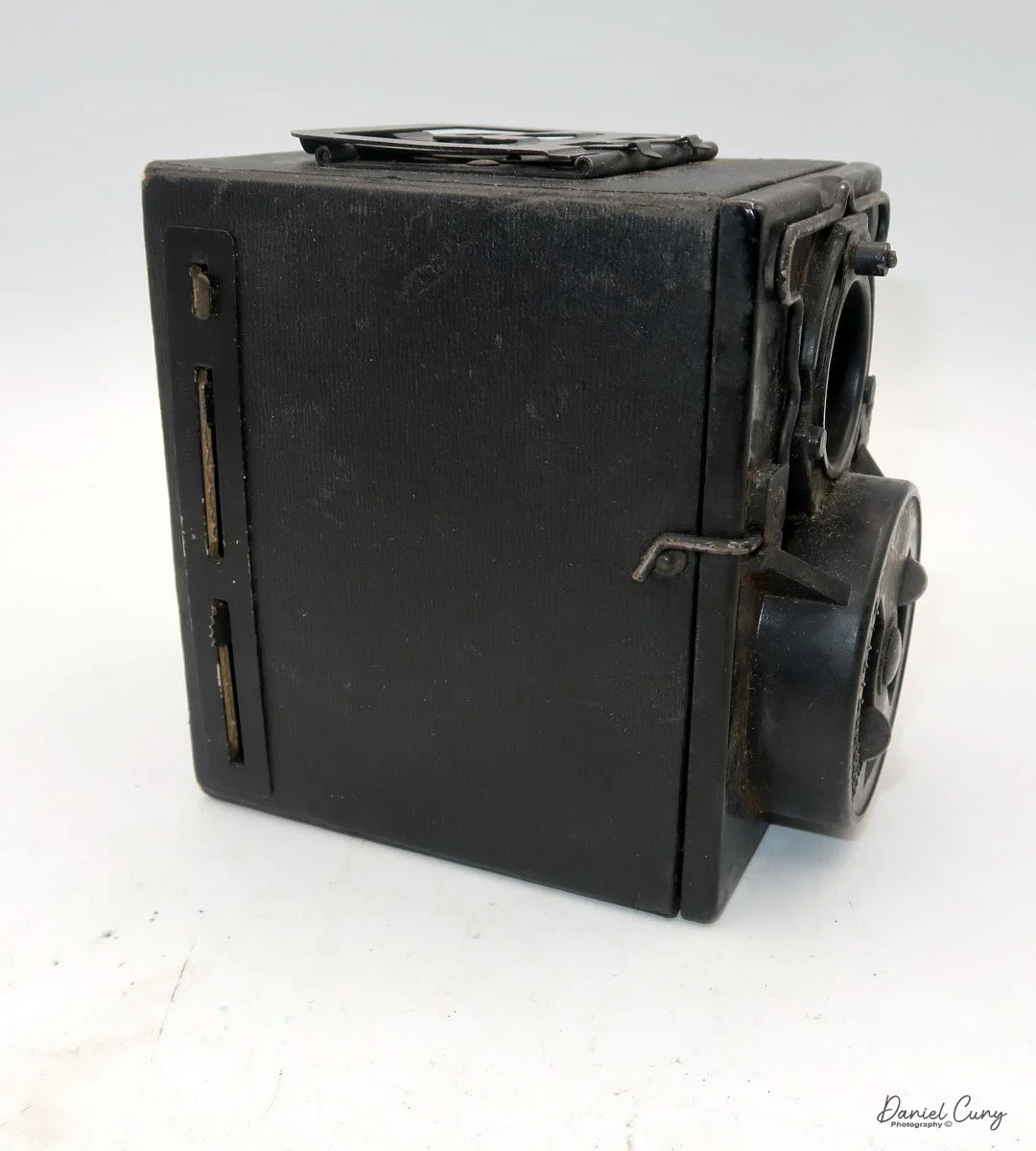
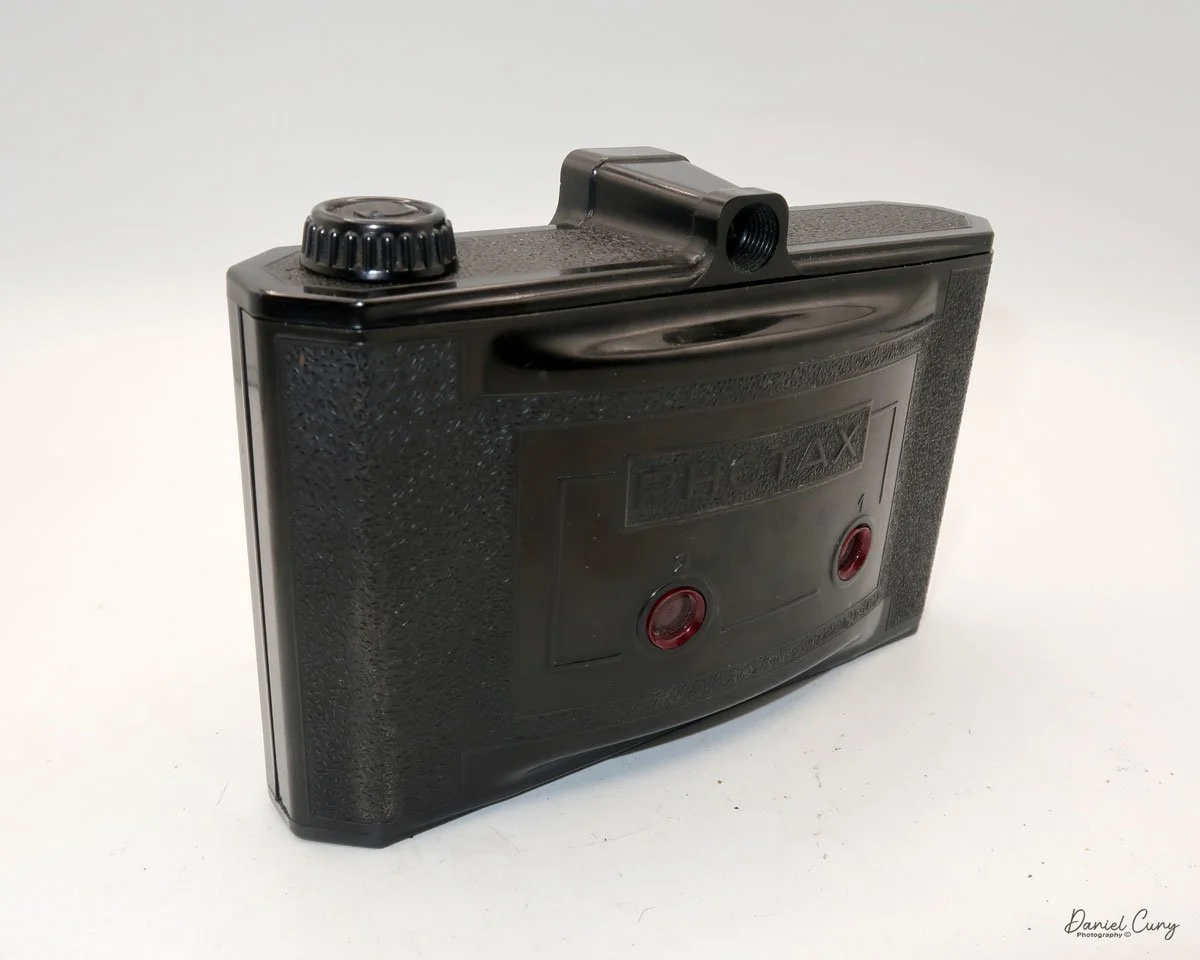
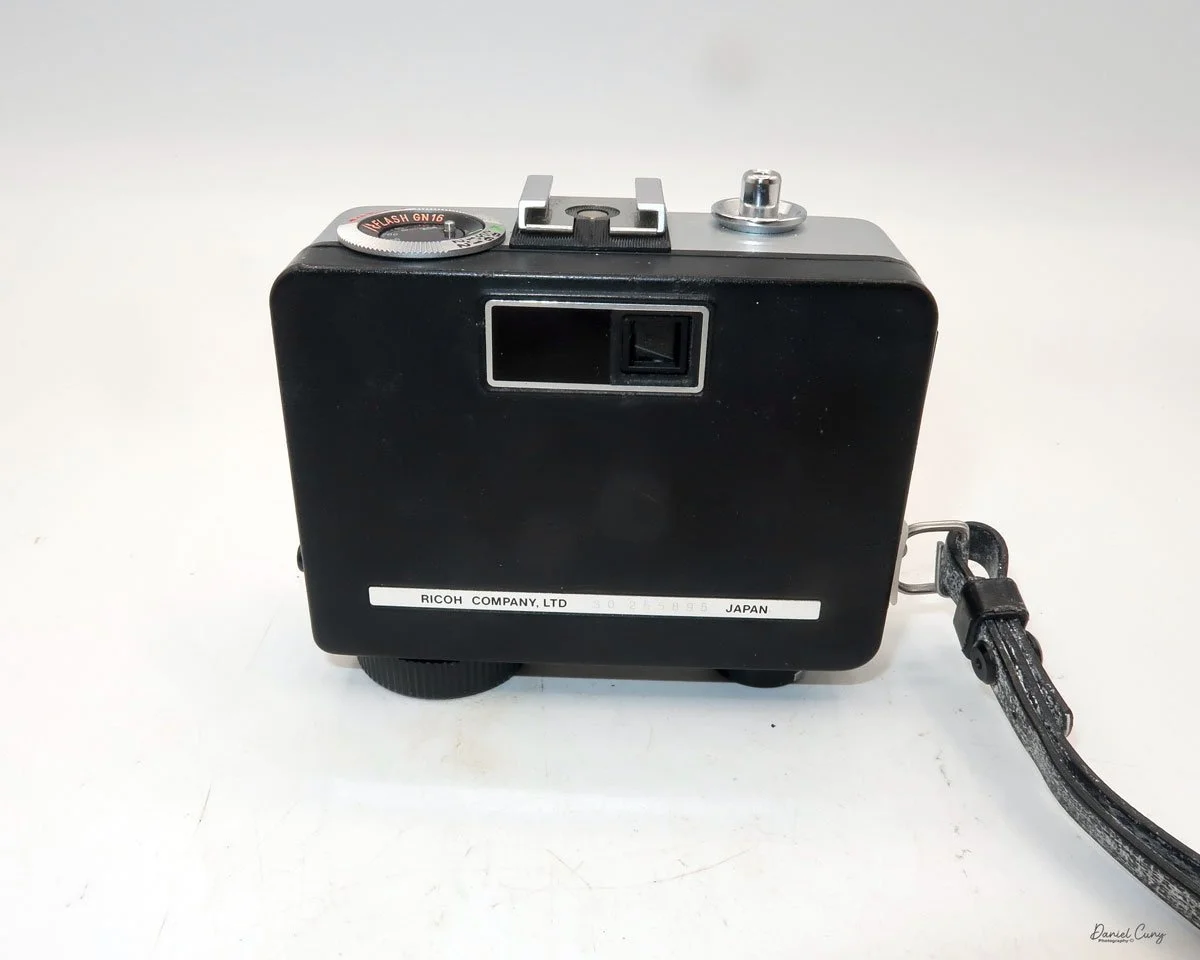
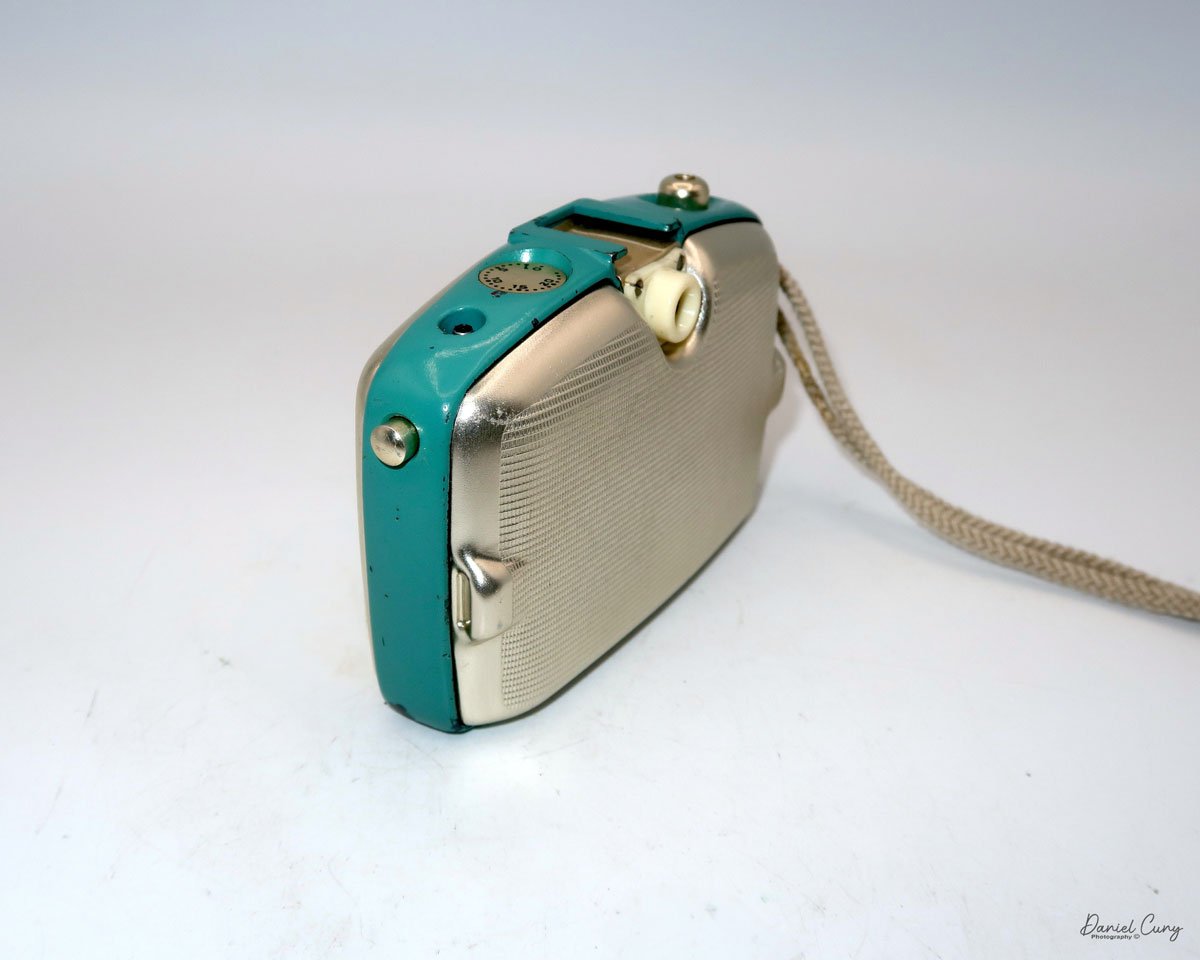
Back side of GOMZ Malyutka camera
Once I received the items from the auction, I noticed this really nice brown bakelite camera with Russian Cyrillic writing on the back. As I've mentioned before, I have a love for colored cameras, so when I saw this Gomz Malutka, I thought it was a nice little camera. I put it away, not really giving the camera much thought until about a year ago when I was going through a box of photo items for a local camera show that was selling at. I pulled the Gomz Malutka from the box, and was ready to add it to the items for the sale. Then, as I was inspecting the camera again, I thought it might be a fun camera to write about sometime in the future. I set the camera aside.
After the camera show, as I returned to my office, I noticed the Gomz Malutka on my desk and started making some basic inquiries about the camera. At this point, I began to see that the camera is indeed somewhat rare, so let's write about it for my blog.
History:
The history of GOMZ (Gosudarstvennyi Optiko-Mekhanicheskii Zavod), the State Optical-Mechanical Plant, reflects Russia's tumultuous and innovative 20th-century history. Located in Leningrad (now St. Petersburg), the factory was the cradle of the Soviet optical industry, responsible for producing the nation's first mass-market cameras and pioneering designs that predated Western equivalents.
Cover of Sovetskoe Foto (Soviet Photo) Magazine
The facility began life in 1914 as a French-Russian joint venture to produce optical sights for the military during World War I. Following the 1917 Revolution, the factory was nationalized and underwent several reorganizations before officially adopting the GOMZ acronym in 1932. While it continued to produce military optics, the Soviet leadership demanded a domestic photographic industry to reduce reliance on German imports, pushing GOMZ toward consumer cameras.
The 1930s marked GOMZ's golden era of innovation. Its first major success was the Fotokor-1 (1930–1941), a 9x12cm folding plate camera. Based on German designs, the Fotokor-1 became the first mass-produced Soviet camera, with over one million units manufactured. It effectively democratized photography in the USSR, serving as the primary tool for documenting the Soviet state's industrialization.
Even more technically significant was the Sport (1937), a 35mm single-lens reflex (SLR) camera. Historians often debate whether the GOMZ Sport or the German Kine Exakta was the world's first proper 35mm SLR. Regardless of the title, the Sport was a marvel of engineering for its time, featuring a vertical metal shutter and a reflex viewfinder that allowed photographers to see exactly what the lens saw—a standard feature today, but revolutionary in the 1930s.
Logo of Gomz camera
During World War II, the factory suffered heavily during the Siege of Leningrad. Production shifted entirely to military needs, such as sights for tanks and artillery. After the war, GOMZ pivoted back to consumer goods, focusing on affordable, simple cameras for the recovering population.
This post-war period gave rise to the legendary Lubitel series (starting in 1949). Based on the German Voigtländer Brilliant, the Lubitel was a twin-lens reflex (TLR) camera made of Bakelite and later plastic. It was cheap, durable, and capable of producing excellent medium-format images, introducing millions of amateurs to photography. Similarly, the Smena series provided a simple, viewfinder alternative that became a staple in Soviet households.
In 1965, GOMZ underwent a final restructuring, becoming the Leningrad Optical-Mechanical Association (LOMO). Under this new name, the factory would later produce the LOMO LC-A, the camera that accidentally sparked the global "Lomography" art movement in the 1990s. However, the foundation of this success was laid during the GOMZ era, which transformed a military optics plant into a titan of Soviet creativity and engineering.
My Camera:
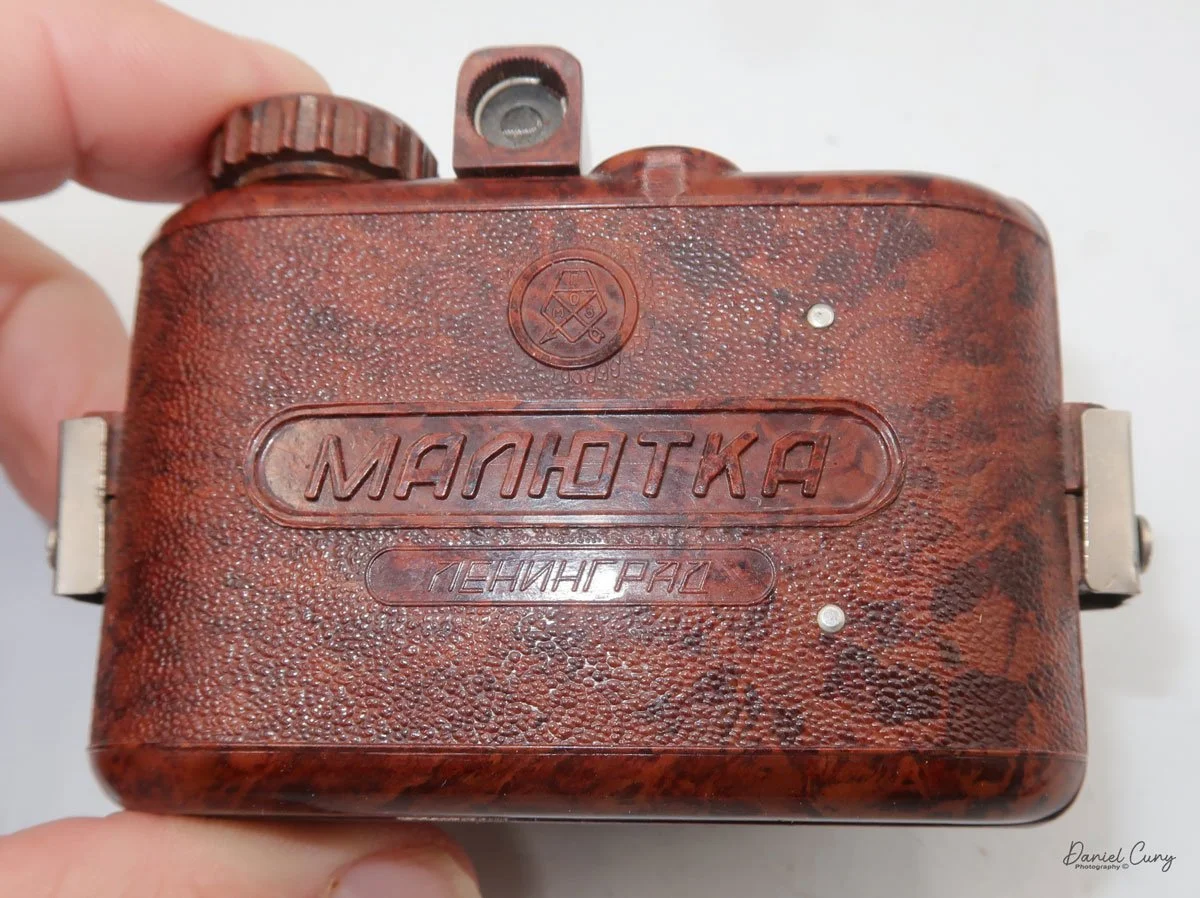
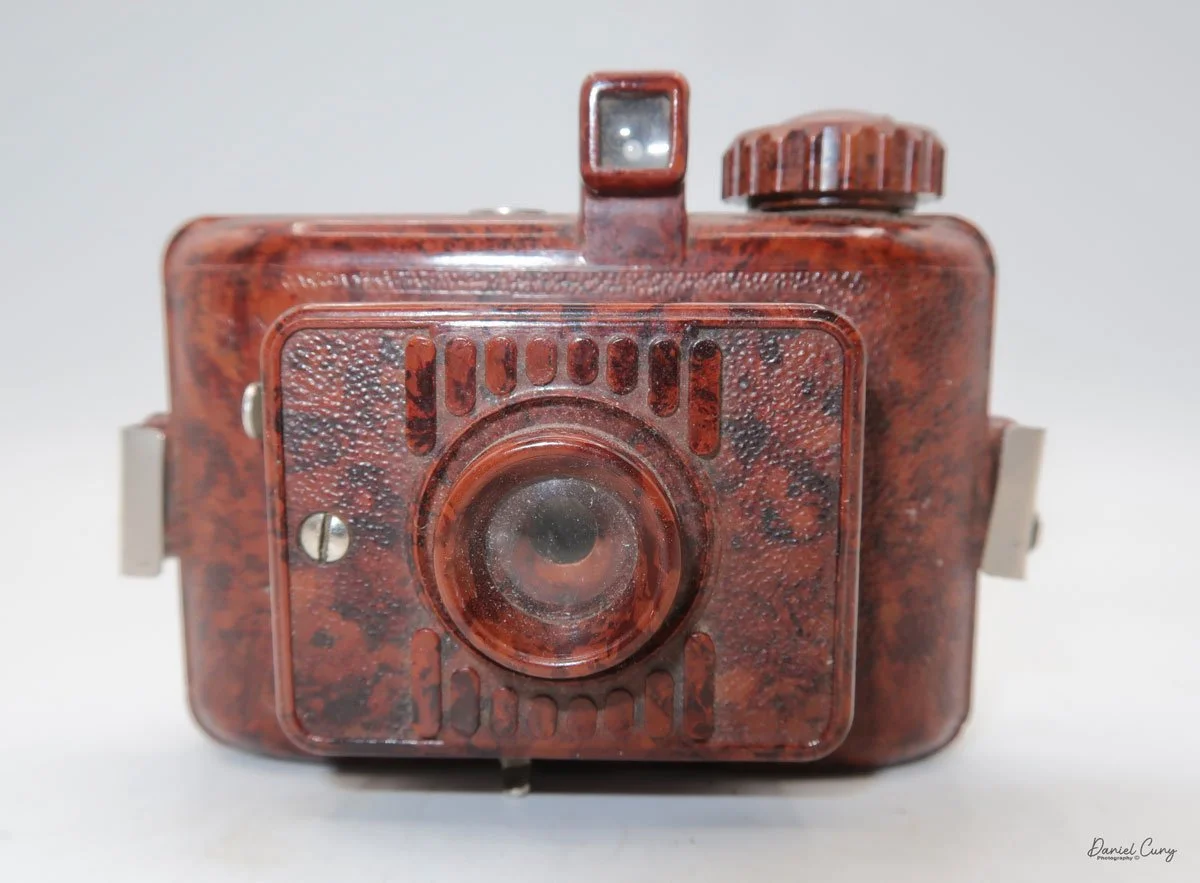
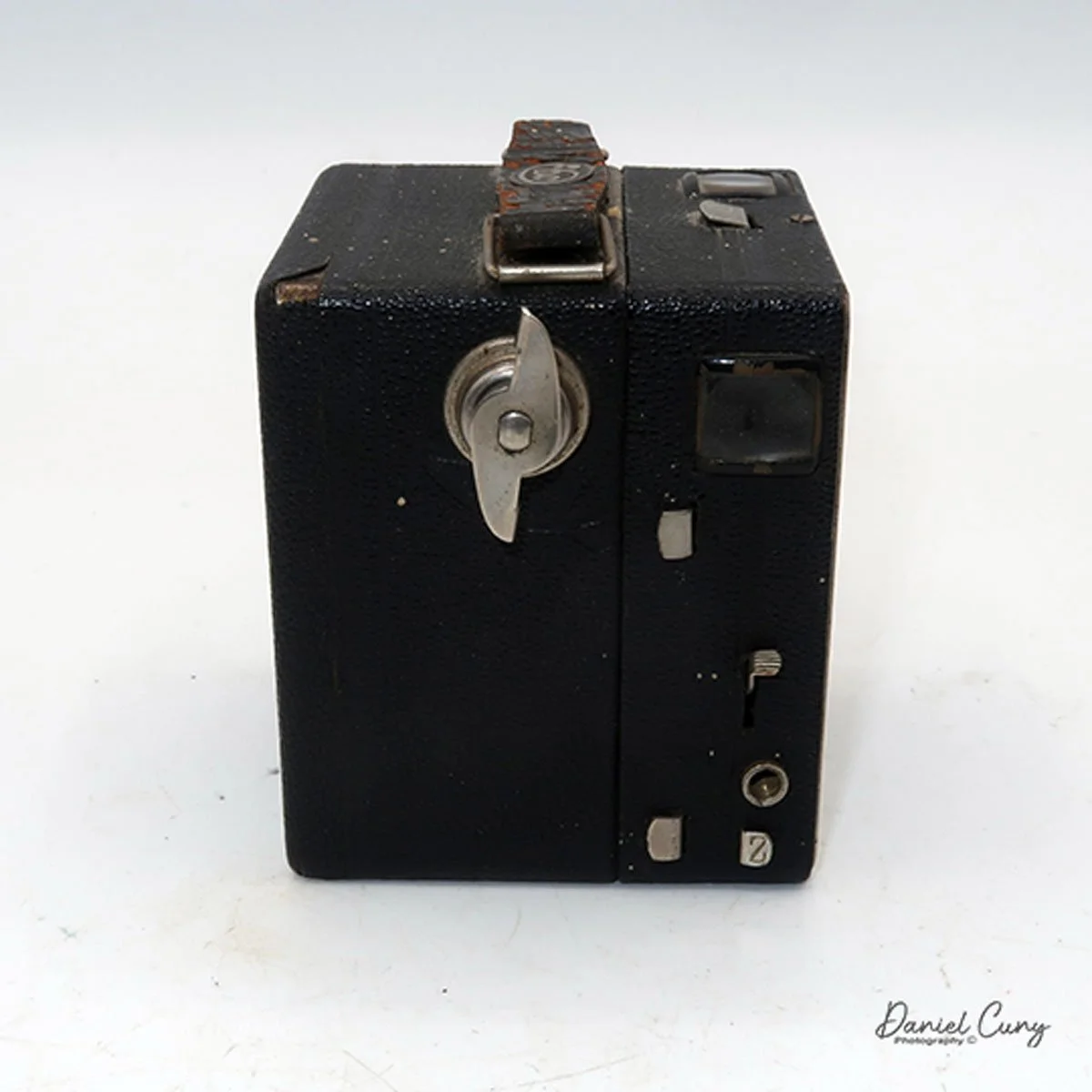
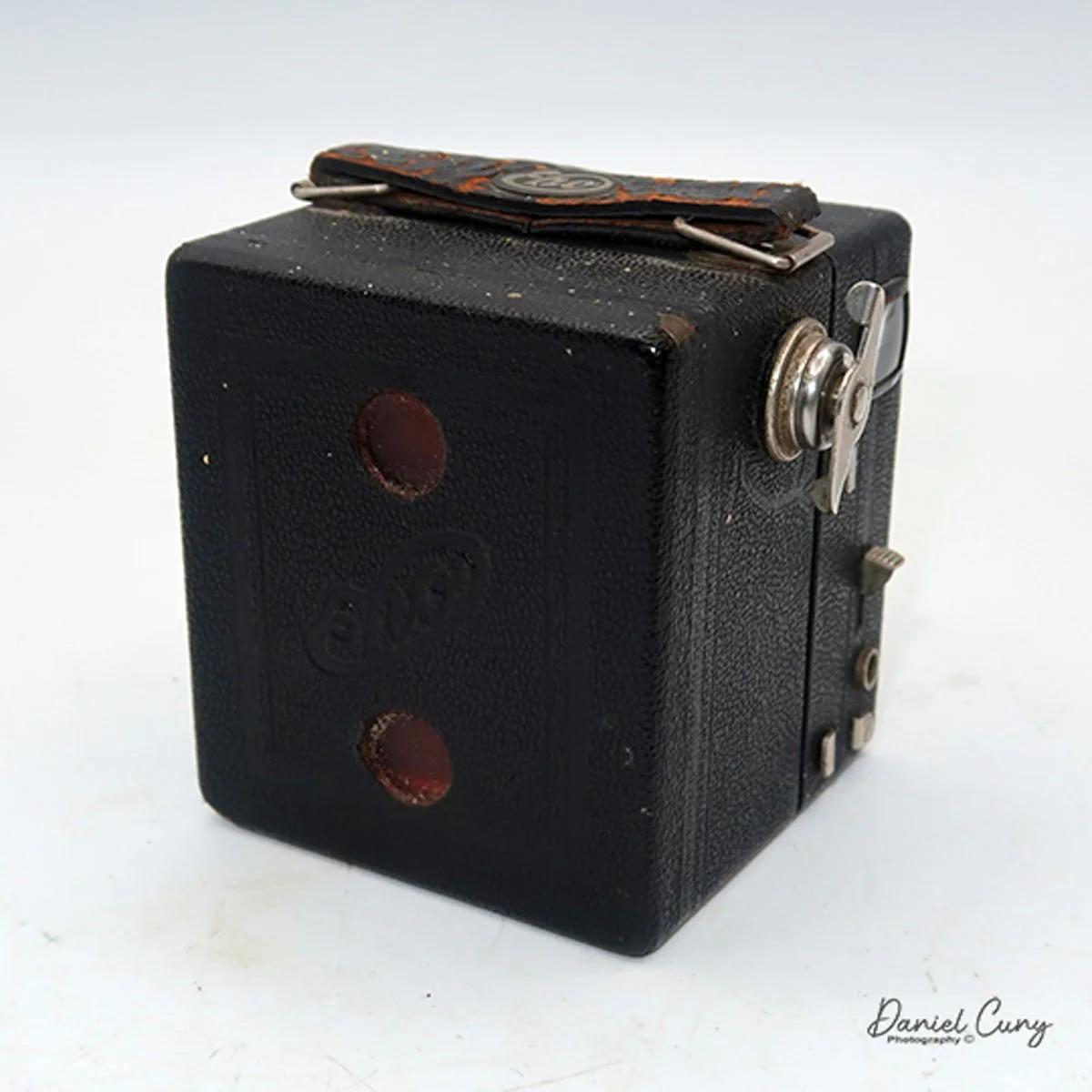
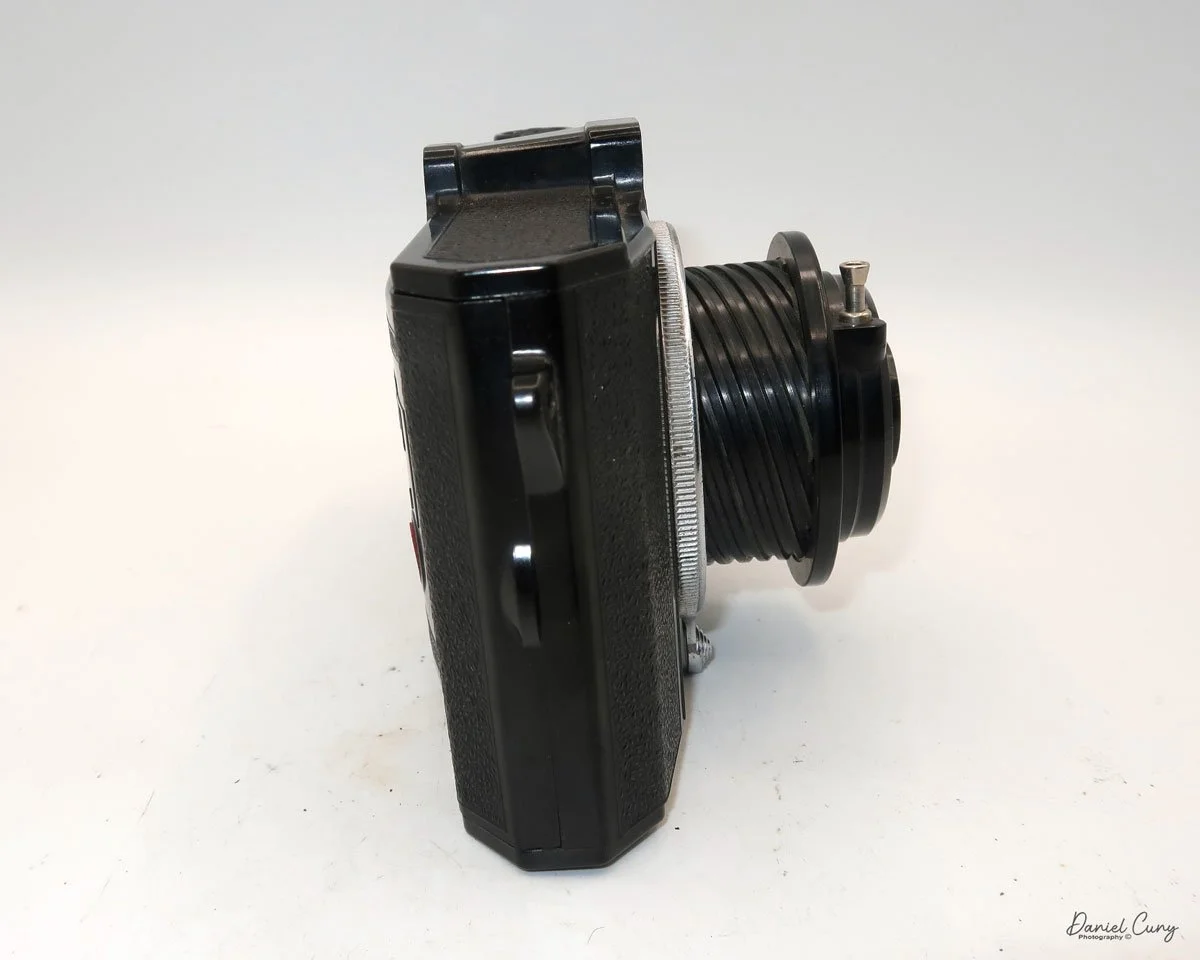
My GOMZ Malyutka is small, measuring 2" wide, by 1.5" tall and 1.5" deep from the front of the lens to the rear of the camera, and it weighs only 2.3 ounces without film. The Gomz Malutka is based on the SIDA camera from Sida GmbH, Berlin, Germany, which was made in the mid-1930s and came in both metal and Bakelite. "Malyutka" (малютка) is a Russian word that means "baby," "little one," or "tiny thing". It is also very similar to a camera made by Gomz, Liliput camera.
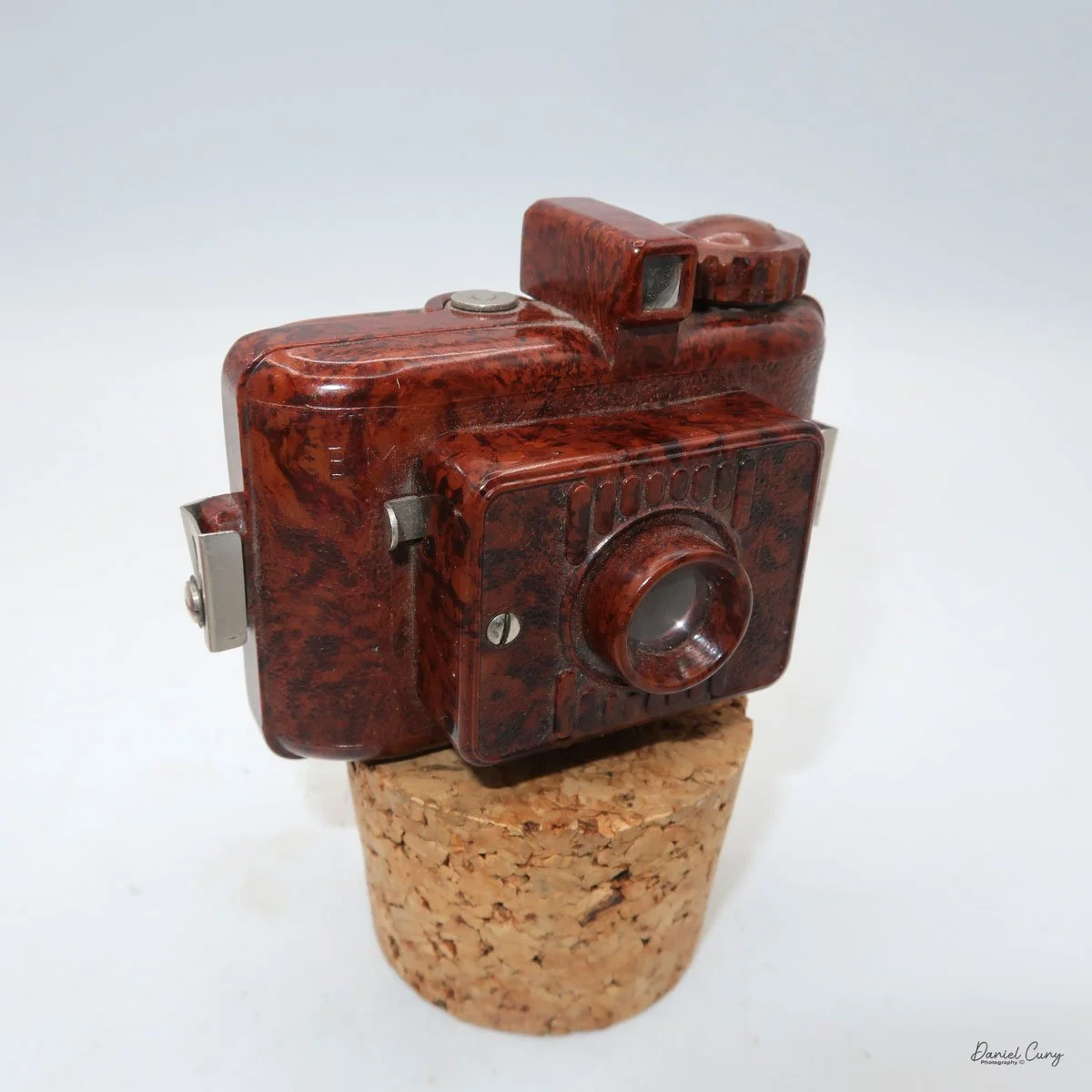












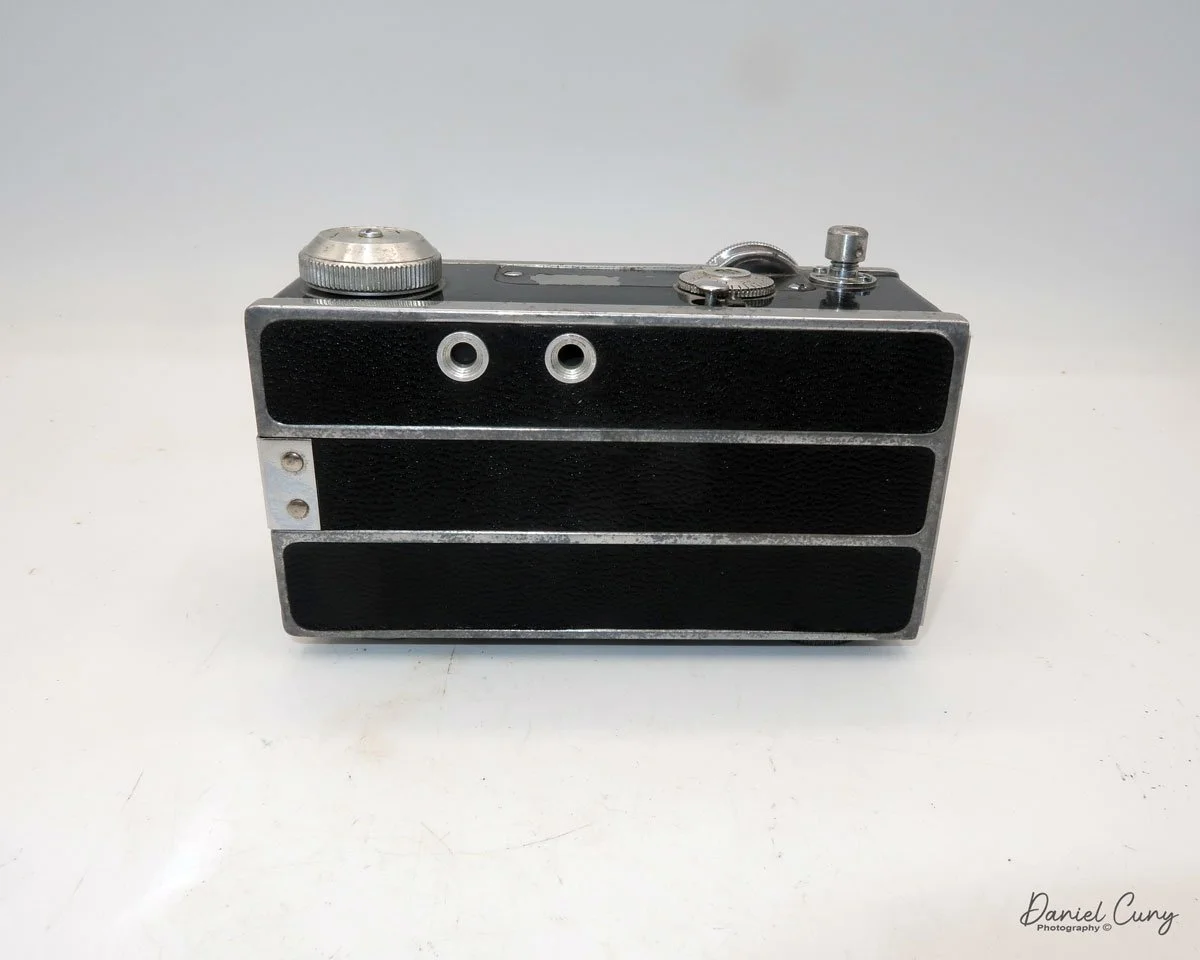
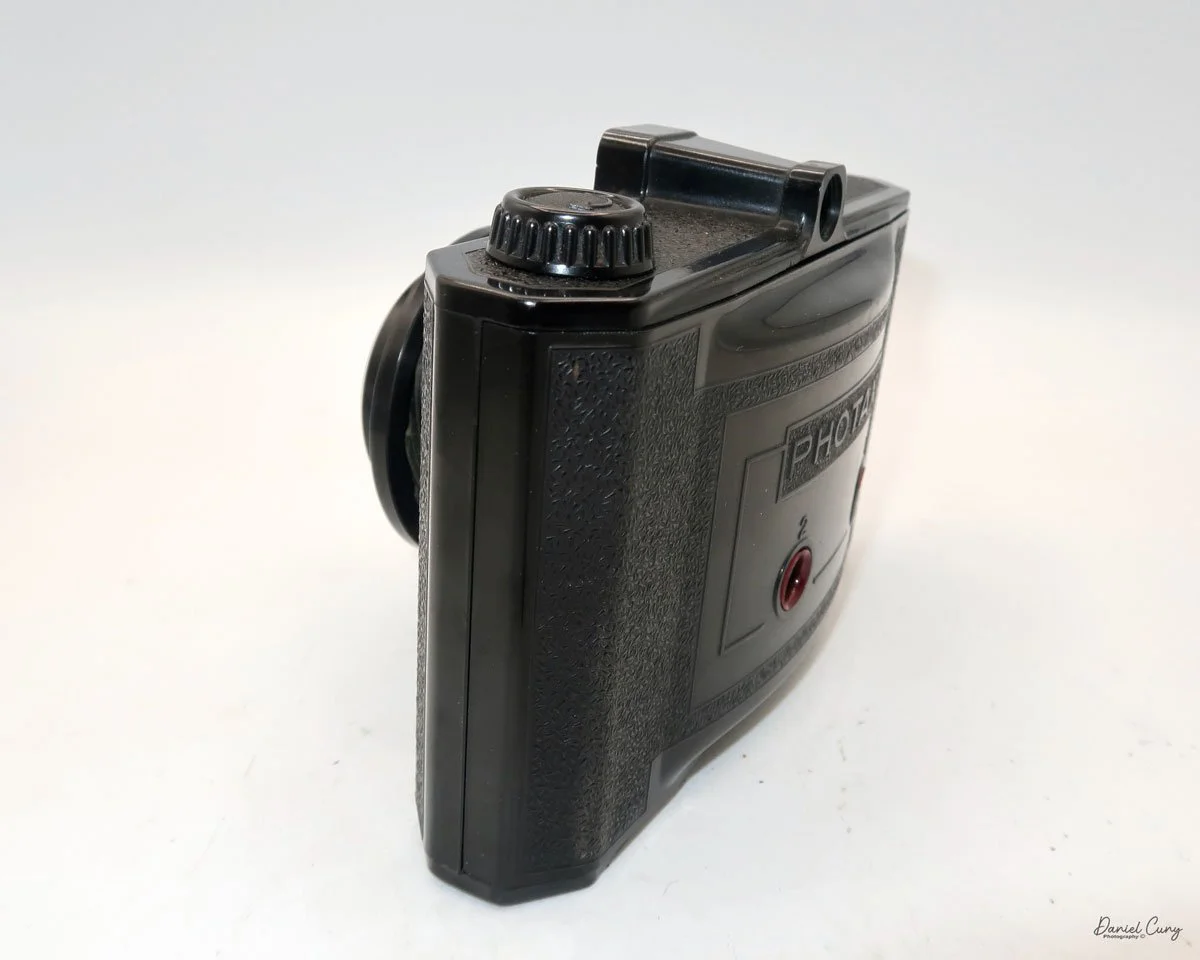
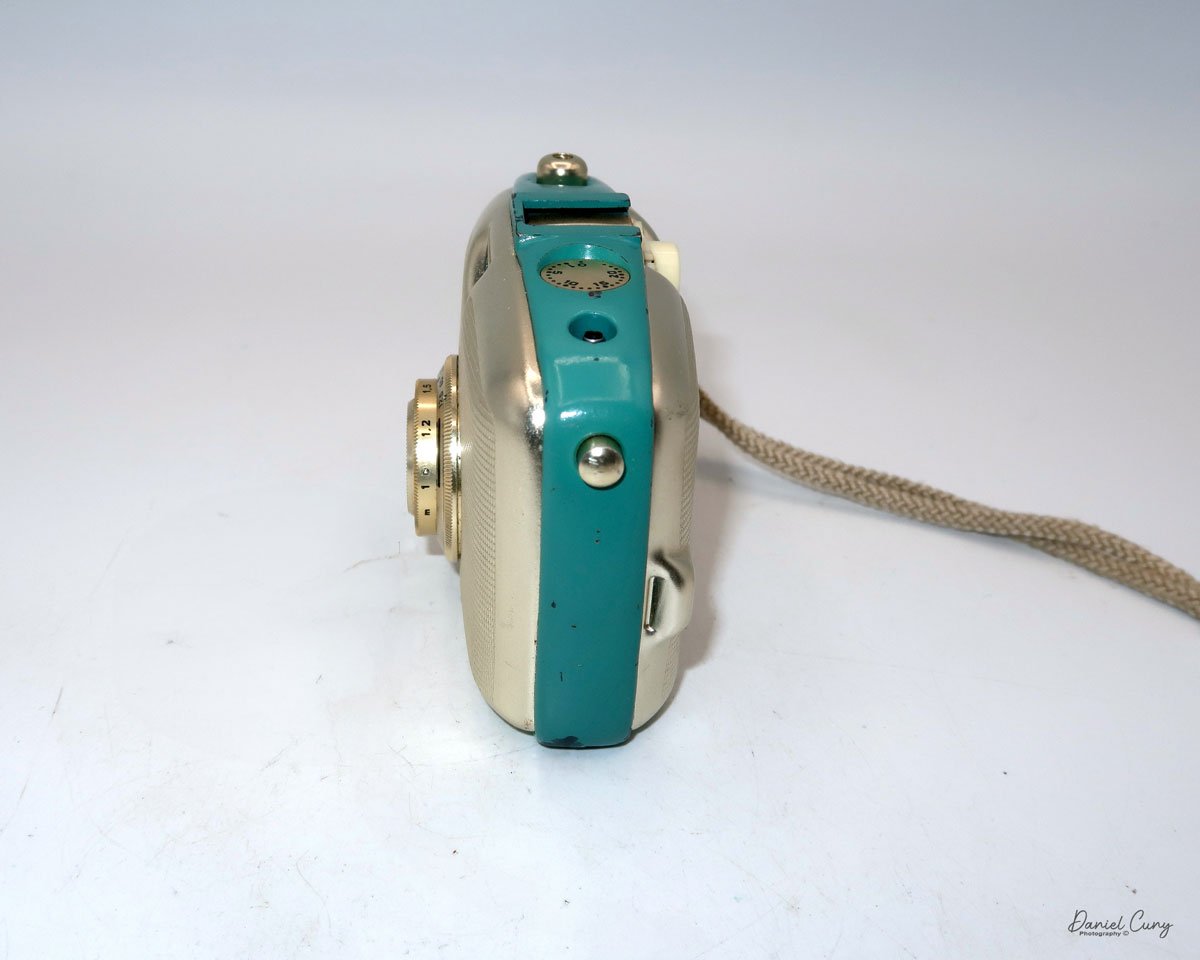
The camera's controls are very straightforward. There is only the shutter release at the bottom of the camera, along with the shutter control on the right side next to the lens. The shutter control consists of two settings: "M" (moment) for normal shutter speed, generally around 1/50 sec, and "B" for time exposures. Sliding a bar out from the side of the camera makes these settings. Sliding the shutter release under the lens takes the photo.
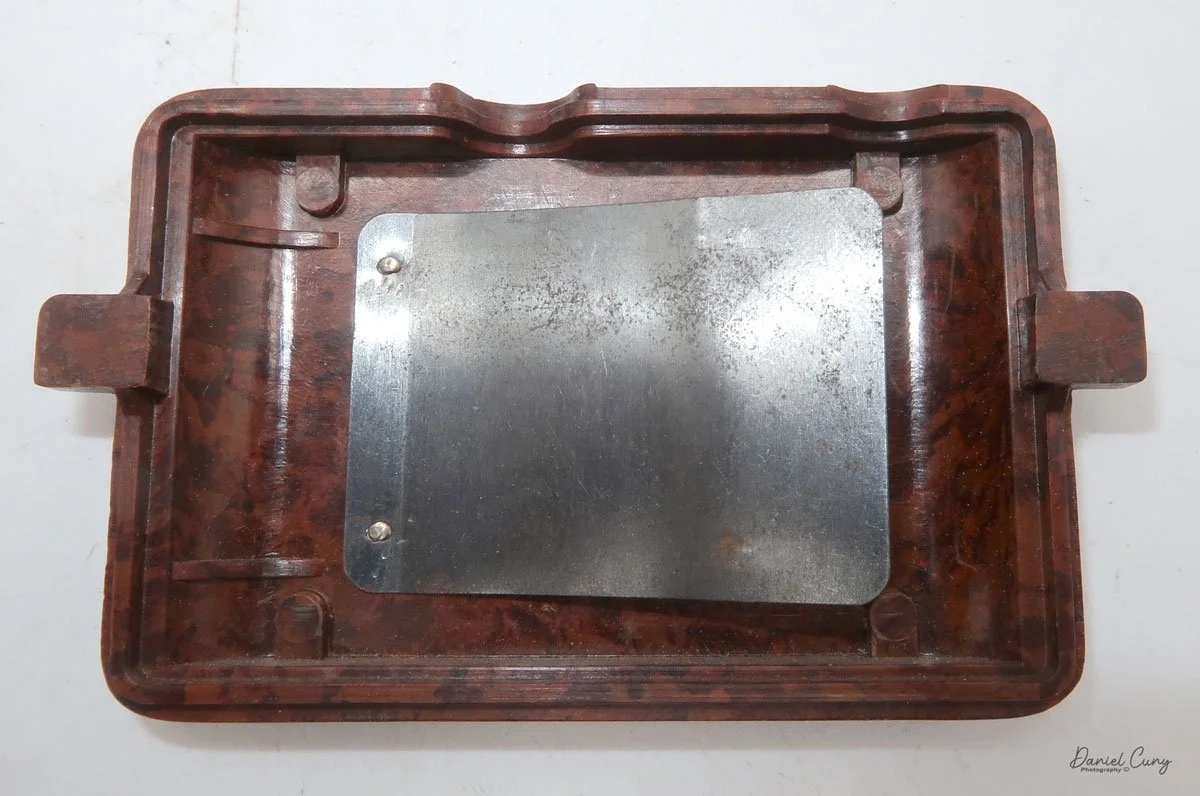
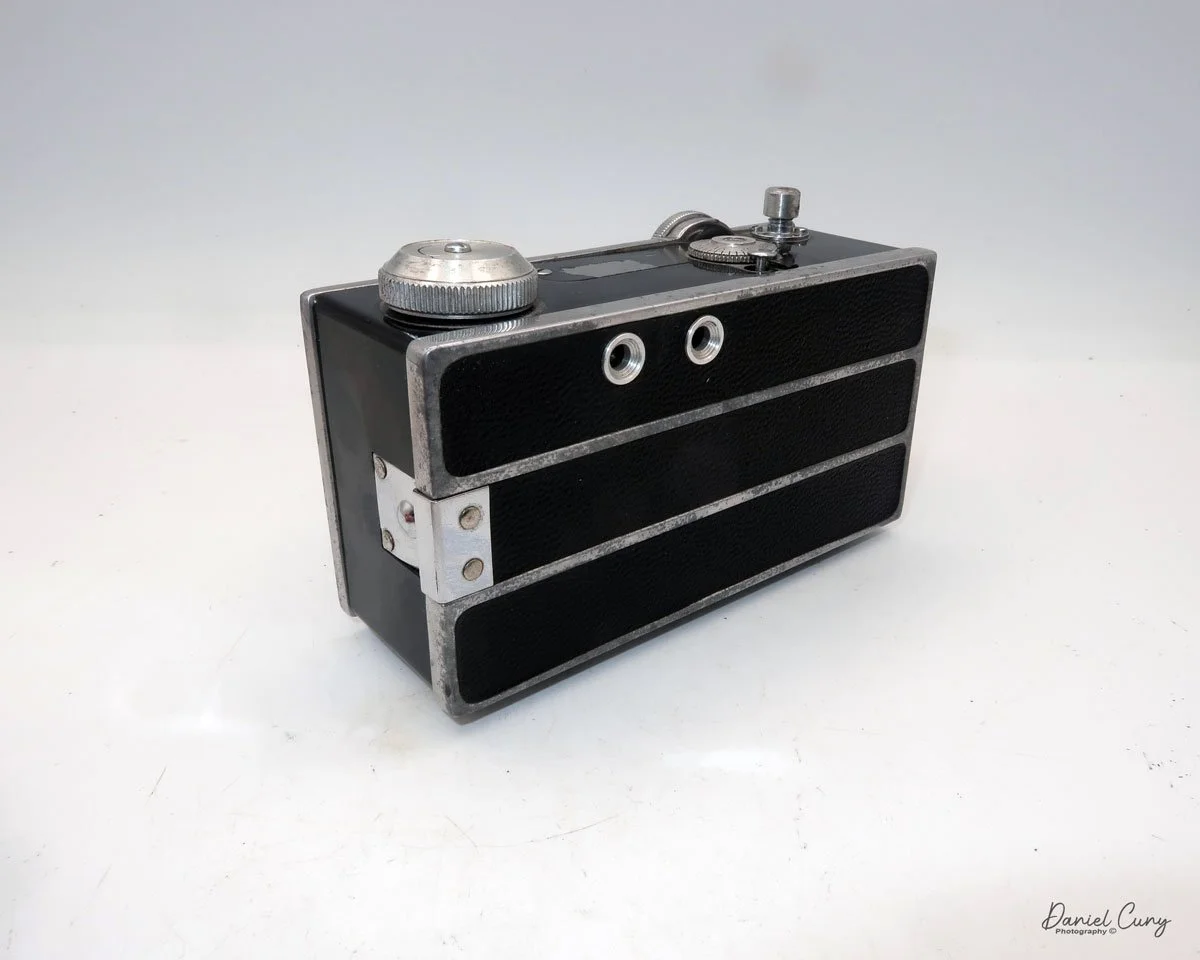
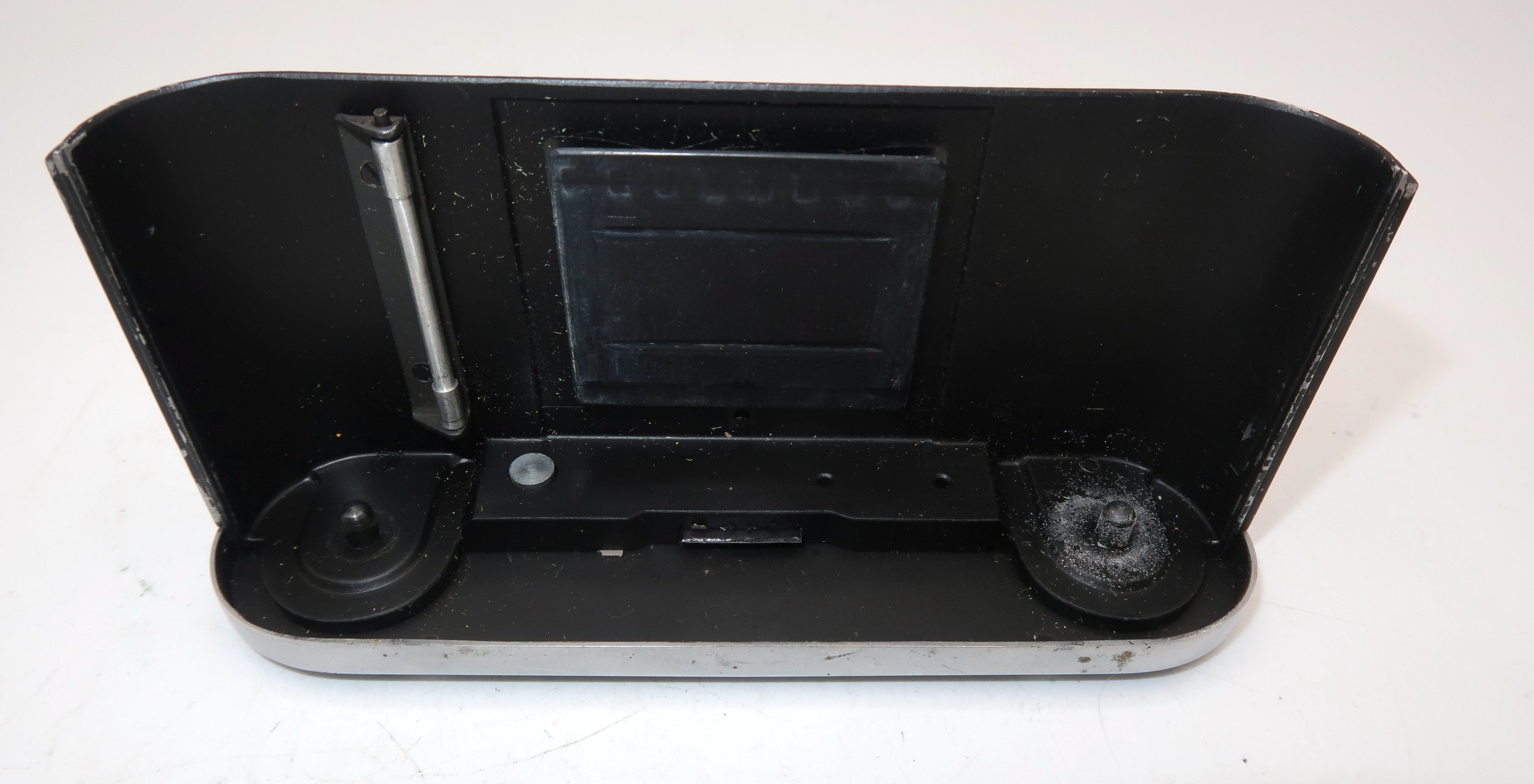
To open the back of the camera to load film, there are clips on either side that you move to the down position to remove the back. The camera takes Boltax film, a special 35mm film that produces a 24 mm x 24 mm negative. You load the camera similarly to any roll film camera: put the empty spool on the take-up reel side and the fresh film on the opposite side. Bring the leader to the slot on the take-up spool and start winding. Put the back on the camera and slide up the clips to lock it in place. Wind the film and advance it to the first frame.
There is a small viewfinder at the top of the camera to frame your photo, and a tripod socket at the bottom to steady the camera during long exposures. Also at the top is a small, round metal disk that rotates as the film moves within the camera. Since the camera doesn’t have a red window on the back of the film door, you need to watch the disk rotate a few times to make sure the film is moving inside the camera.
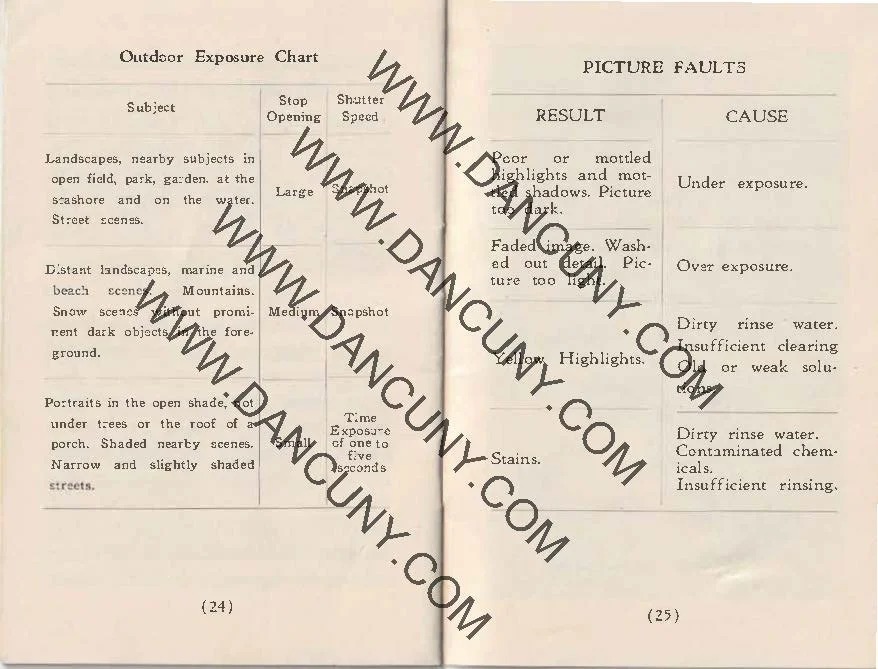
Results:
Since I don't have any Boltax film, I wasn't able to take photos with the Malutka camera, but possibly in the future, I'll try and use some paper backing I have from a few rolls of 828 film and run some film through it using 35mm to see how the camera performs.
Conclusion:
The Gomz Malyutka is an excellent small camera that I enjoy having in my collection. It's in fantastic condition and is another color camera that sits proudly amongst the other miniature and subminiature cameras on my shelf.
Thank you for taking the time to learn about this small, odd Russian camera.
I'd love to hear from you. Please get in touch with me if you have questions, concerns, or comments.
Here's a link to my other Camera Reviews.
Cuny's Camera and Photo has many cameras I've reviewed for sale, along with other camera and photo oddities. If interested in any items, email me, and I'll offer a nice discount as a friend of the family.
Until next week, please be safe.