A Tiny Full‑Frame Surprise: Shooting the Durst Duca
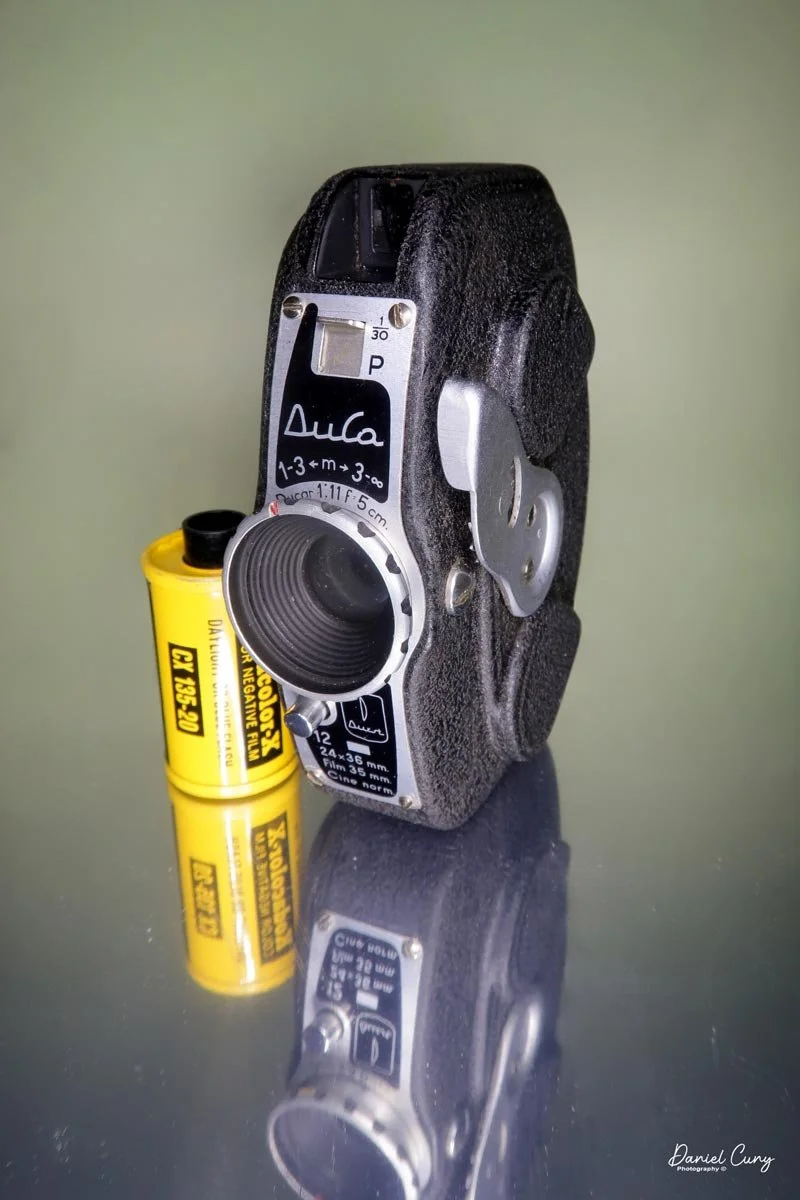
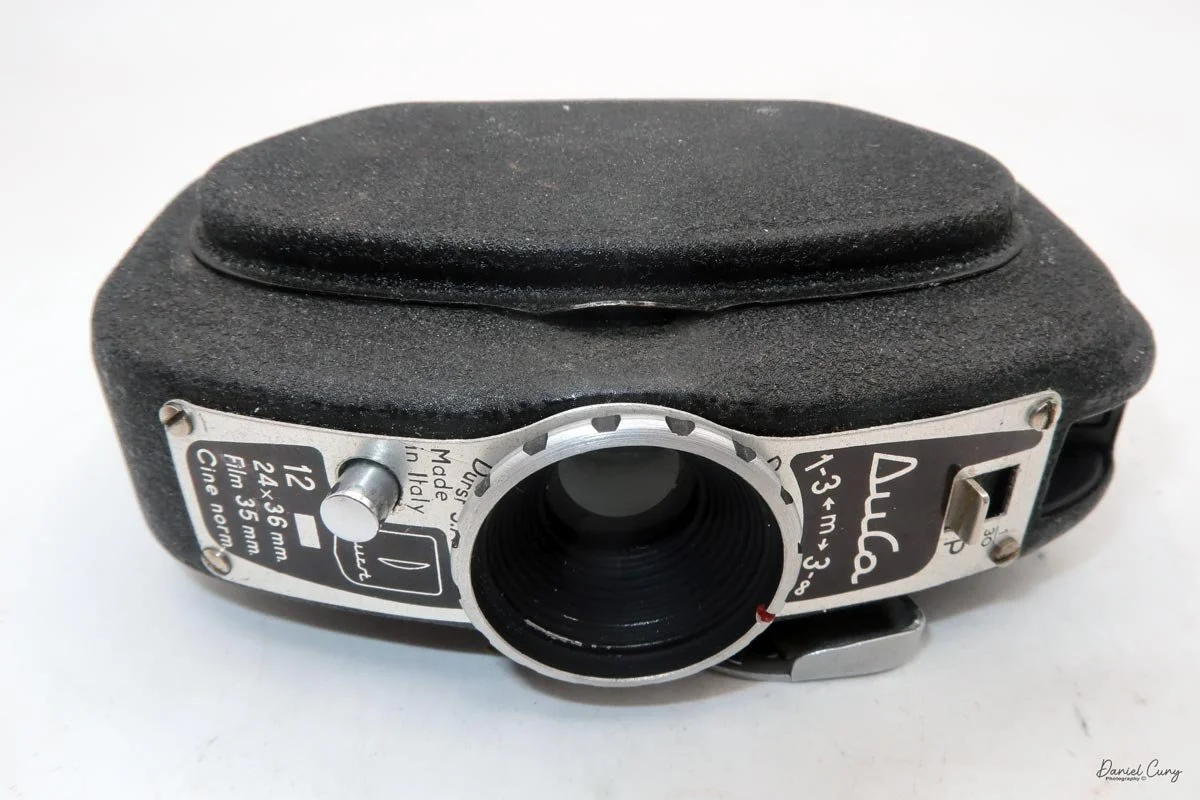
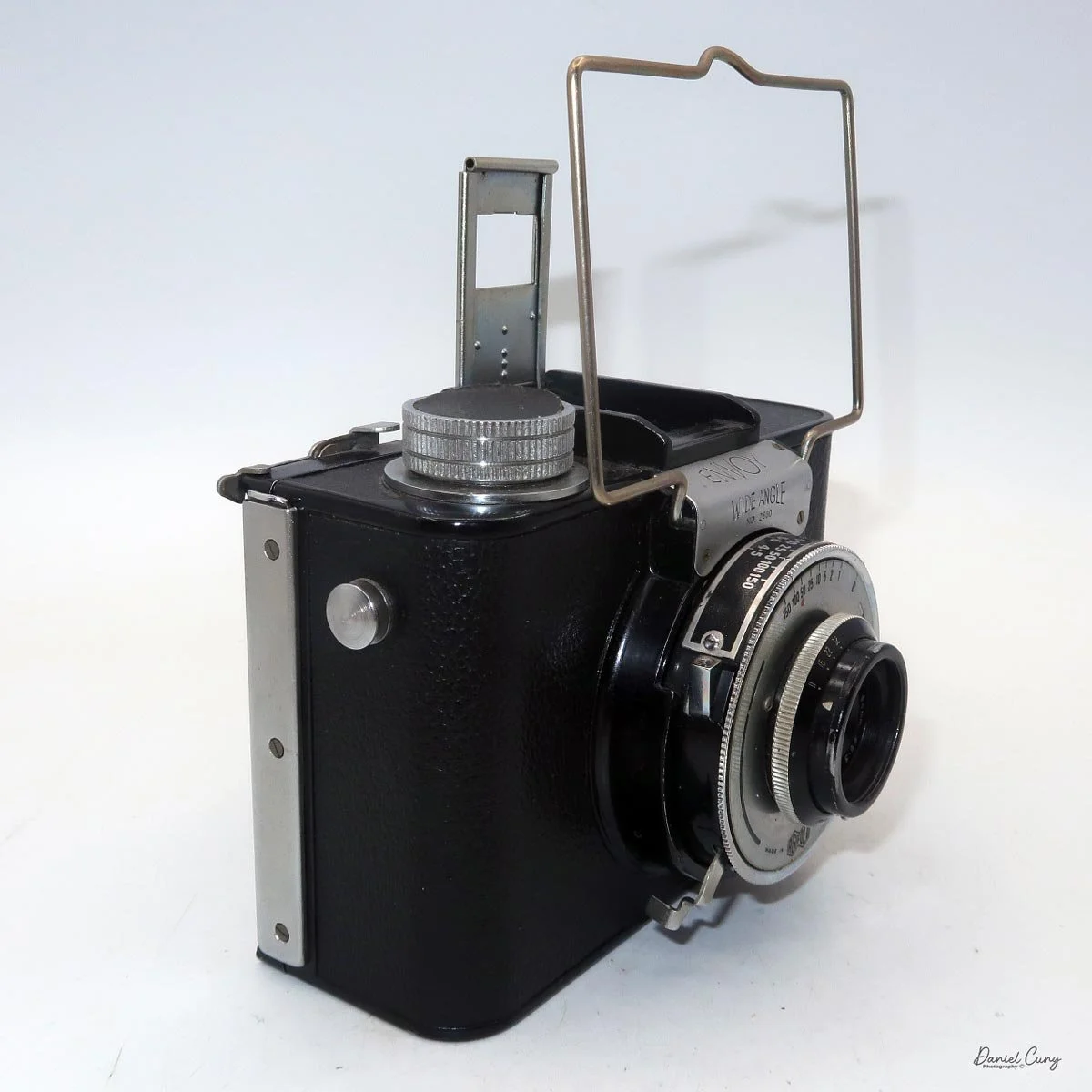
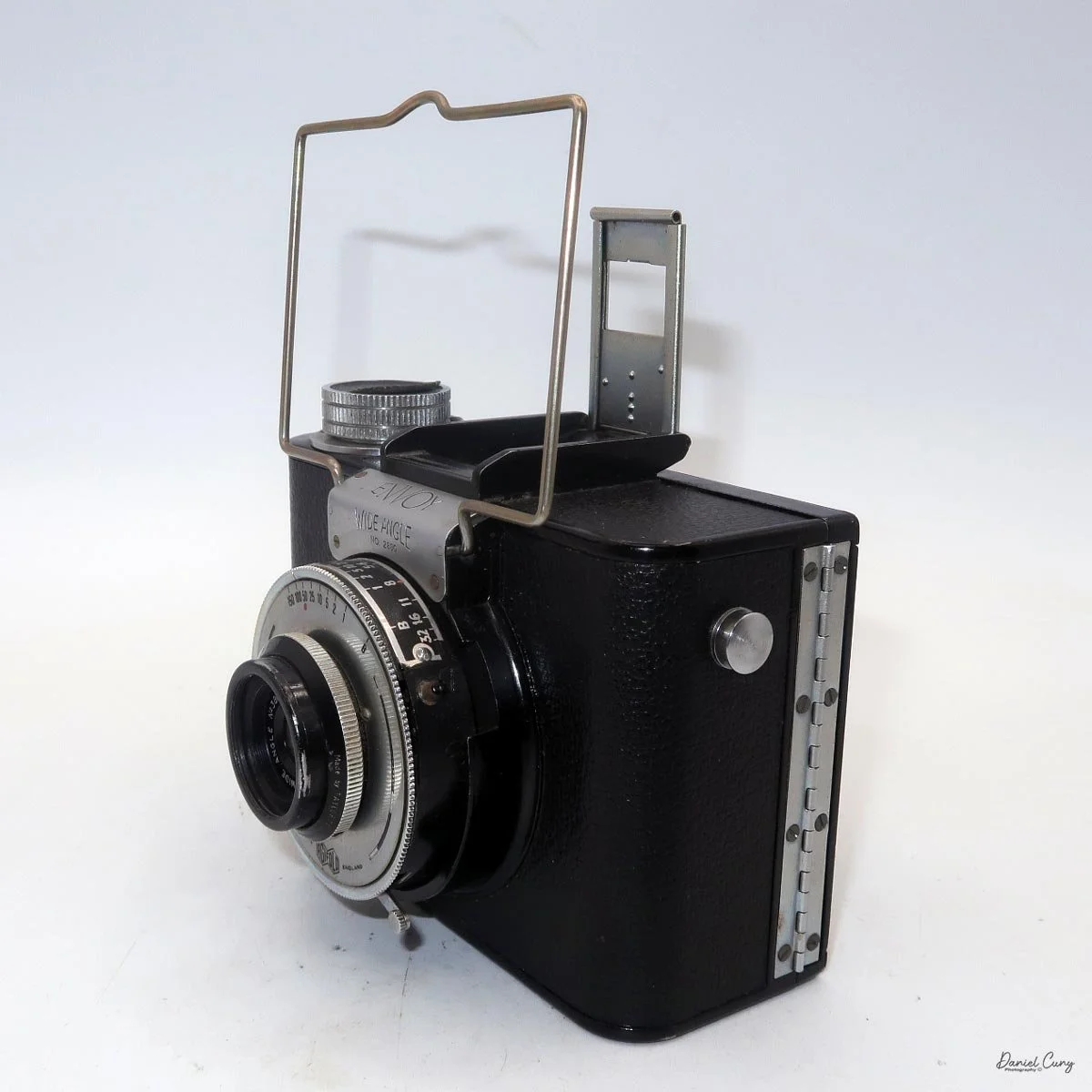
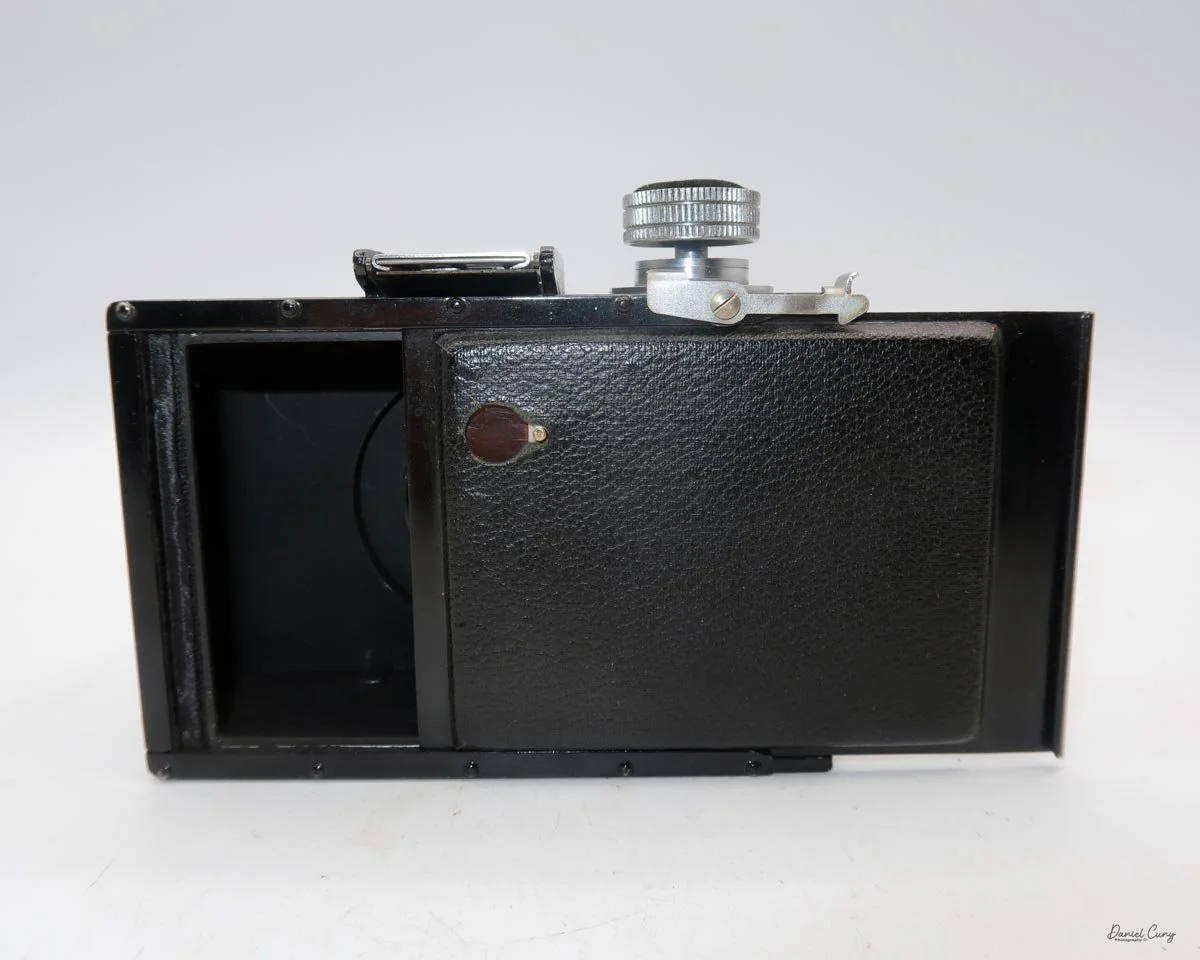
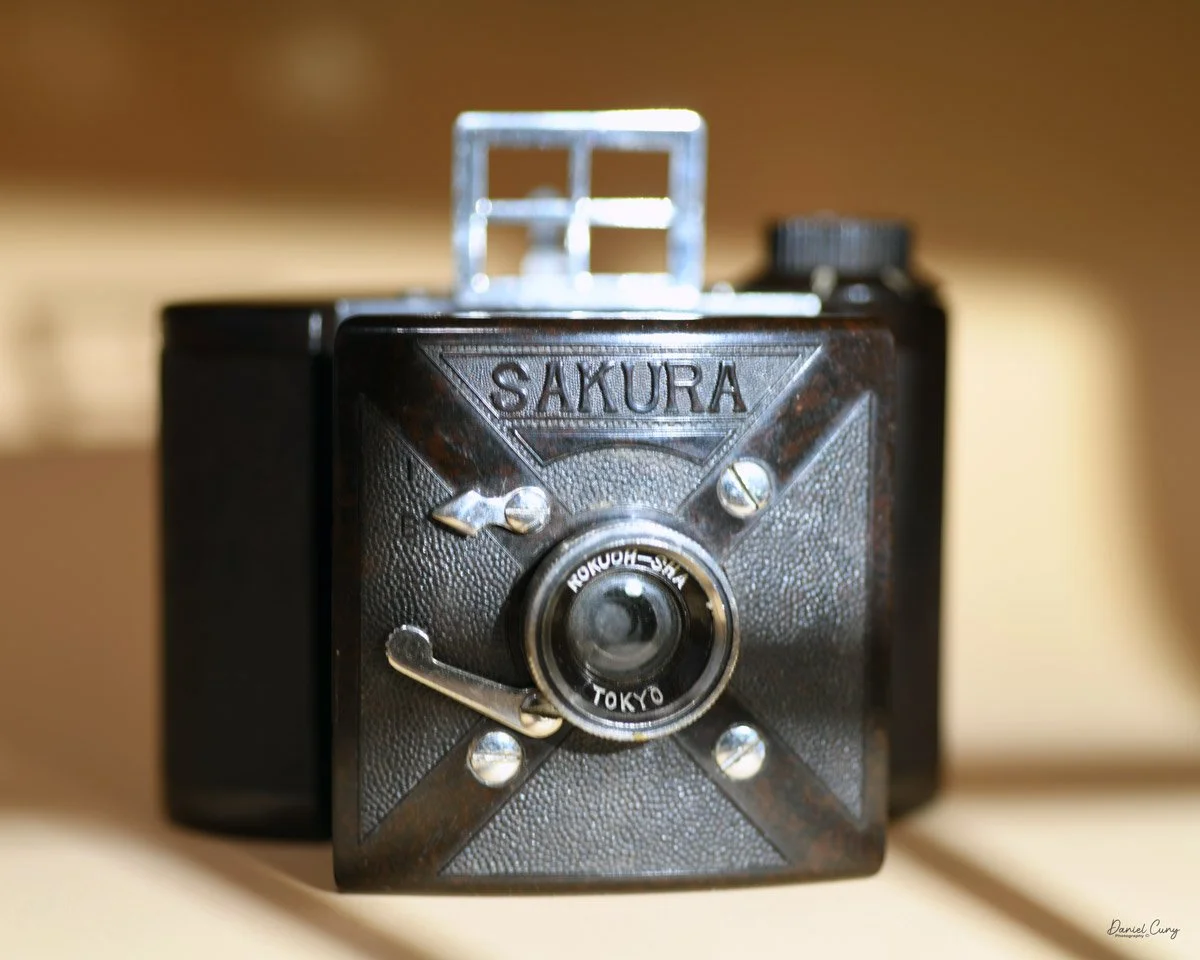
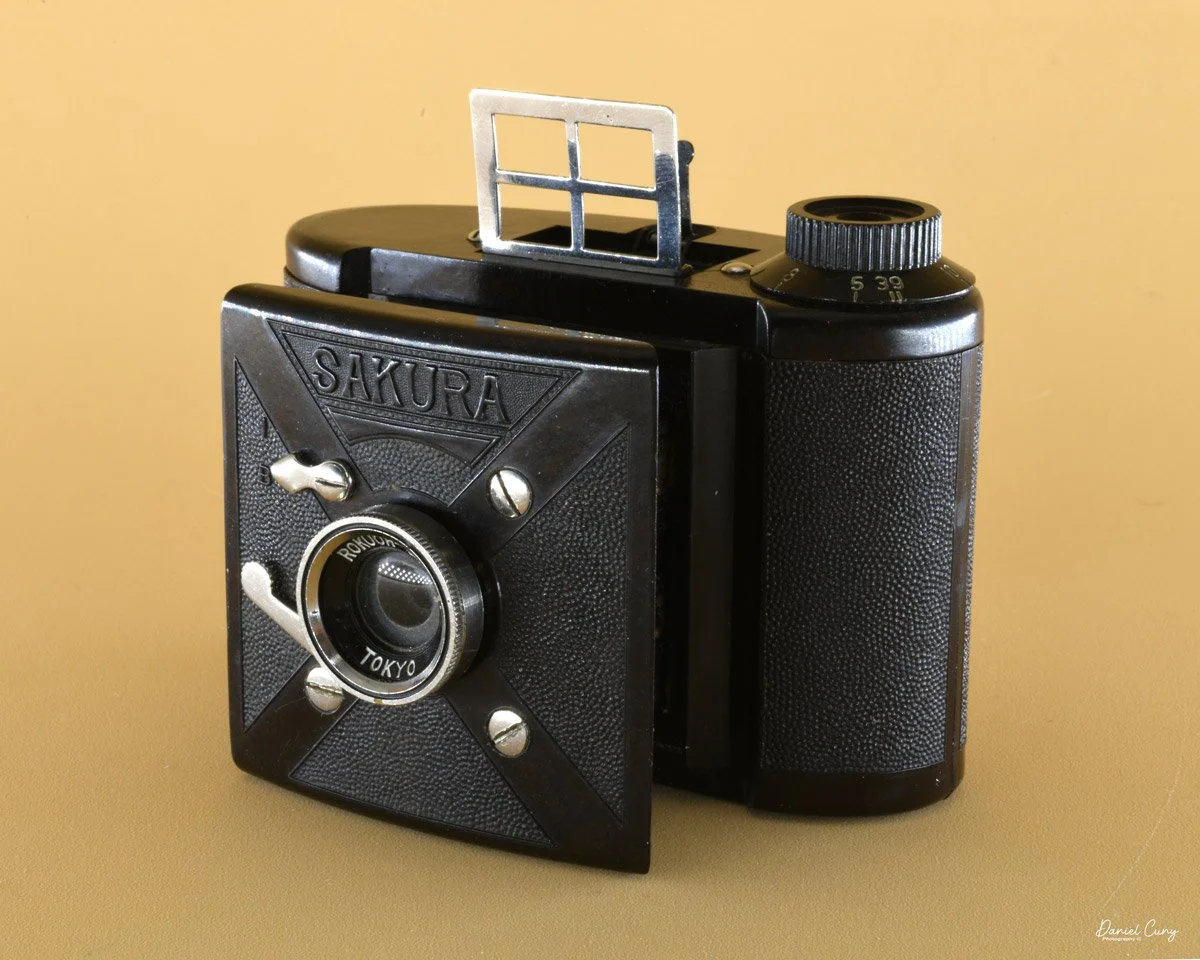
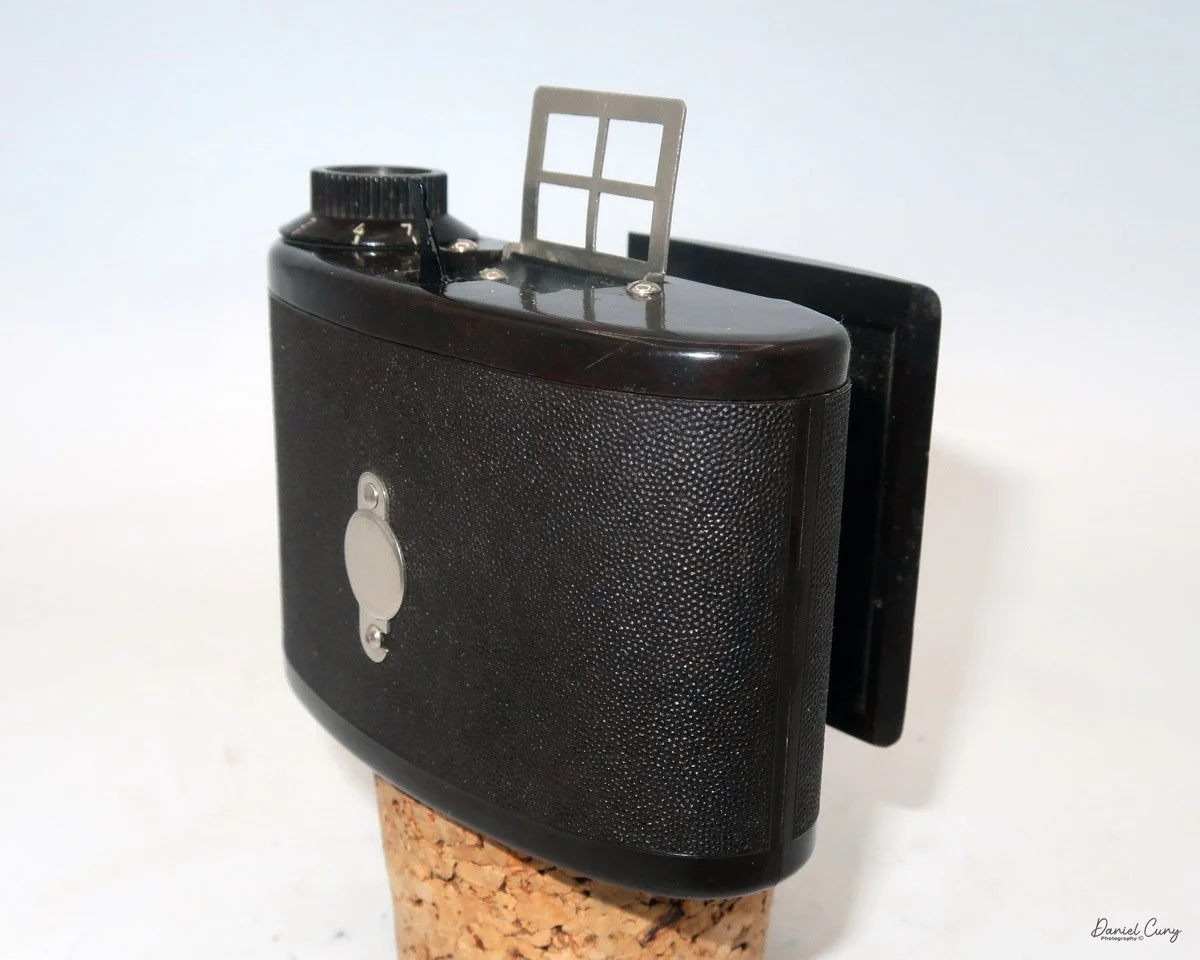
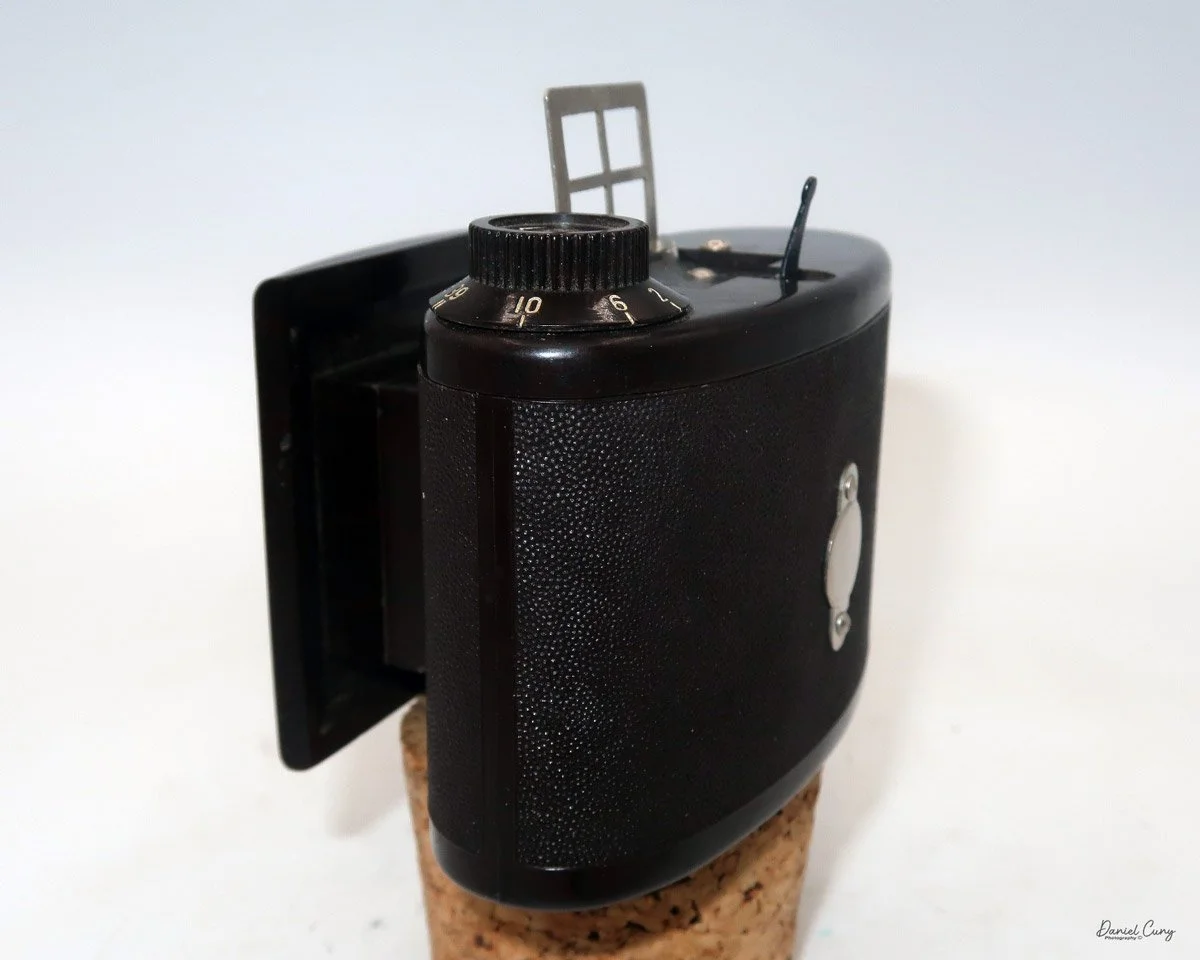
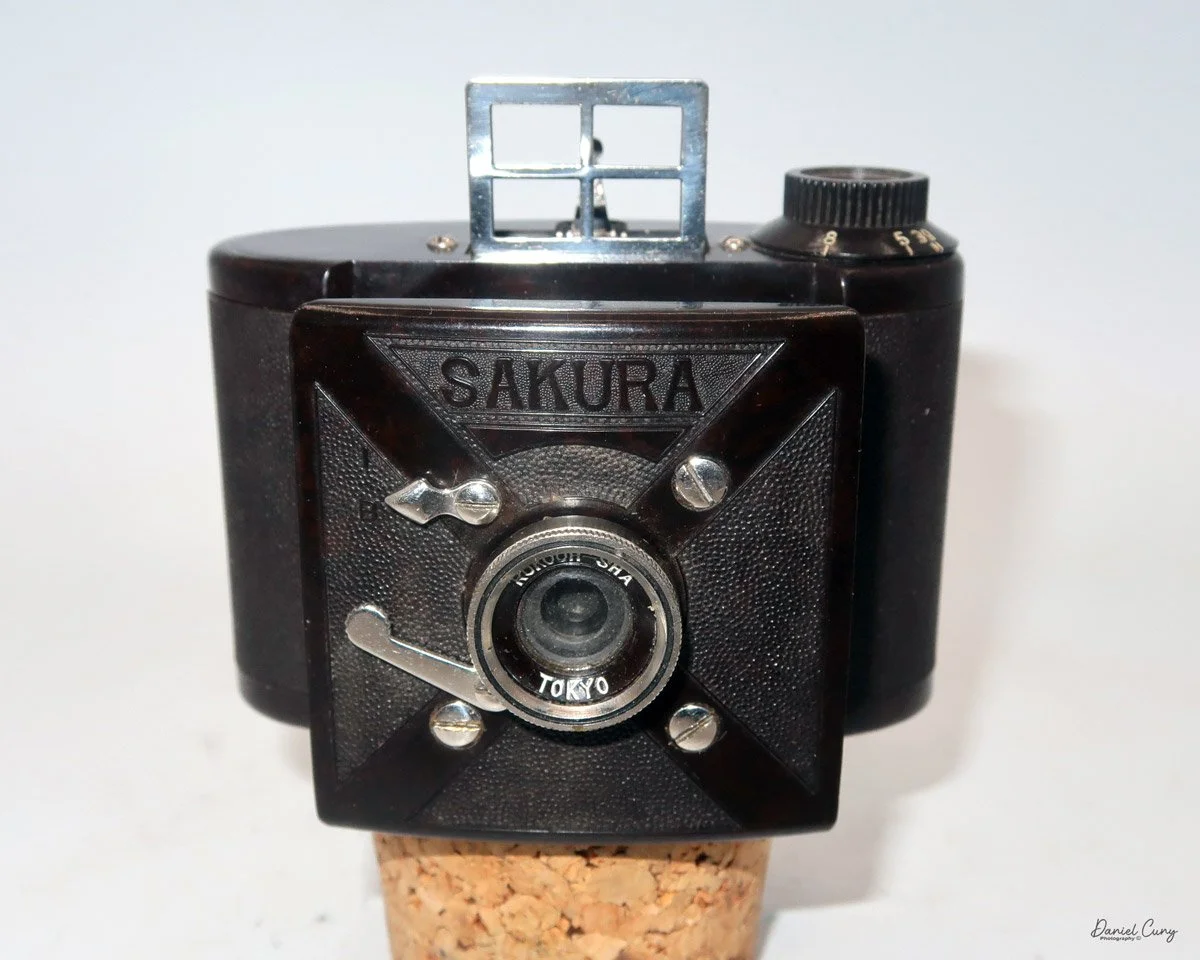
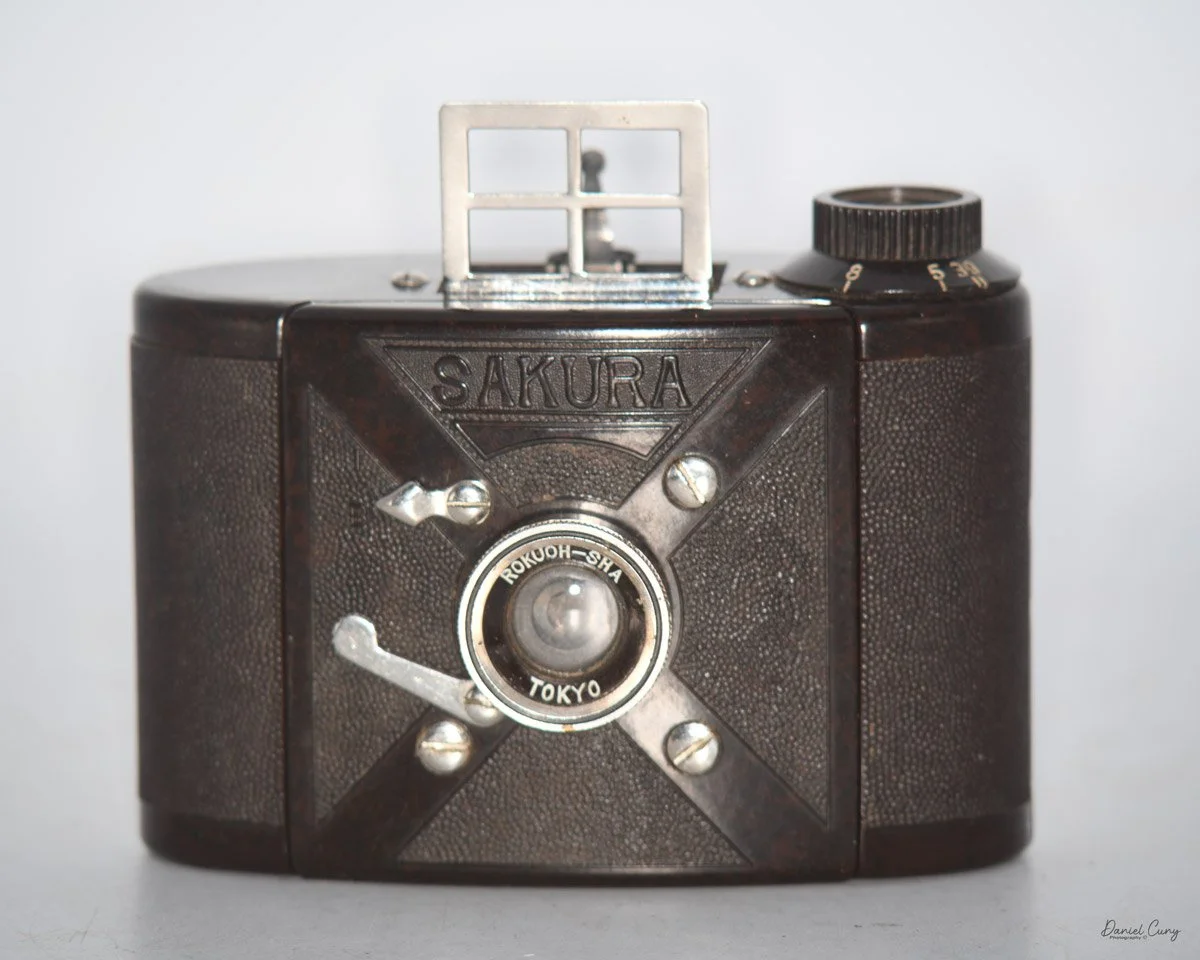
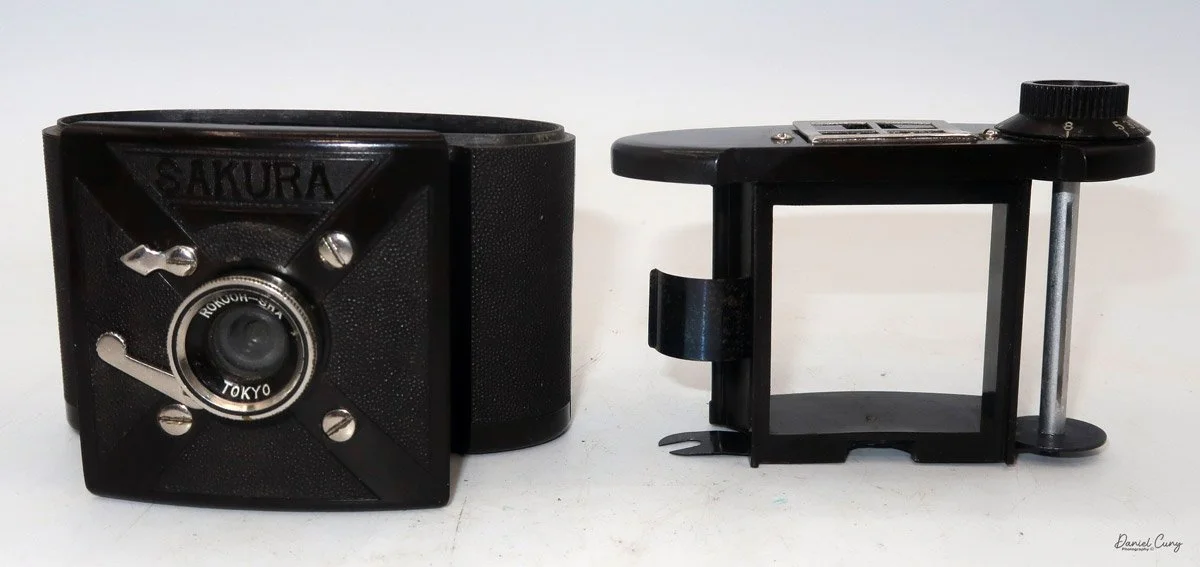
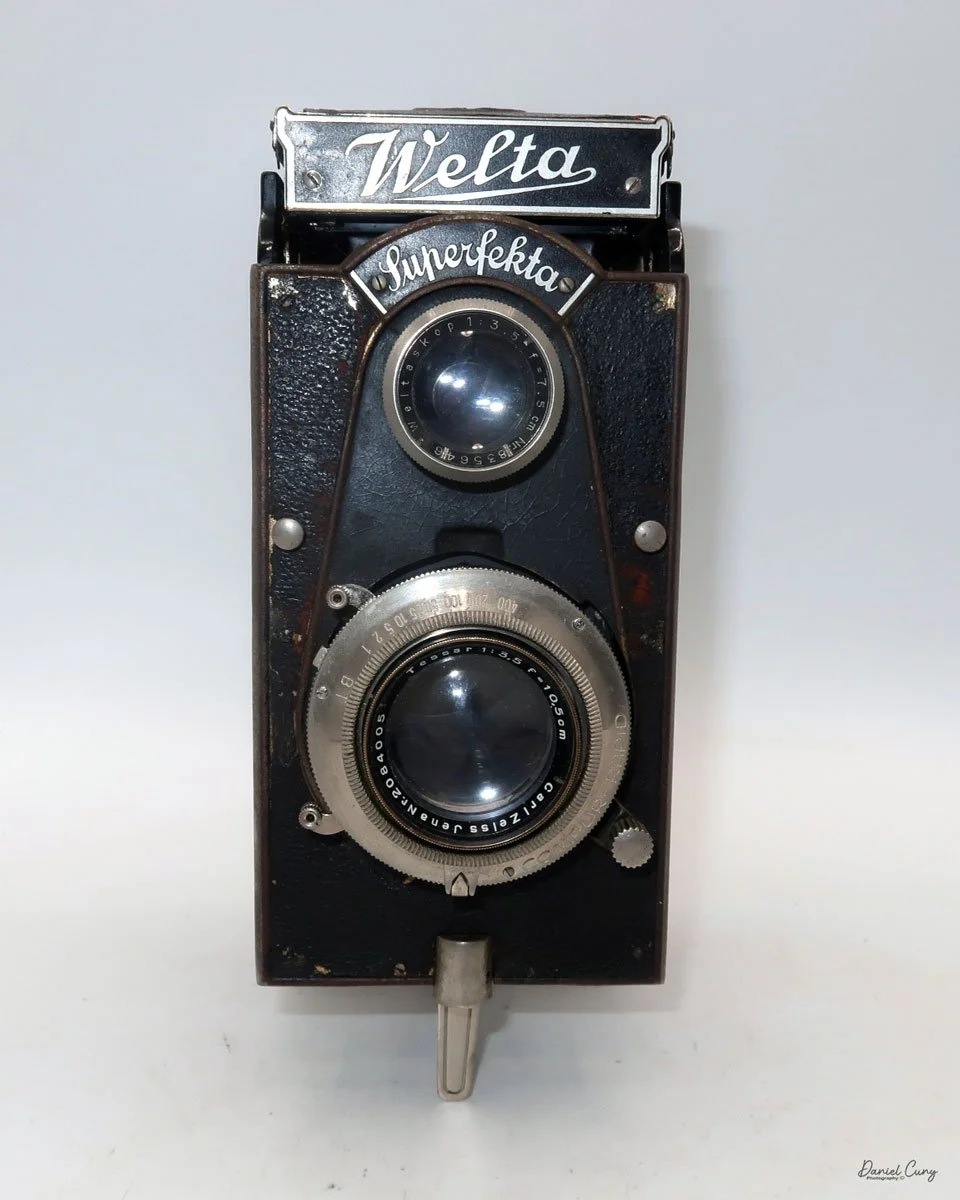
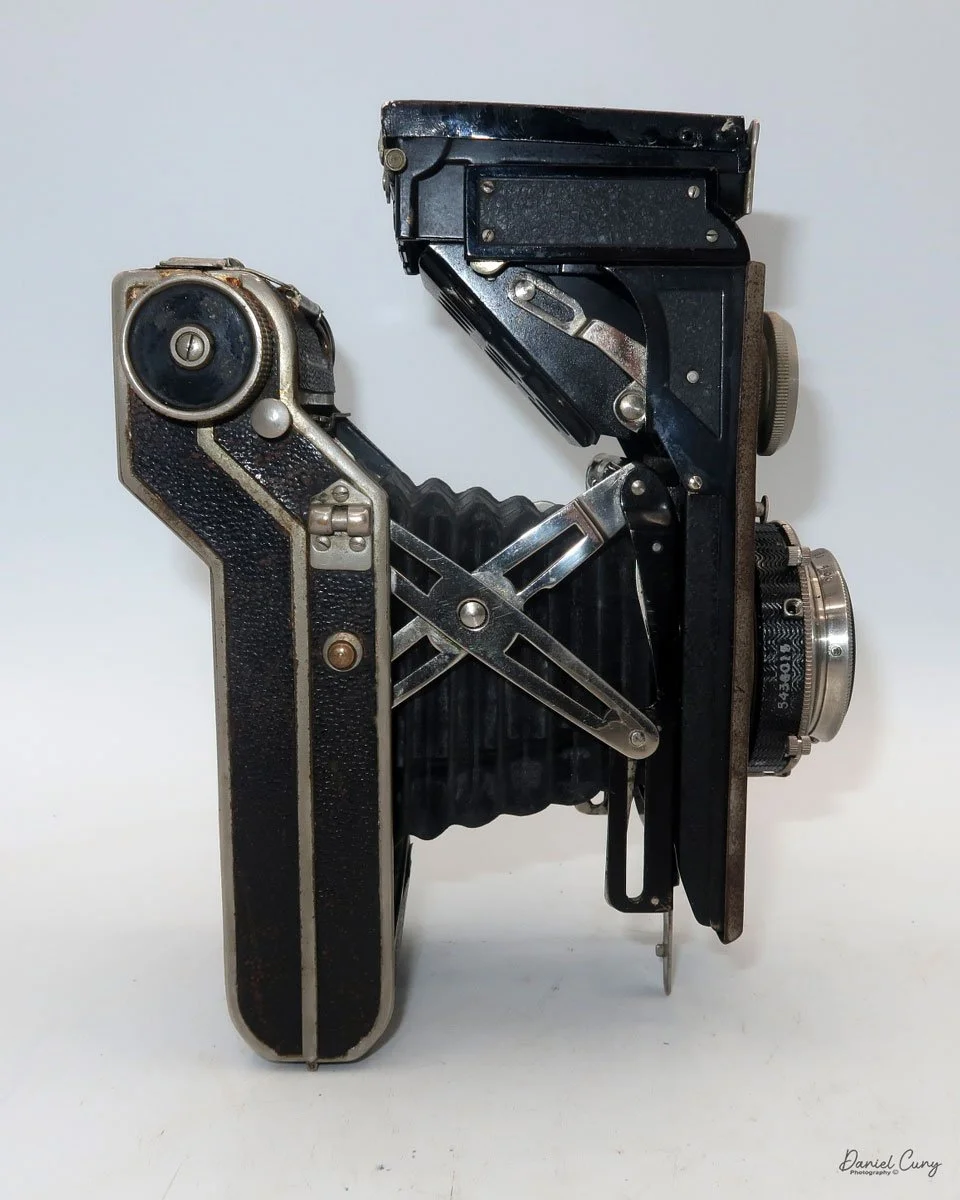
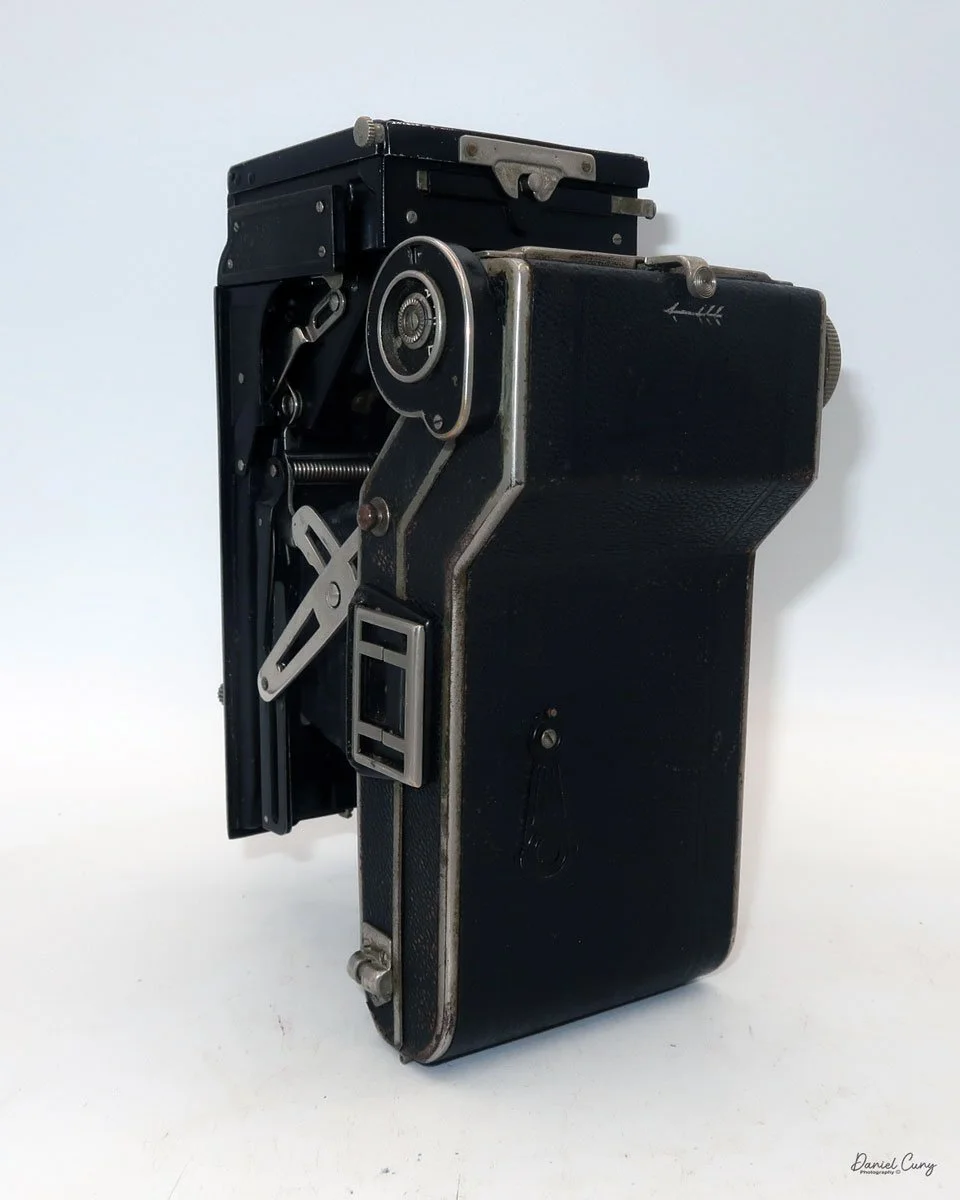
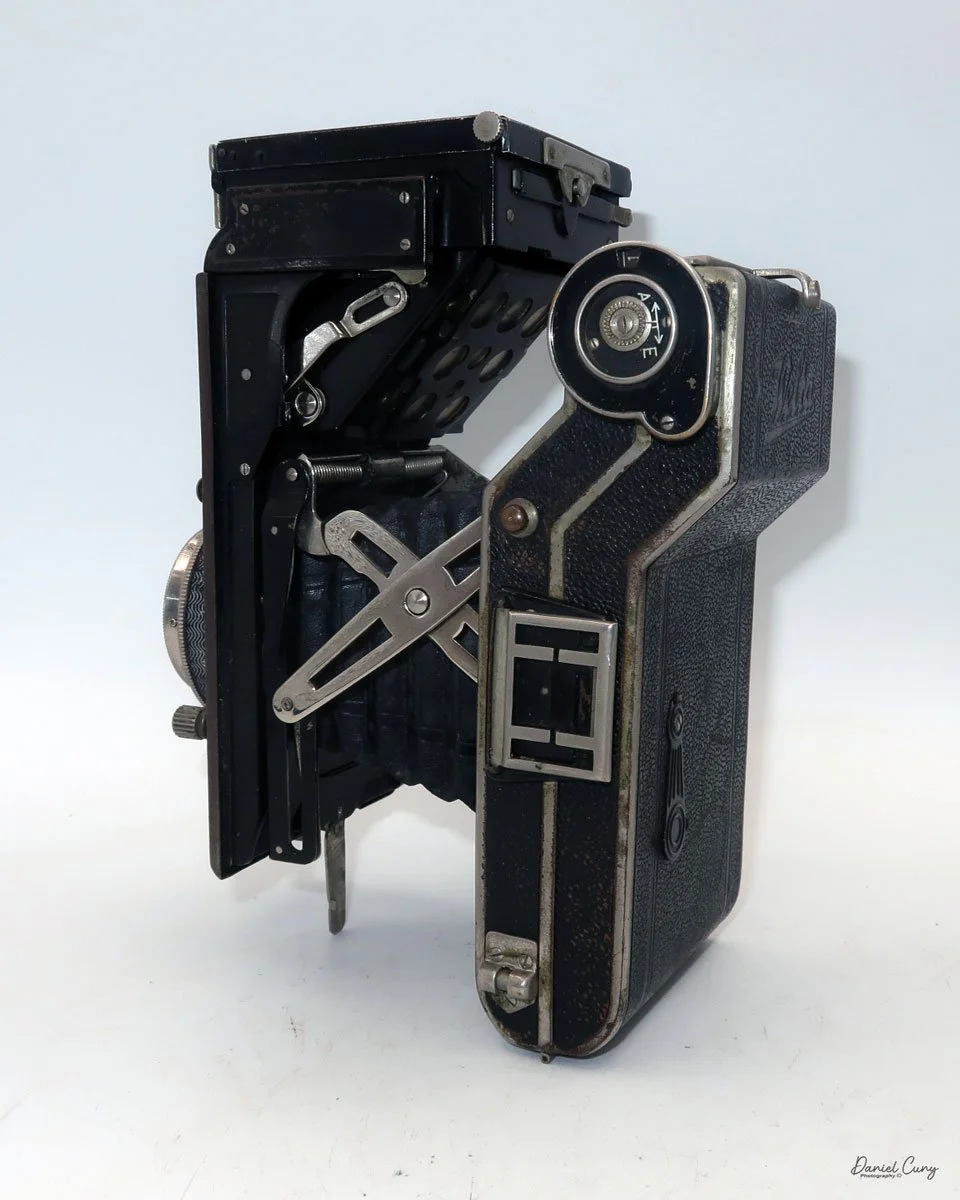
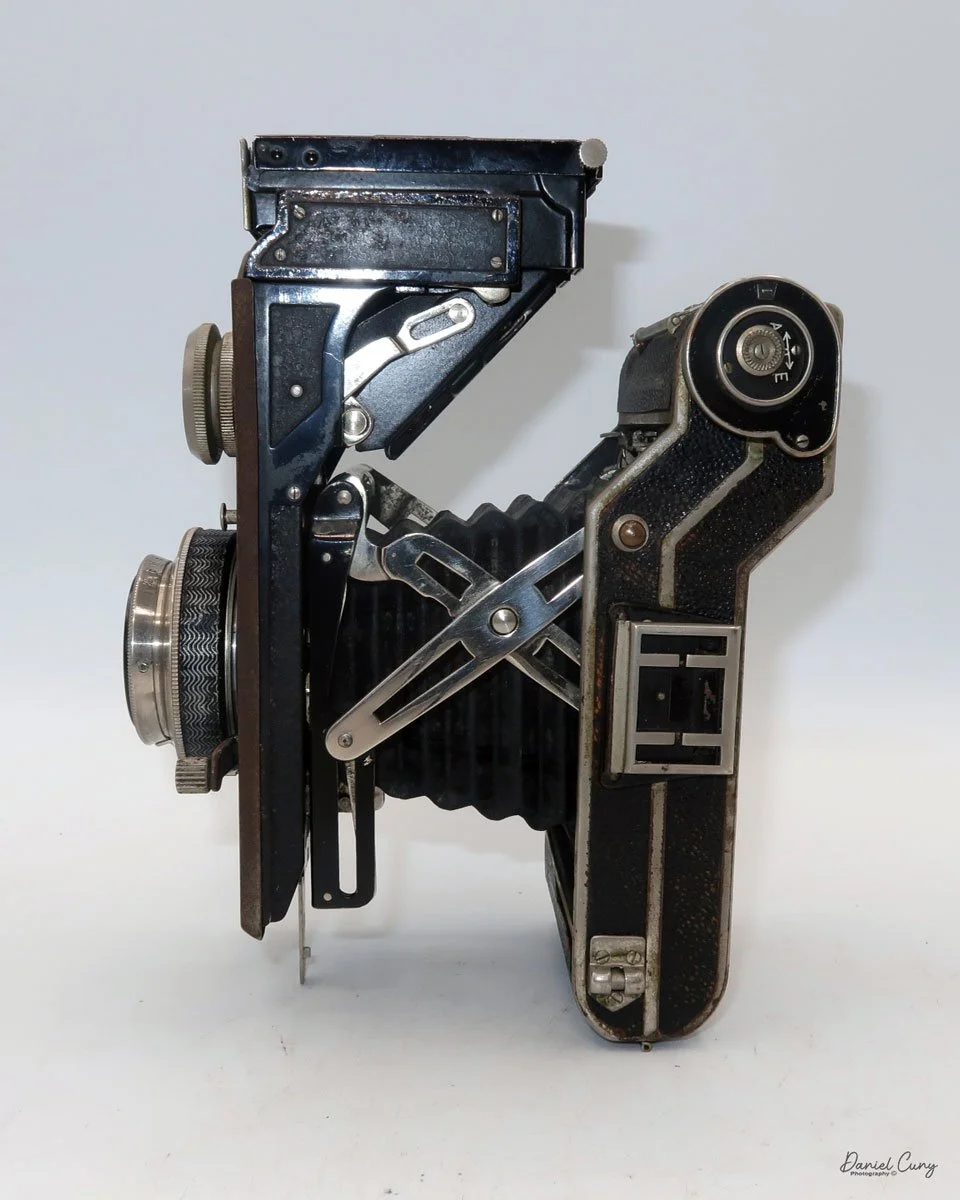
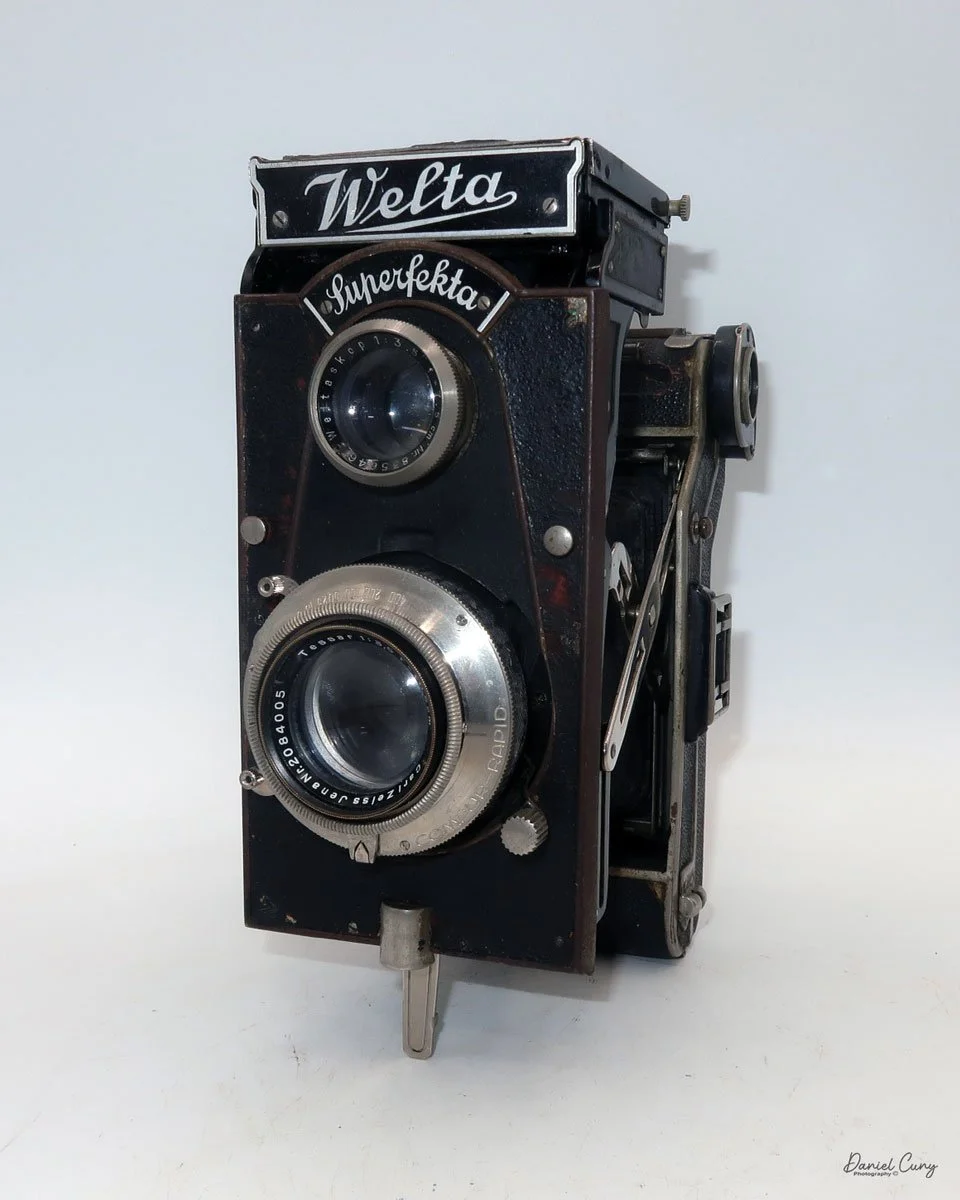
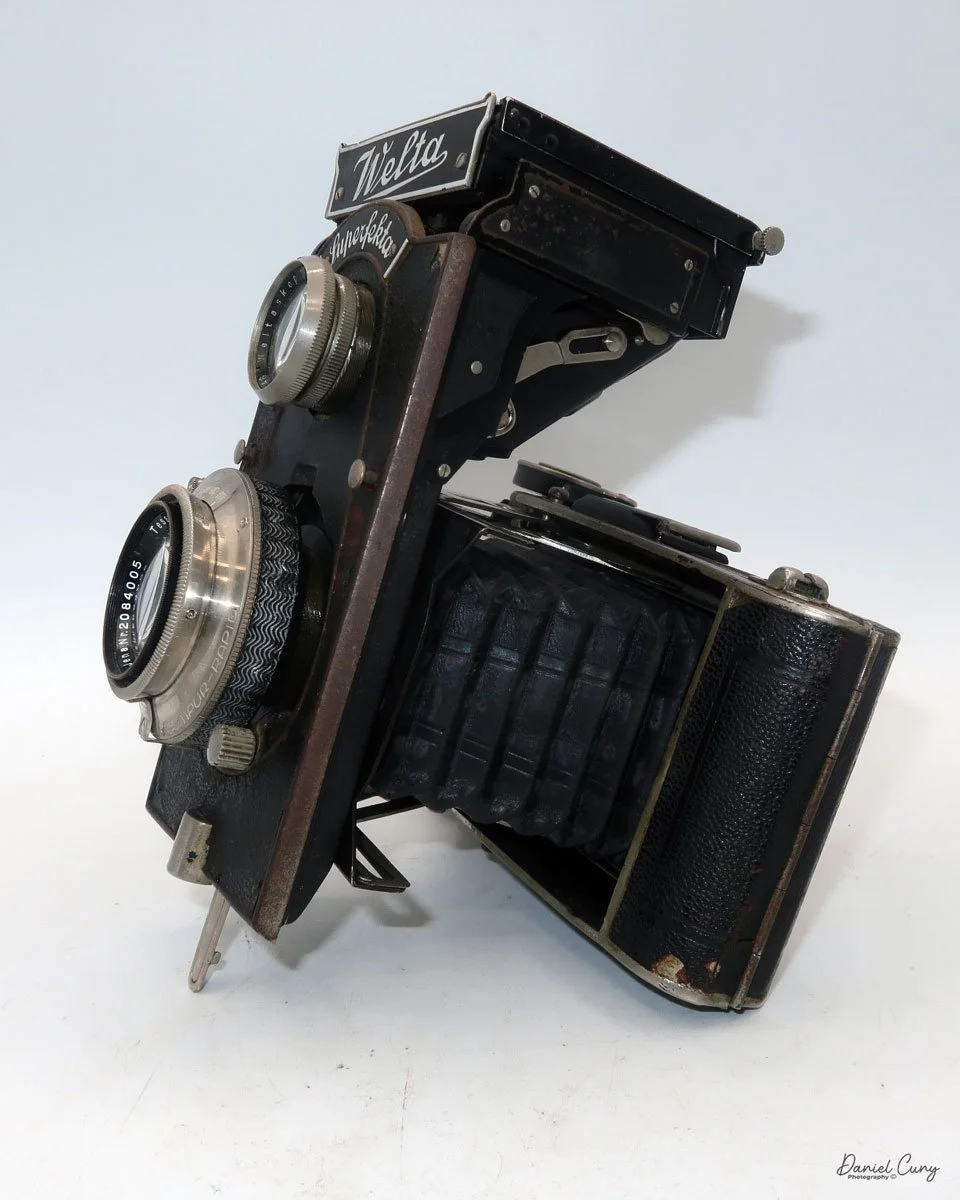
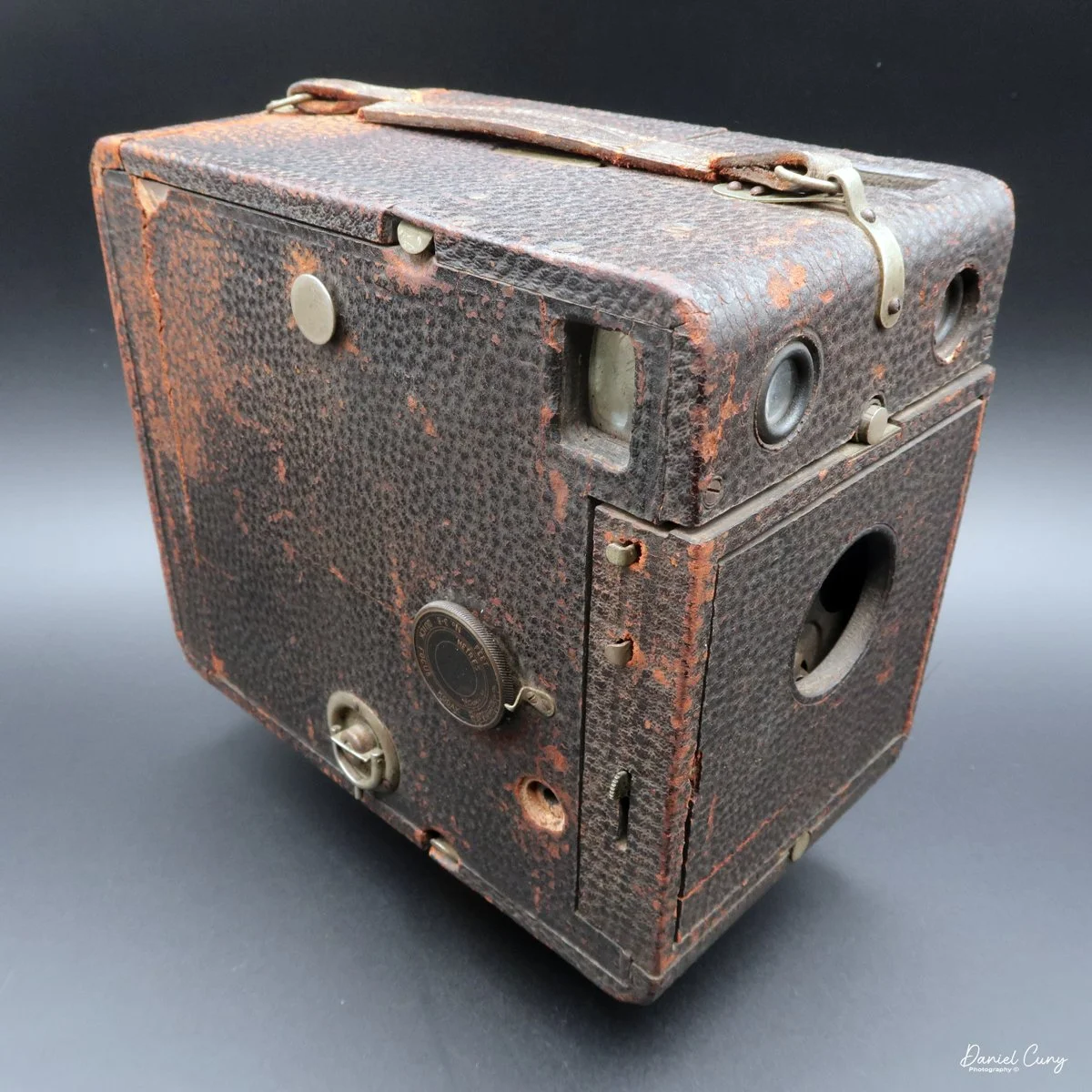
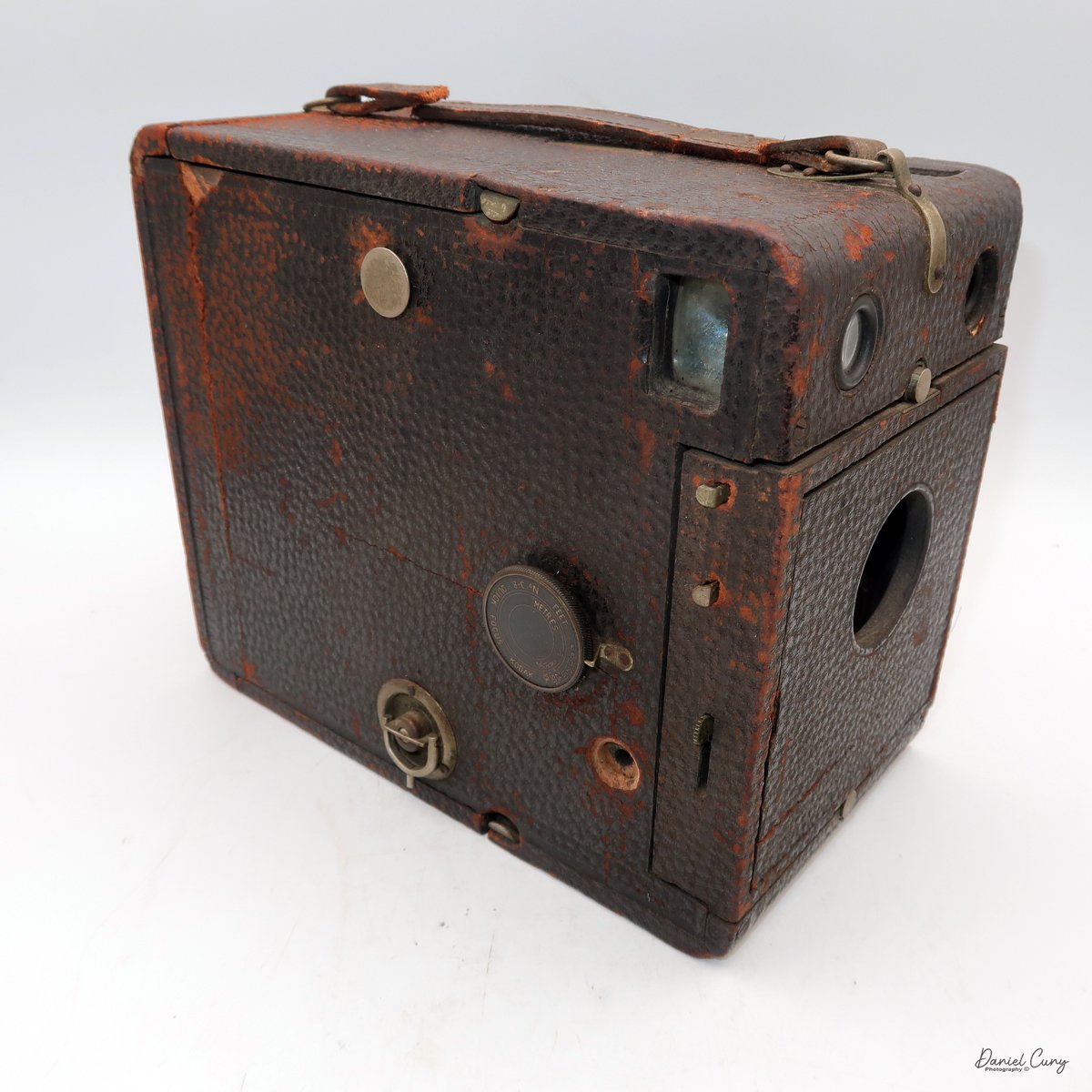
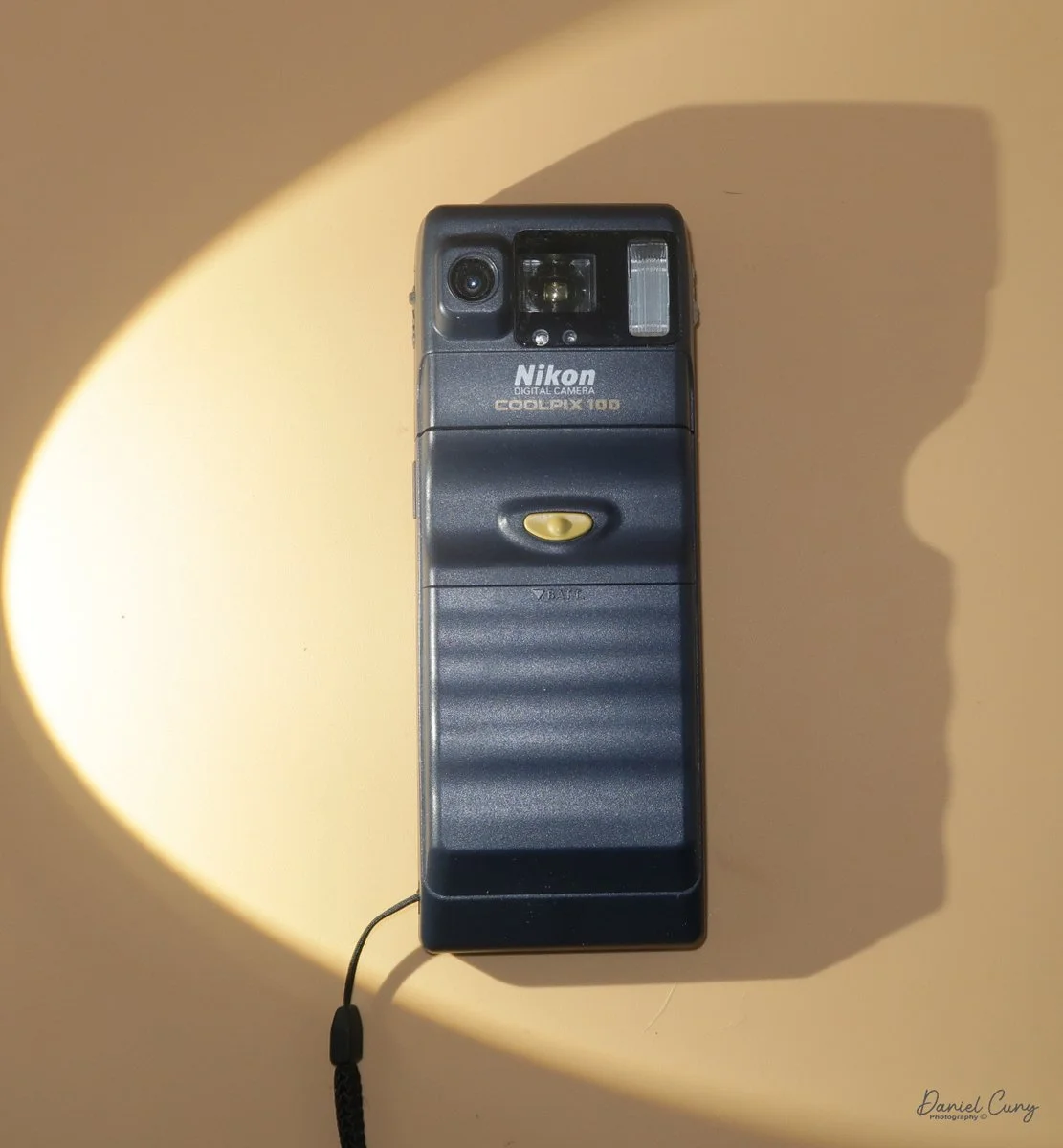
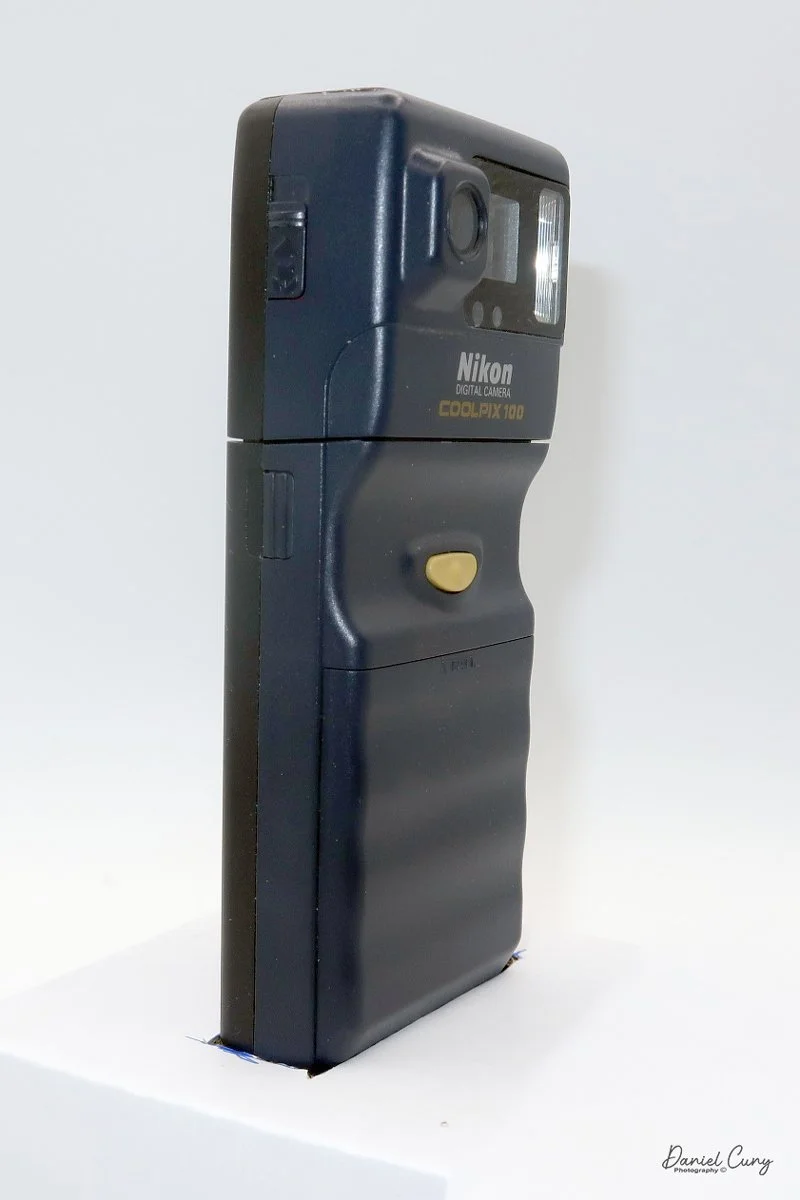
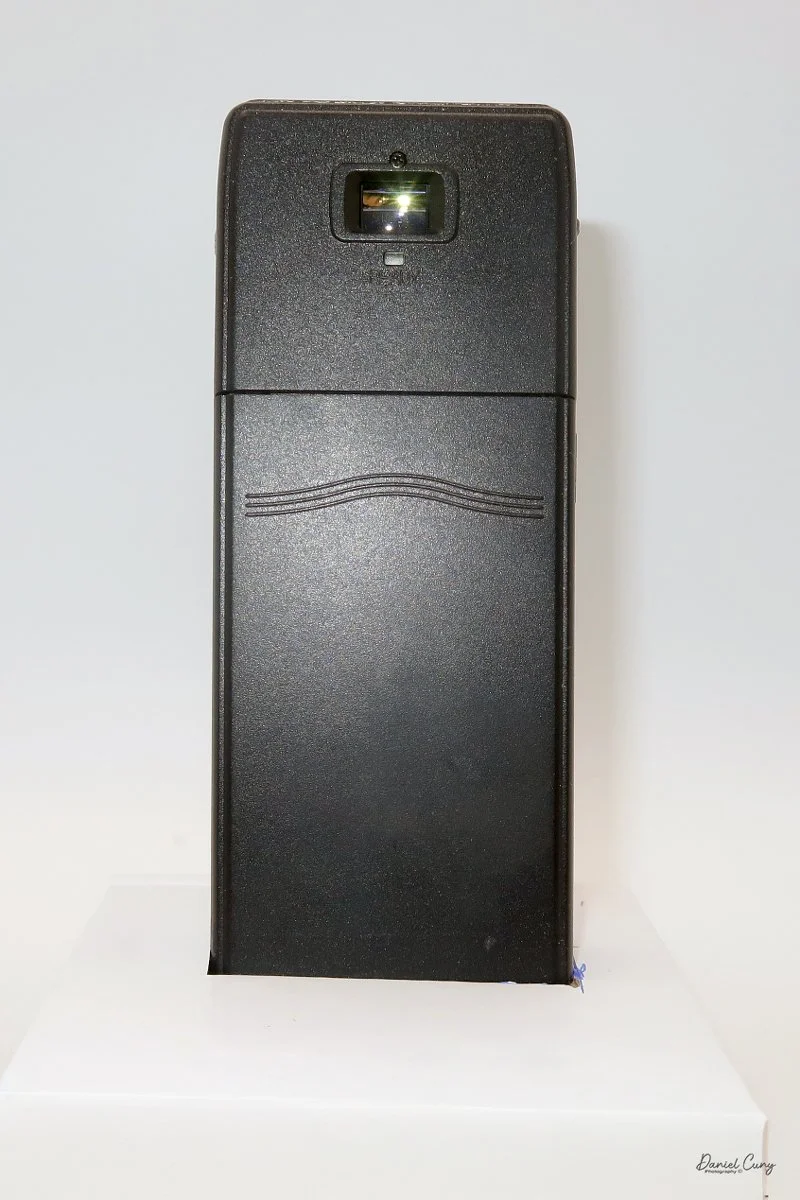
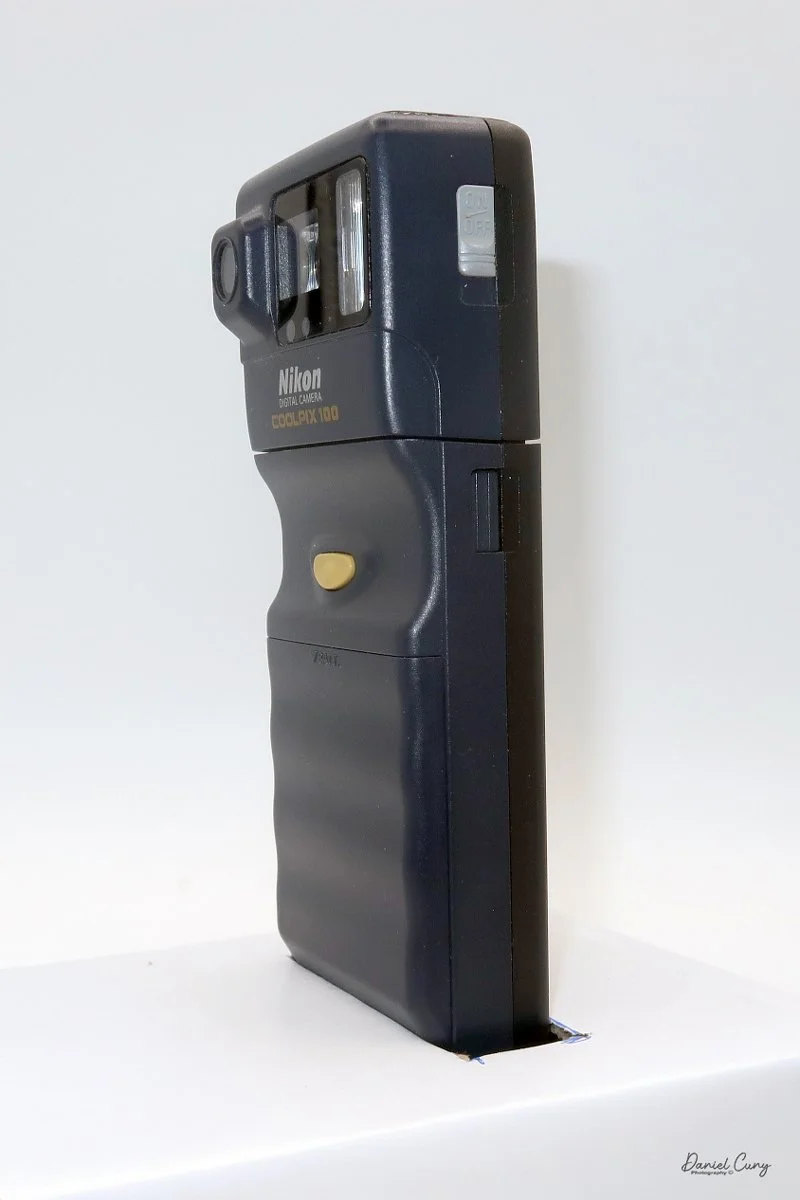
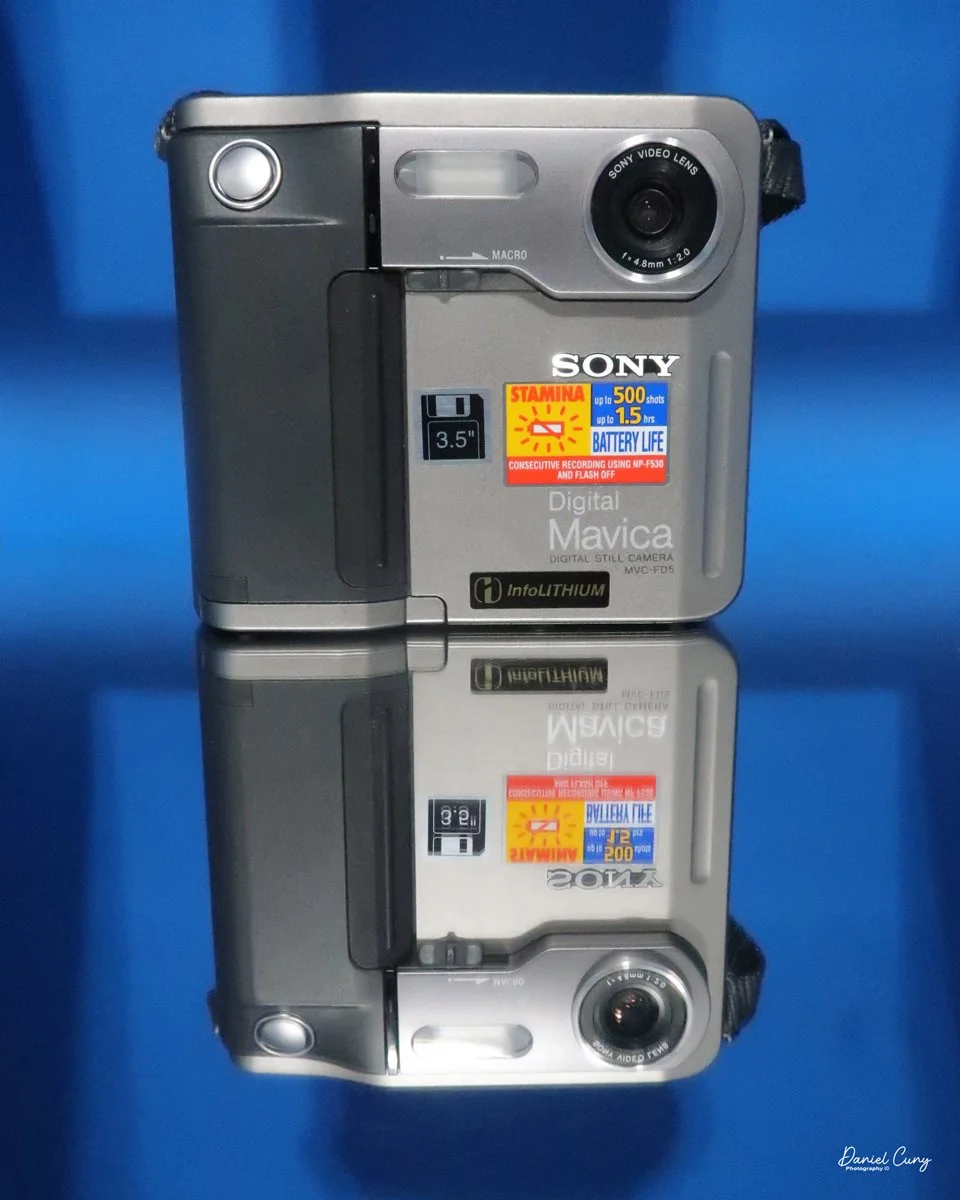
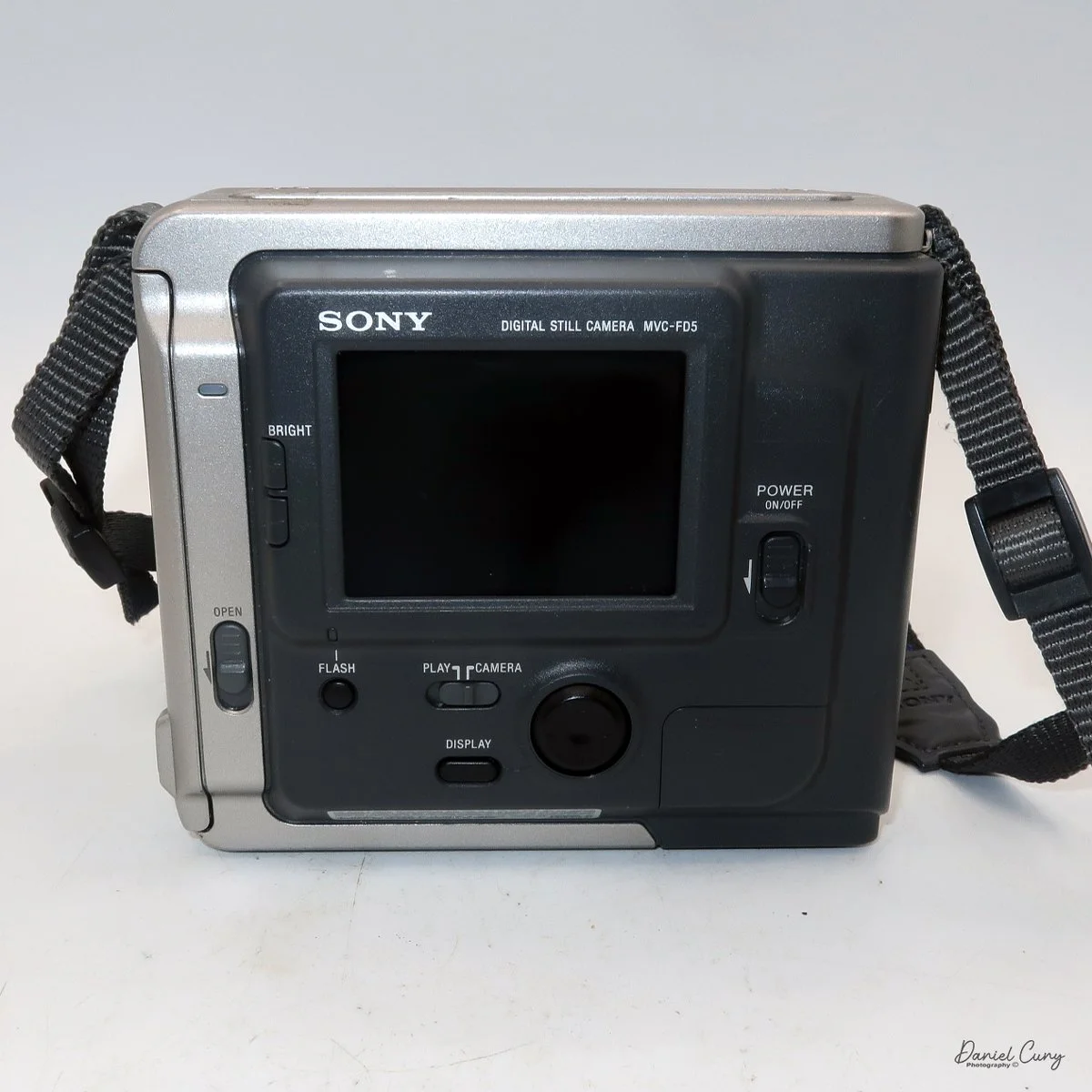
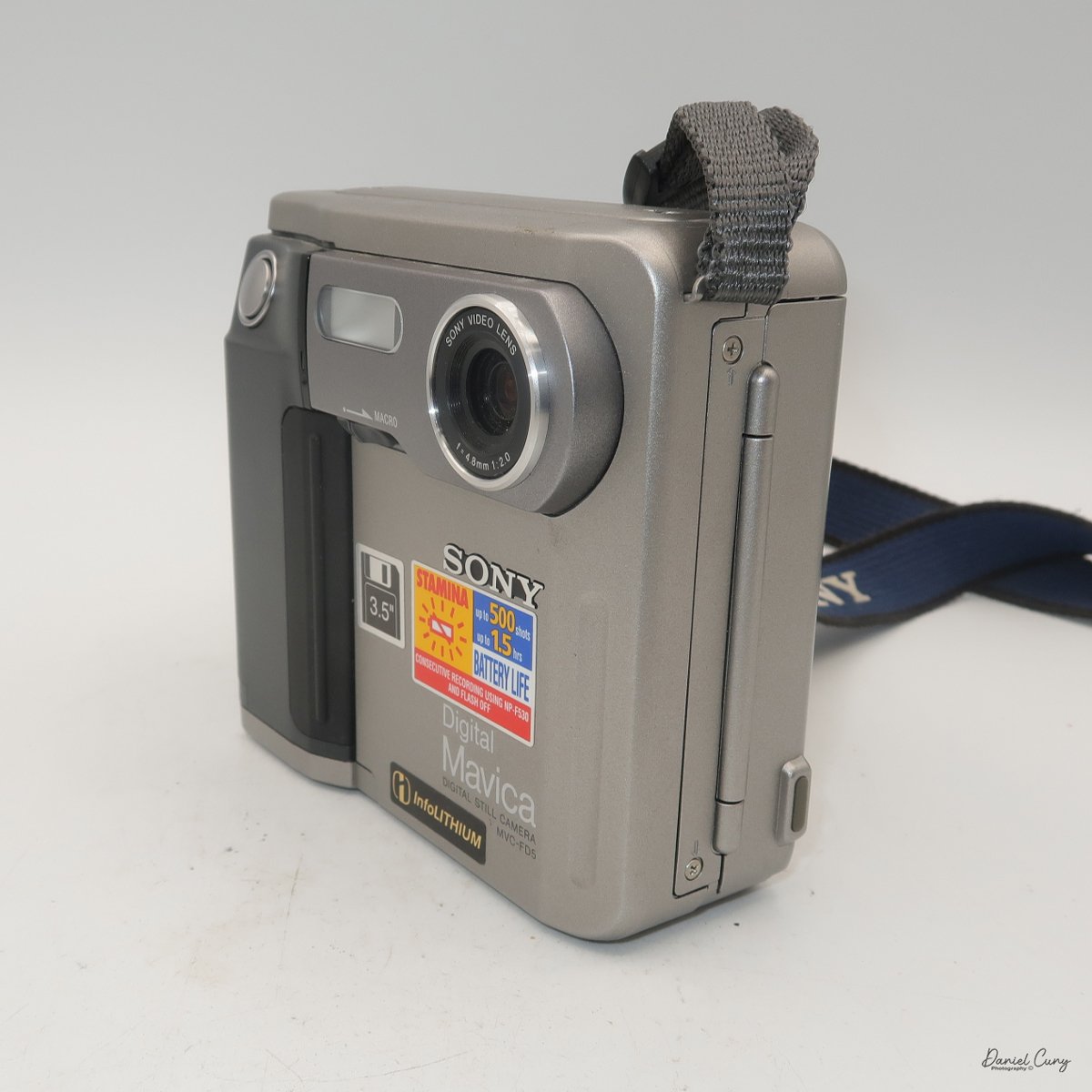
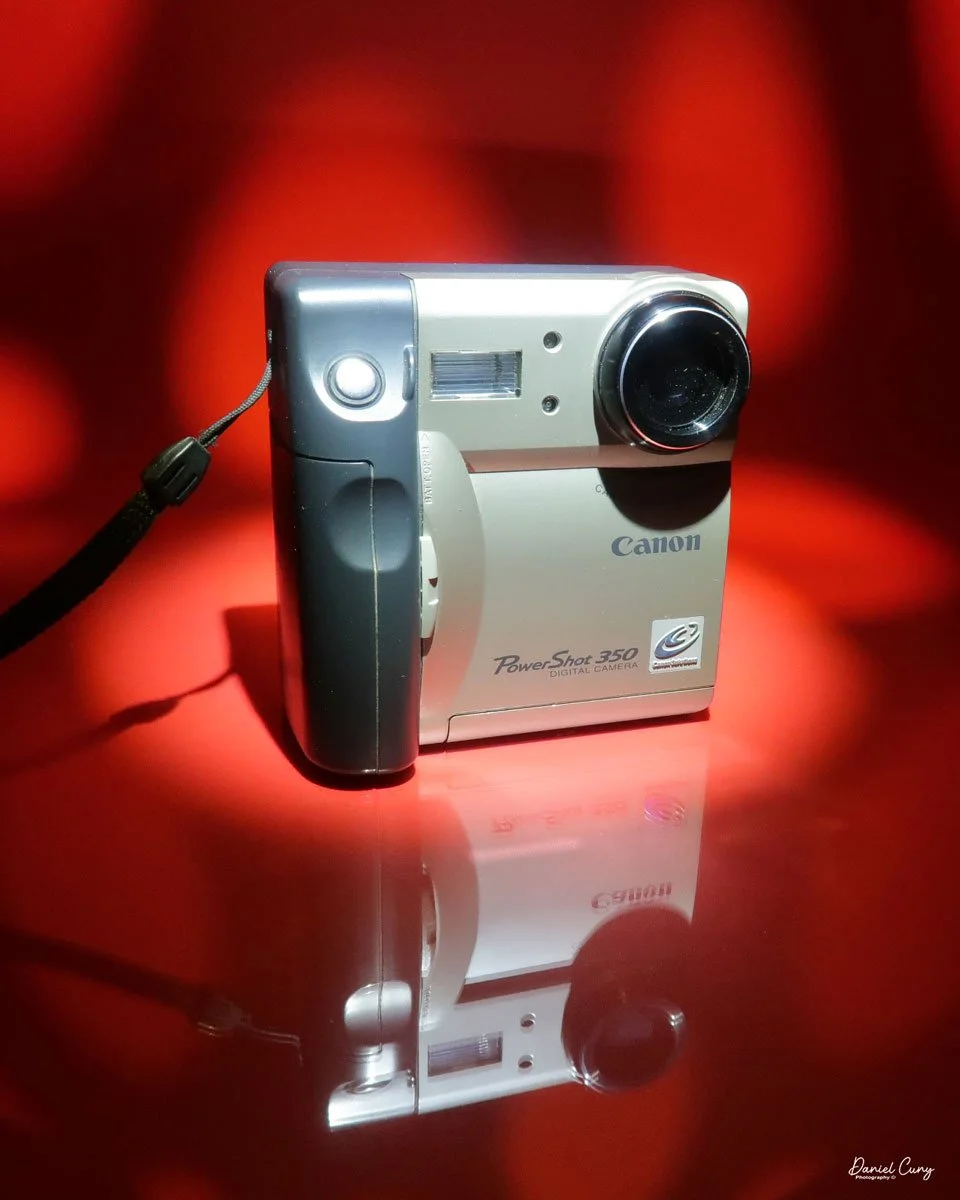
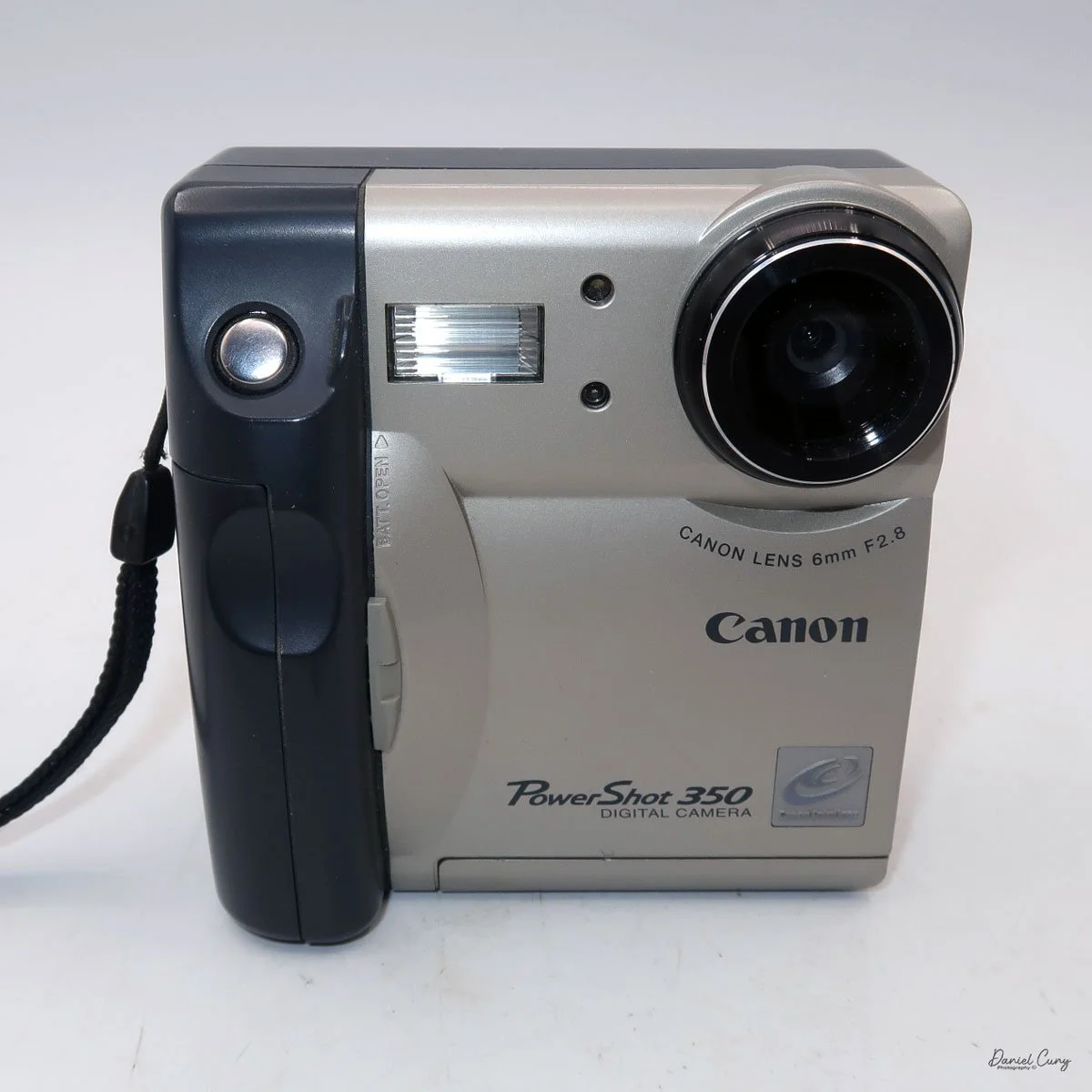
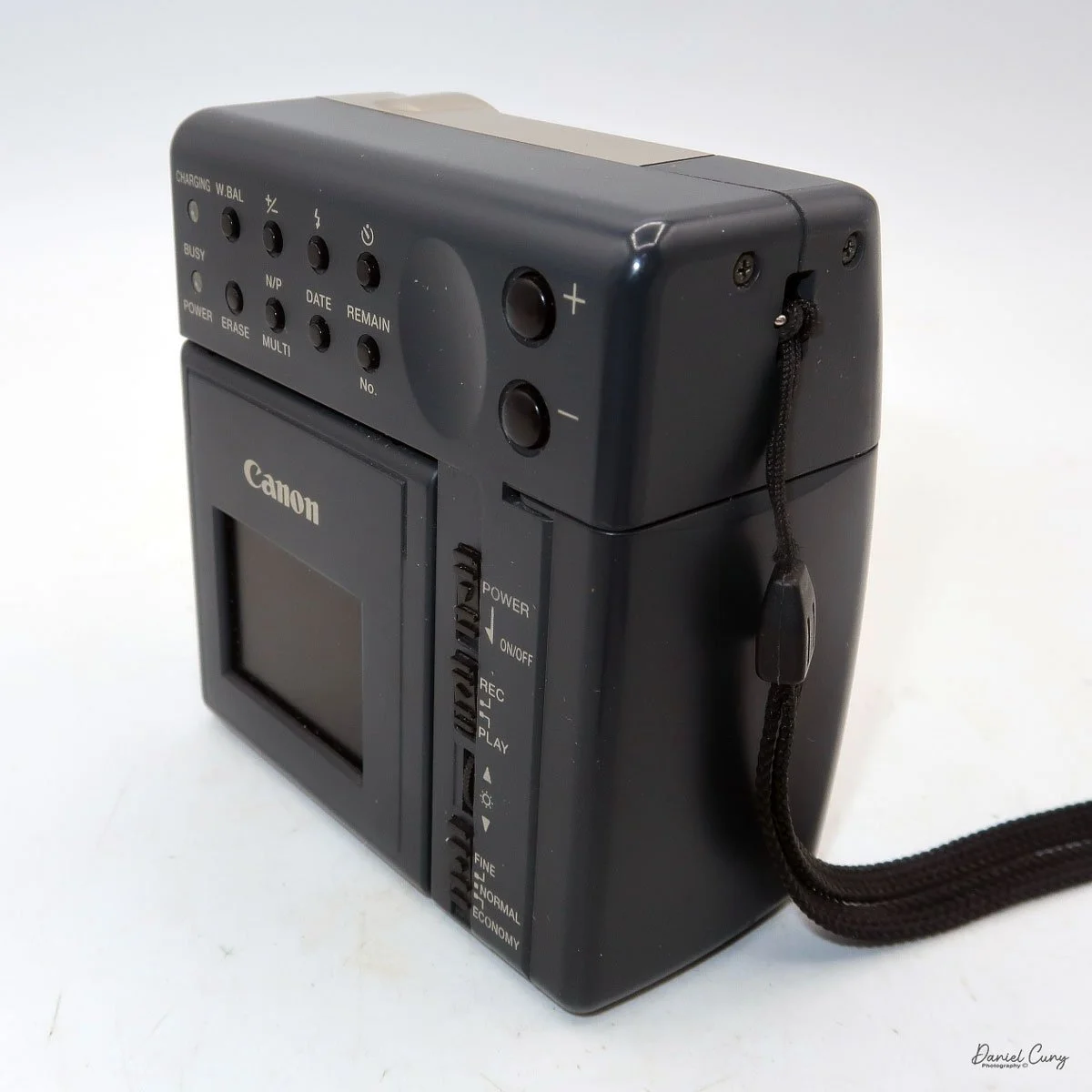
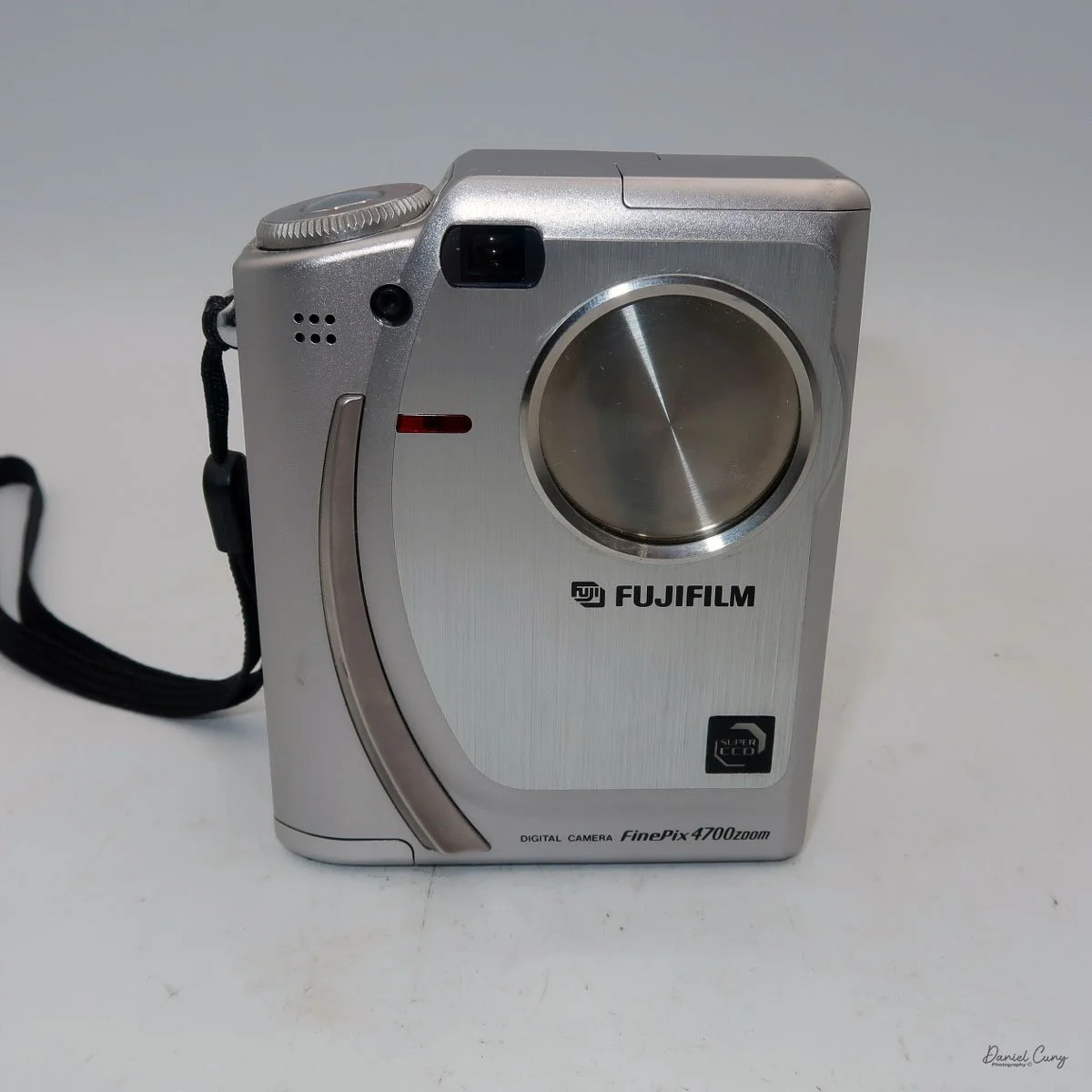
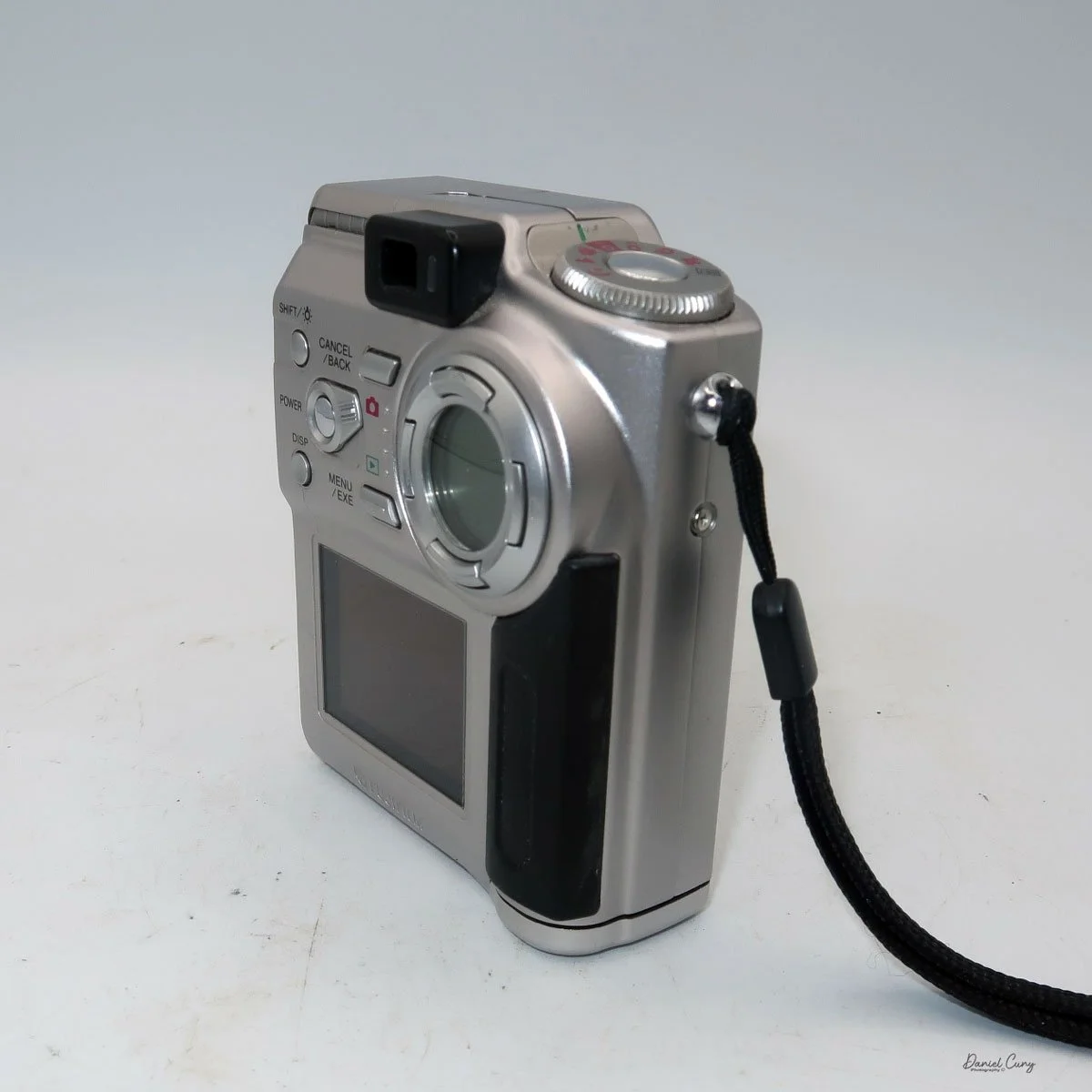
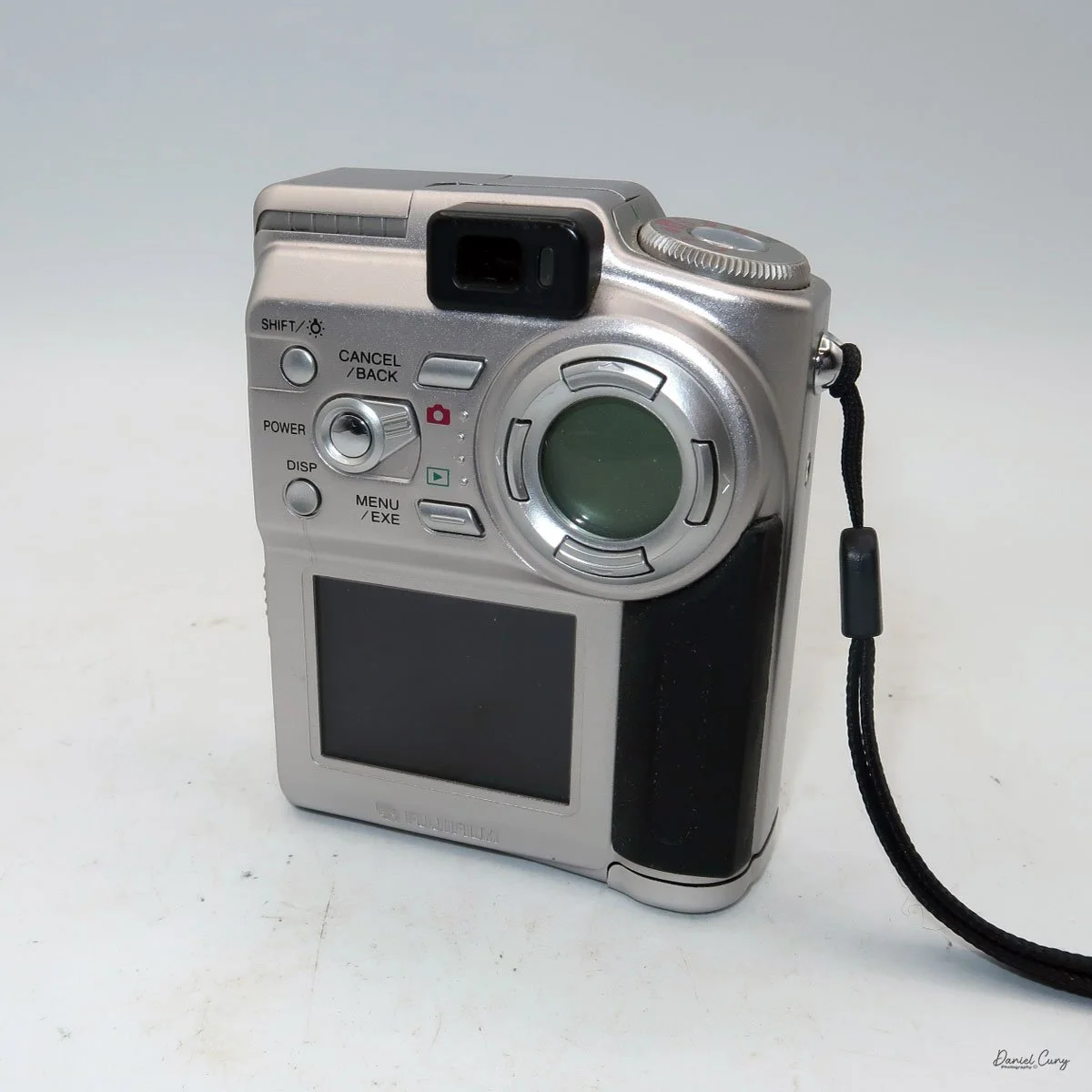
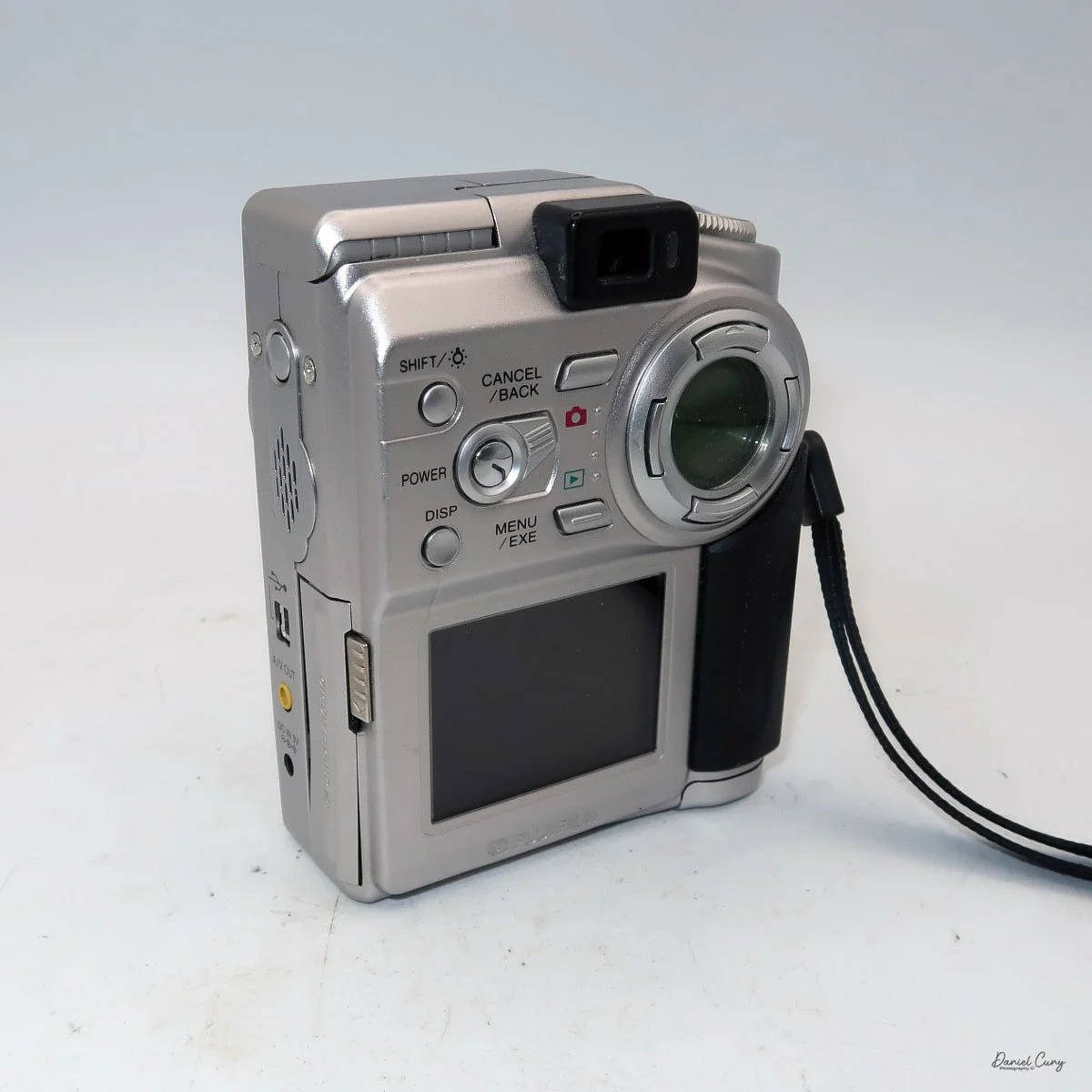
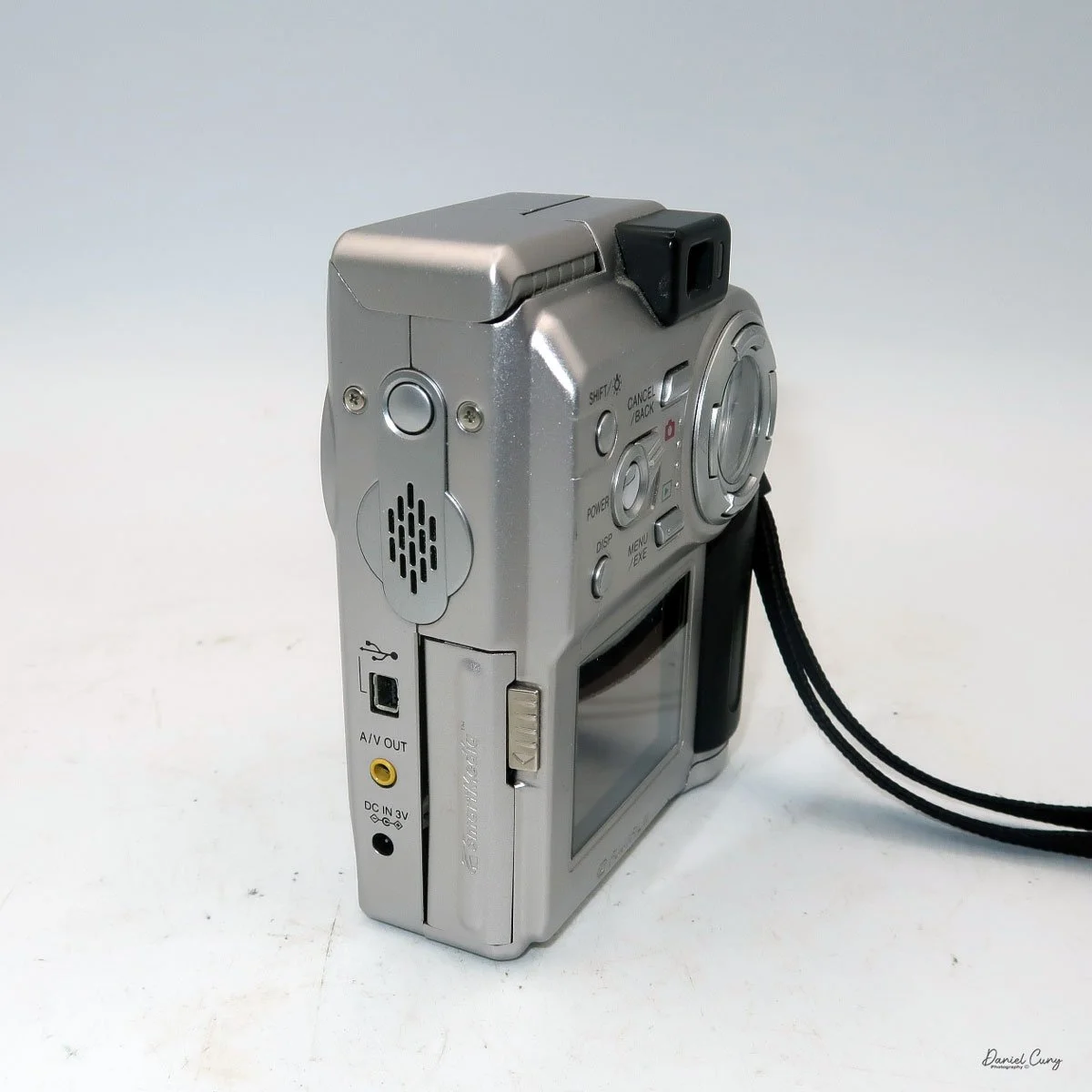
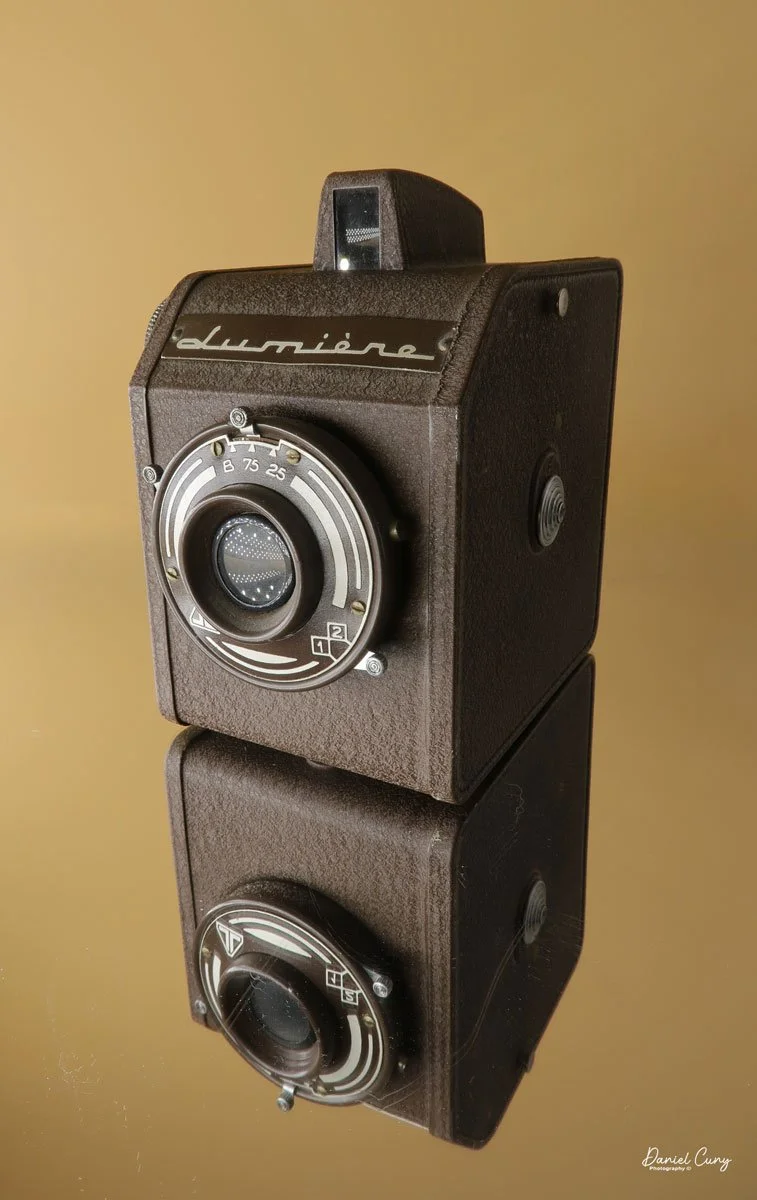
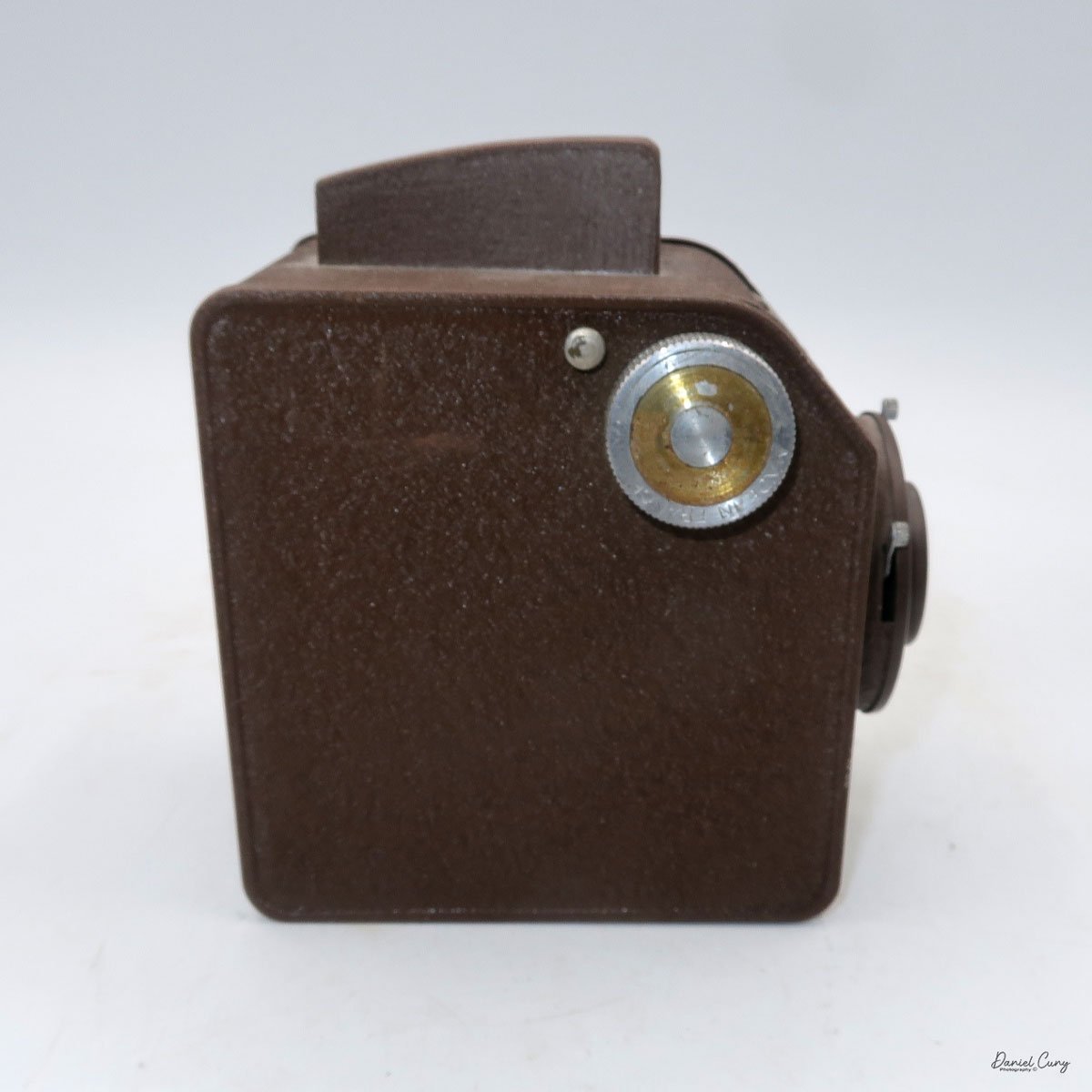
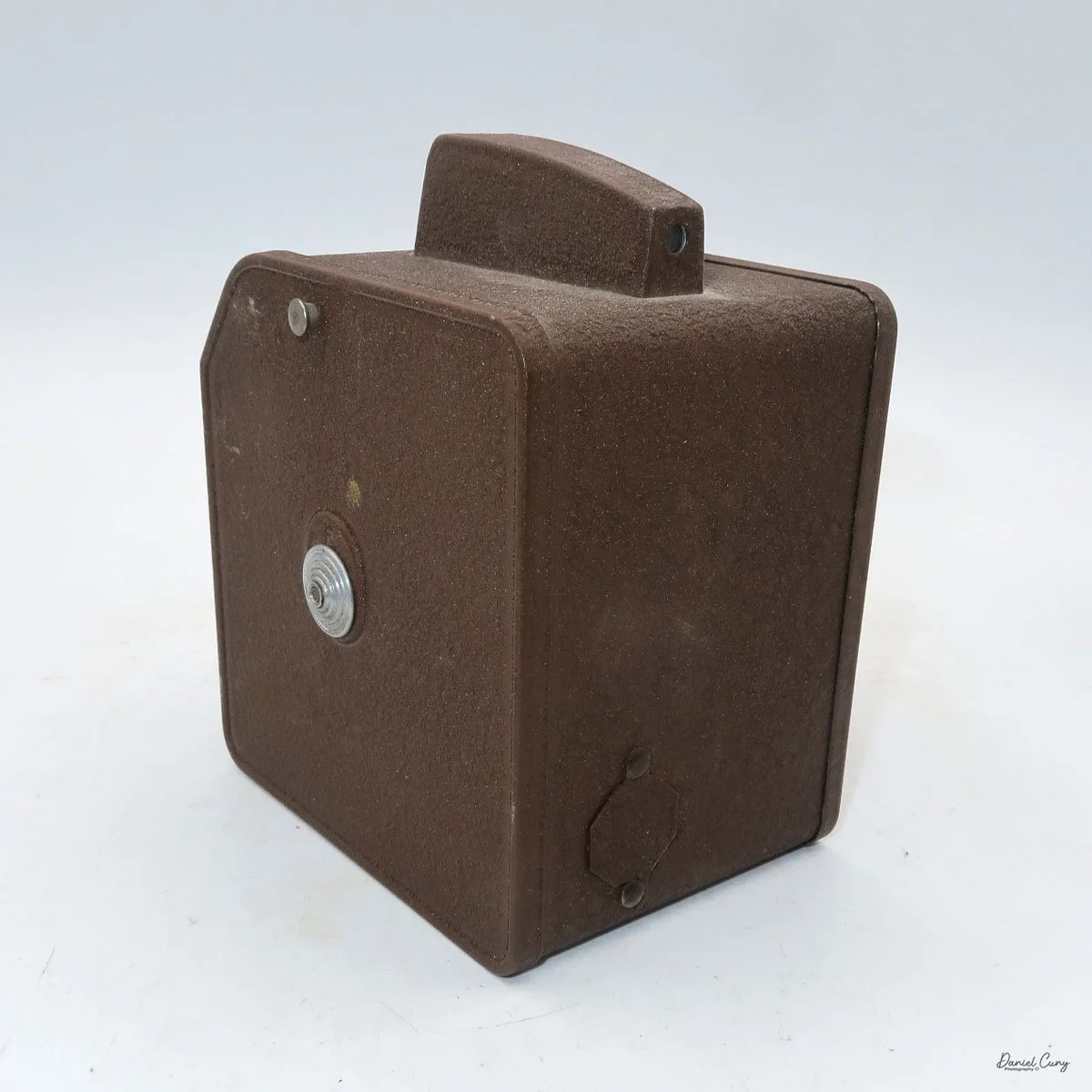
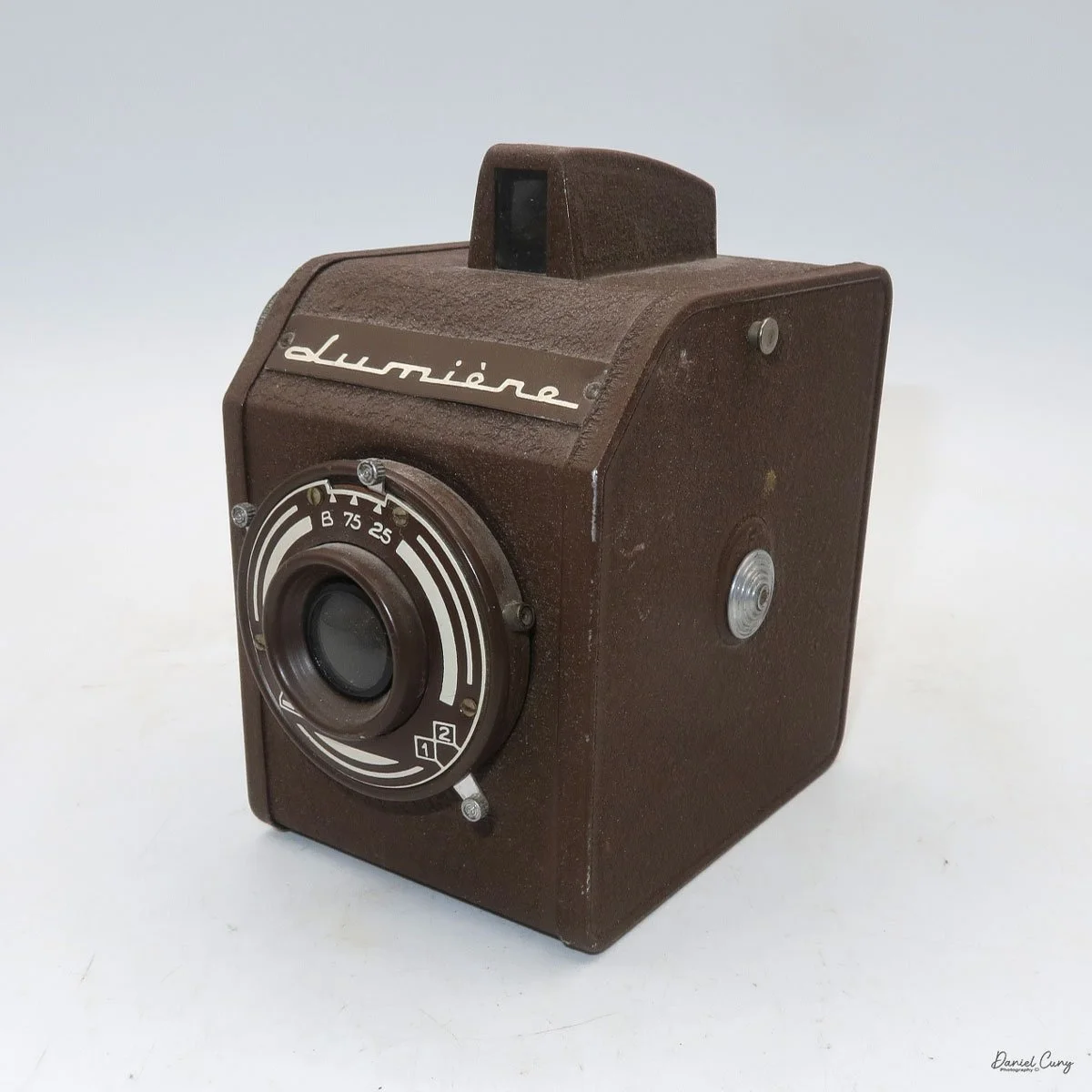
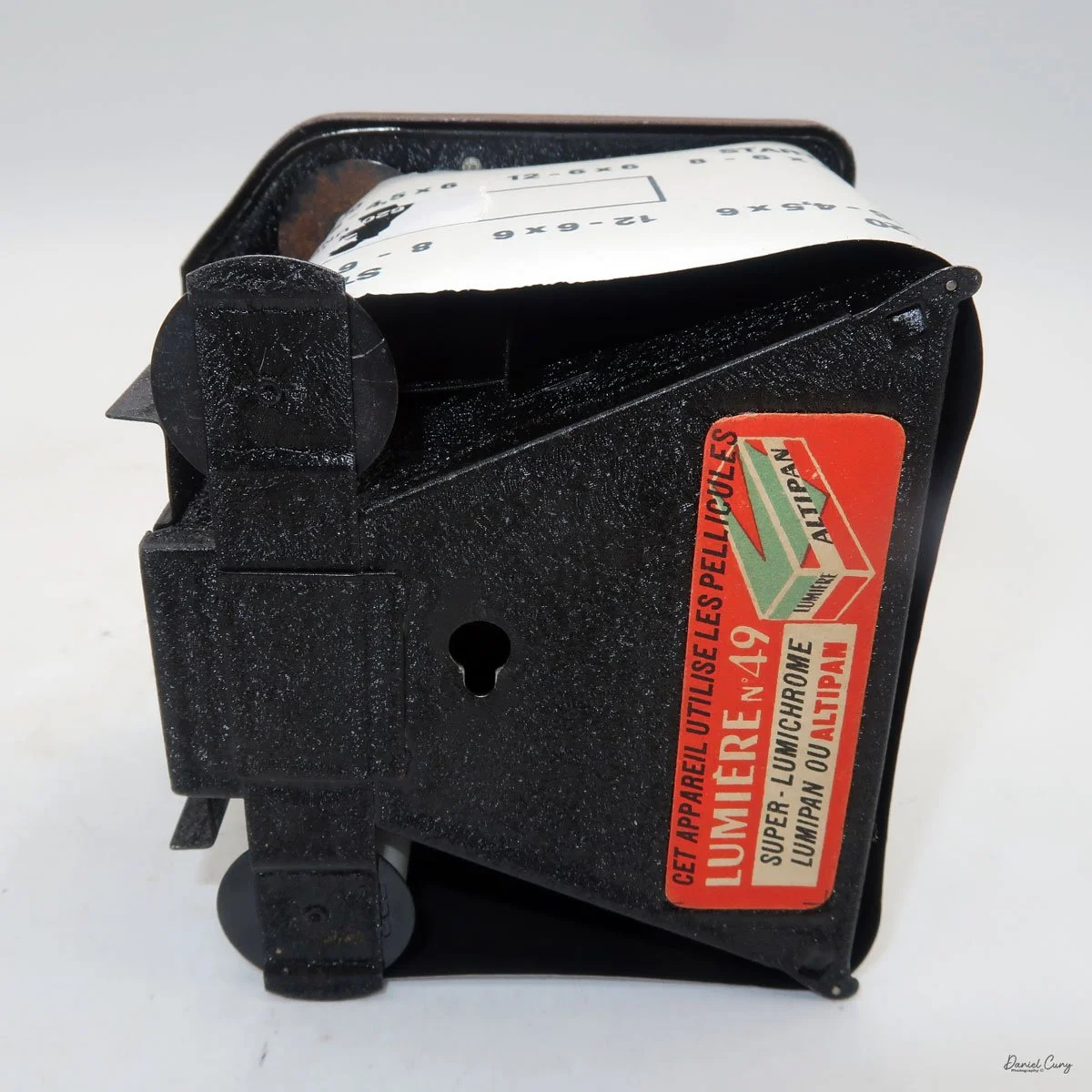
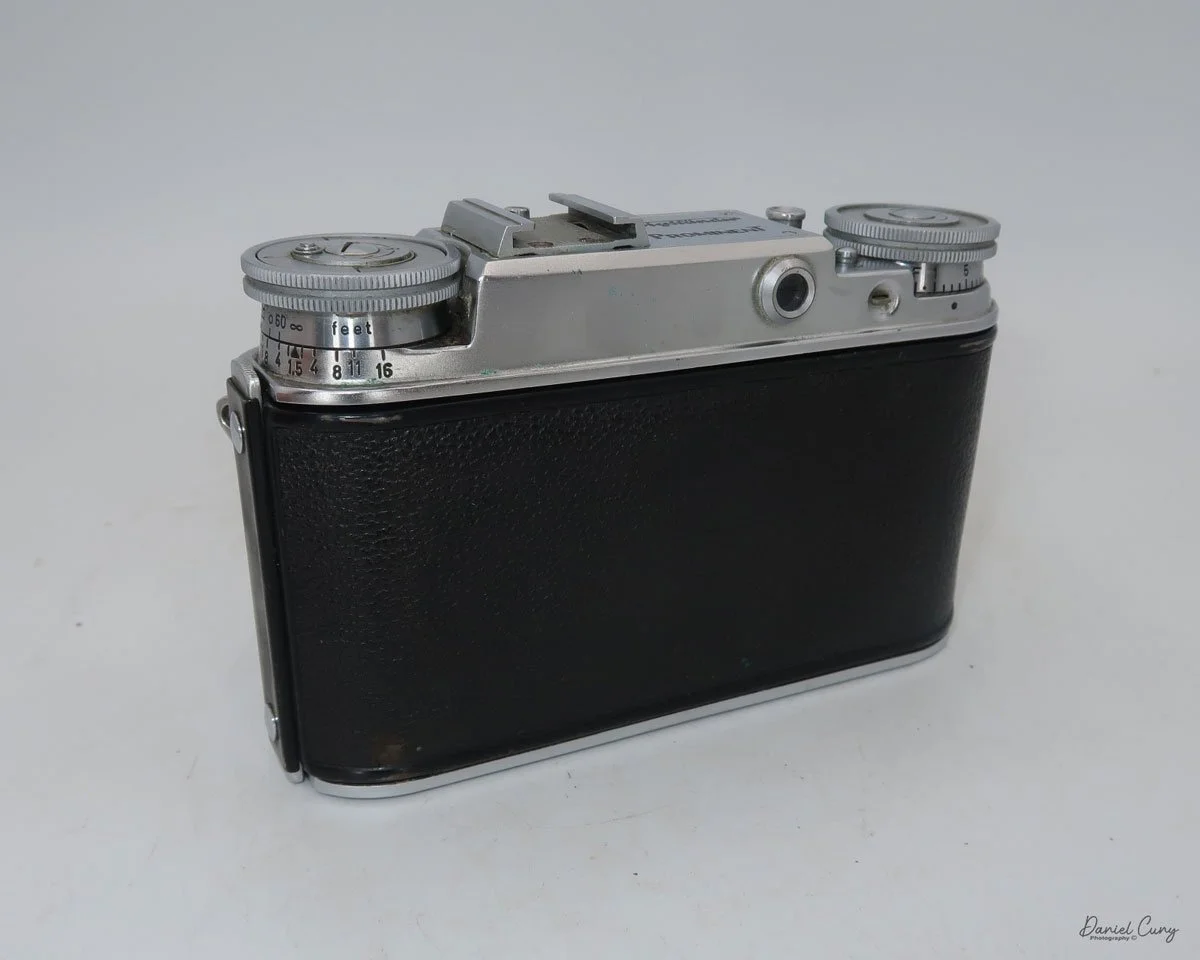
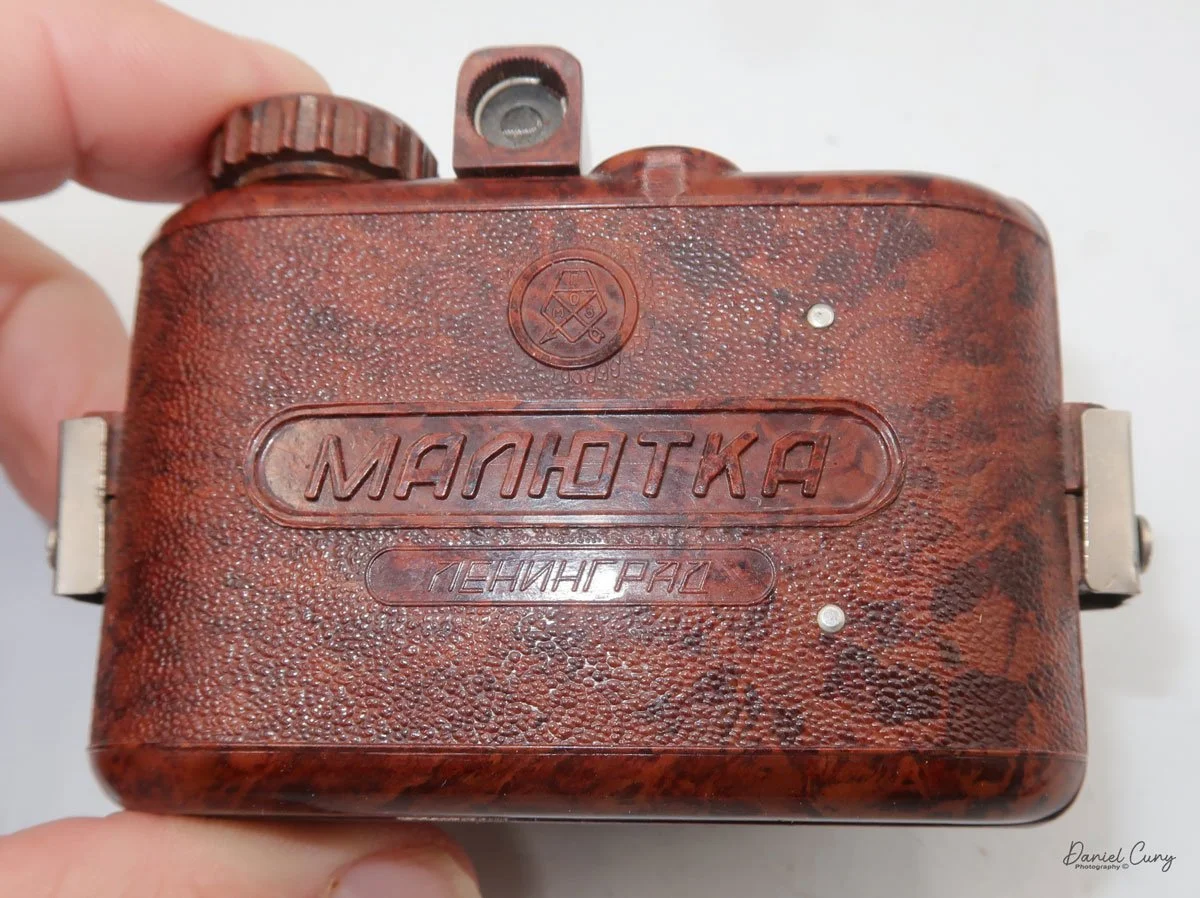
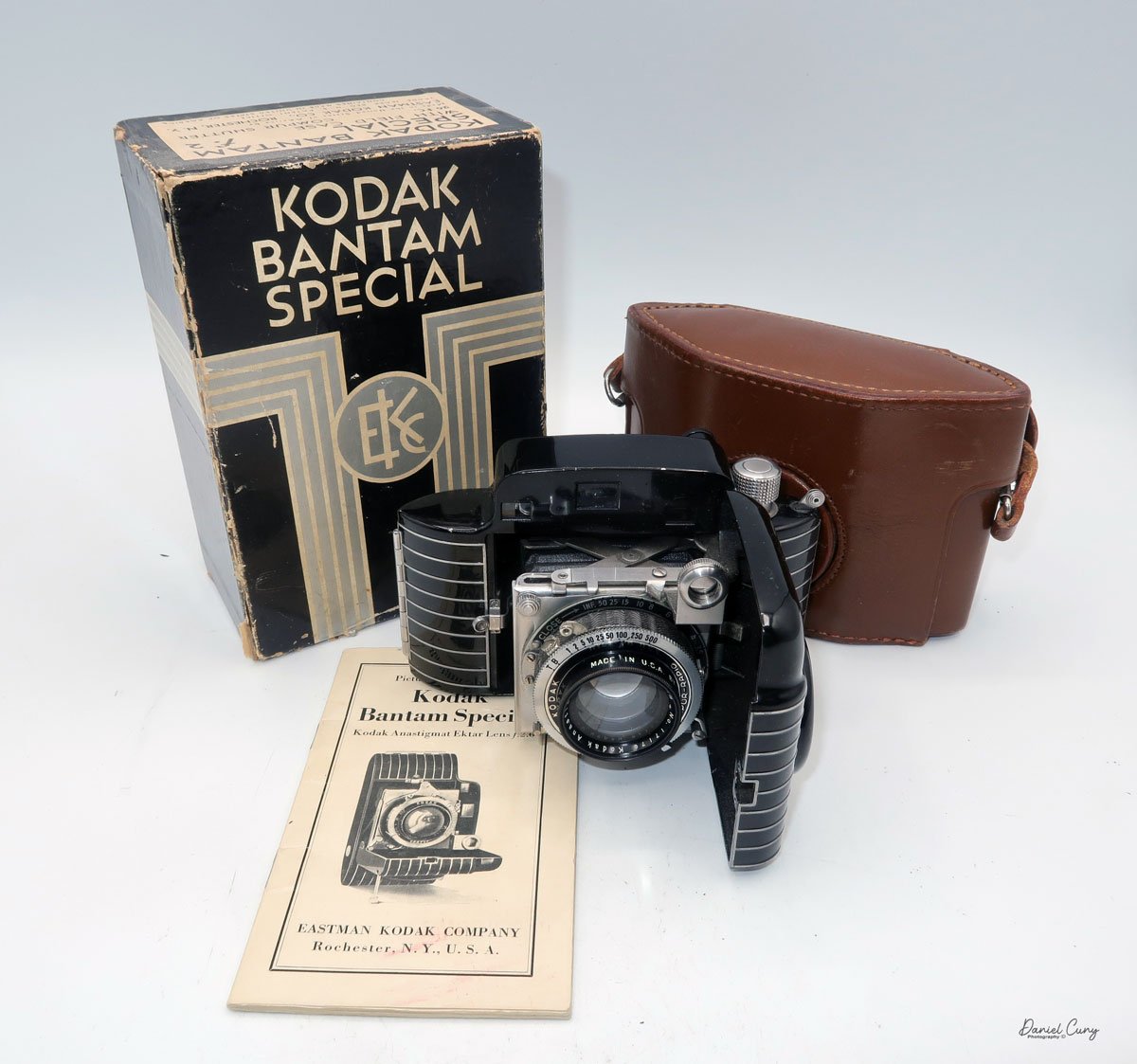
My Durst Duca camera.
I first saw the Durst Duca in McKeown's Camera Guide probably 30 years ago, and I can still remember my first instinct: this had to be a miniature camera. The tall, narrow body looked more like a tiny cine camera than anything that could handle standard 35mm film. With its vertical form, I assumed it used a 16mm cassette like a Minolta 16. So when I read that the Duca is actually a full‑frame 35mm camera, I was shocked.
It just didn't seem possible. The camera looked too small and too skinny to hide a 35mm cassette sideways, especially with that unusual vertical format. For years, it stayed in the back of my mind as one of those oddball cameras I never expected to actually run across.
Finding My Duca
Being in the U.S., this little Italian camera rarely shows up at the usual places I haunt for gear—flea markets, garage sales, estate sales. On the big auction sites, I do see them once in a while. Still, they're usually priced higher than I'm willing to pay, especially once you tack on international shipping.
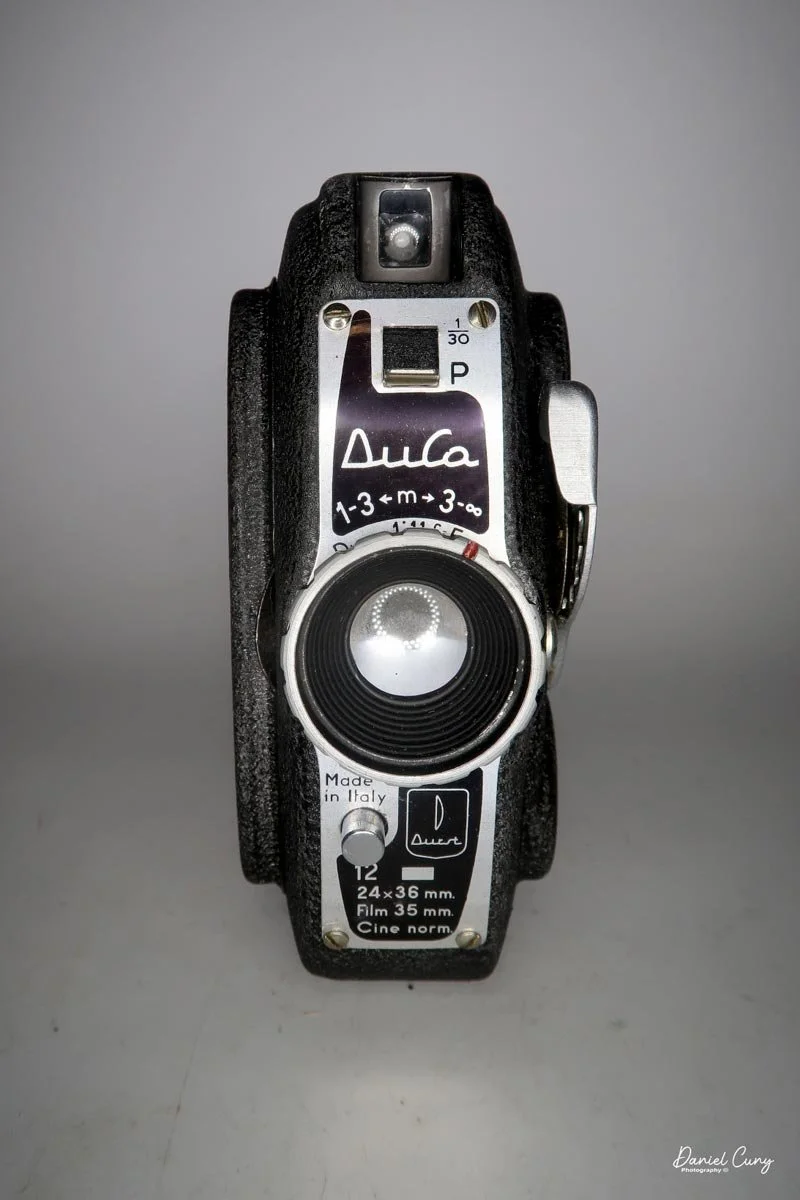
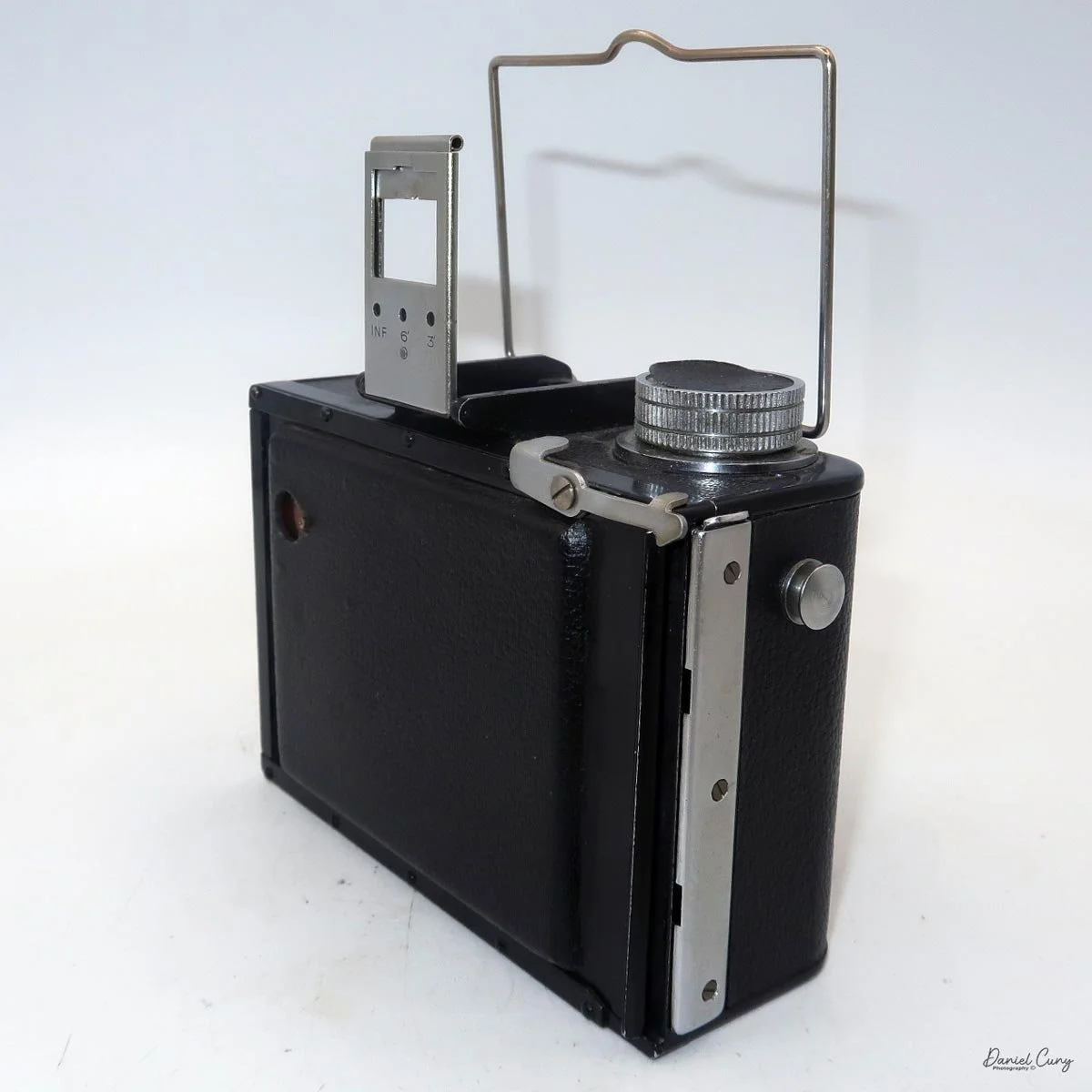
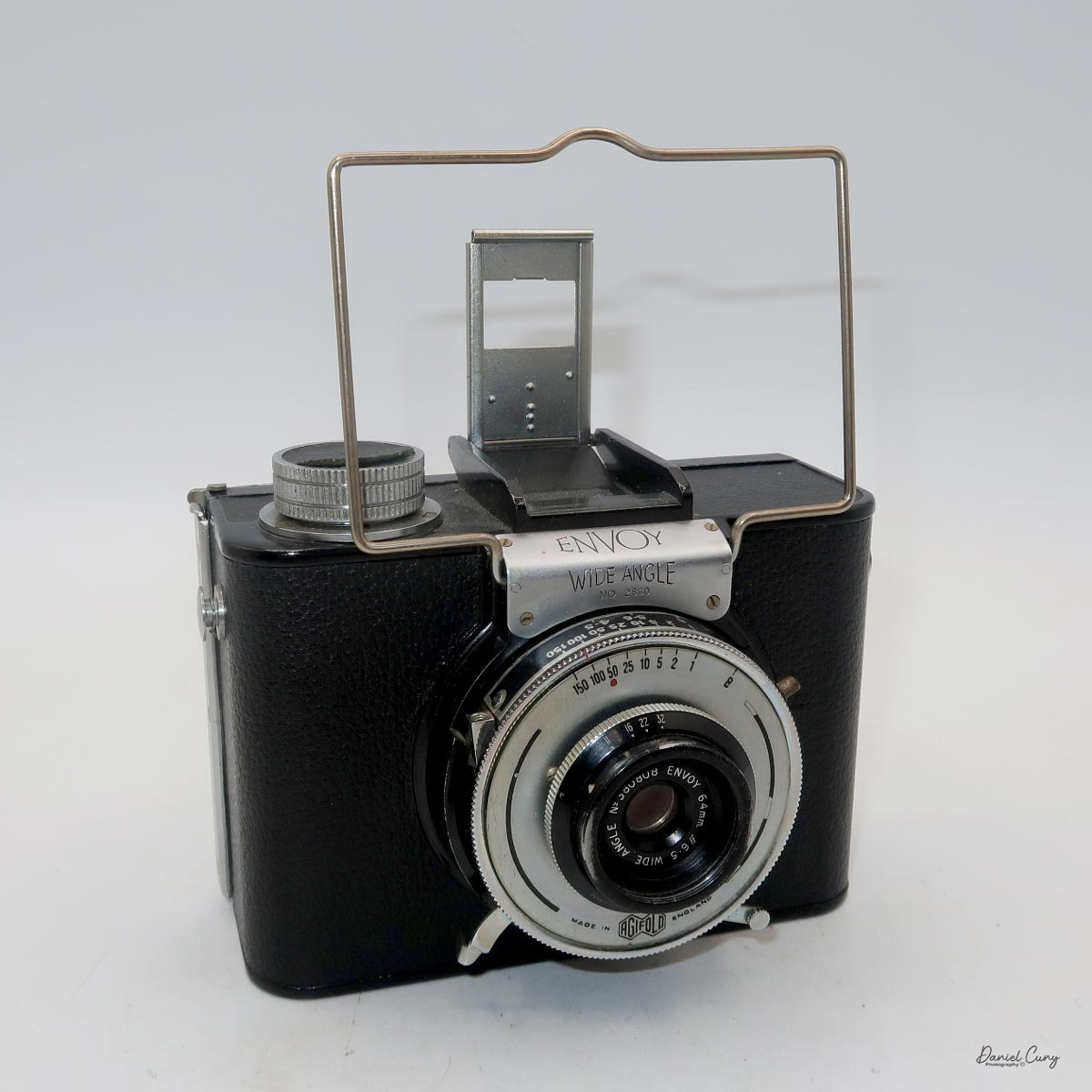
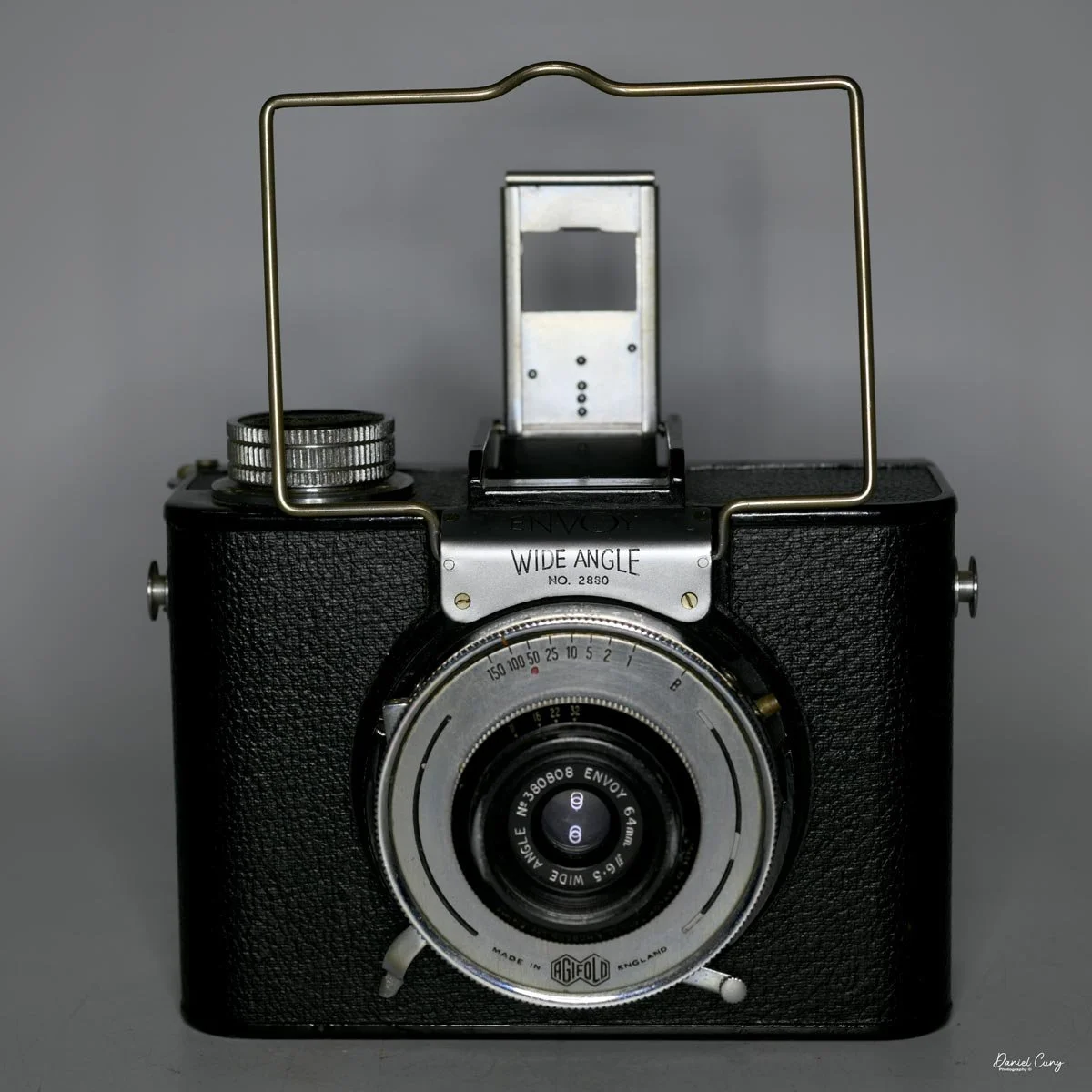
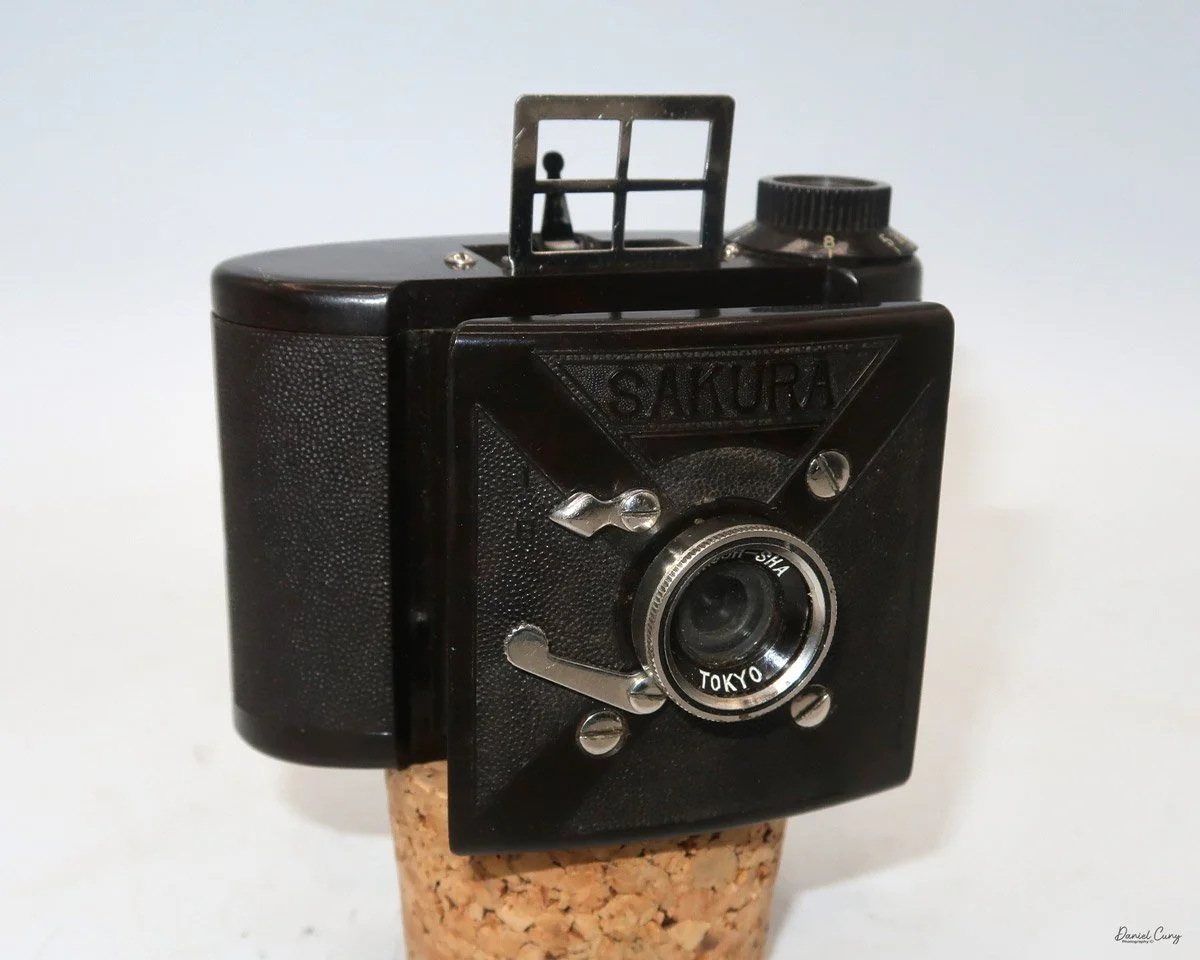
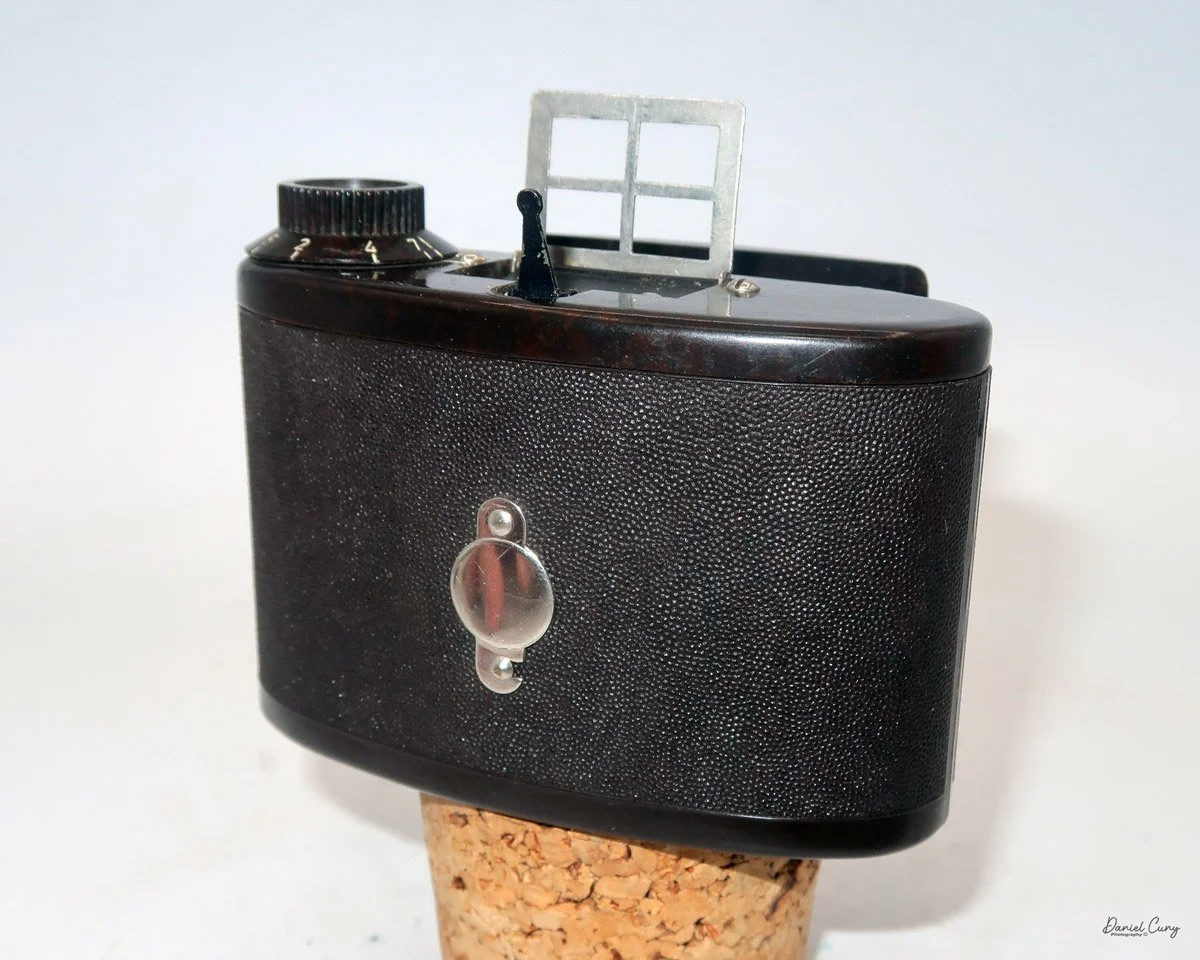
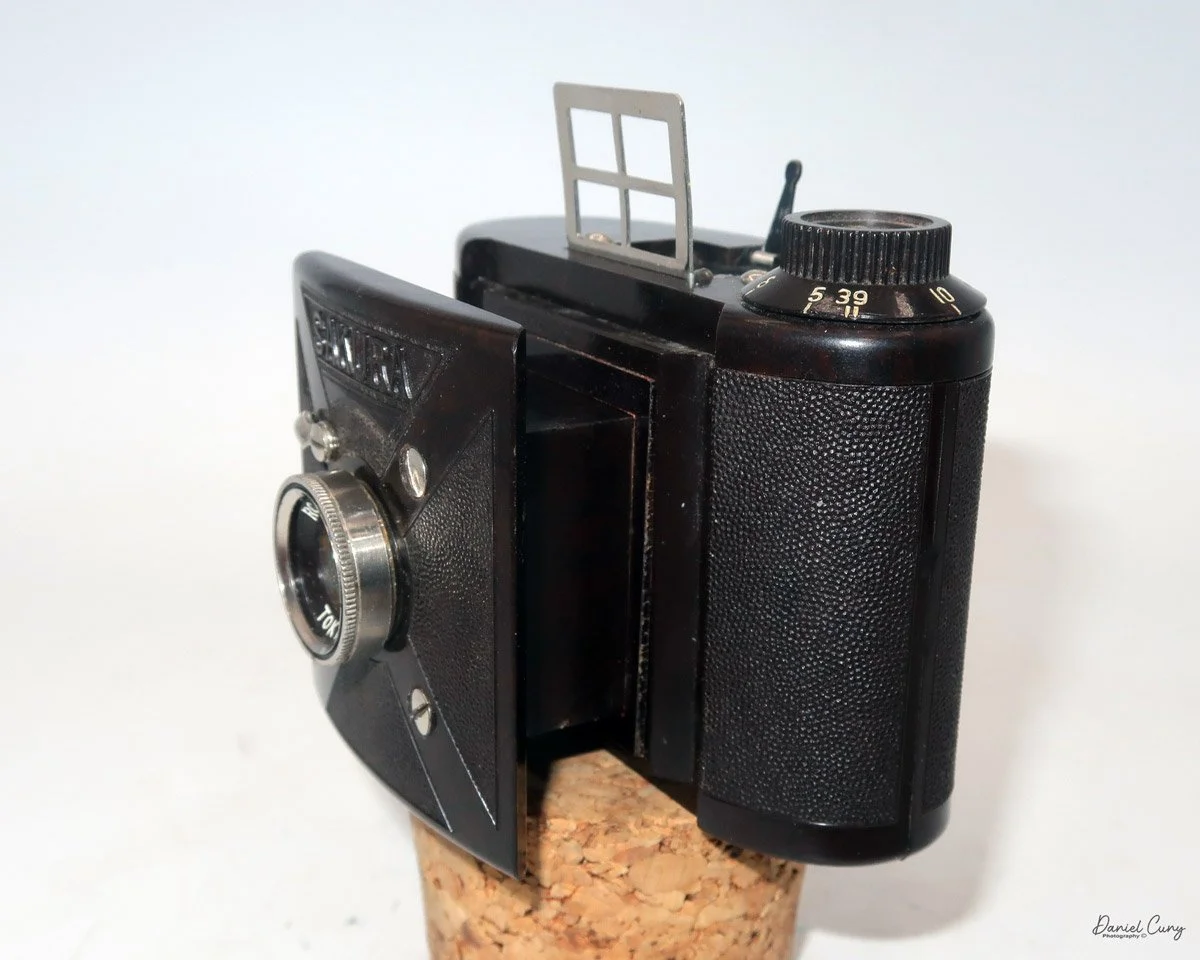
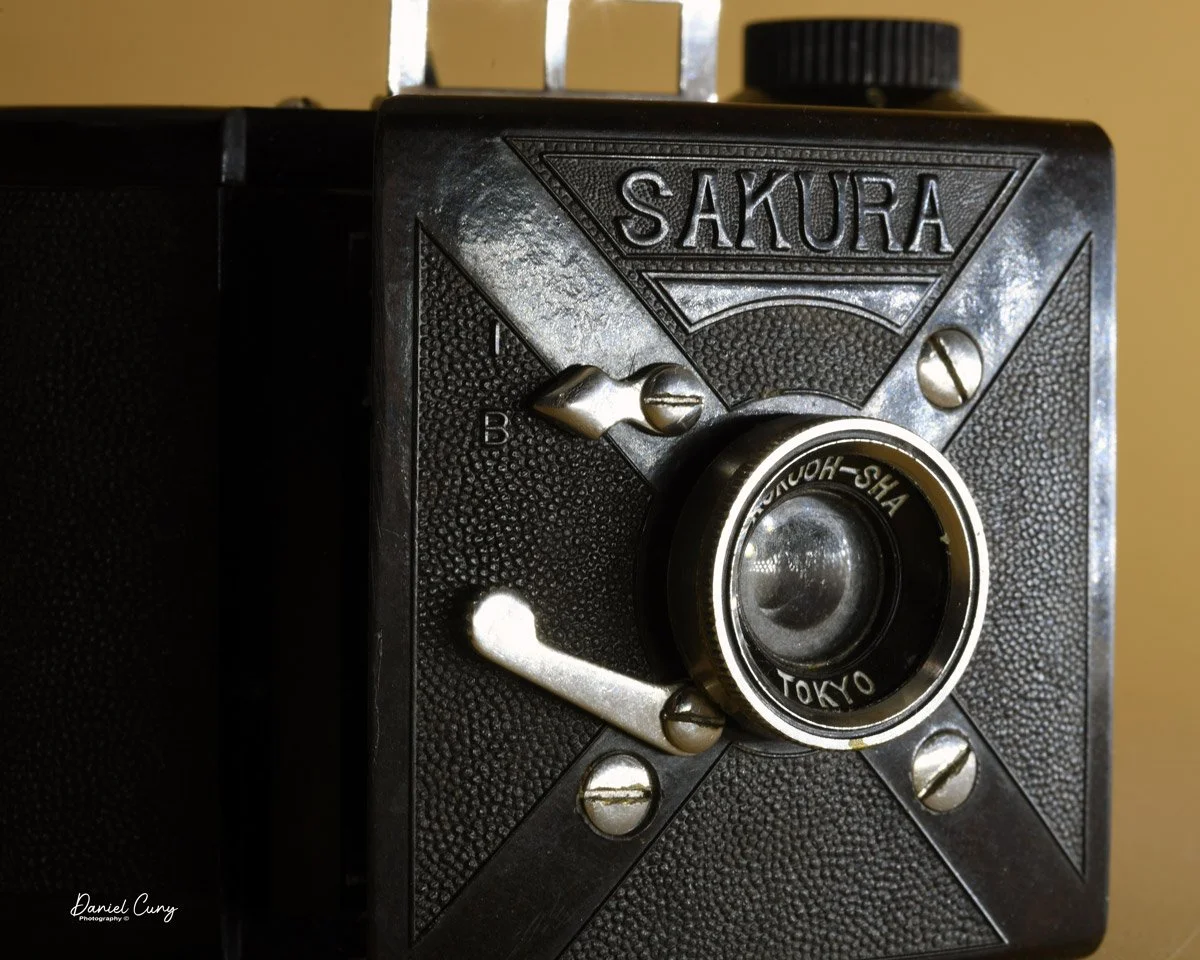
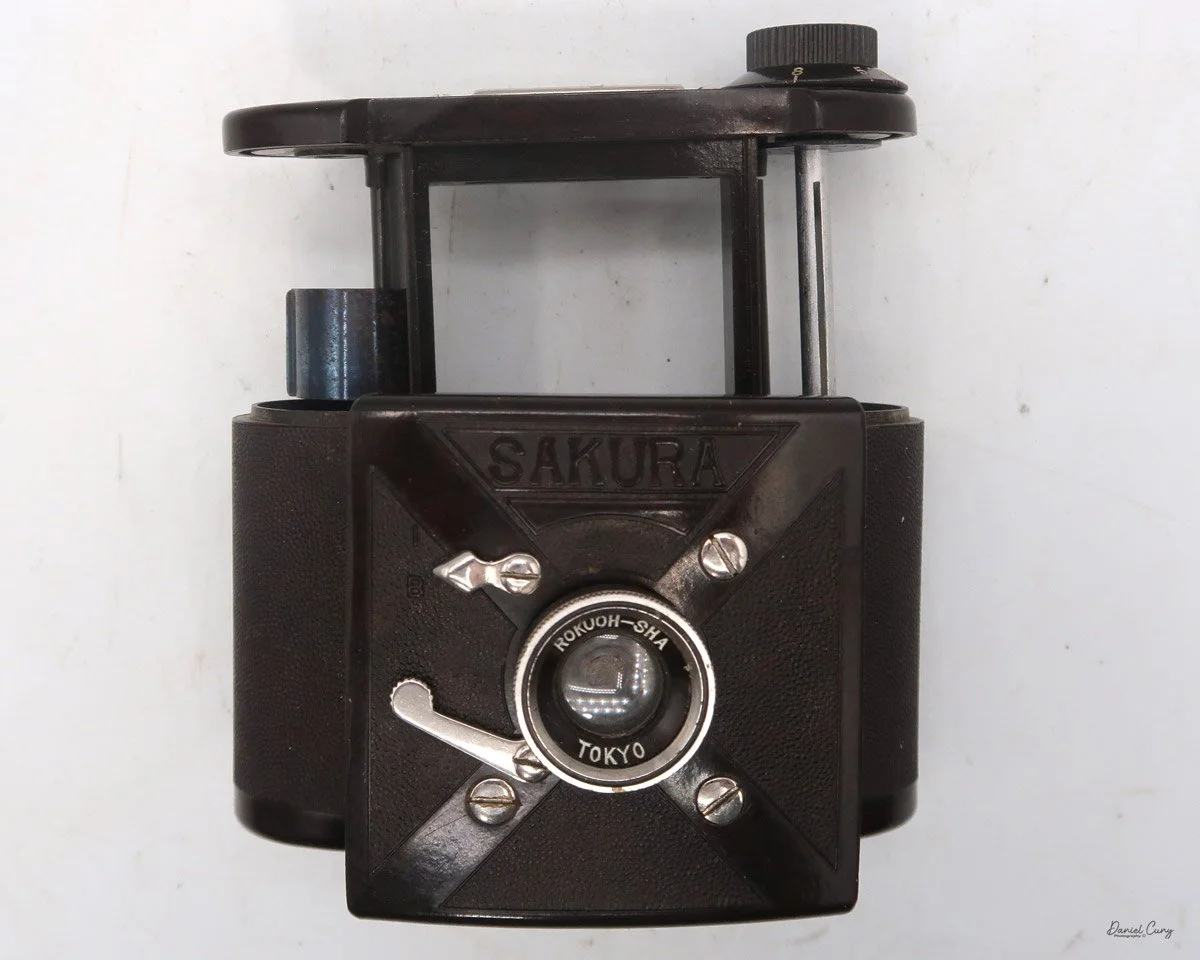
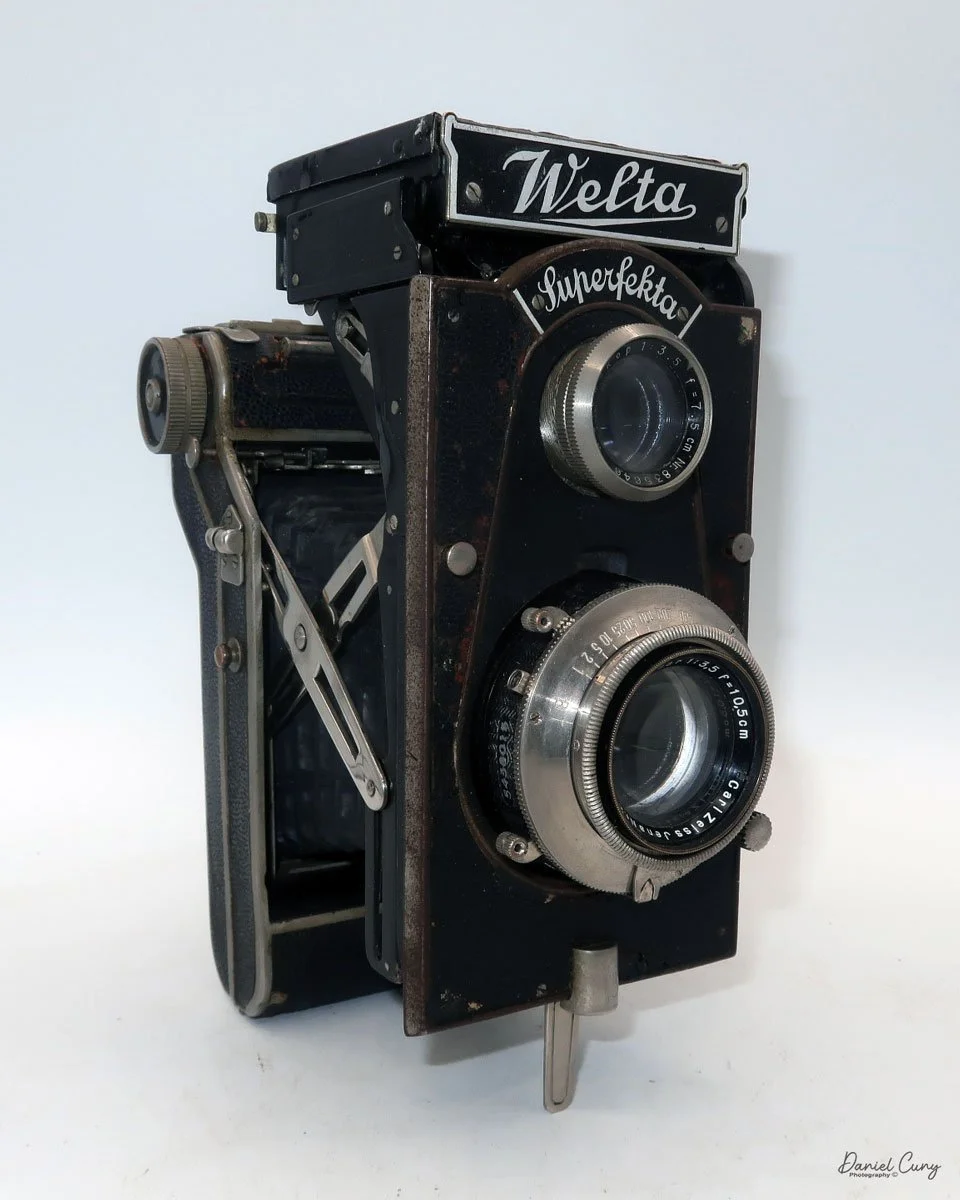
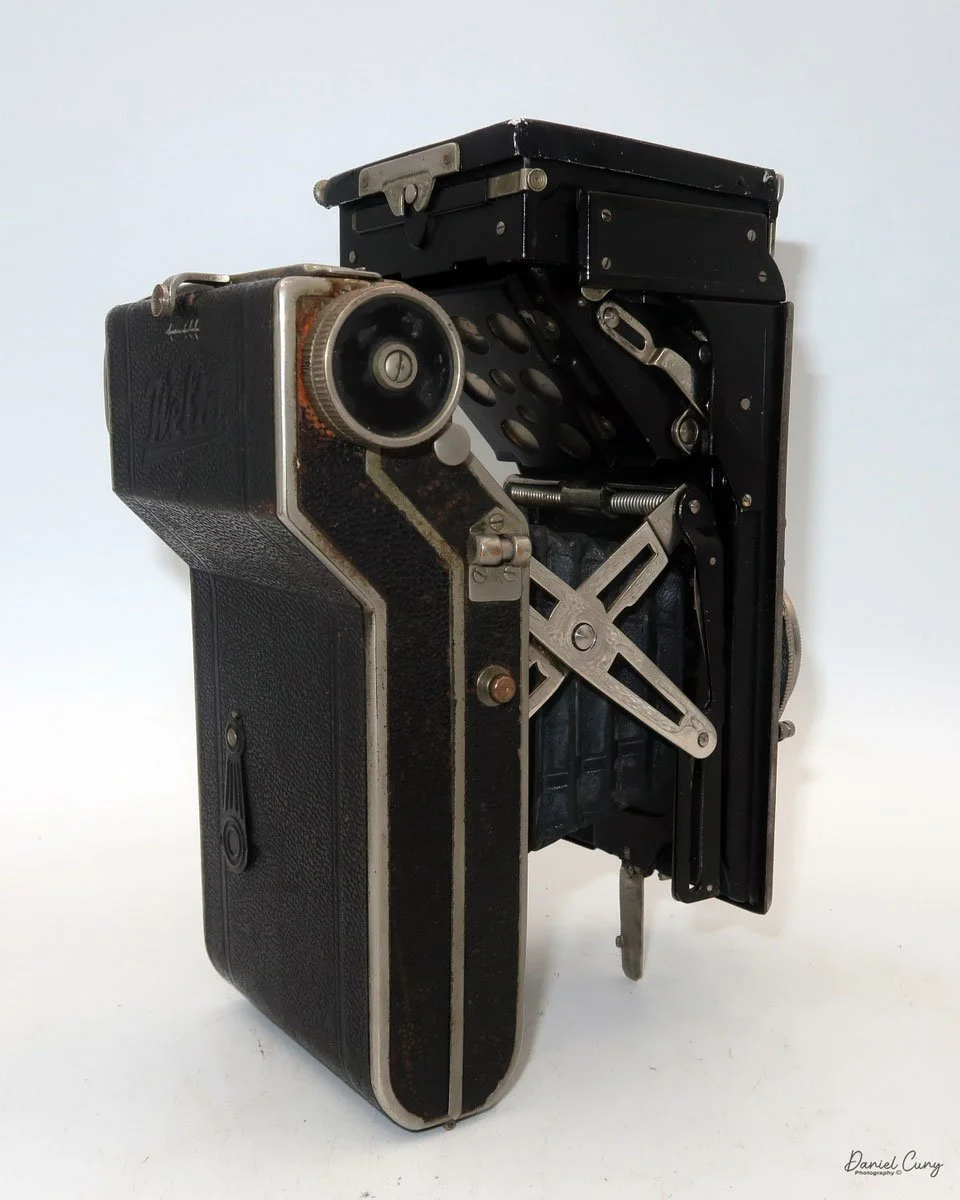
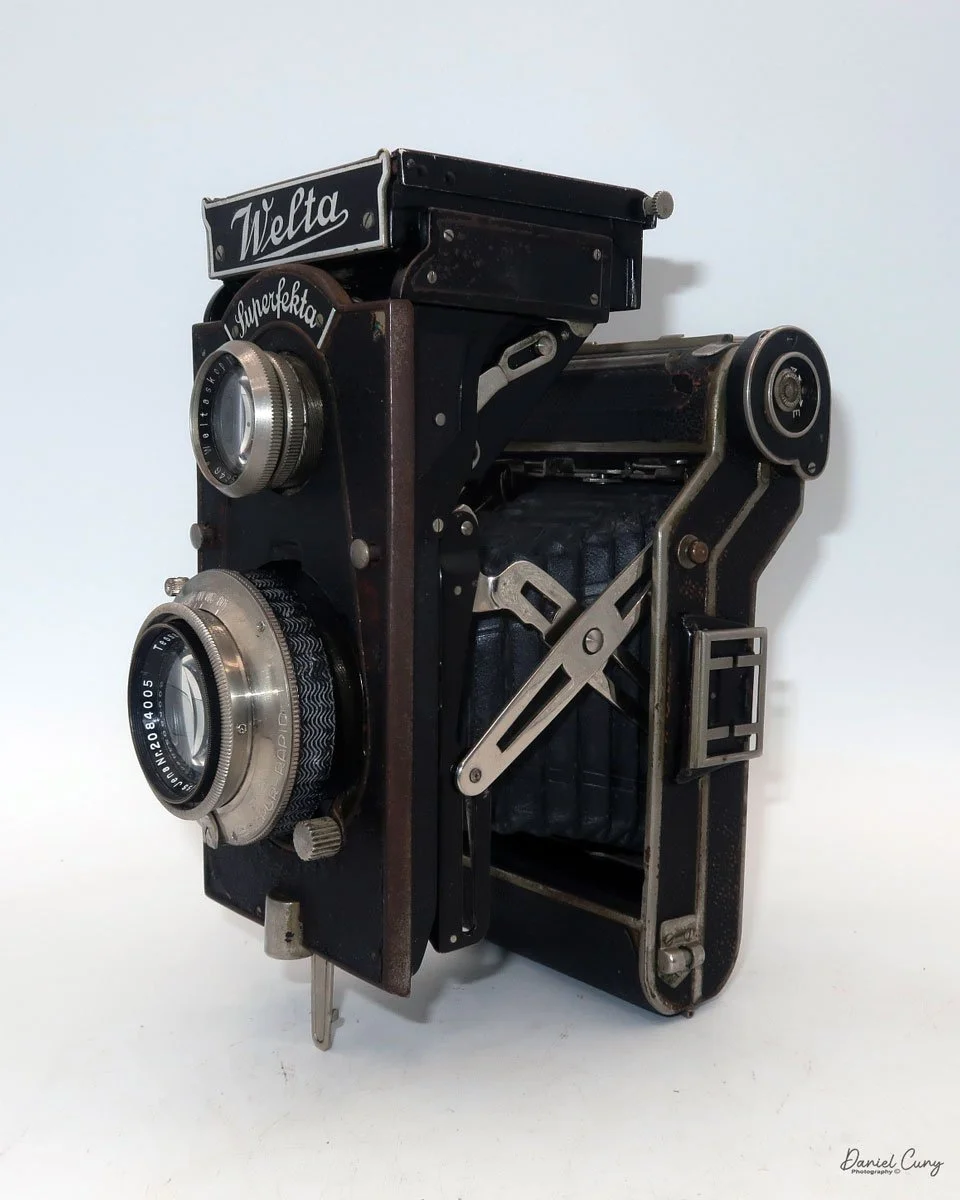
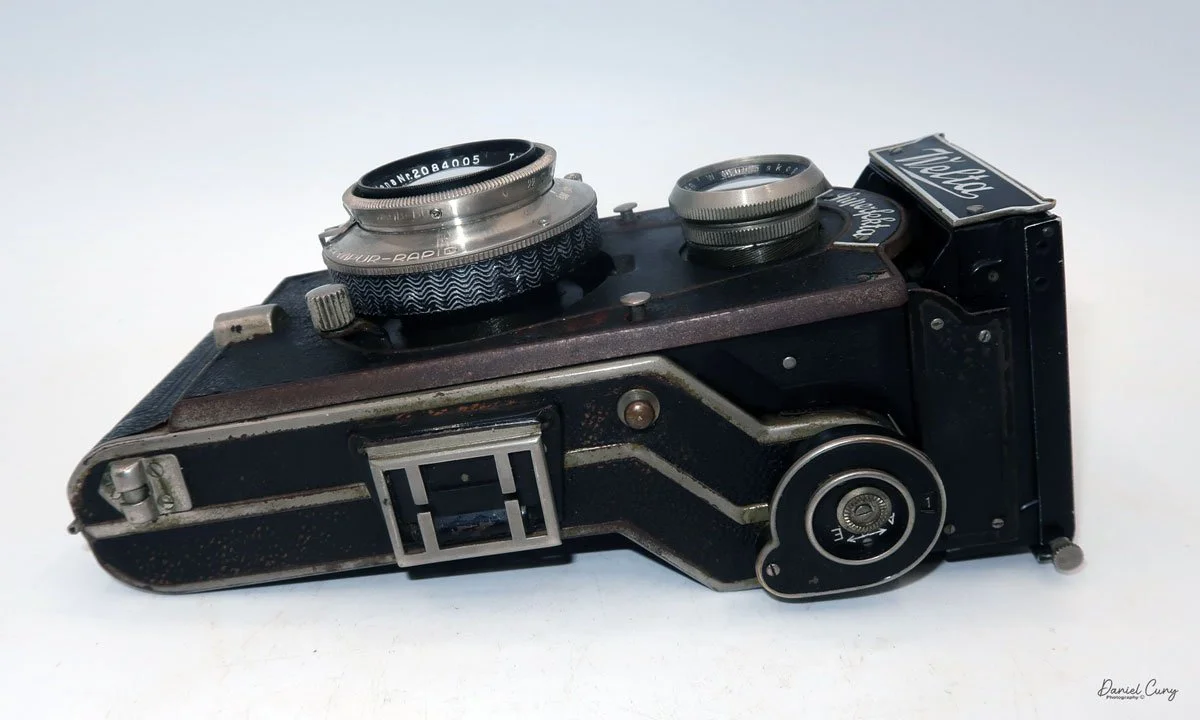
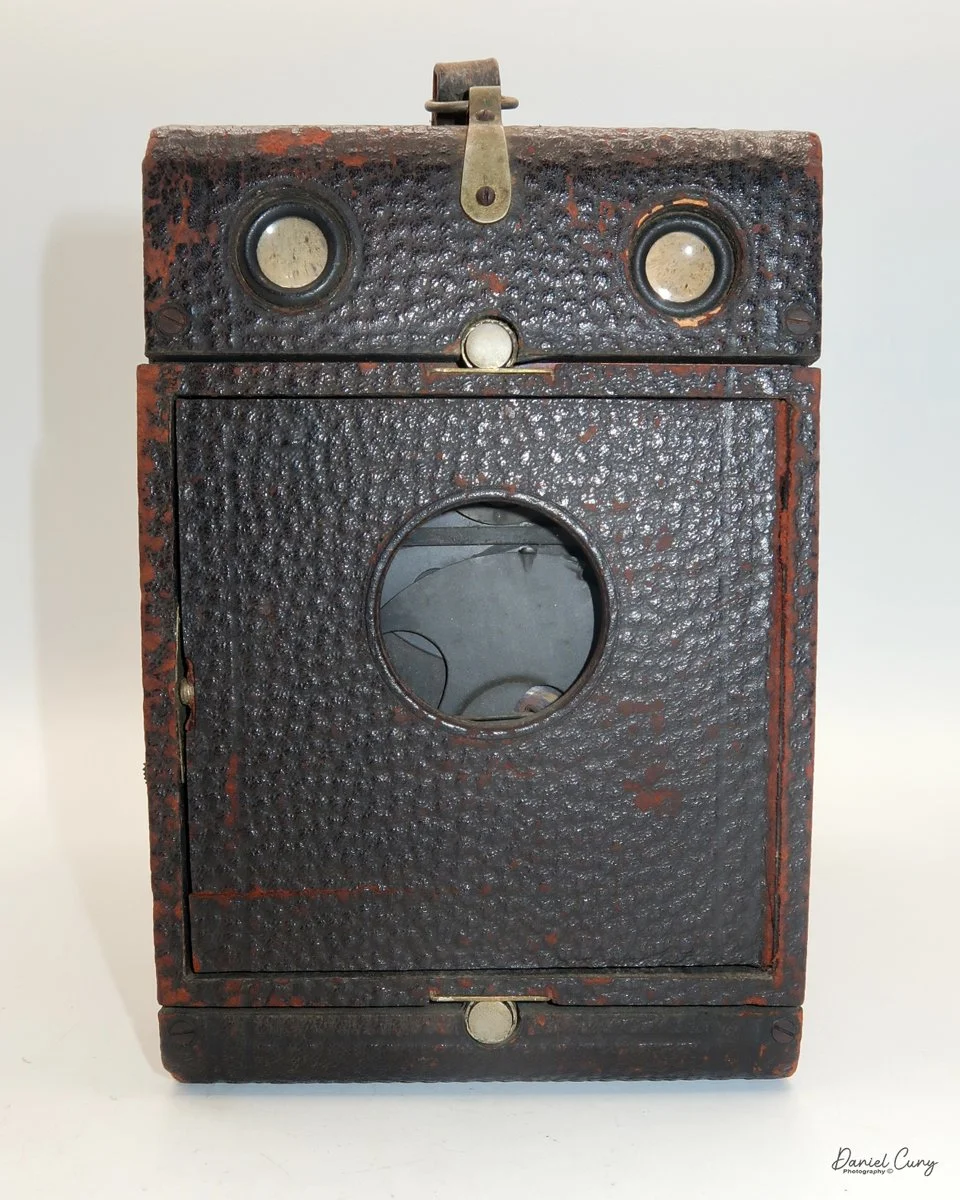
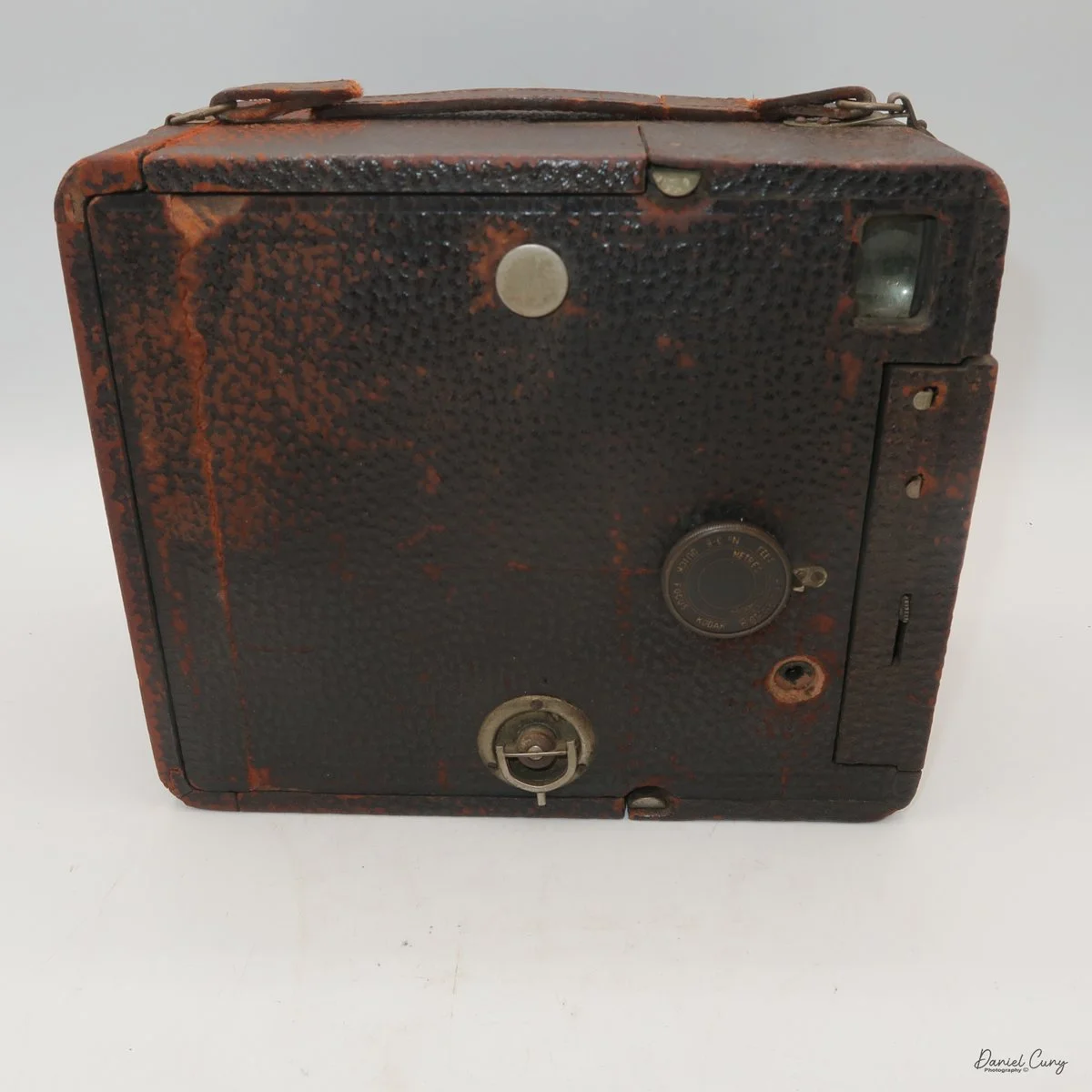
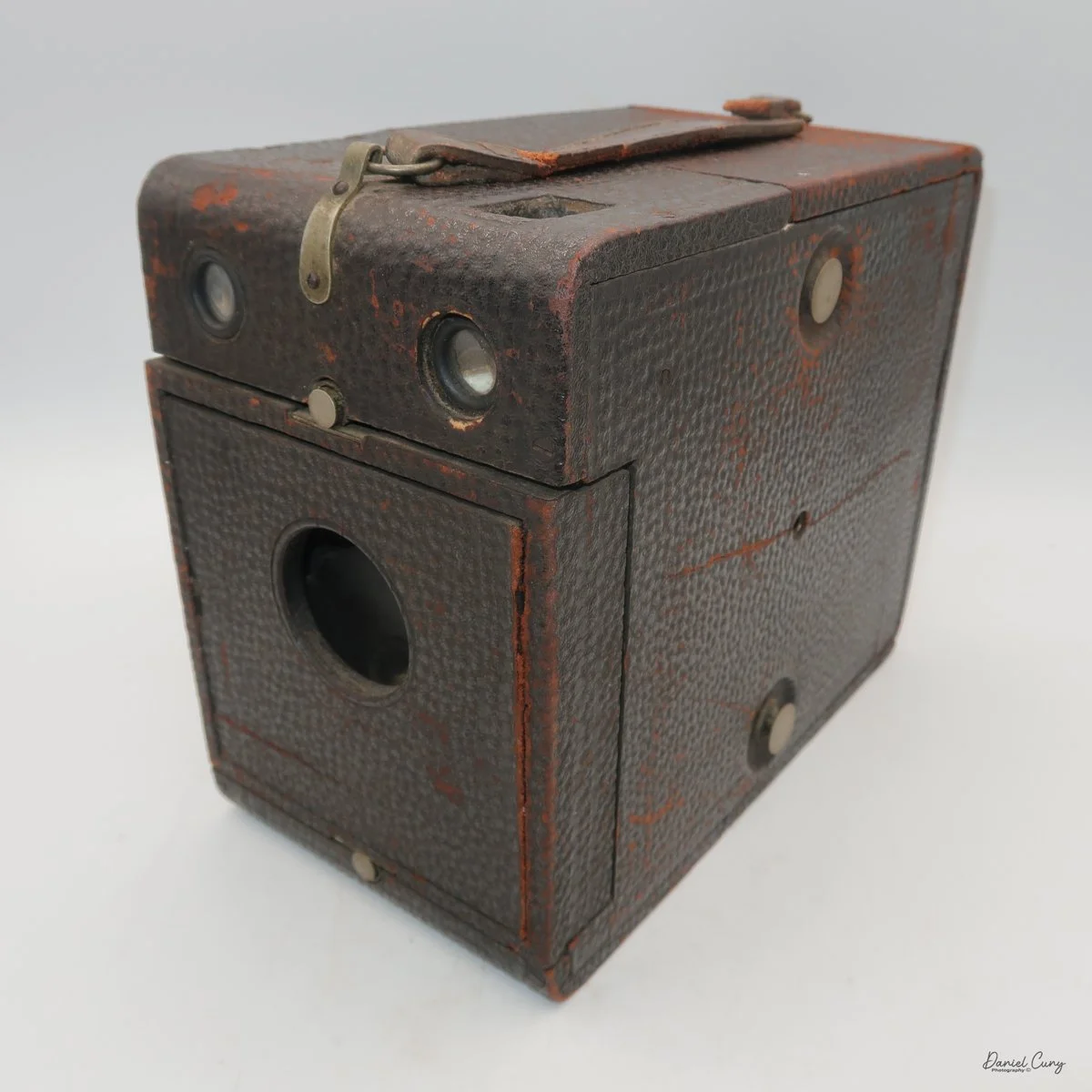
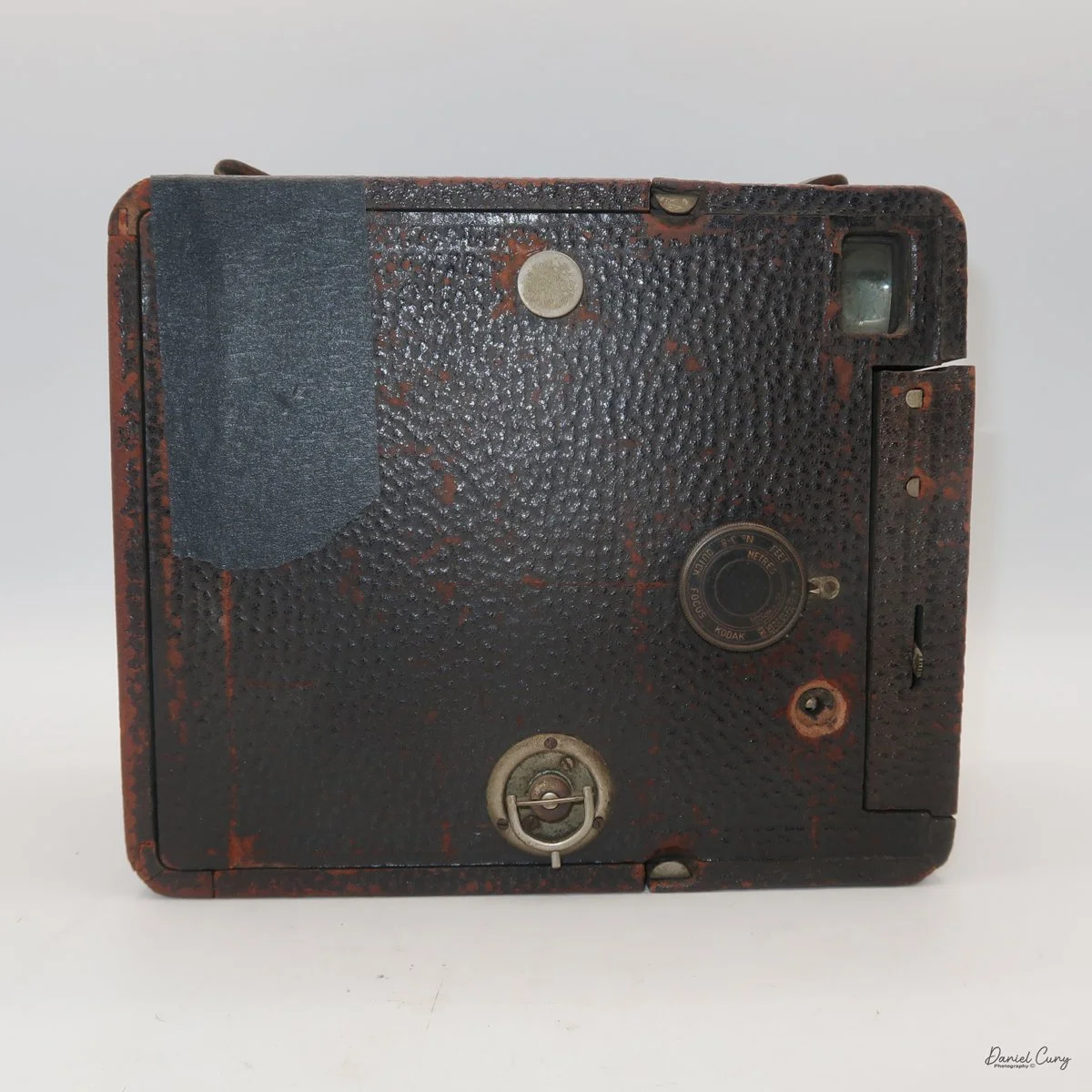
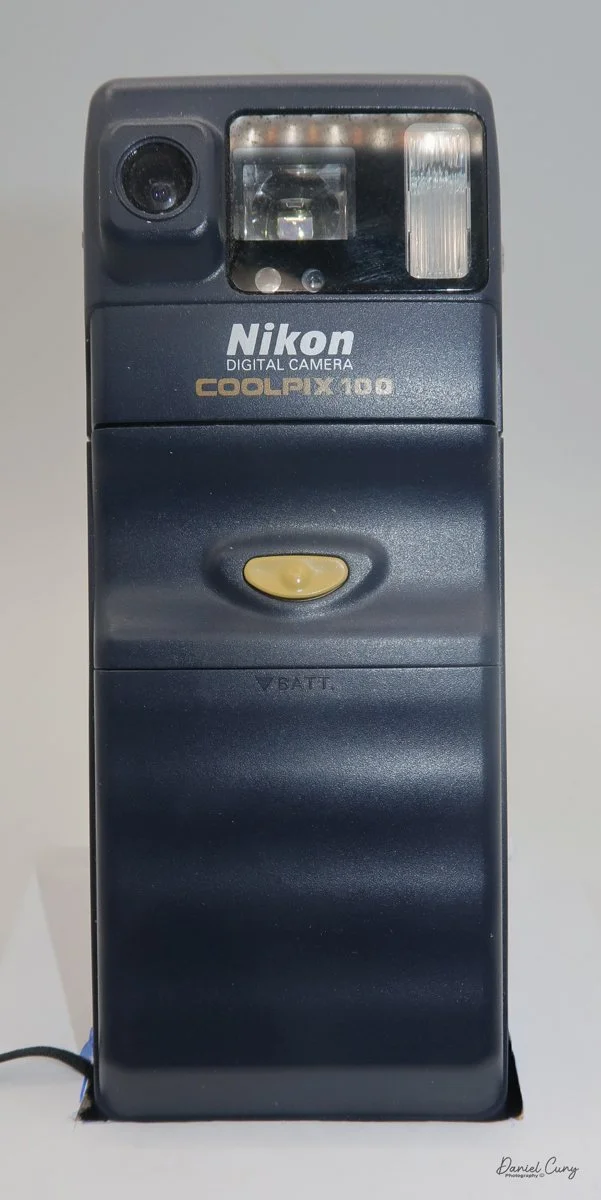
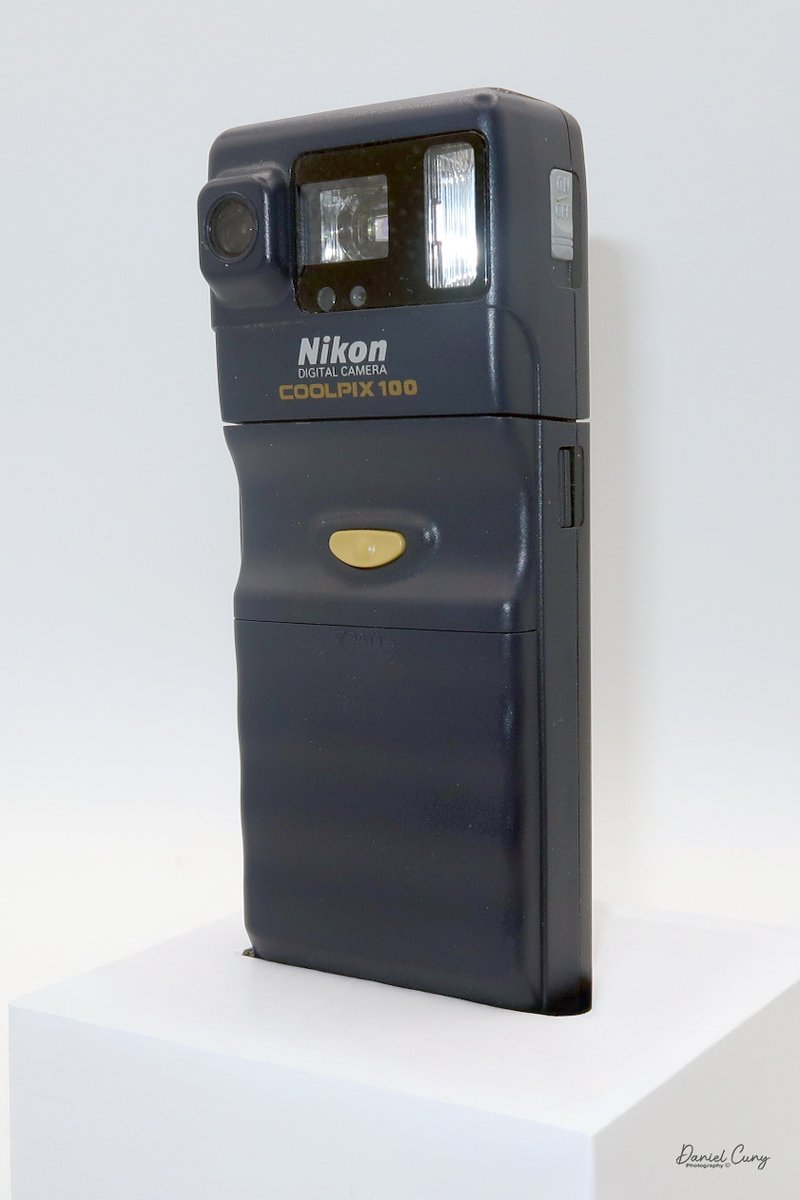
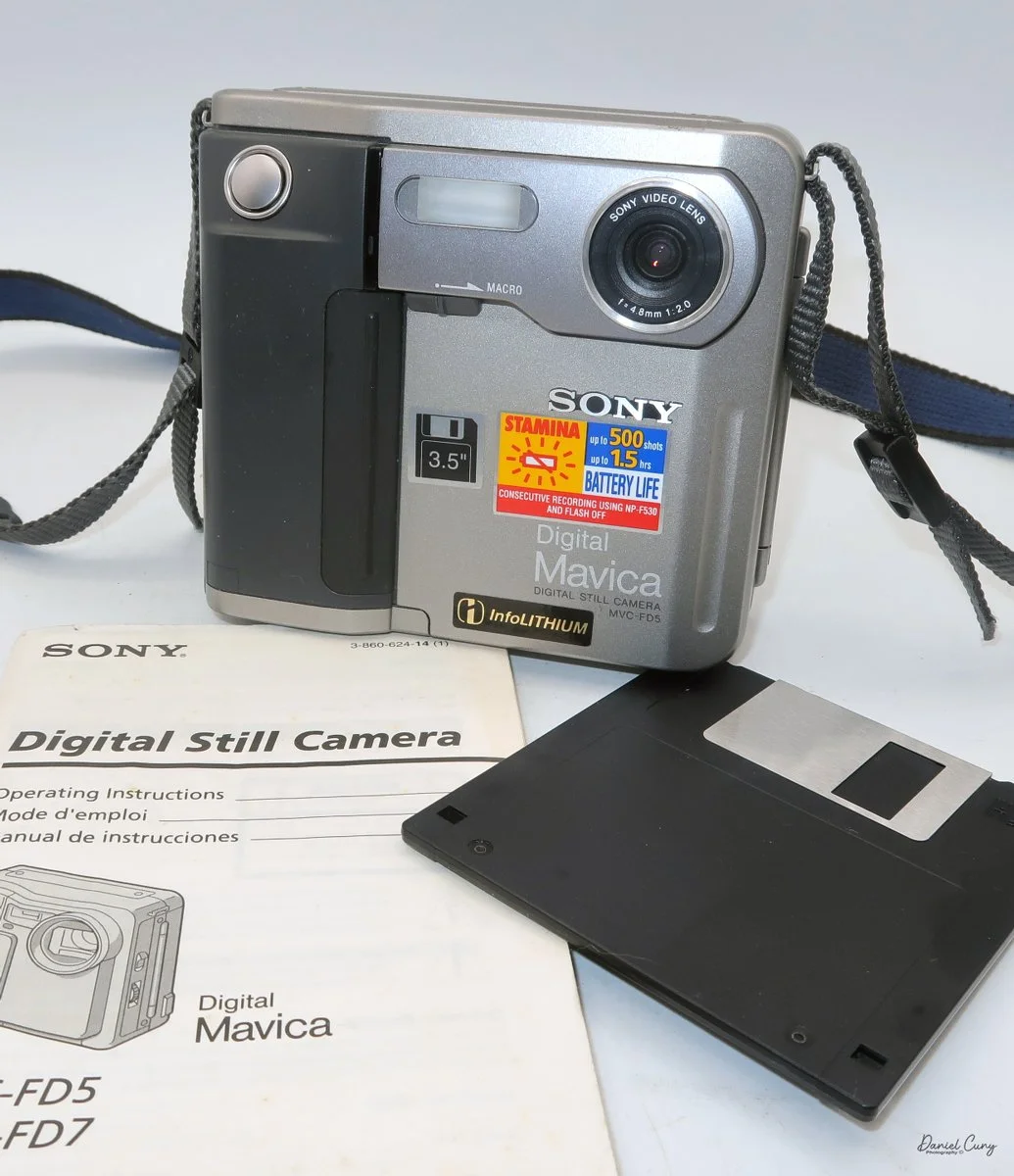
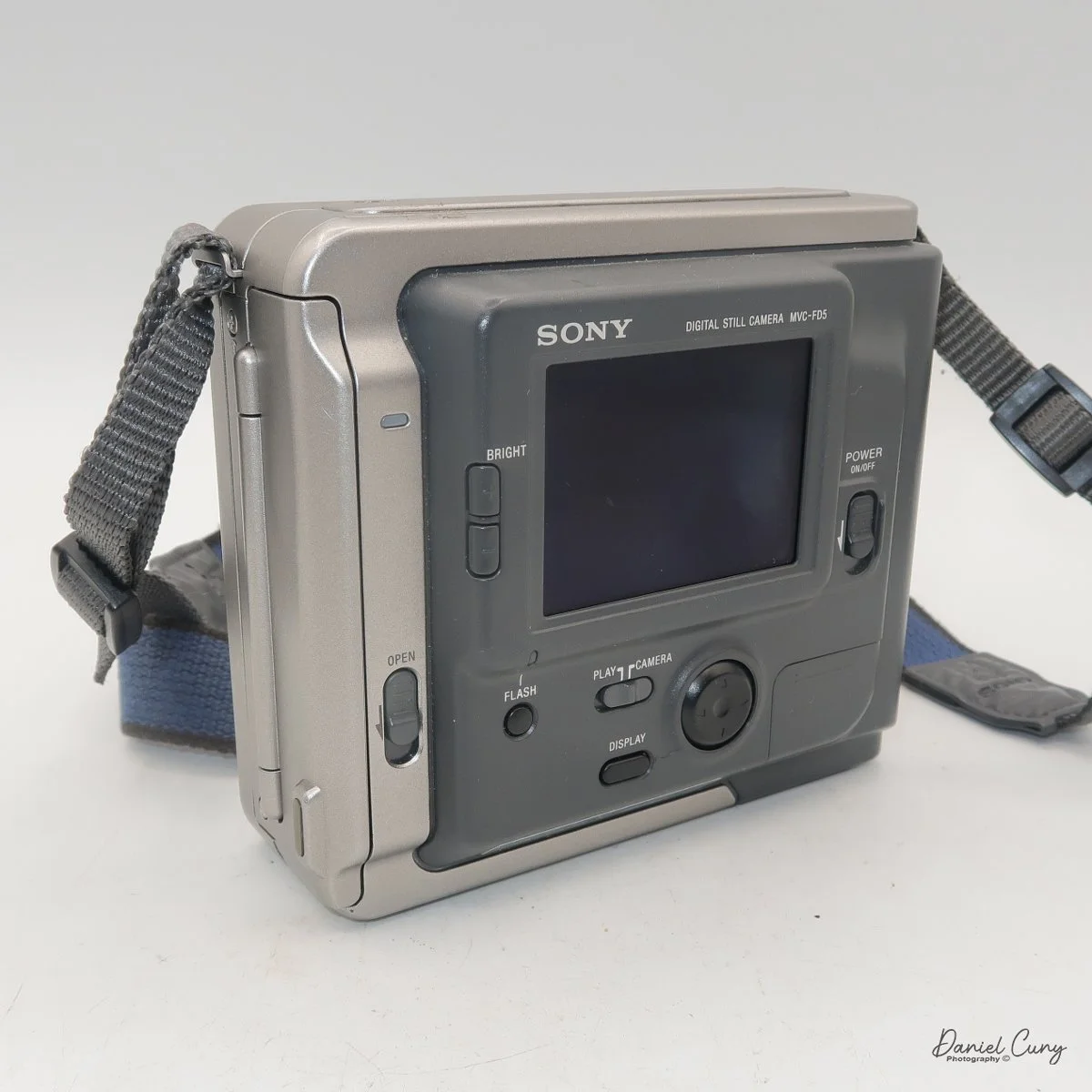
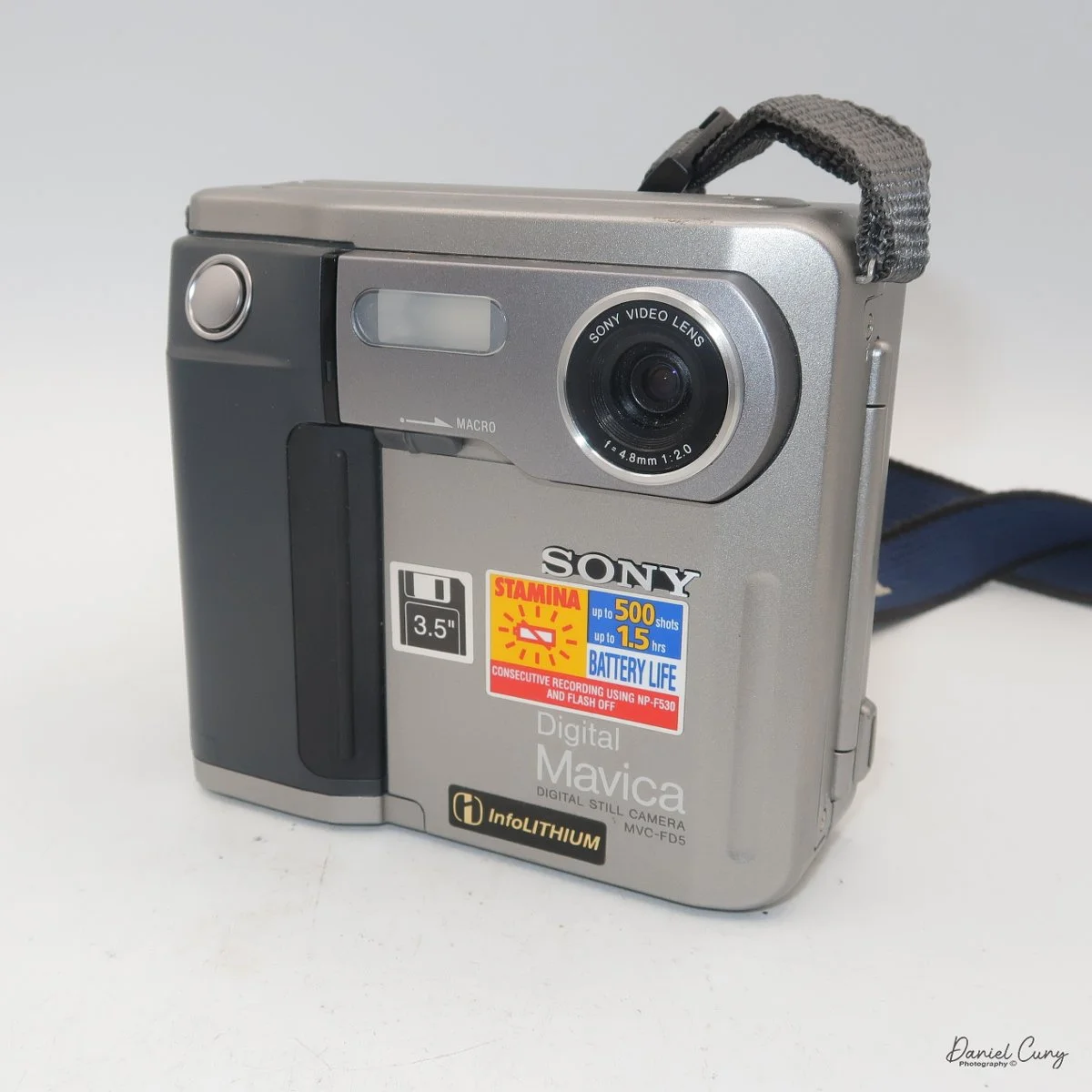
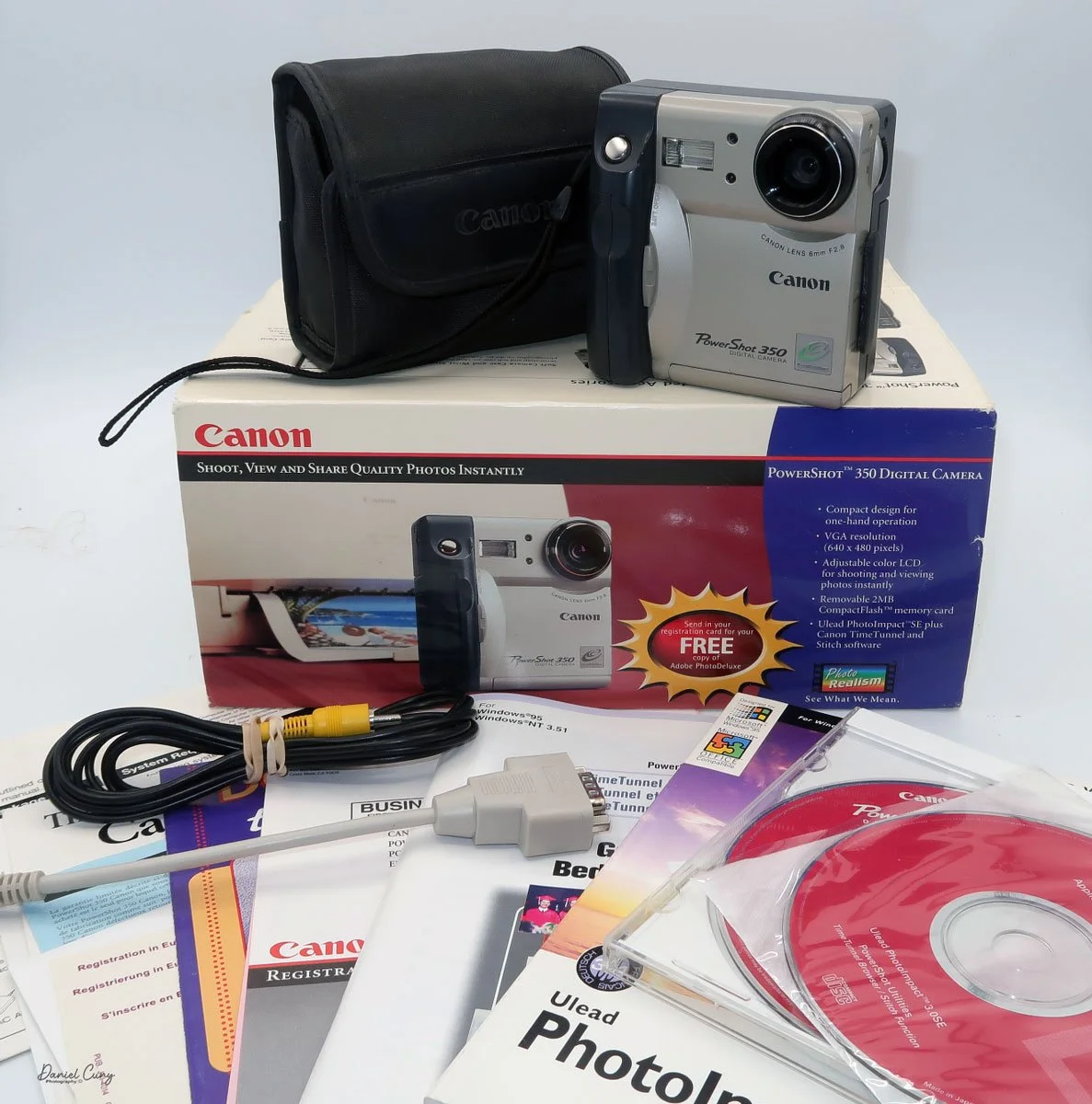
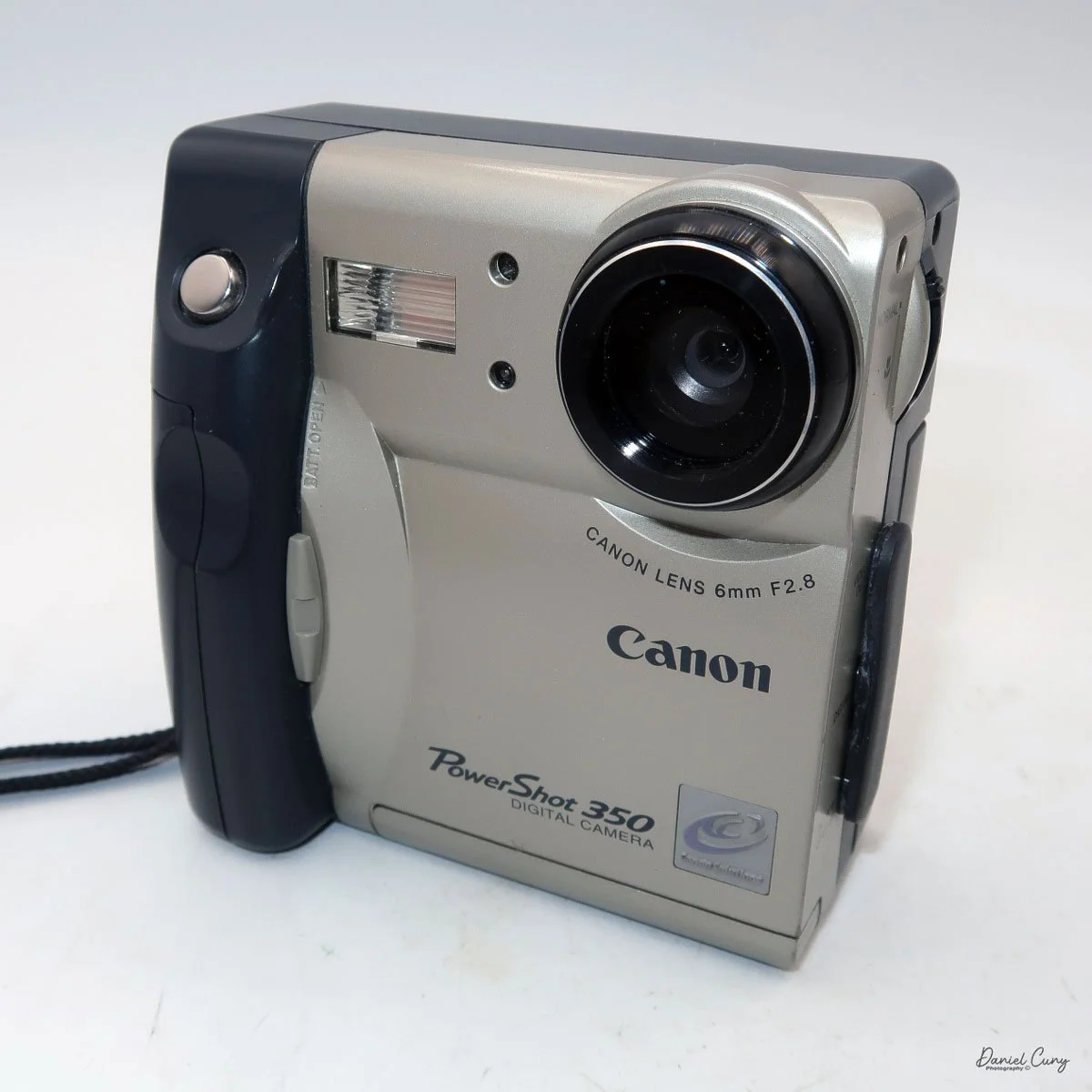
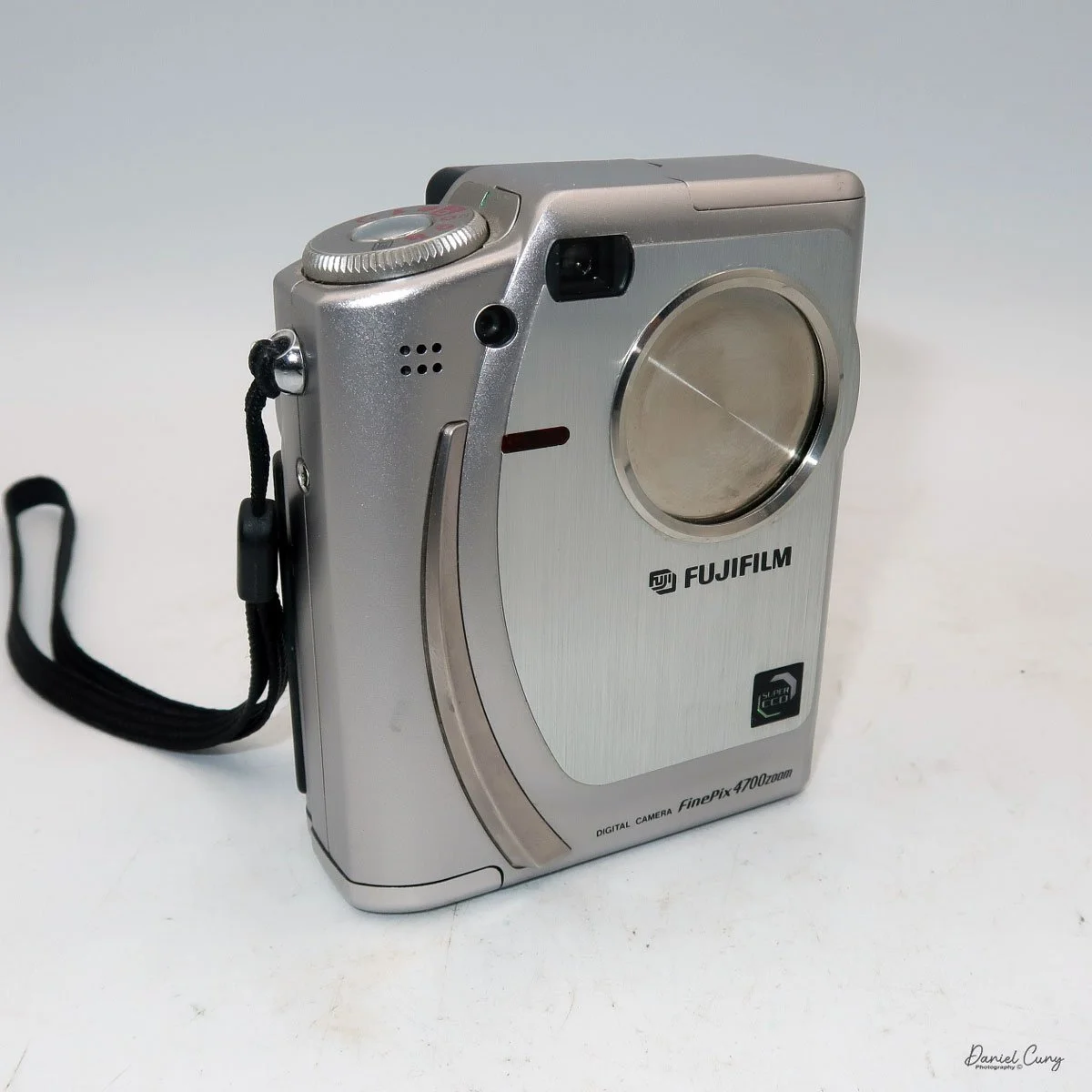
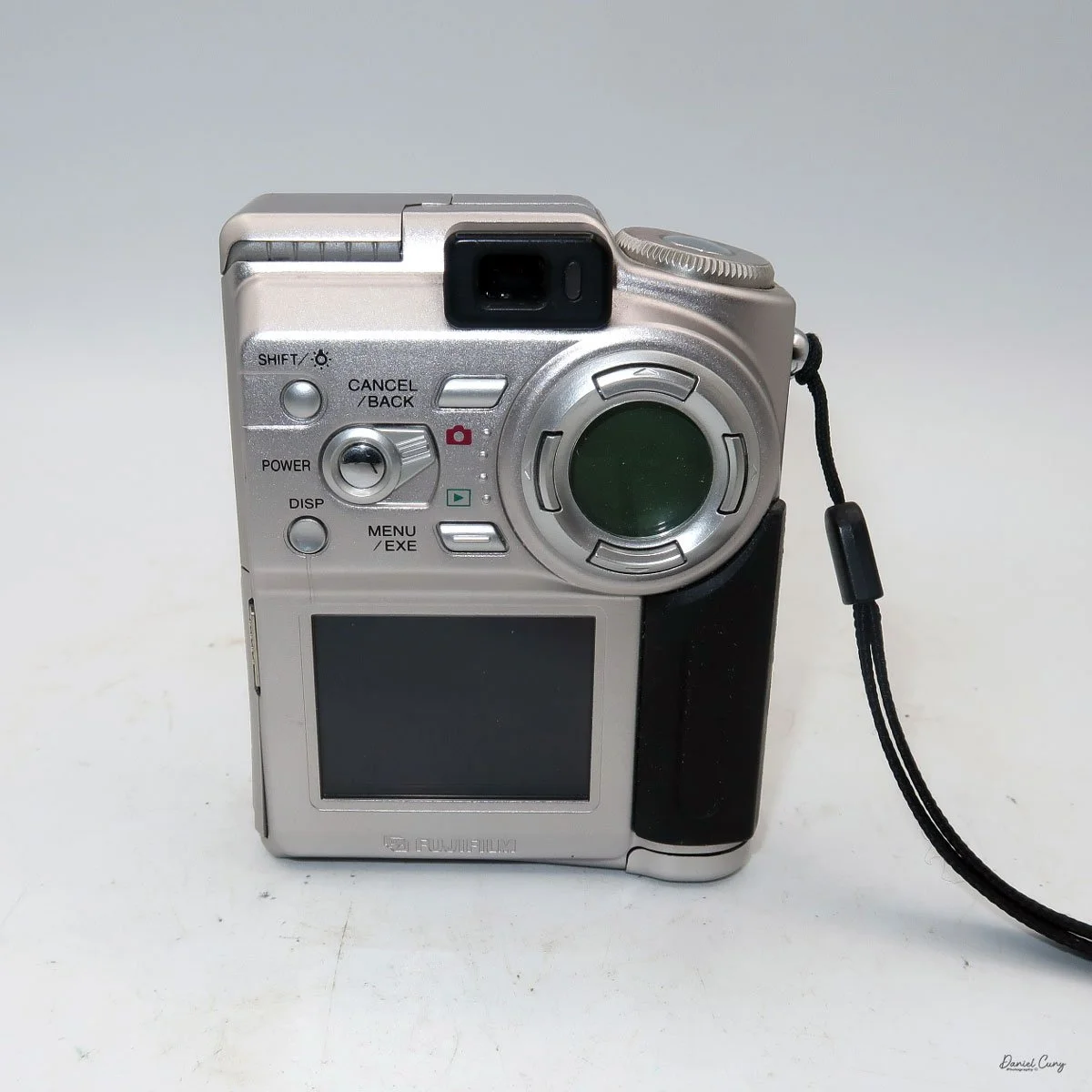
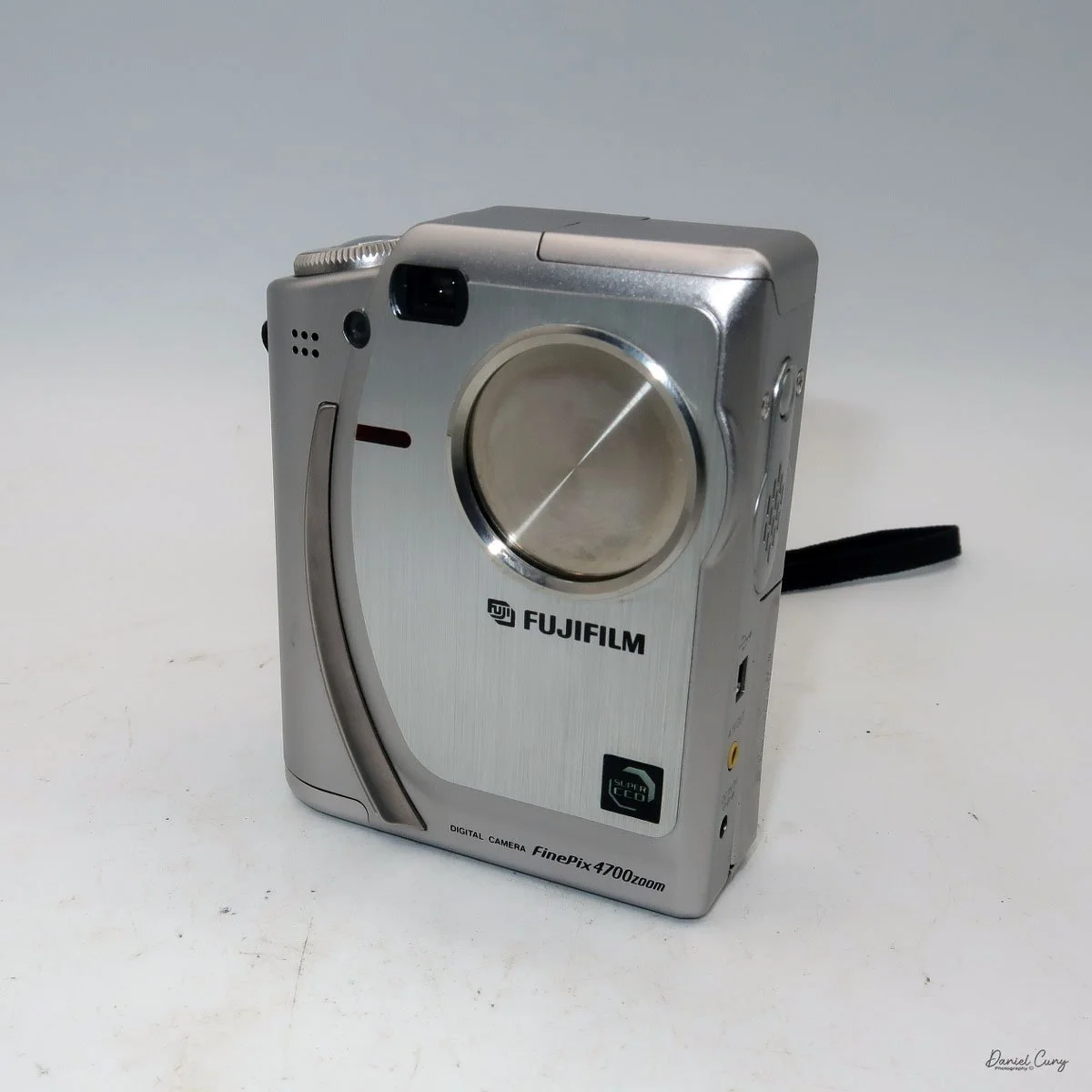
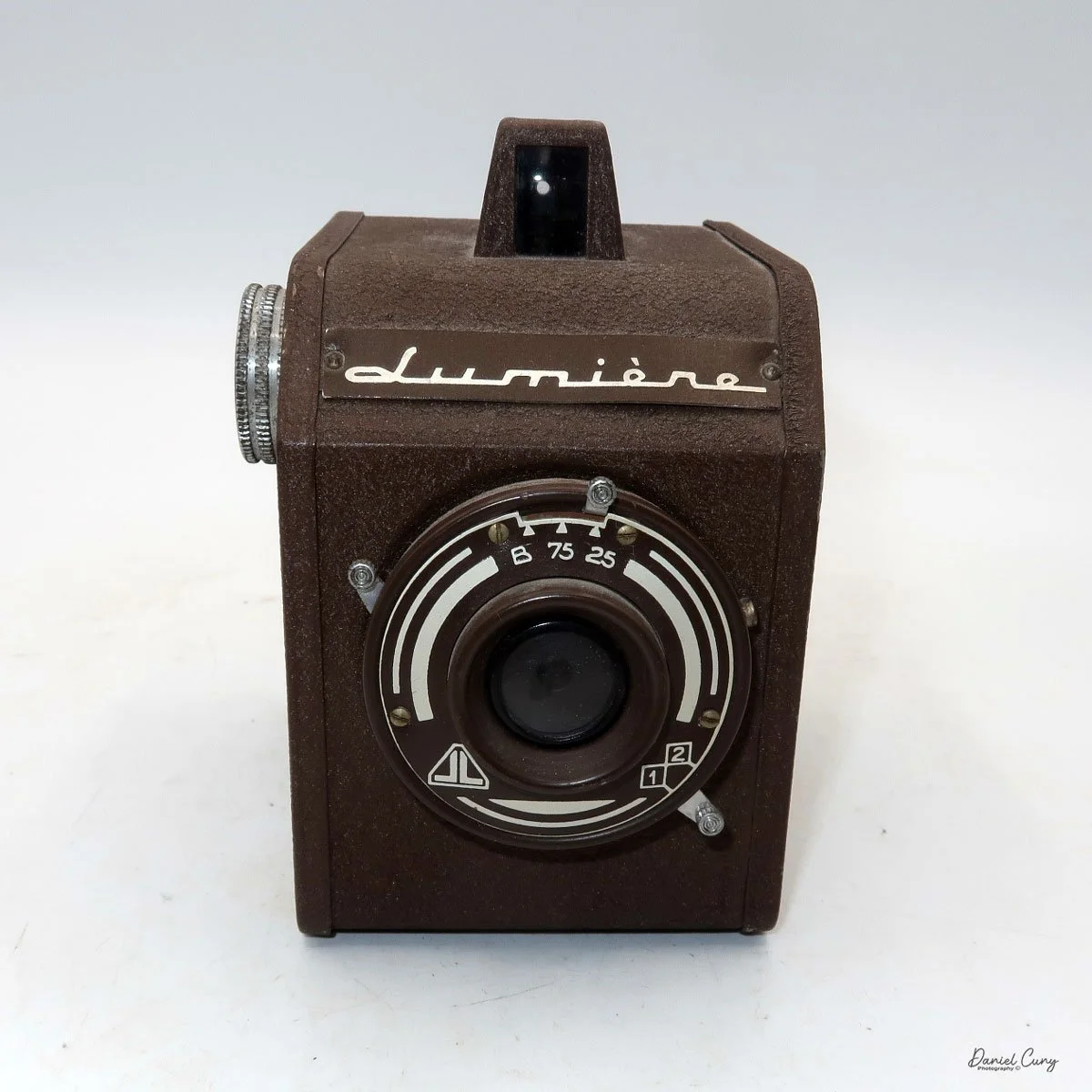
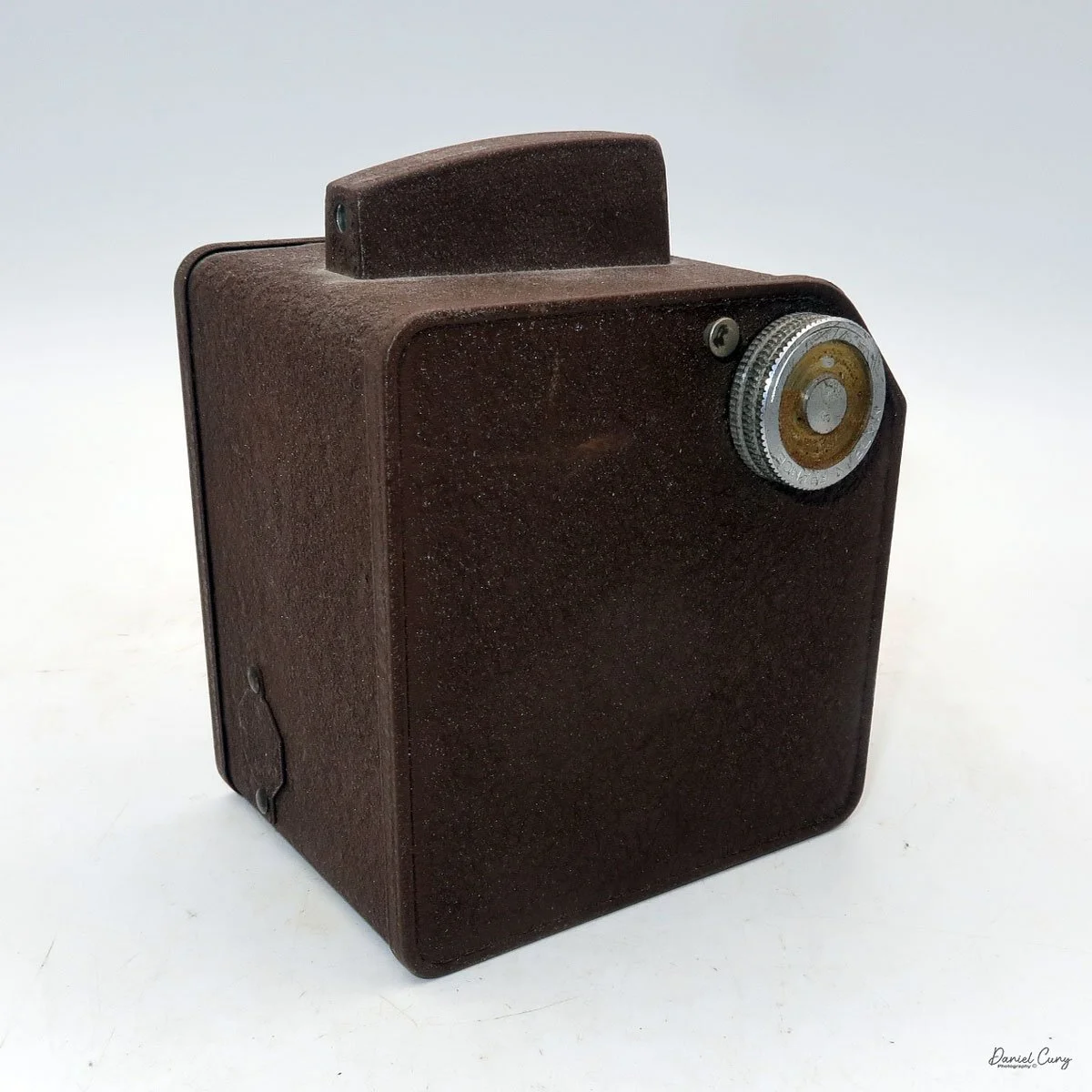
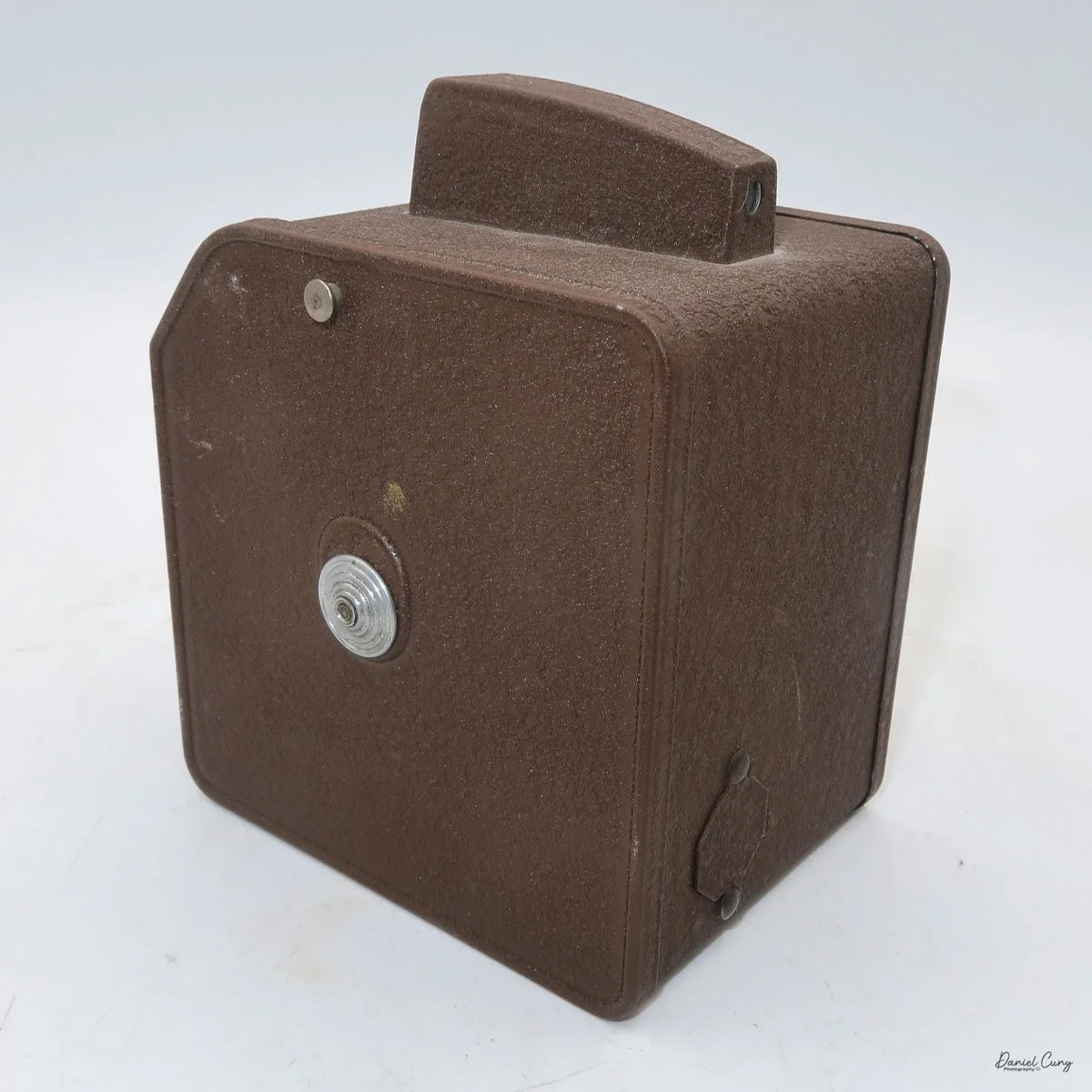
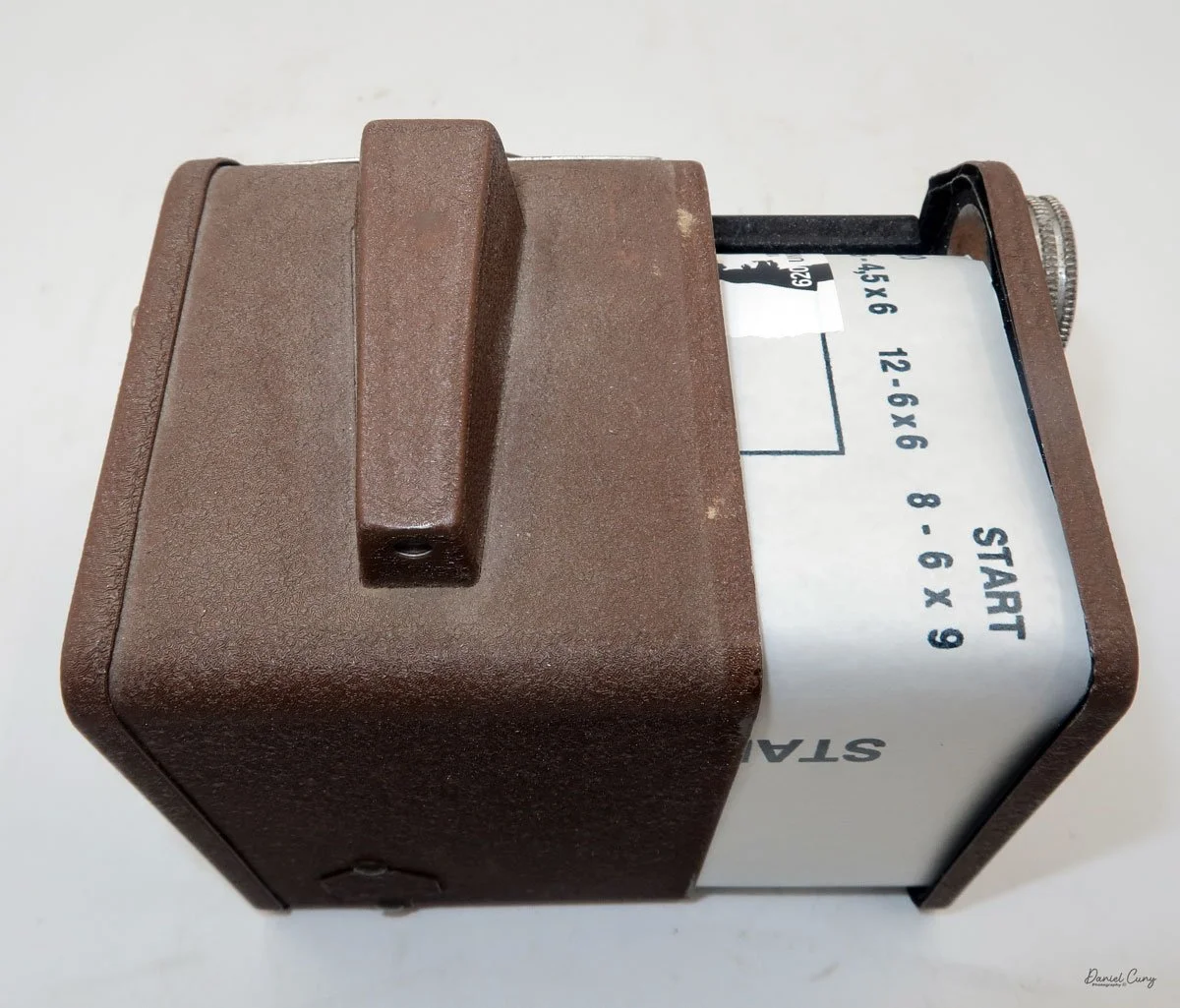
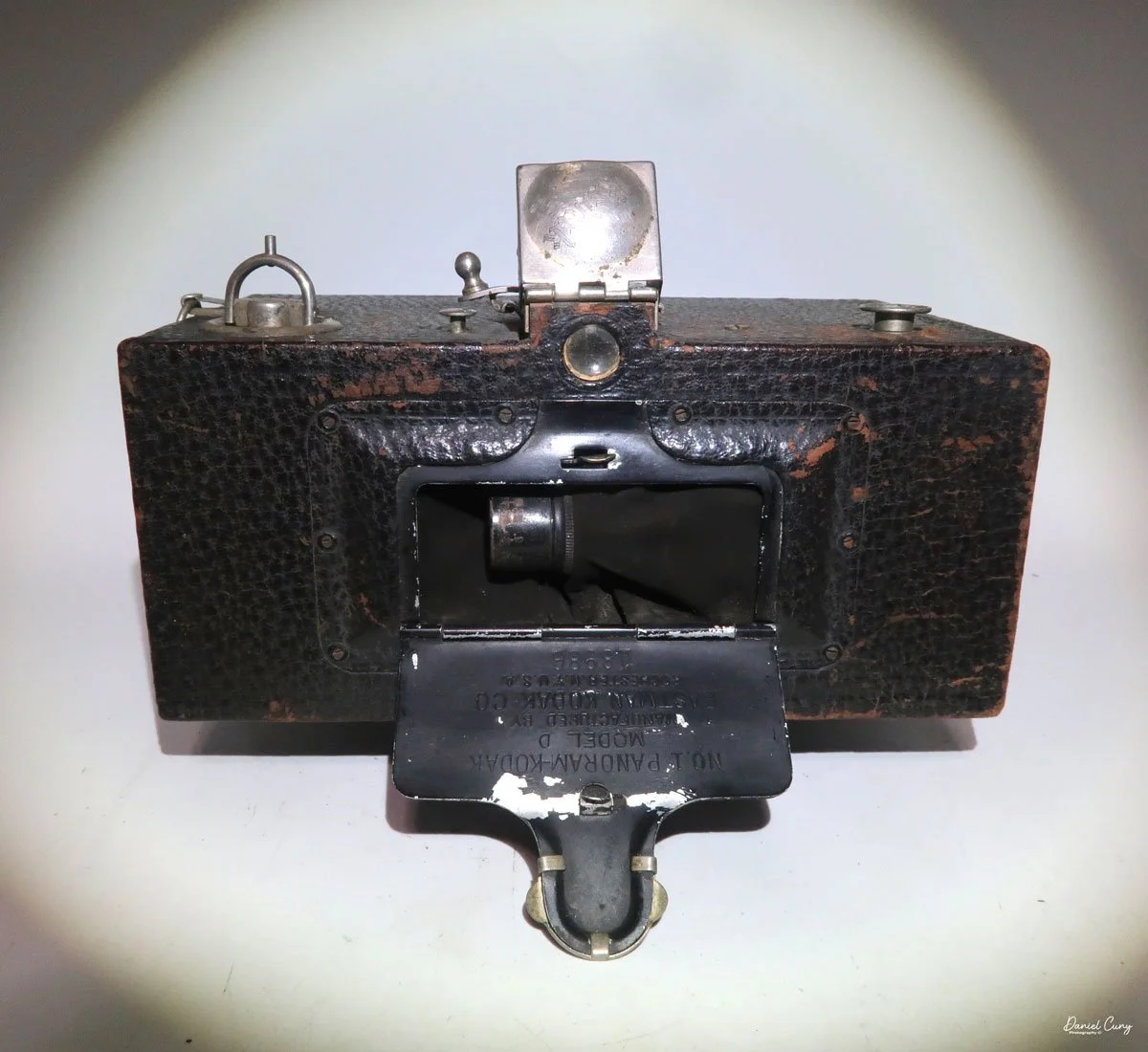
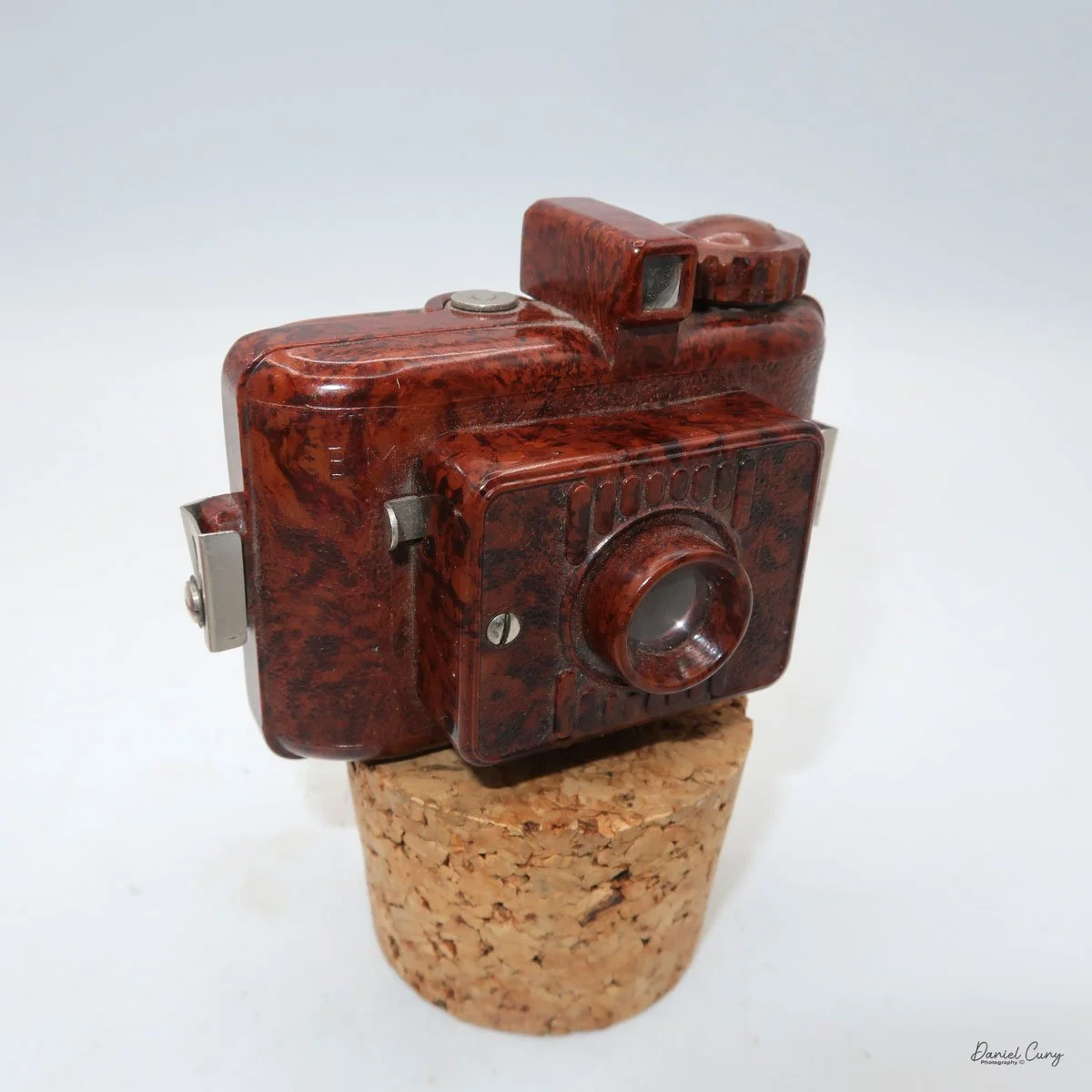
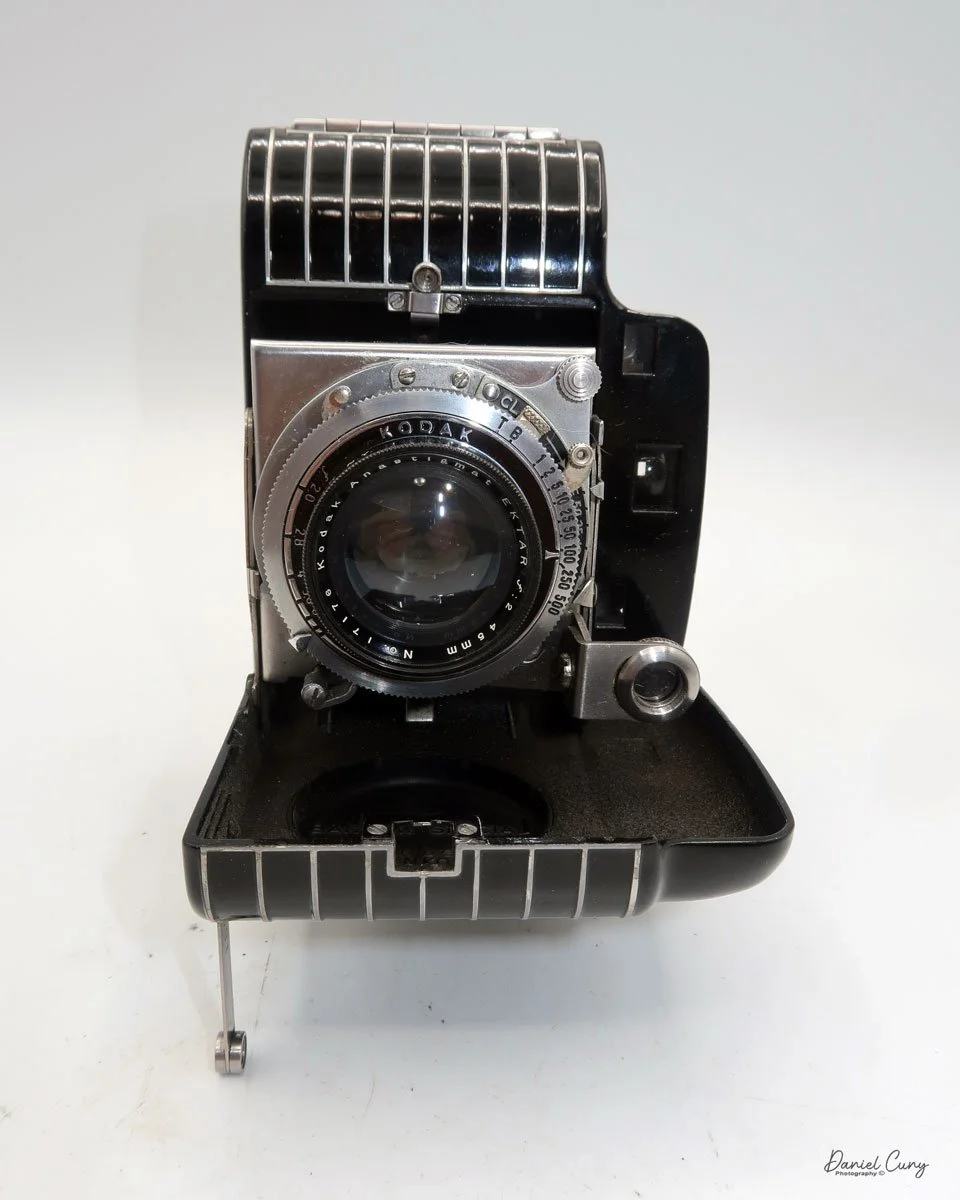
Front view of Durst Duca camera.
When the auction was about to end, I logged in about 10 minutes before the finish. The price on the Duca had jumped up a bit, and I was outbid, so I nudged my max up—still on the low side—and watched the timer count down. No one else jumped in, and I ended up winning the camera.
The auction house shipped quickly. When I opened the box, I was still surprised by how small the camera is in person. It was even smaller than I'd pictured. I started to check it over, winding the advance lever on the side and cocking the shutter. I heard a faint click, but it was so quiet I wasn't sure the shutter was actually opening and closing.
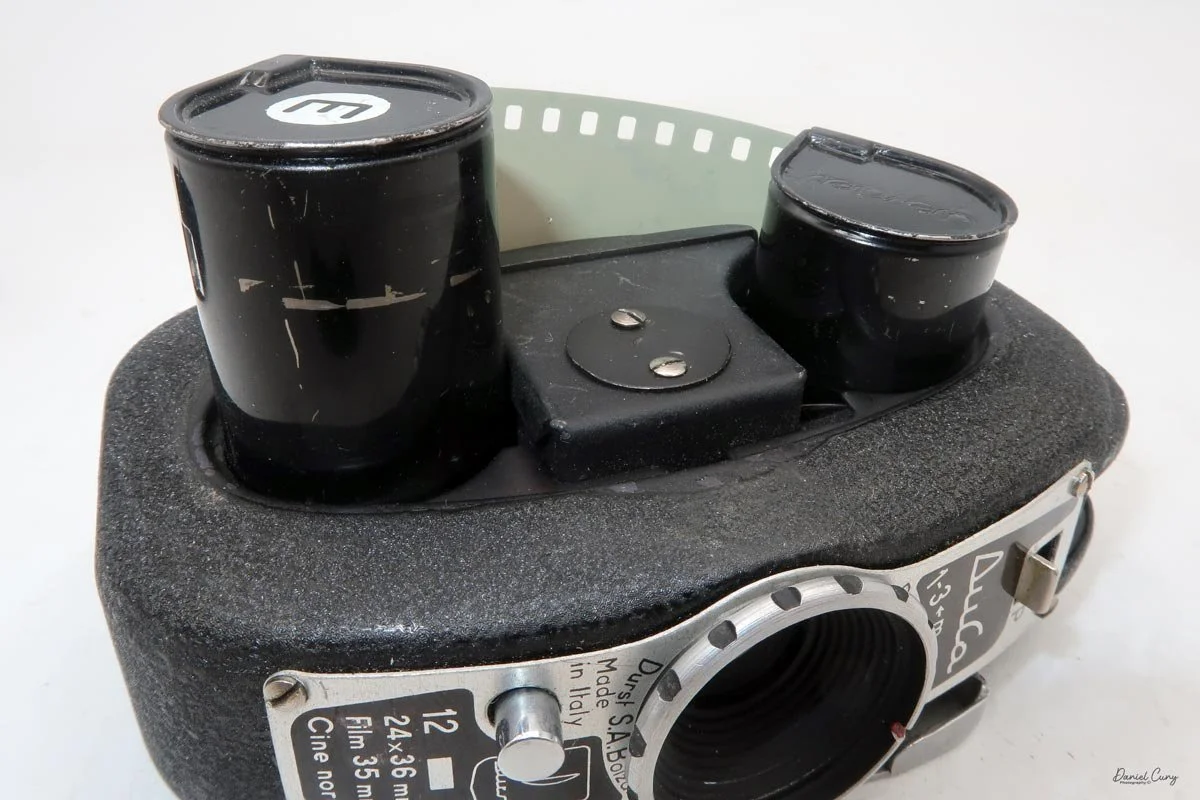
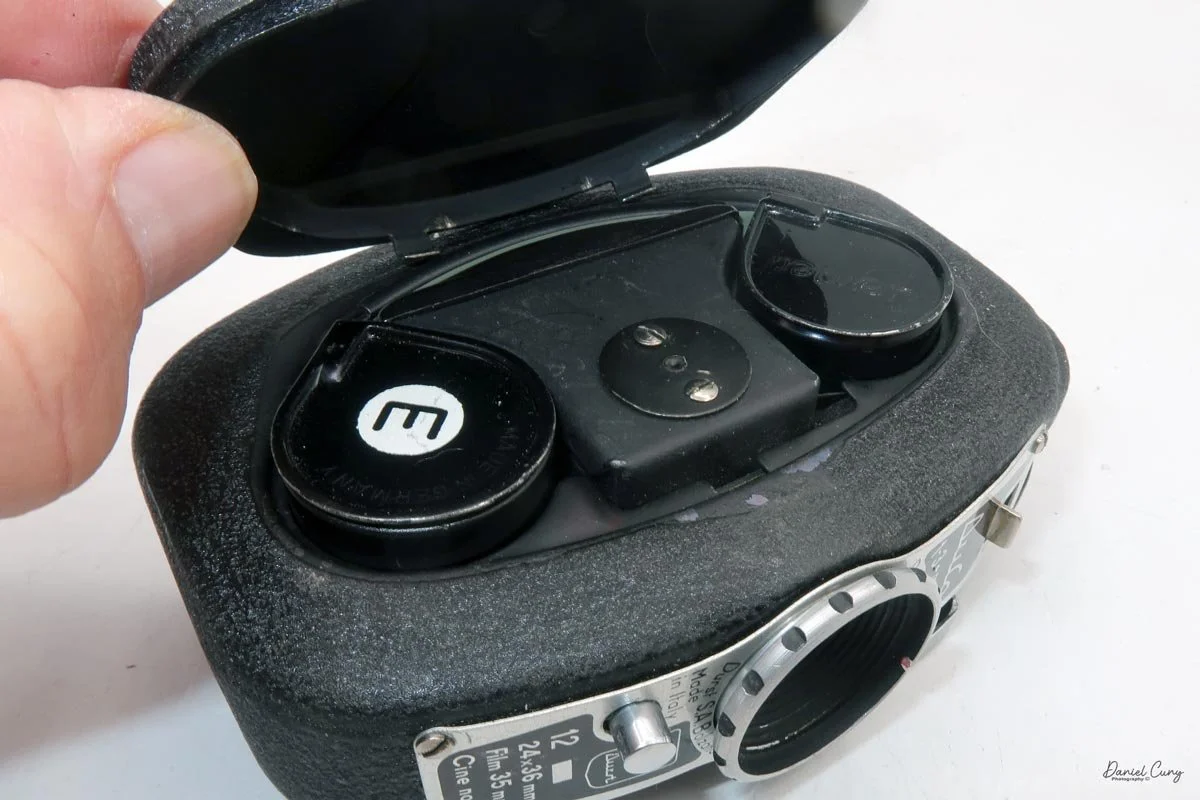
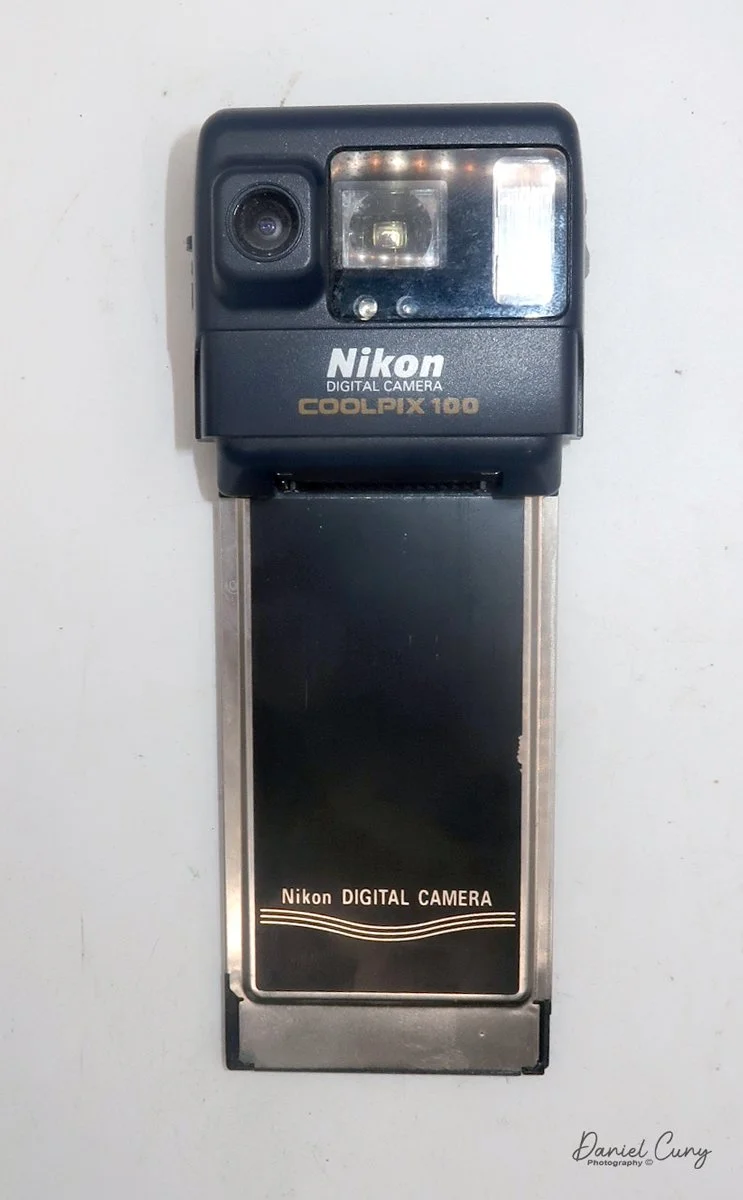
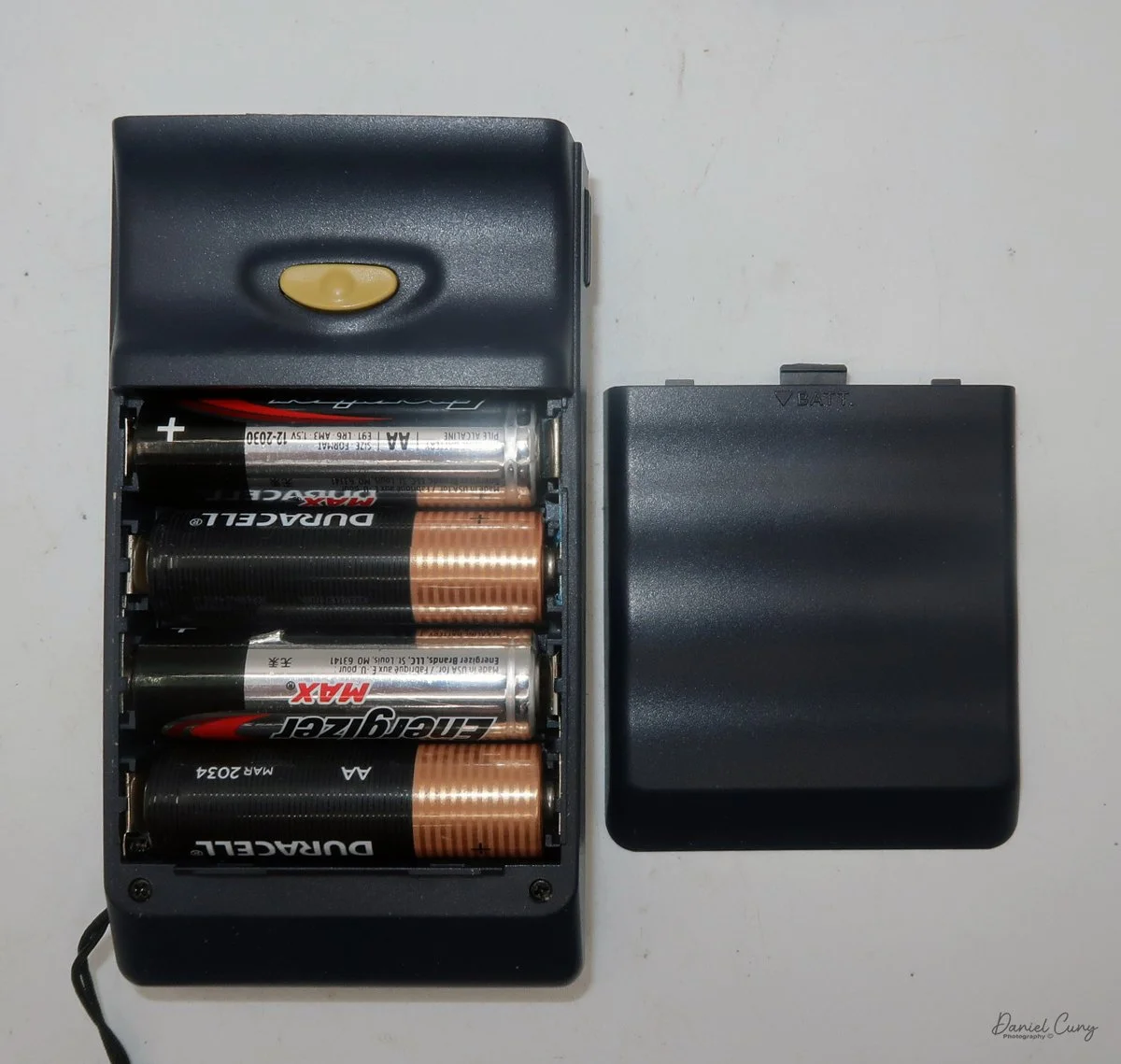
I pulled the side of the camera off to get at the film chamber and saw that one of the two film cassettes was still inside—that was a nice bonus, since it meant I only needed to scare up one more cassette. Digging around in the drawer where I keep odds and ends of camera accessories, I found another cassette that would work.
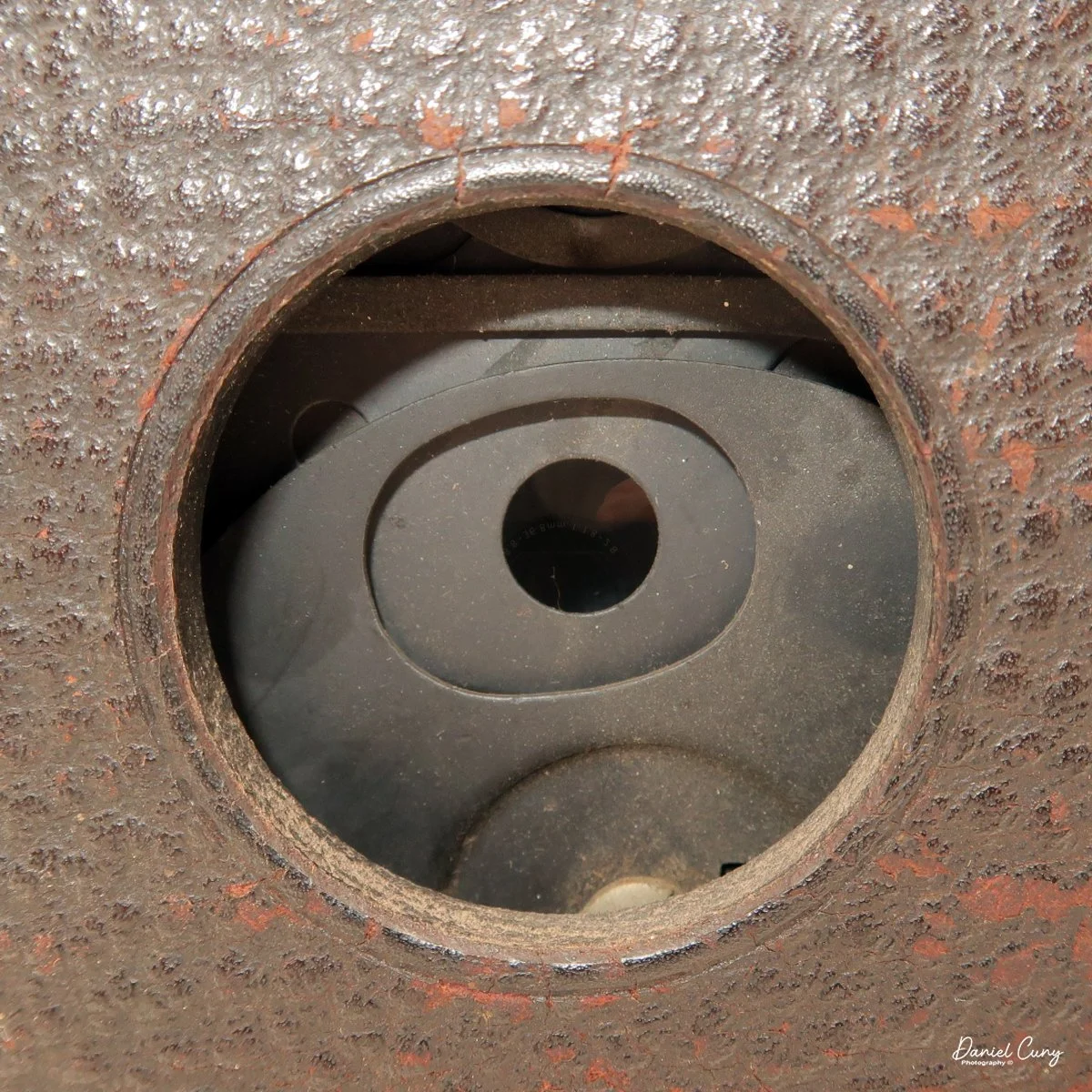
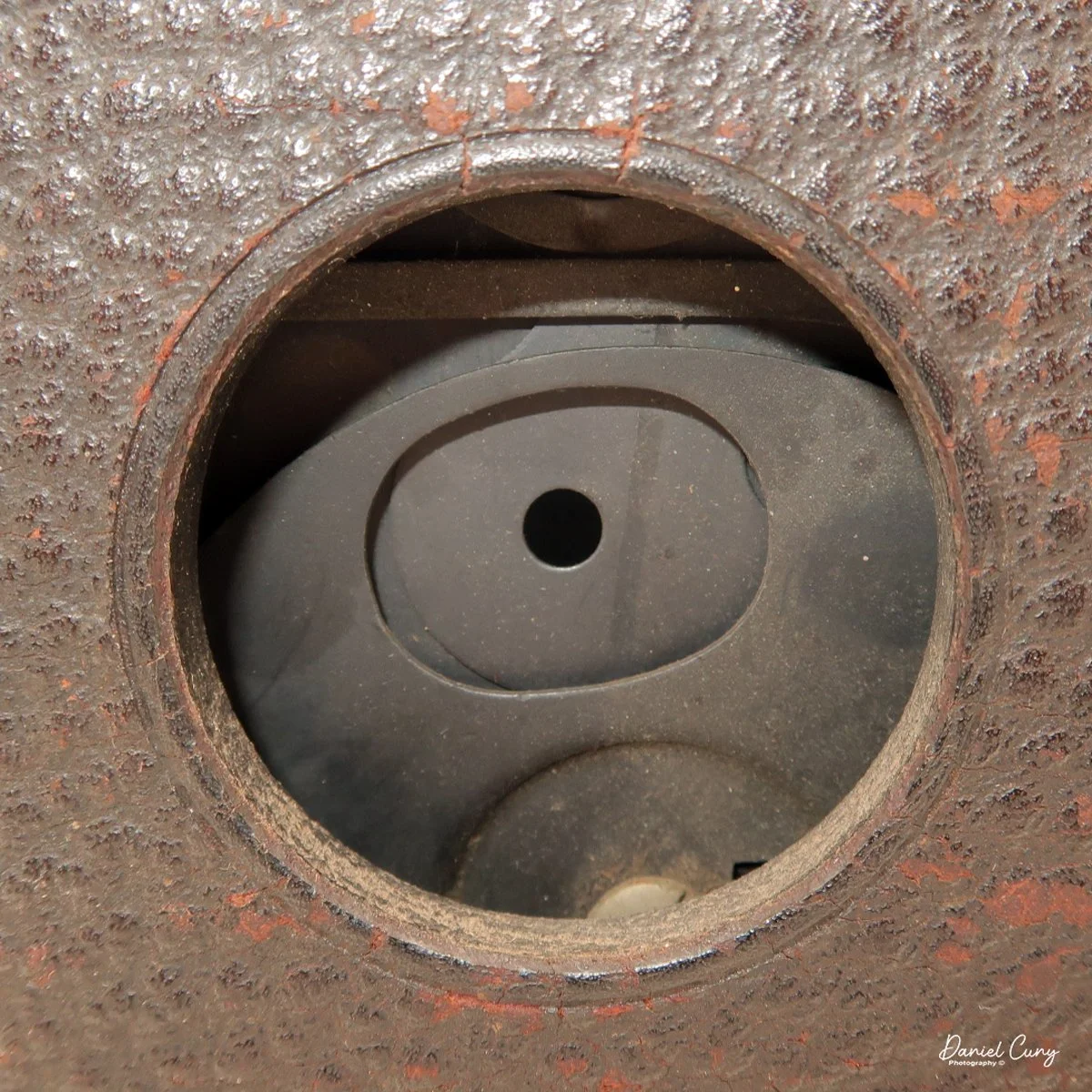
In my darkroom, I shone a flashlight through the lens and fired the shutter. At first, I saw no light at all, and my heart sank; I figured the camera might be dead. Then I noticed the pressure plate that holds the film flat against the rails. I pulled the pressure plate out, pointed the flashlight into the front of the lens again, and tripped the shutter. This time, I saw a brief flash of light through the gate—success. The shutter was working. That was the moment I decided the Durst Duca would be the camera I'd write about for this week's blog.
A Little Durst History
Durst is best known today for its darkroom enlargers. Still, for about 25 years, the company also made a small, innovative line of cameras that reflected the same experimental mindset they brought to the darkroom. Founded in 1936 in northern Italy by brothers Julius and Gilbert Durst, the firm quickly gravitated toward photographic equipment, especially enlargers, which eventually became its main business.
Durst's camera story starts with the Gil, a simple 120 roll‑film box camera introduced in 1938 for the growing amateur market. After World War II, Durst resumed production of the Gil and then shifted toward more compact designs, setting the stage for its 35mm experiments.
Australian Ad for Durst Duca camera
The Duca followed as a tiny 35mm still camera that used Agfa Karat cassettes instead of standard 35mm cartridges. That choice let Durst play with miniaturized body shapes: an oval, cine‑style form in a pocketable size, offered in several colors. This focus on unusual styling and packaging mirrored their enlargers, which often looked different from competitors but emphasized precision and usability.
Next came the Durst 66, a modestly specified camera with an unconventional shutter and a quirky way of measuring exposure. You can already see Durst thinking outside the box, trying to rethink mechanisms rather than just copying others' work.
All of that leads to the Durst Automatica, made from 1956 to 1963 and often regarded as the first 35mm camera with aperture‑priority automatic exposure. It used a pneumatic shutter derived from the Durst 66 and wrapped it in a very elegant body. For such a small camera line, it was an ambitious finale and shows how far Durst was willing to push design and automation.
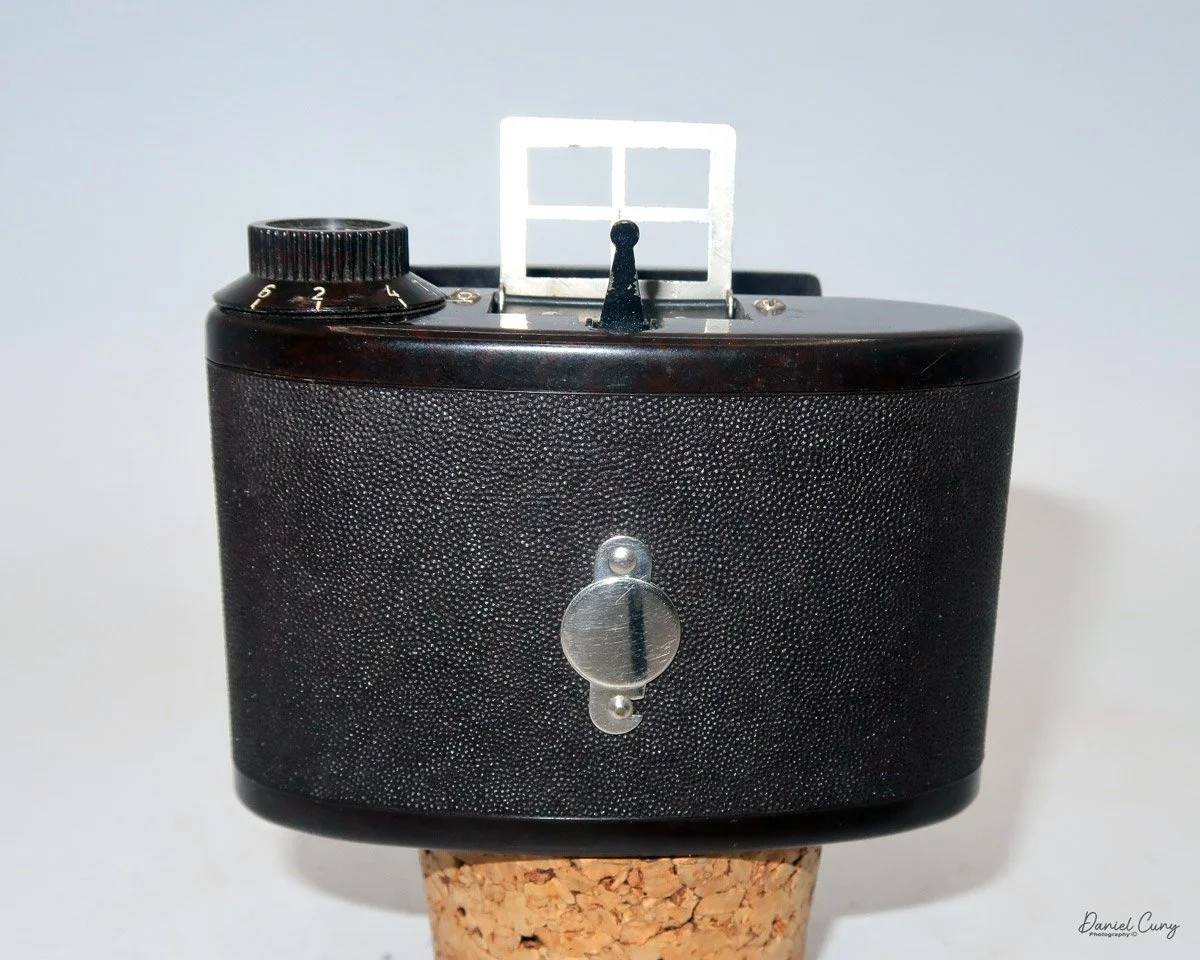
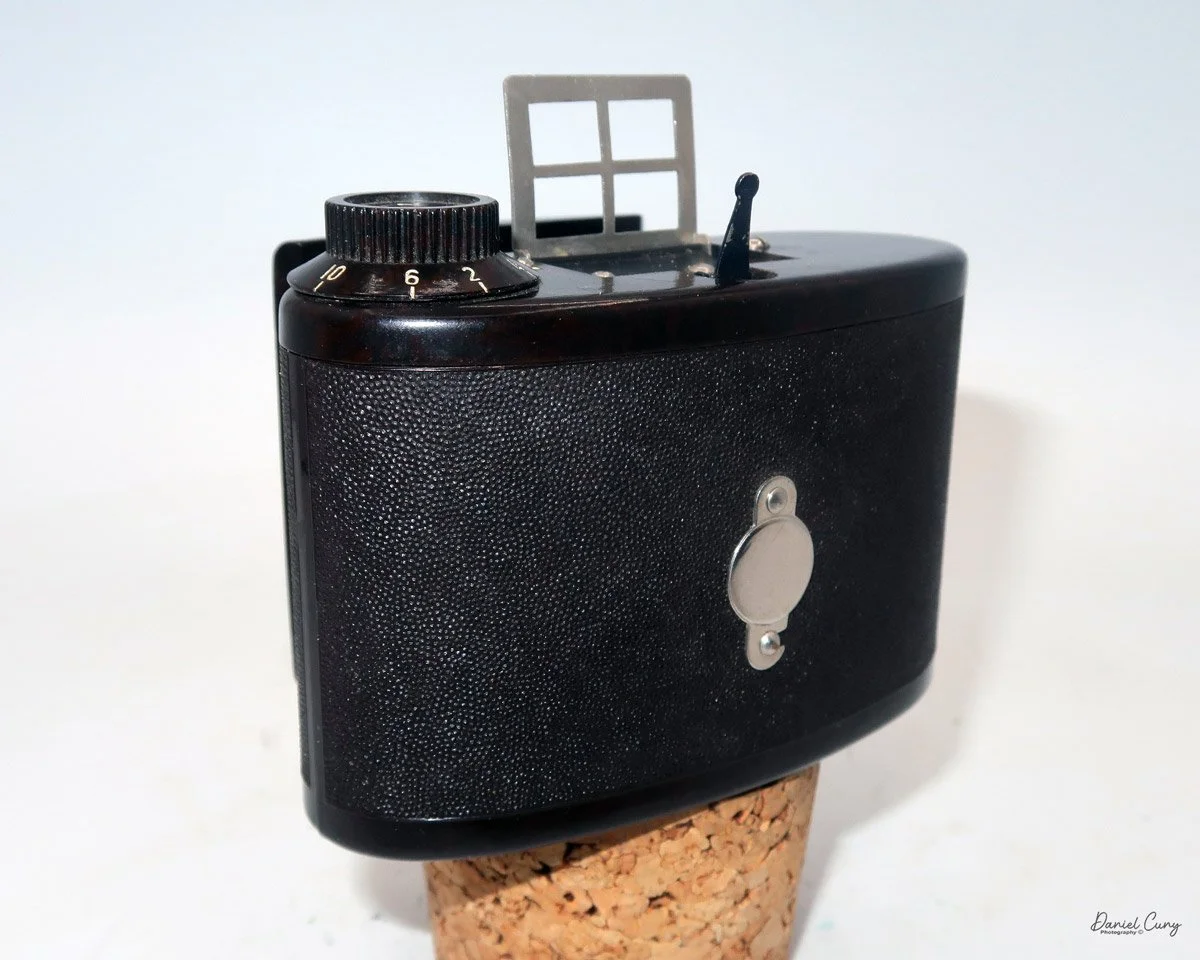
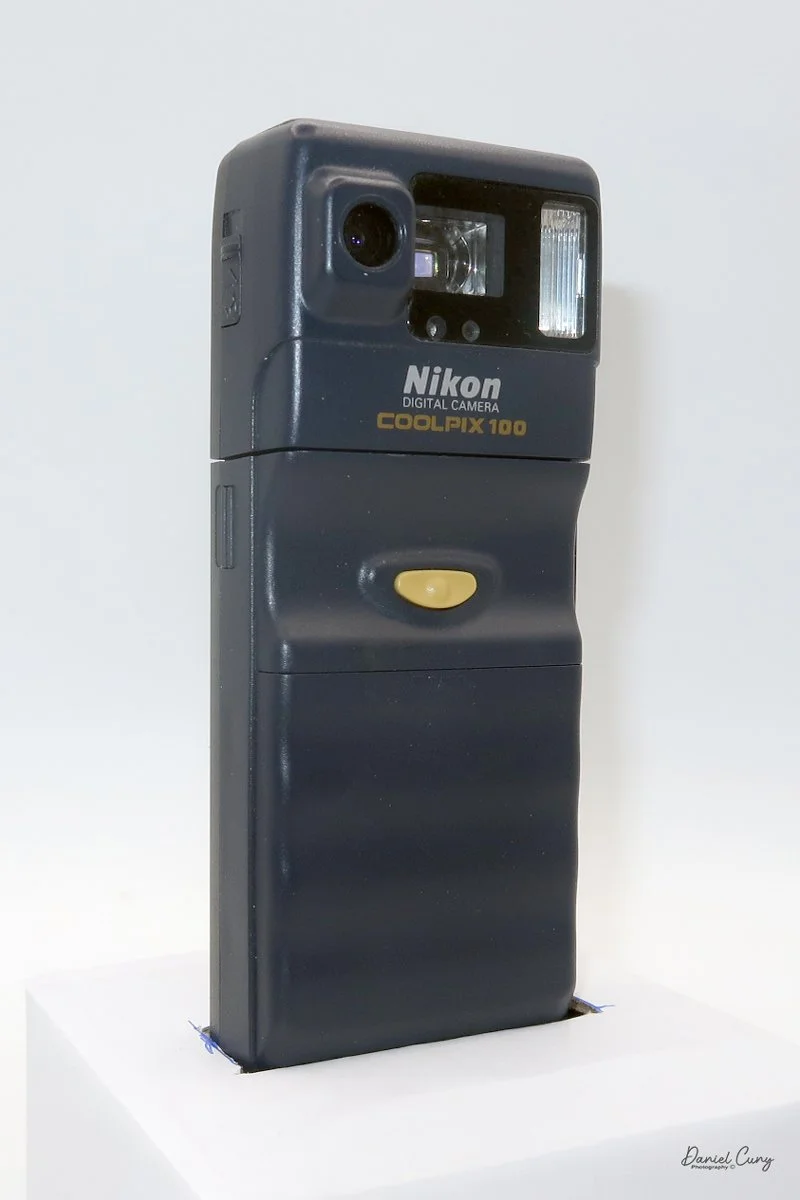
My Durst Duca
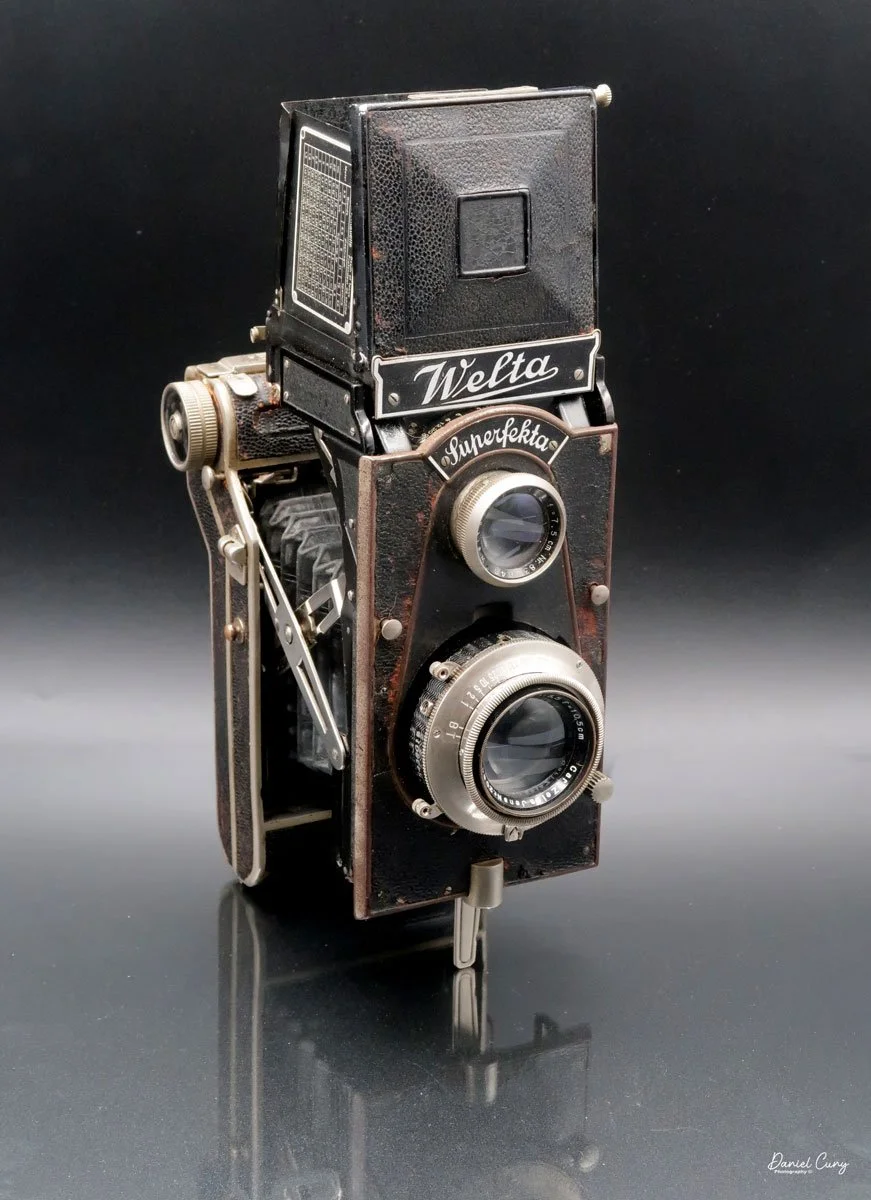
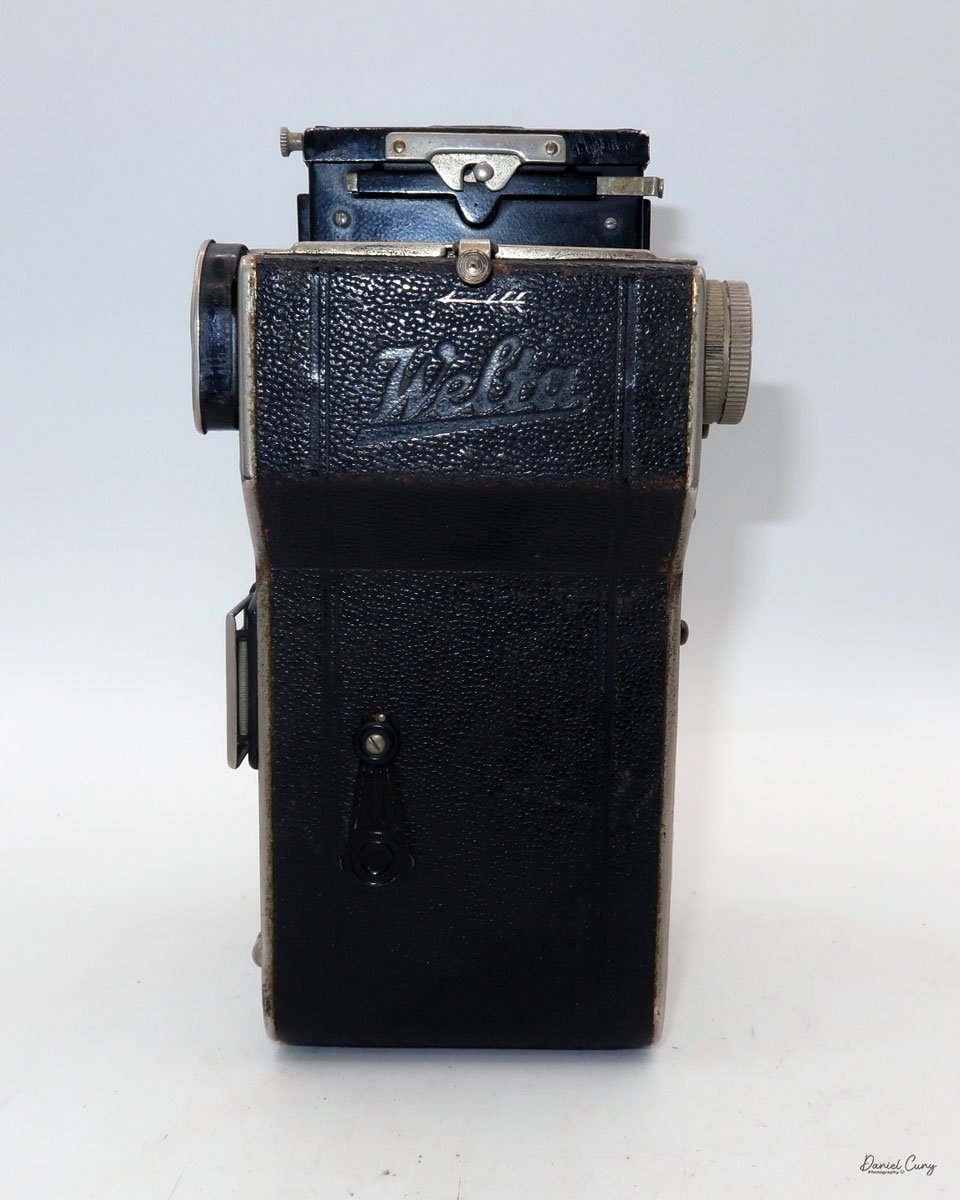
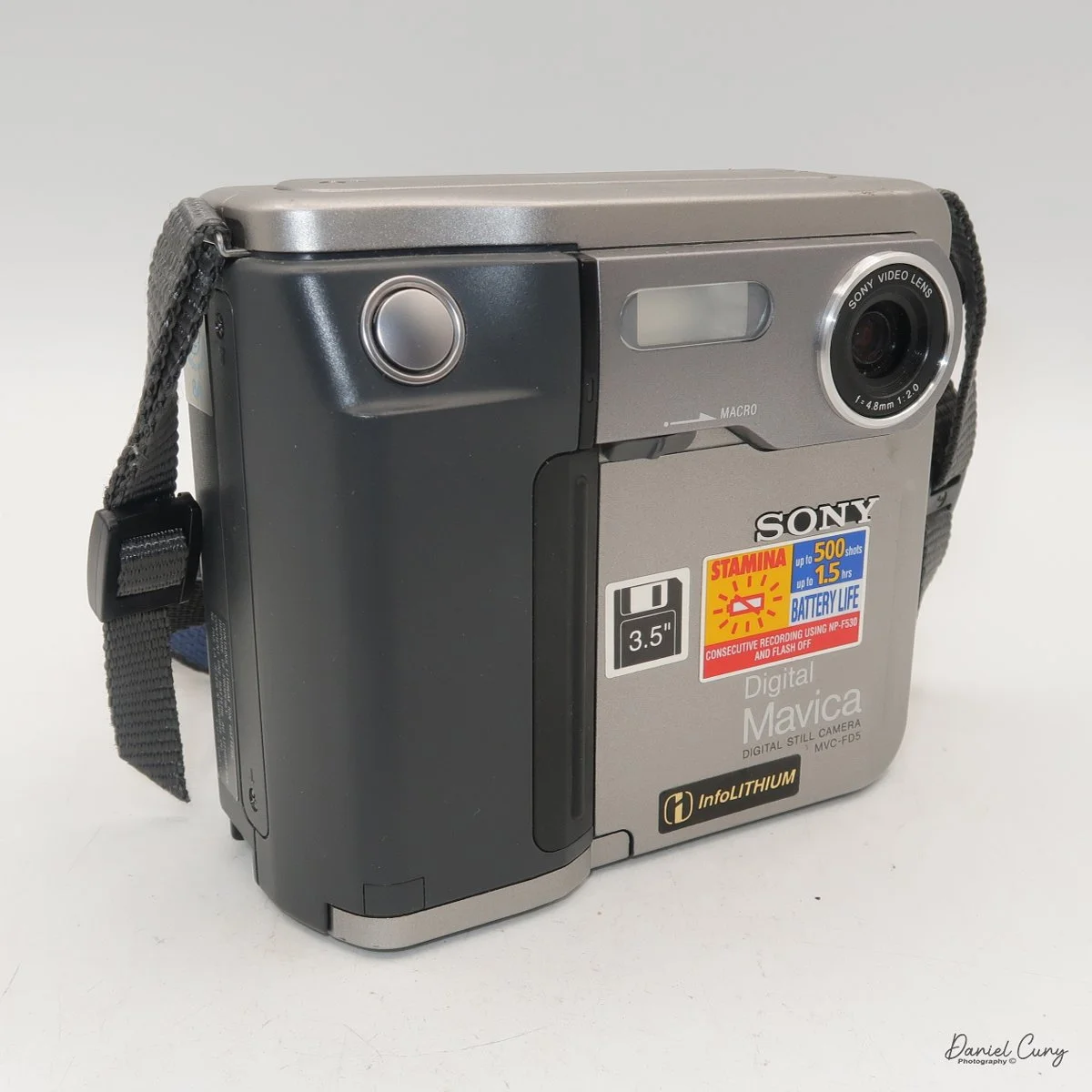
The Durst Duca was introduced at the Milan Trade Fair in September 1946 and stayed in production until around 1952. It's a vertical‑format, full‑frame 35mm camera that uses Agfa Karat cassettes, and it was available in five colors: black, blue, red, white, and brown. I've only ever seen the black, blue, and red versions in photos. Still, now that I know more are out there, I'll keep an eye out—even if I suspect the more unusual colors will be priced higher than I'm willing to pay.
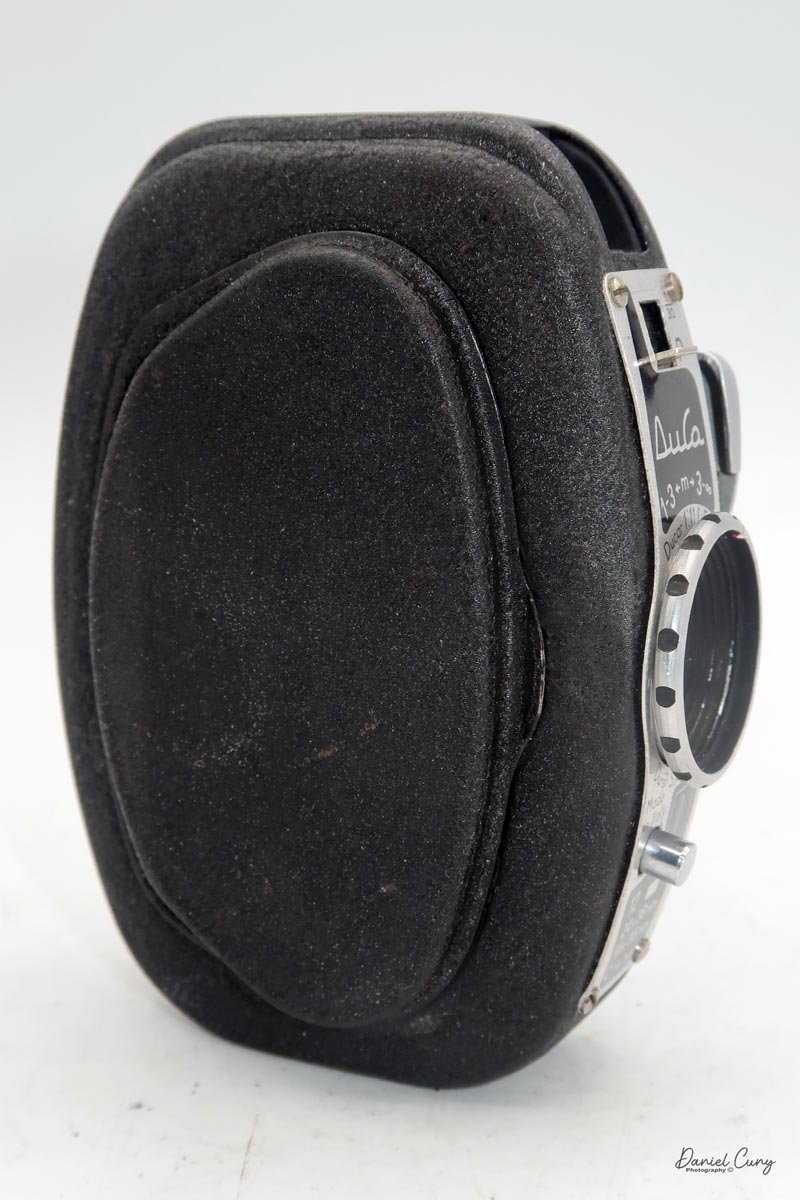
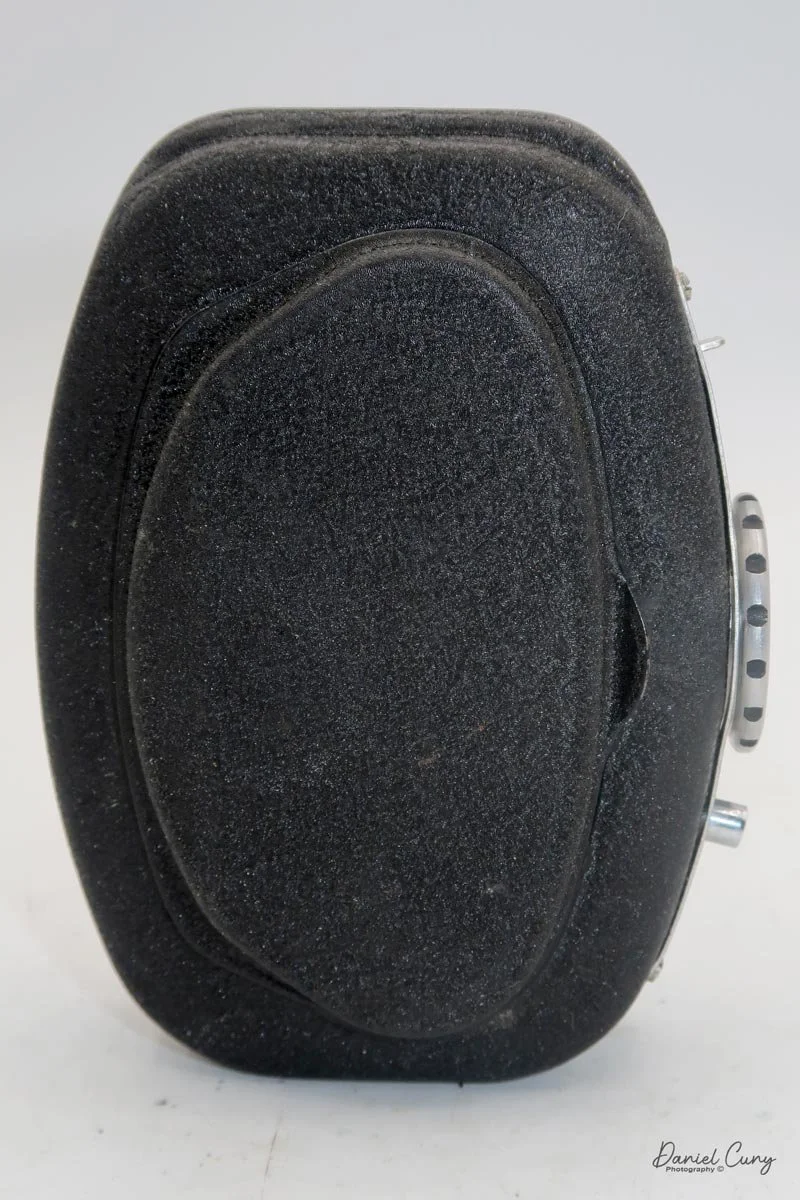
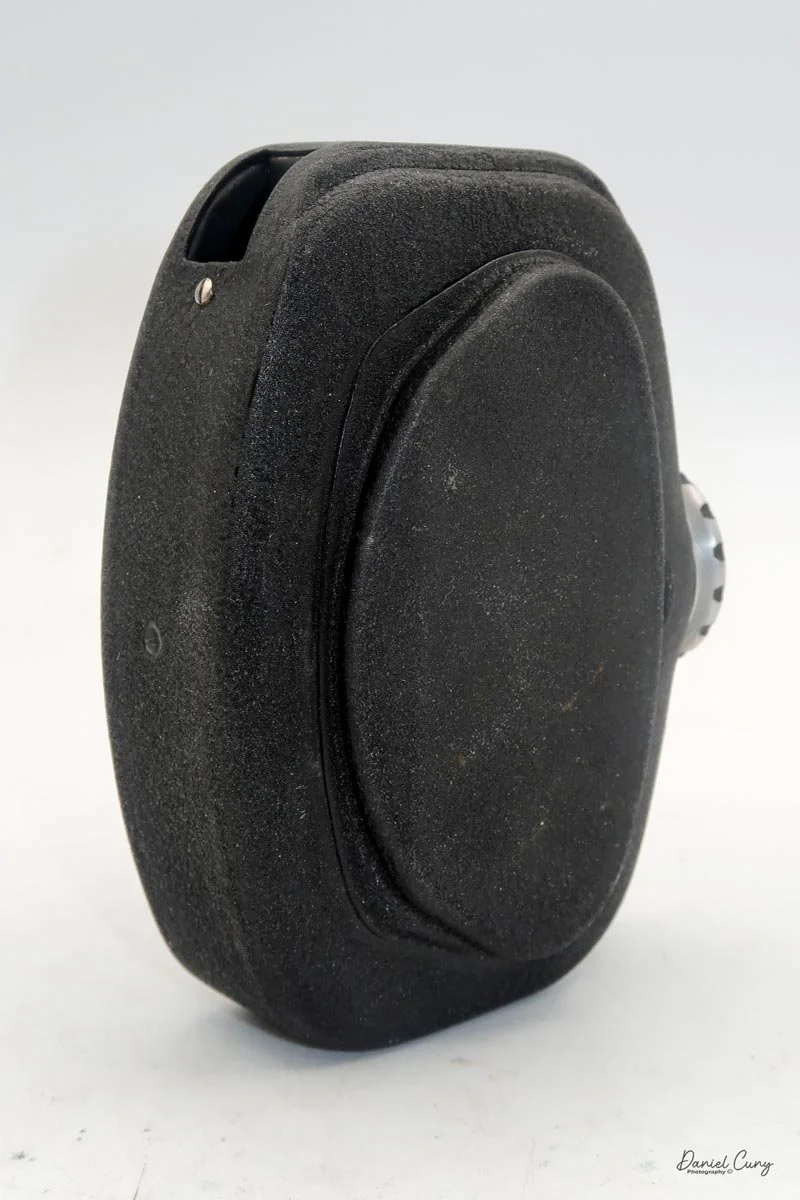
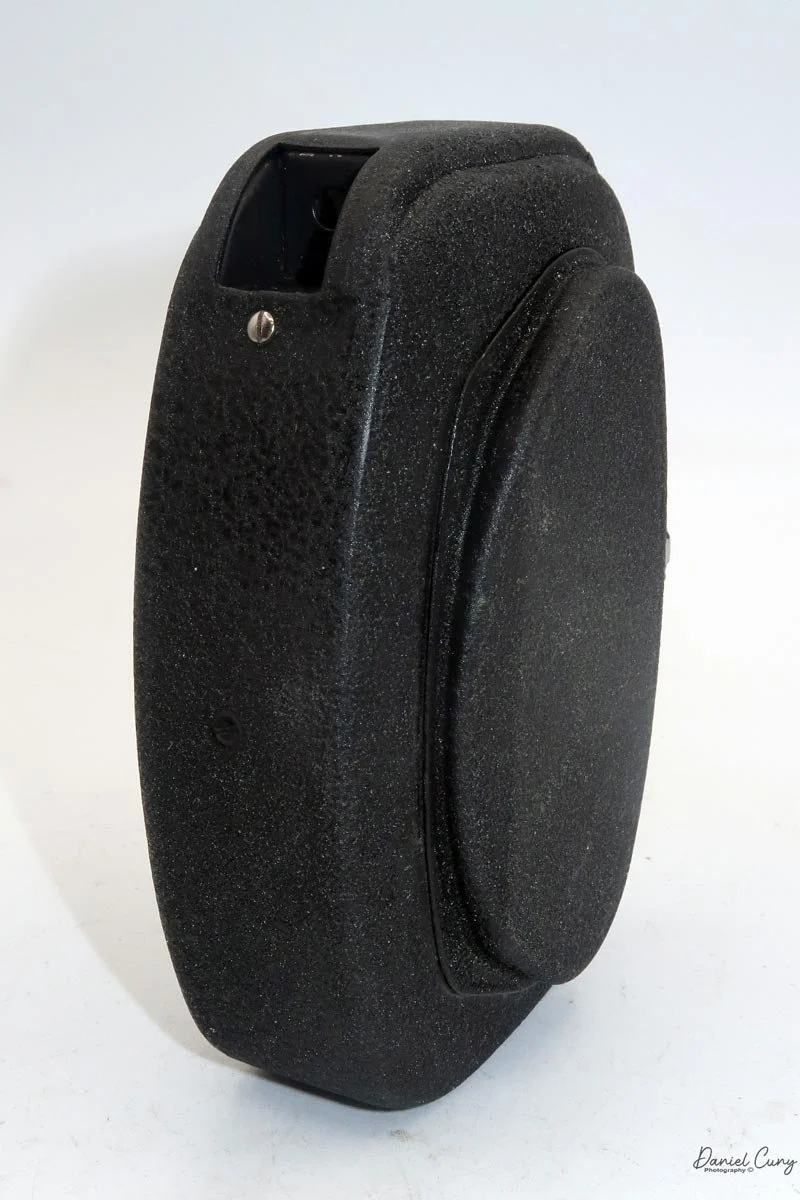
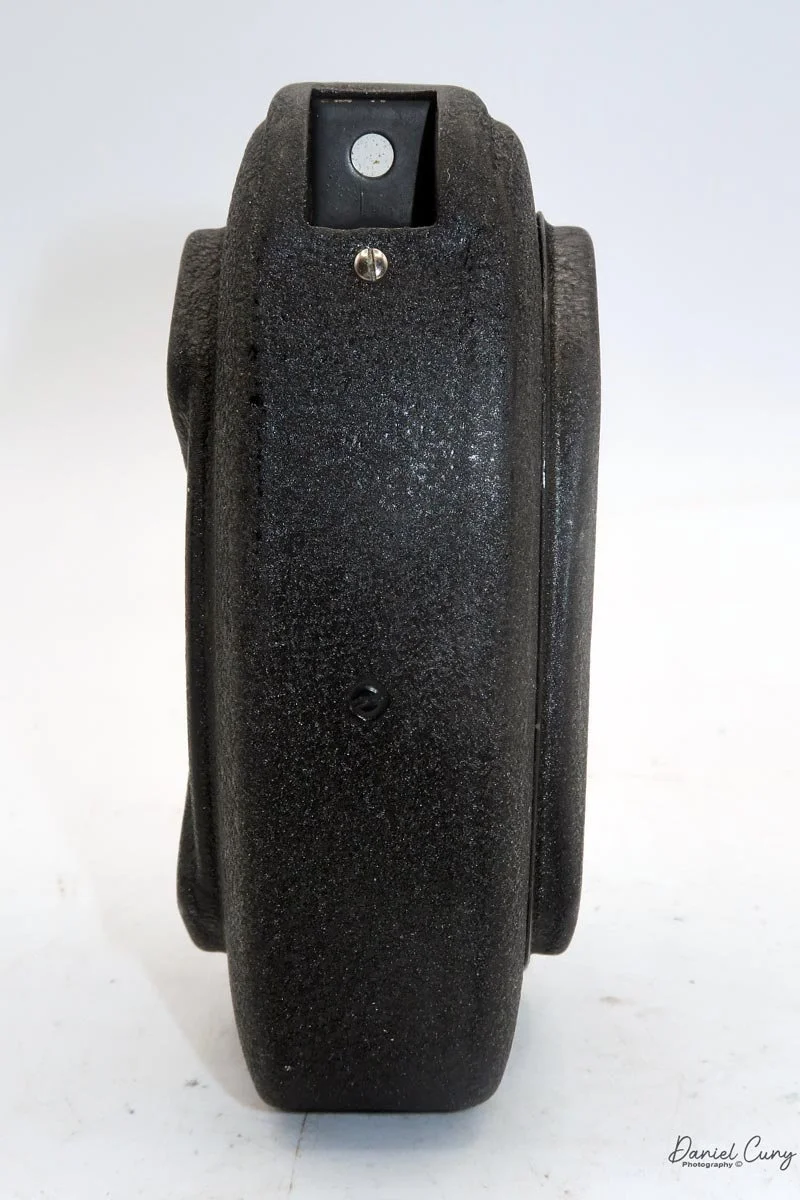
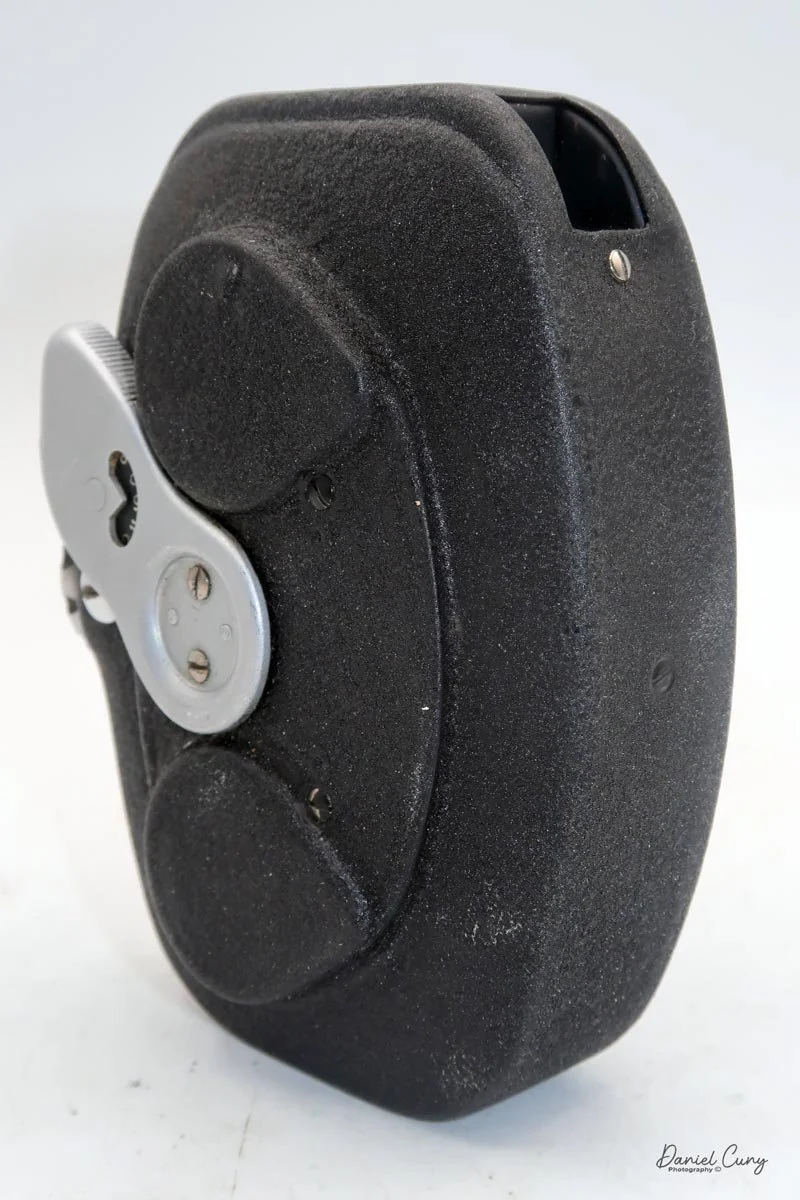
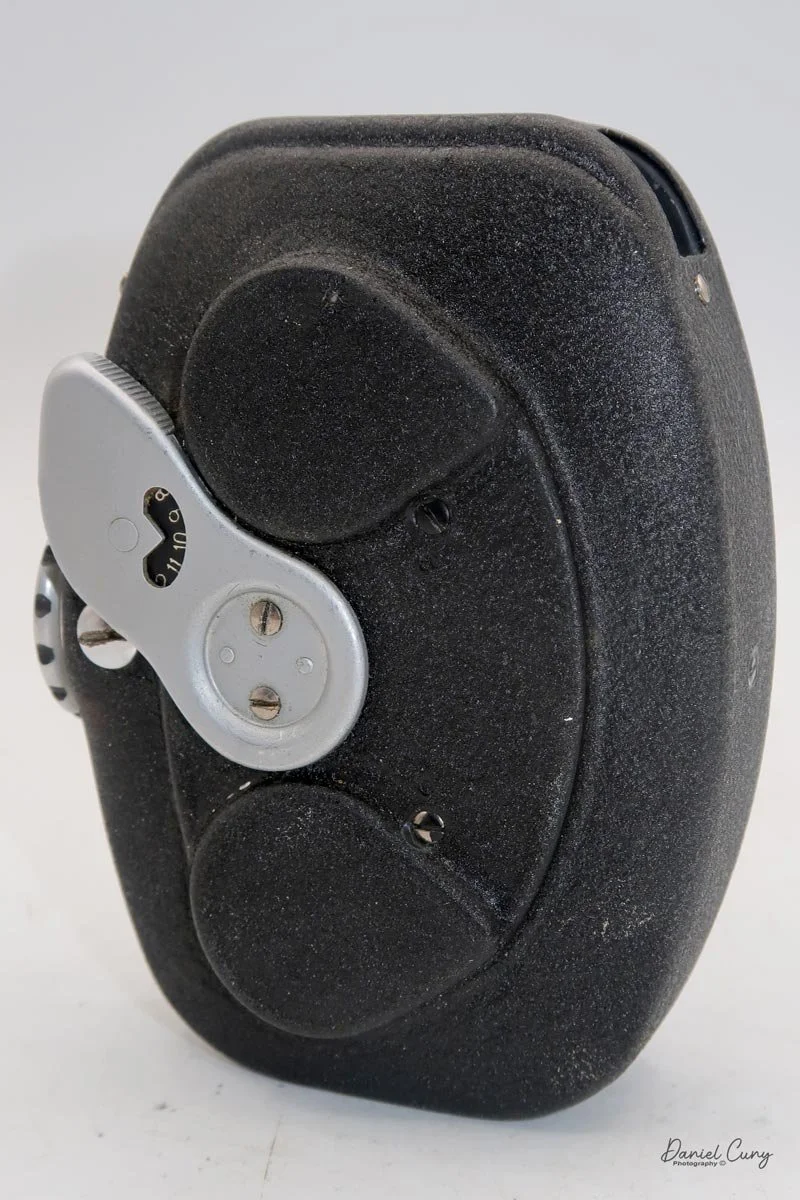
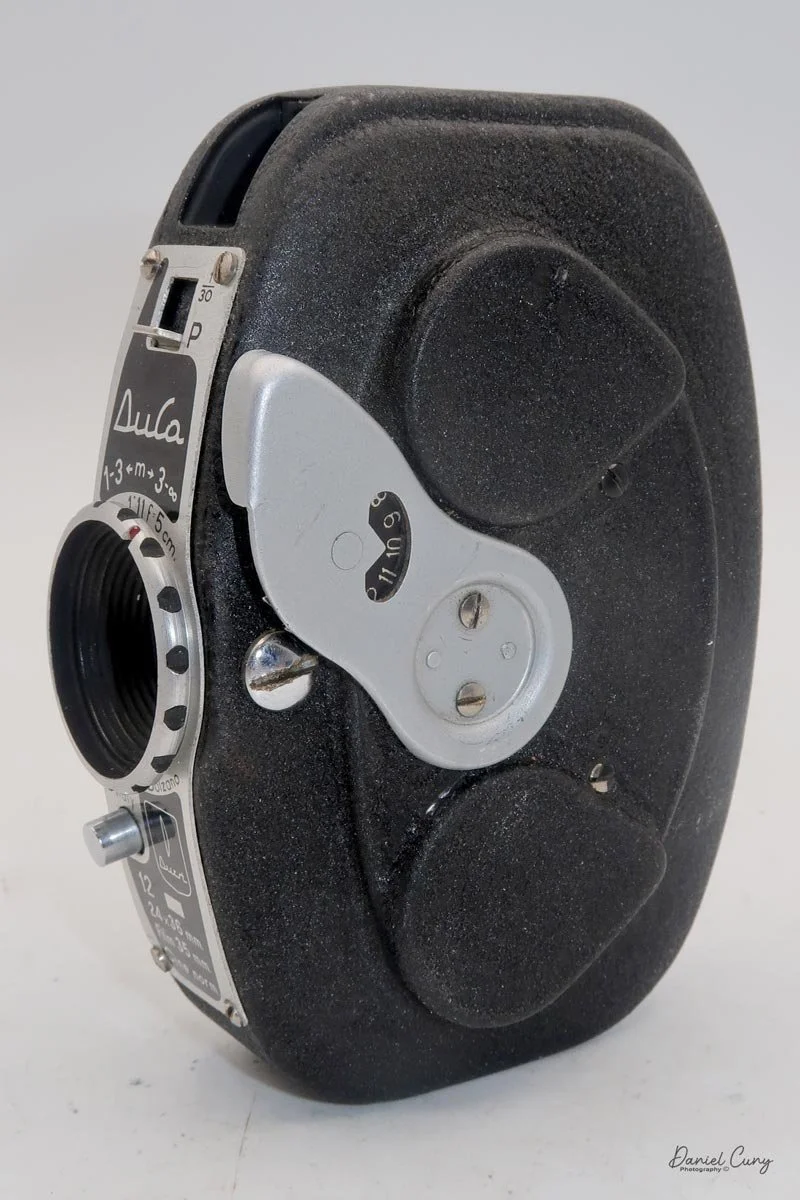












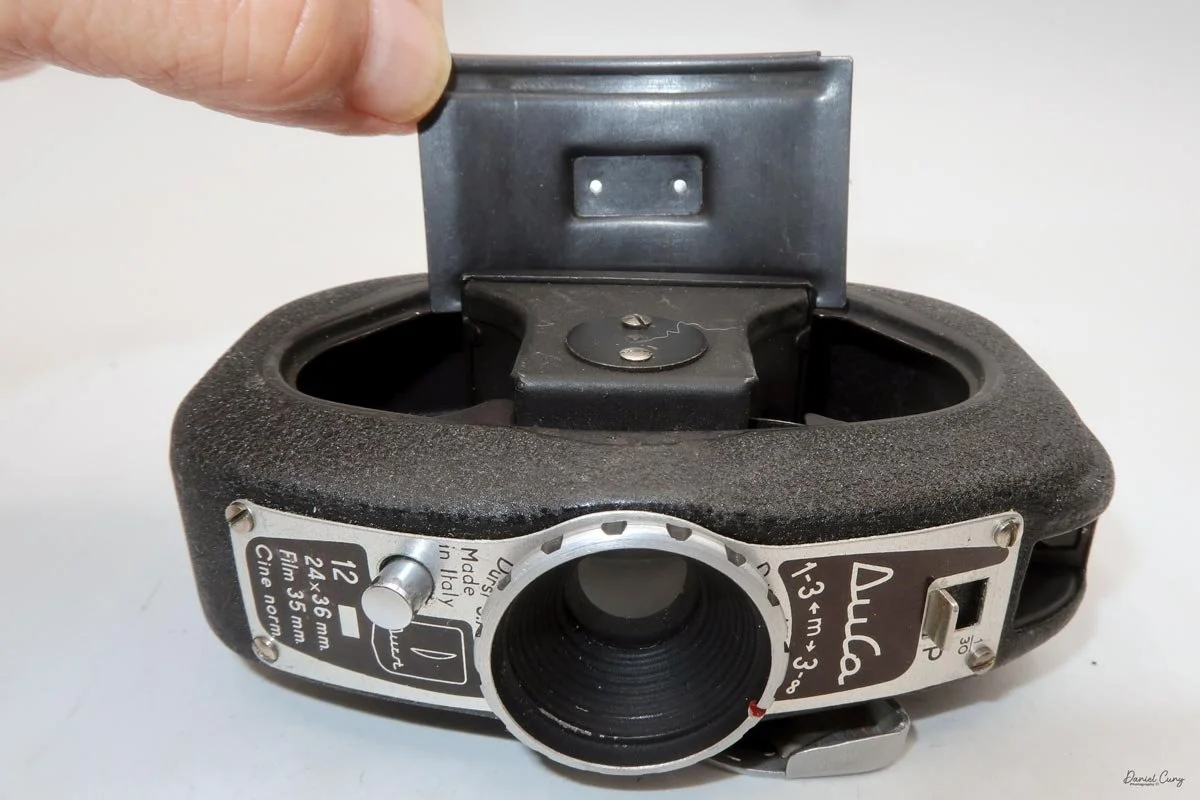
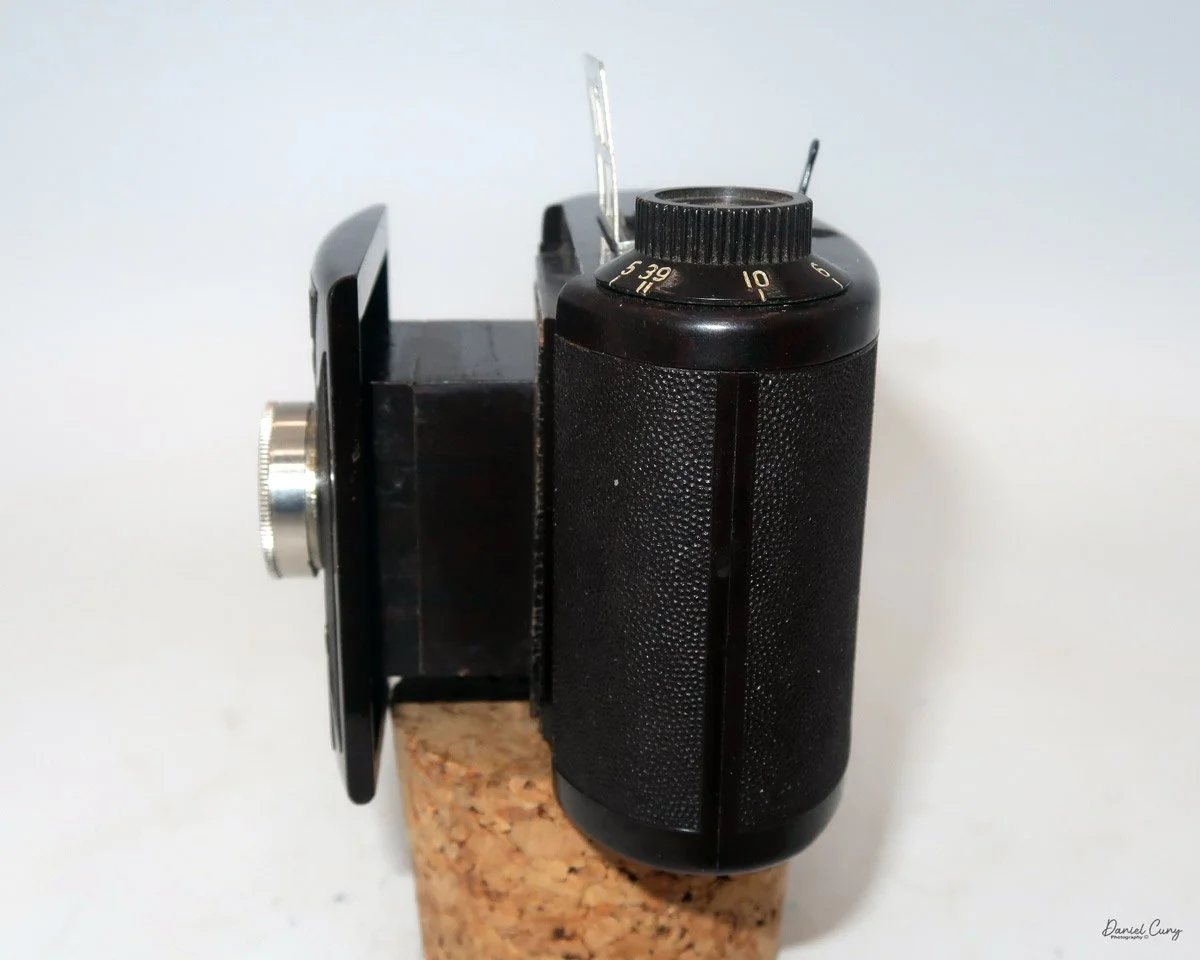
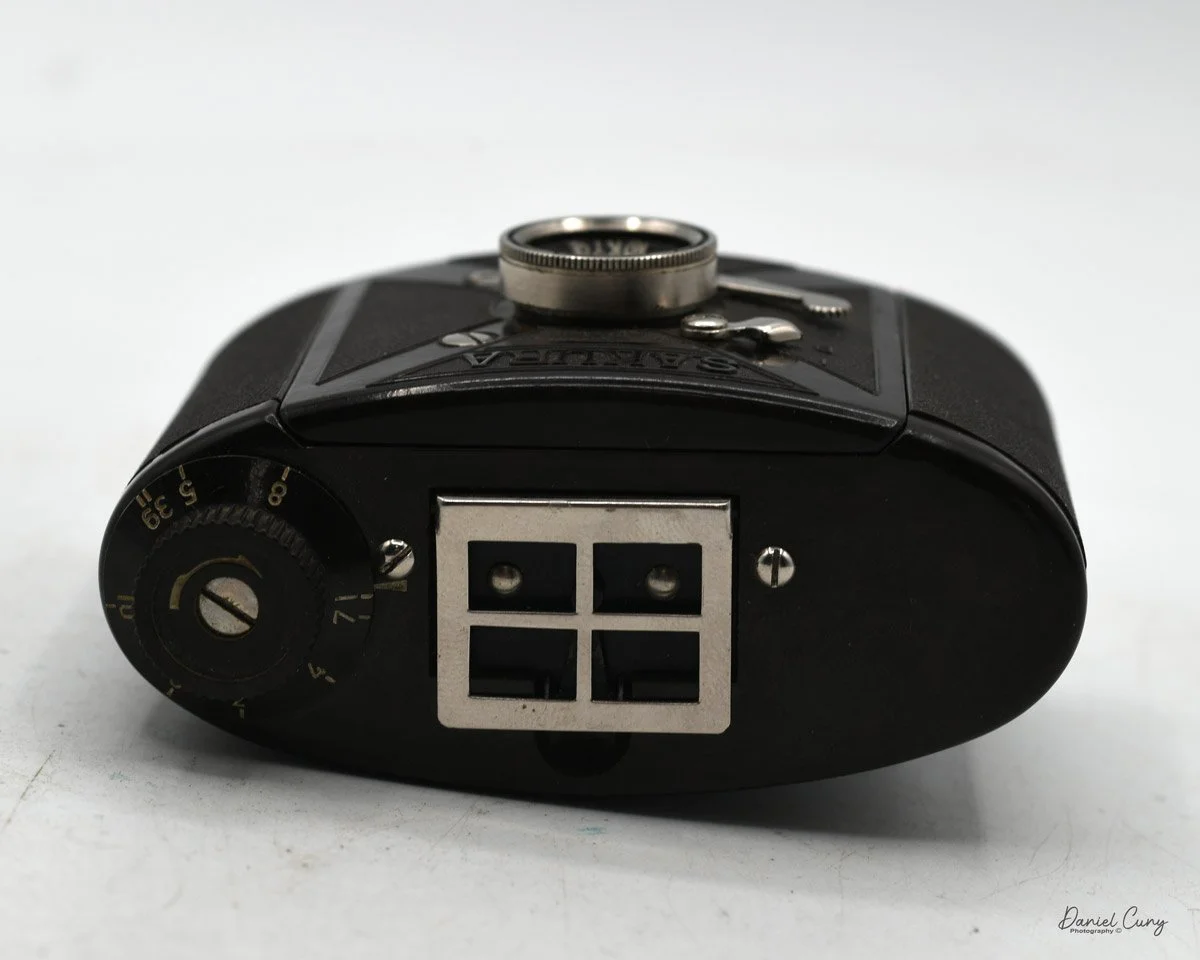
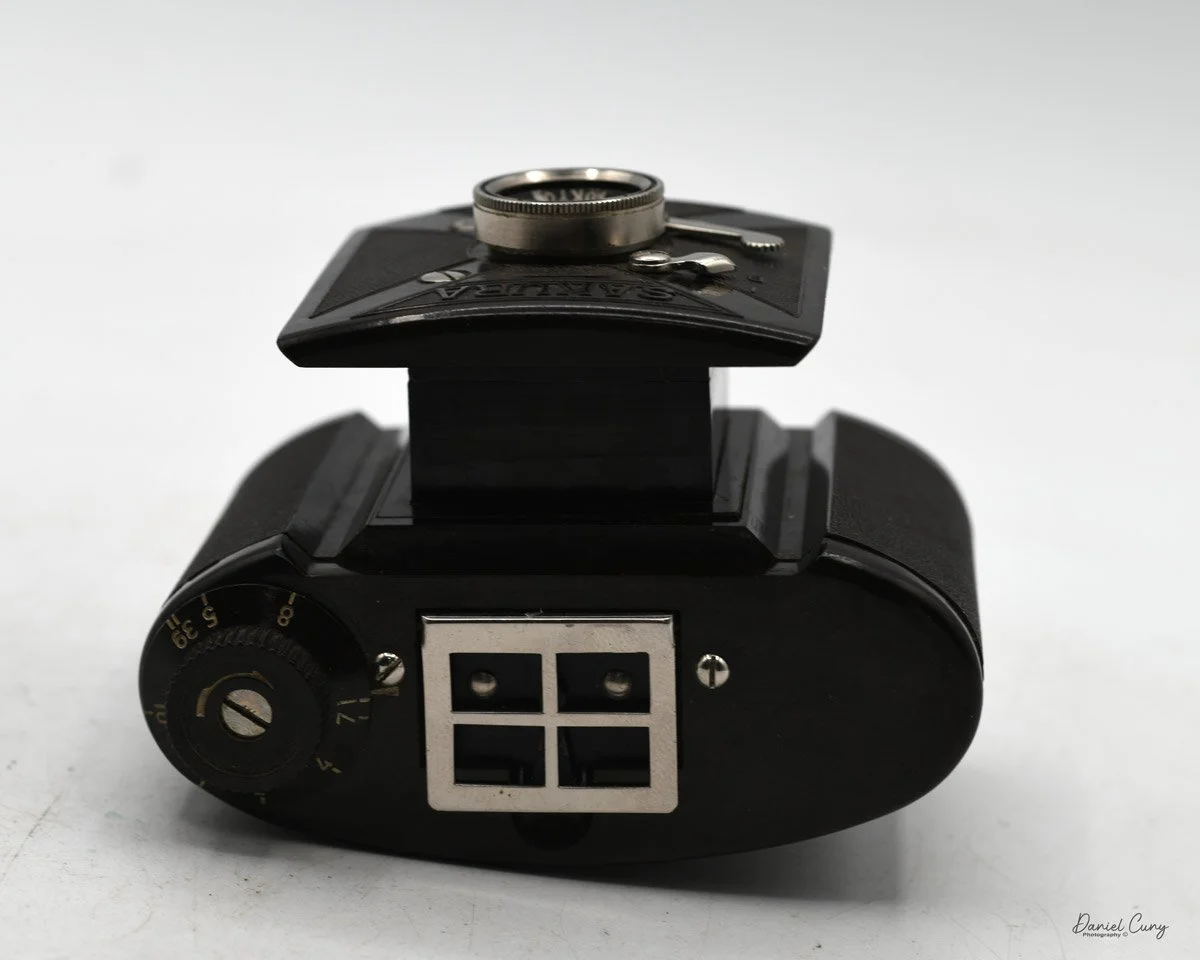
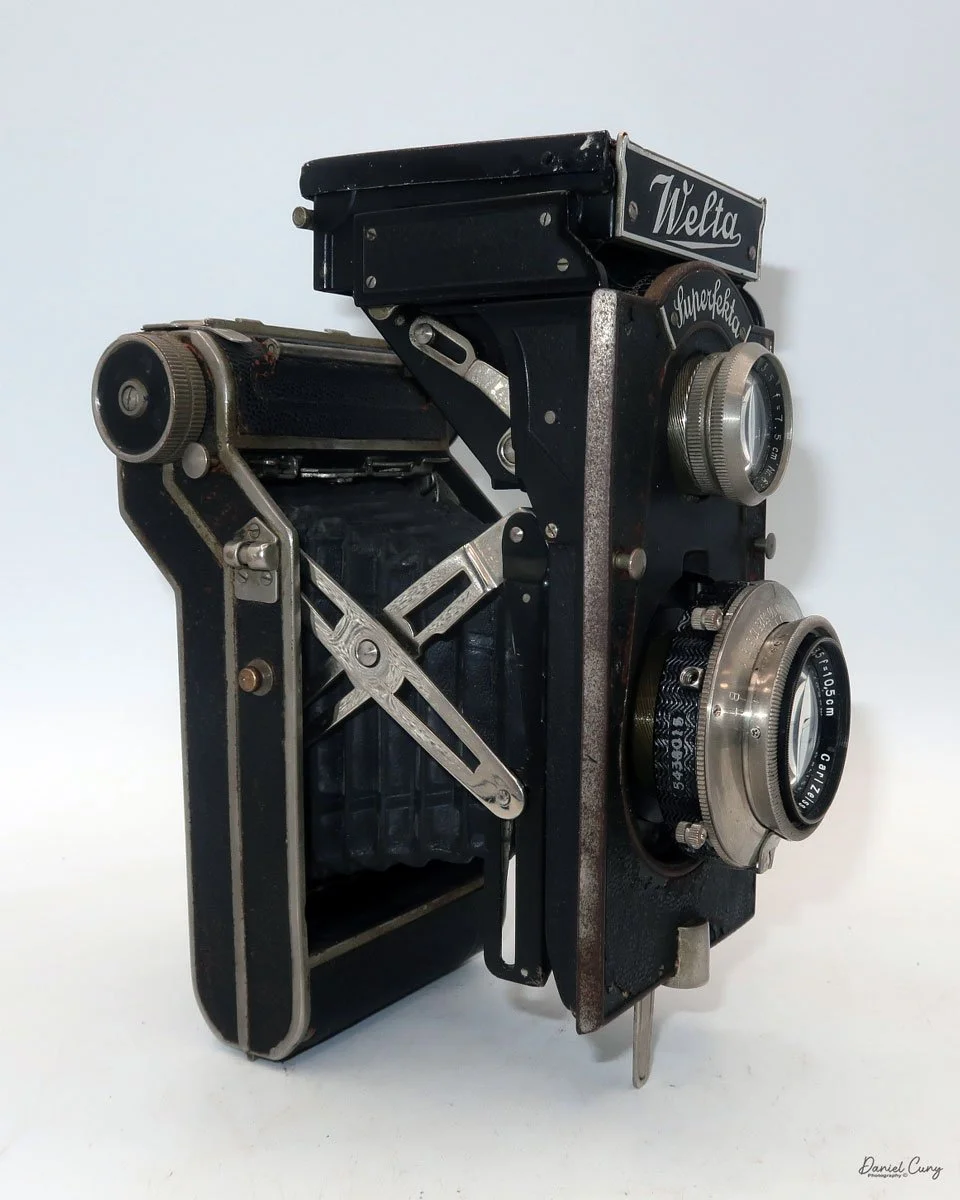
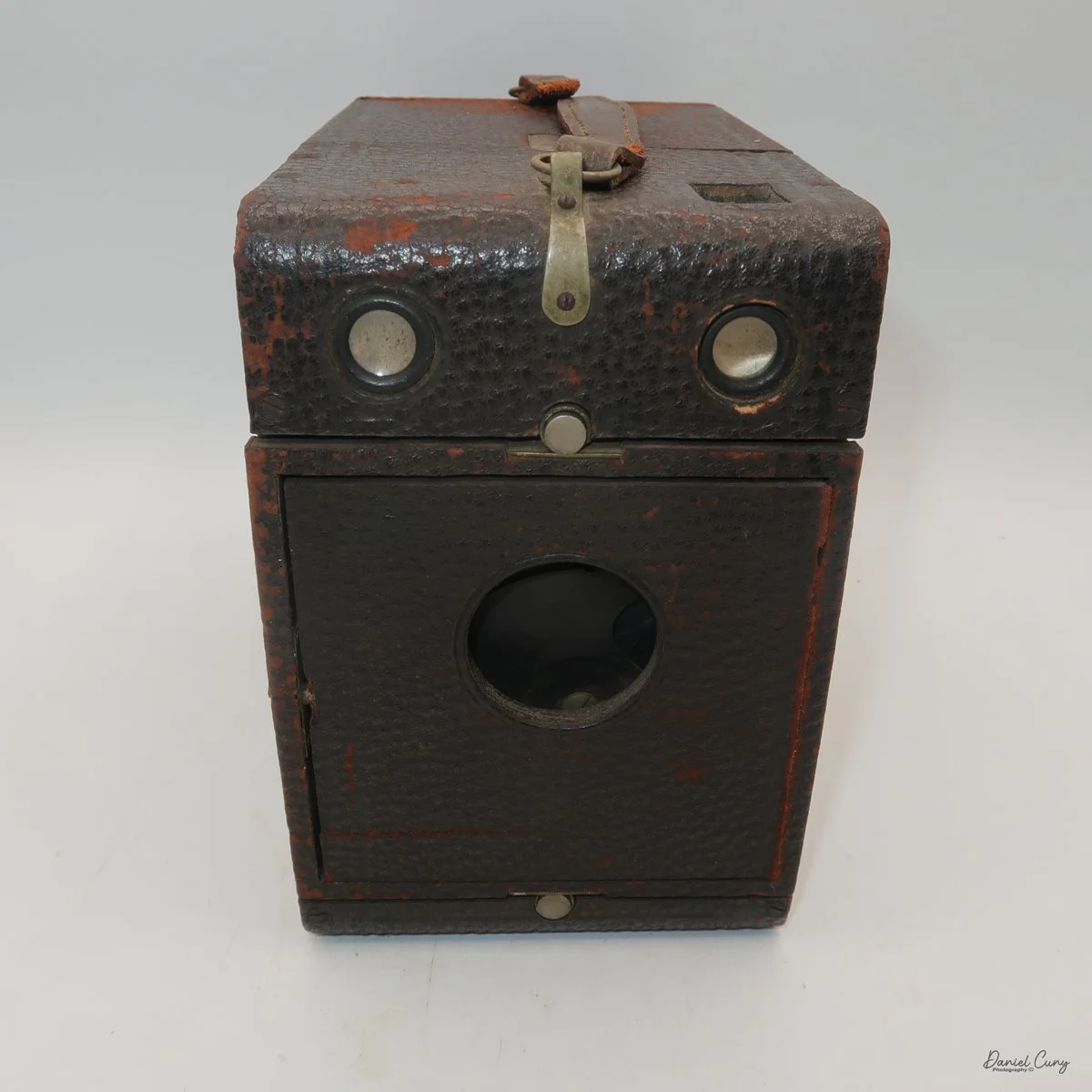
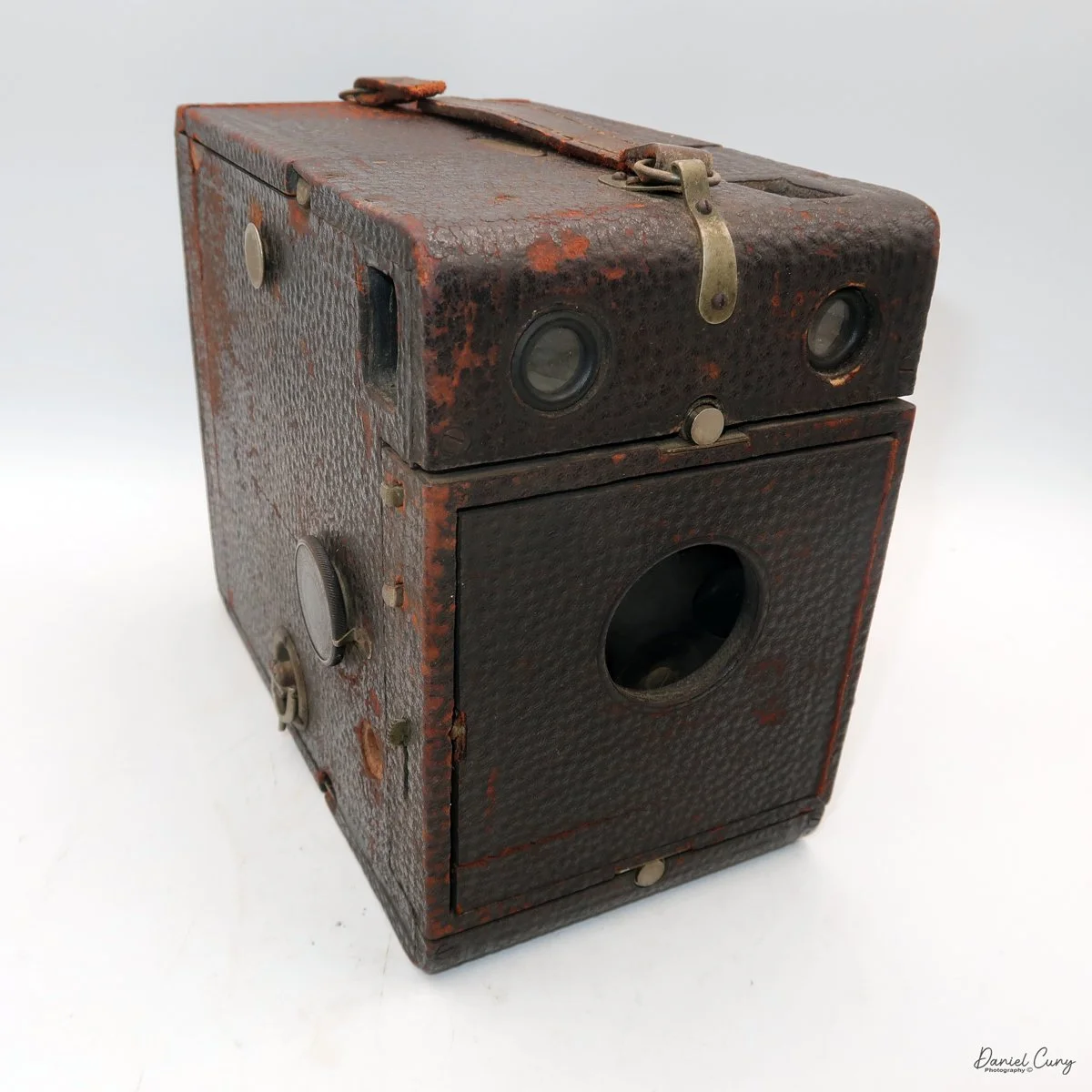
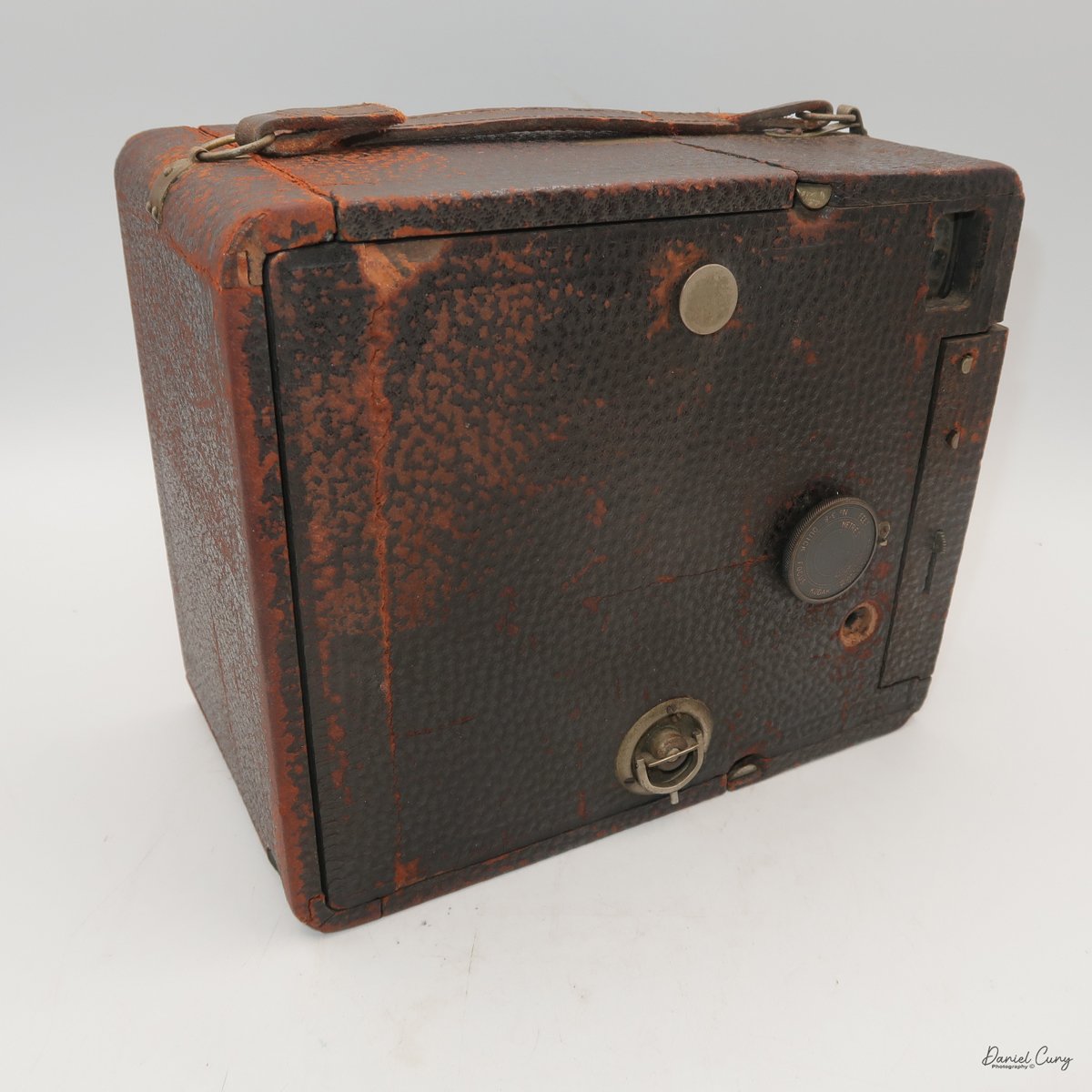
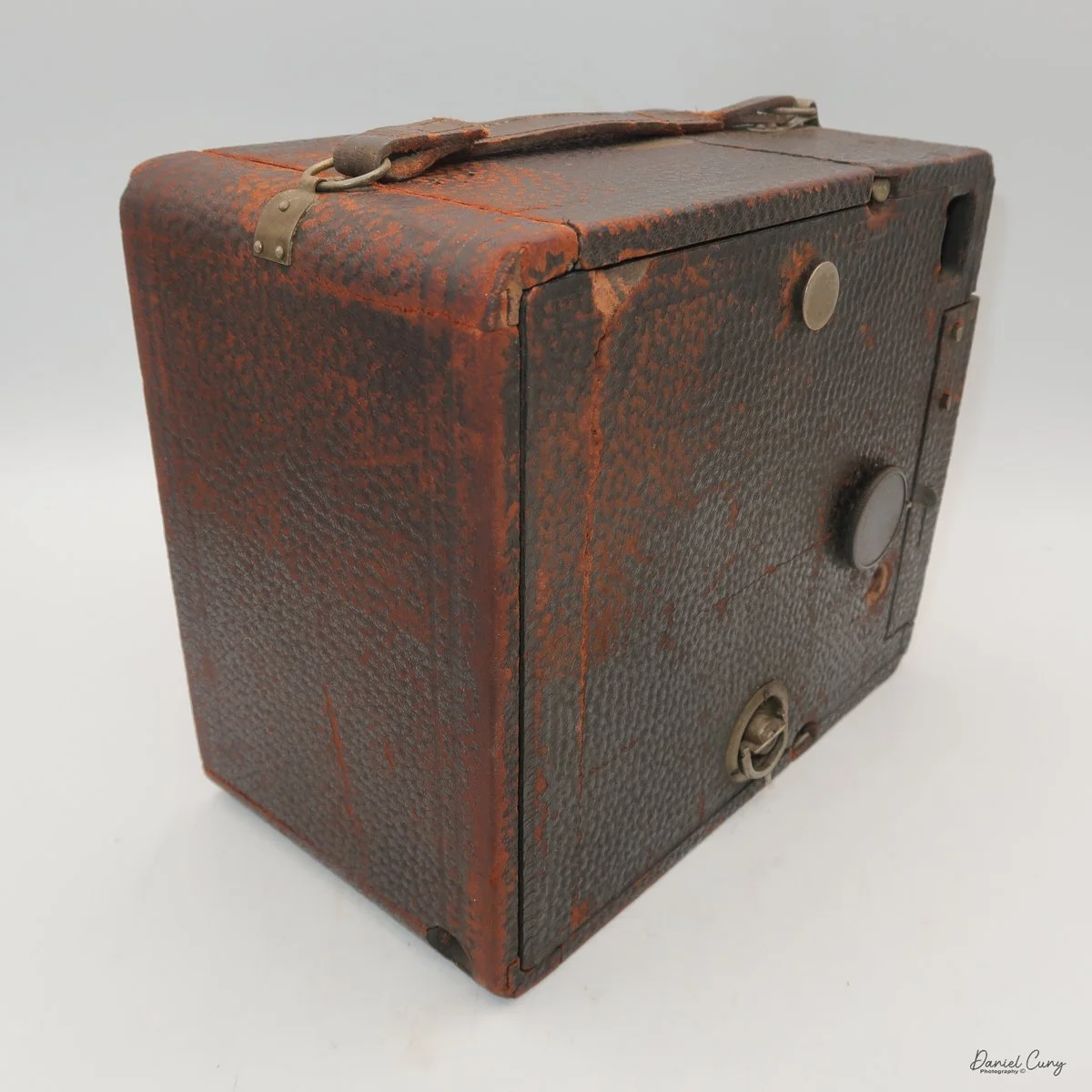
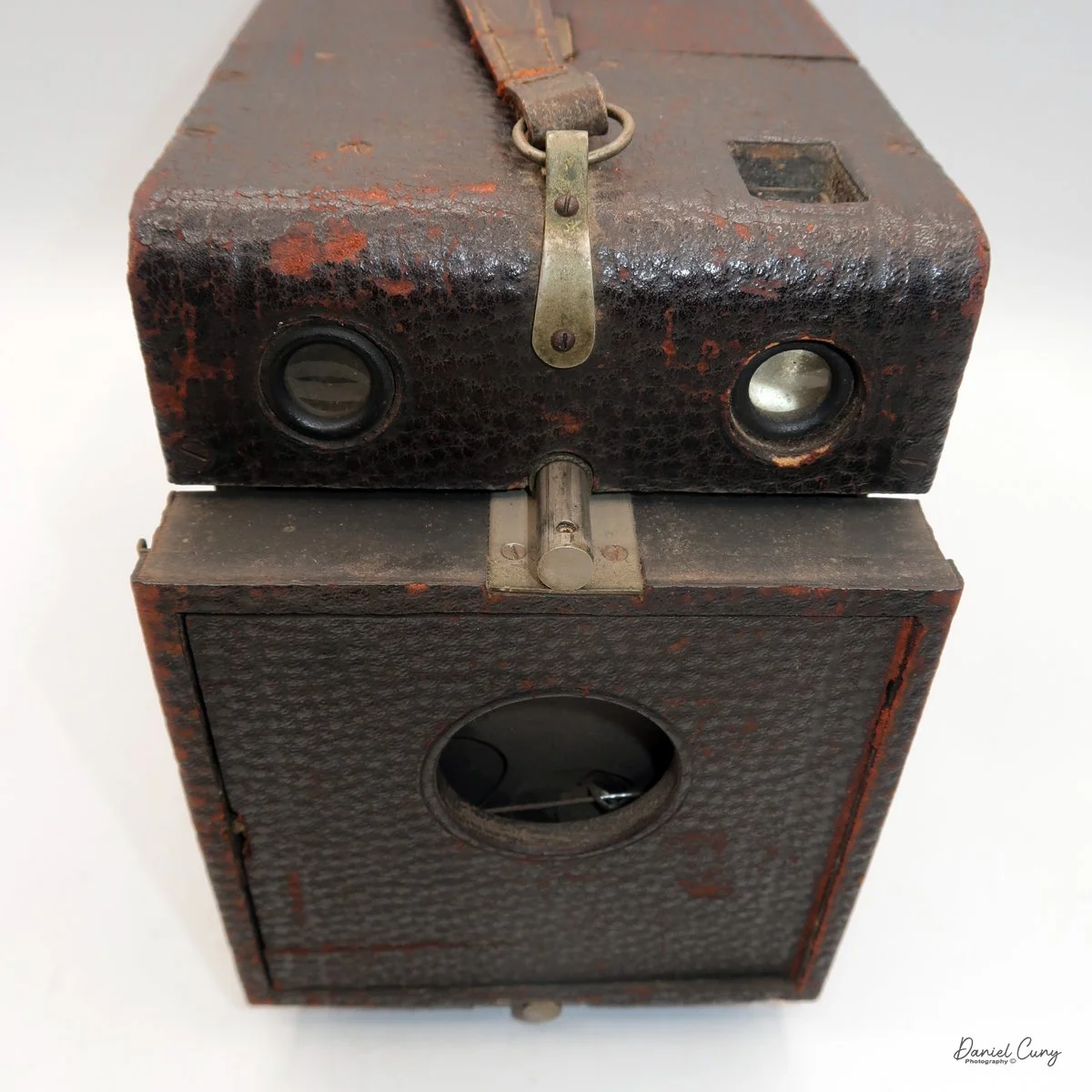
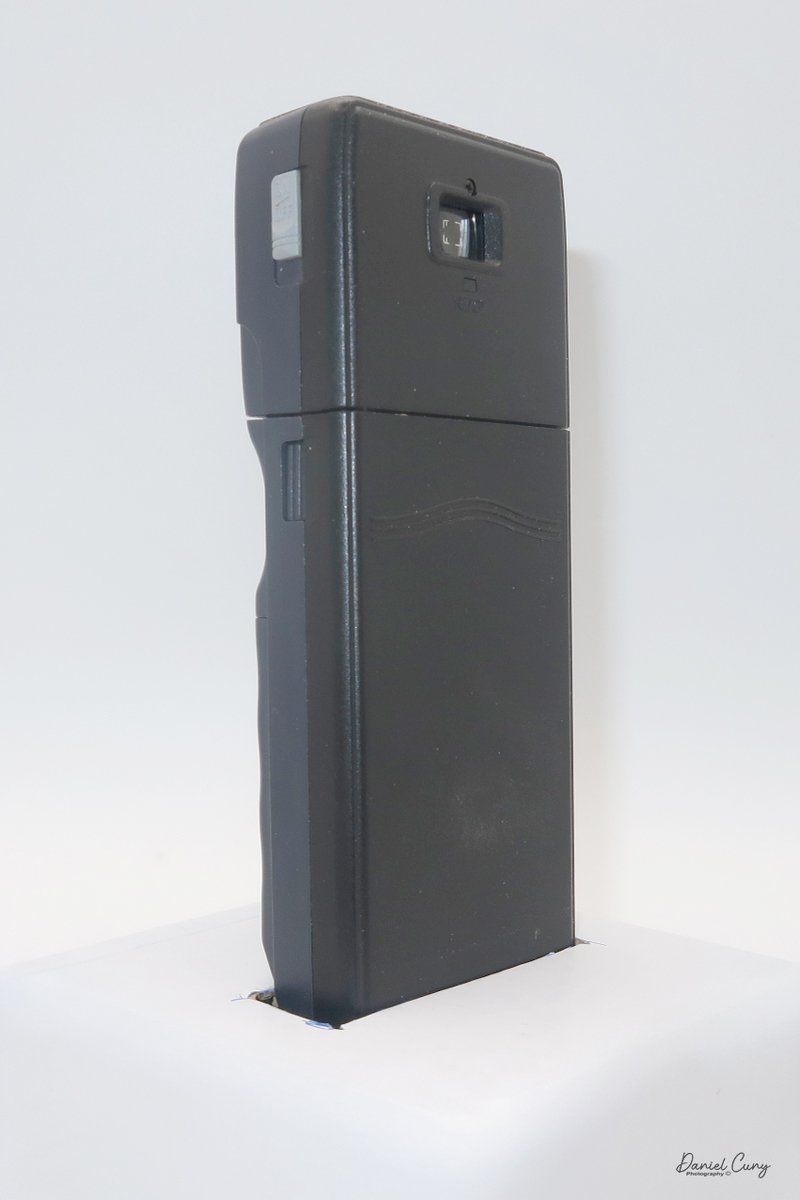
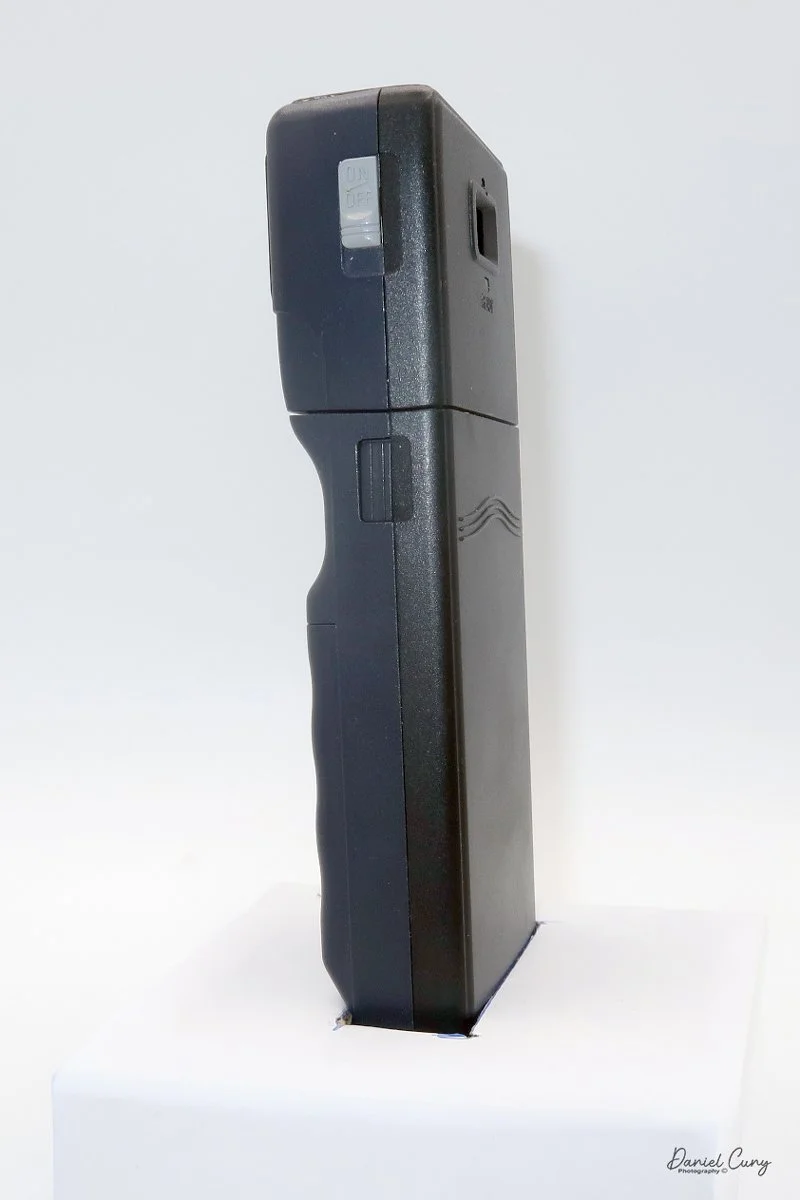
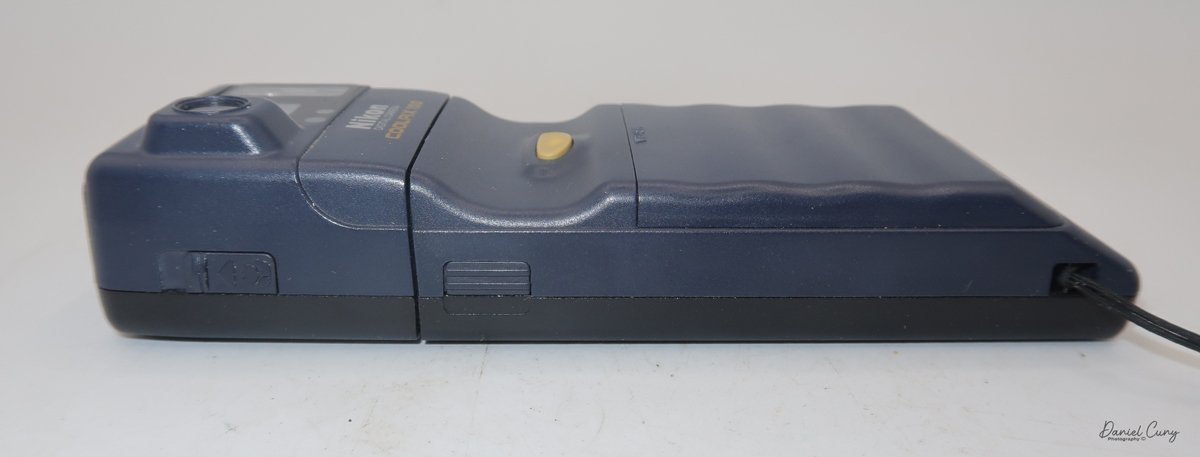
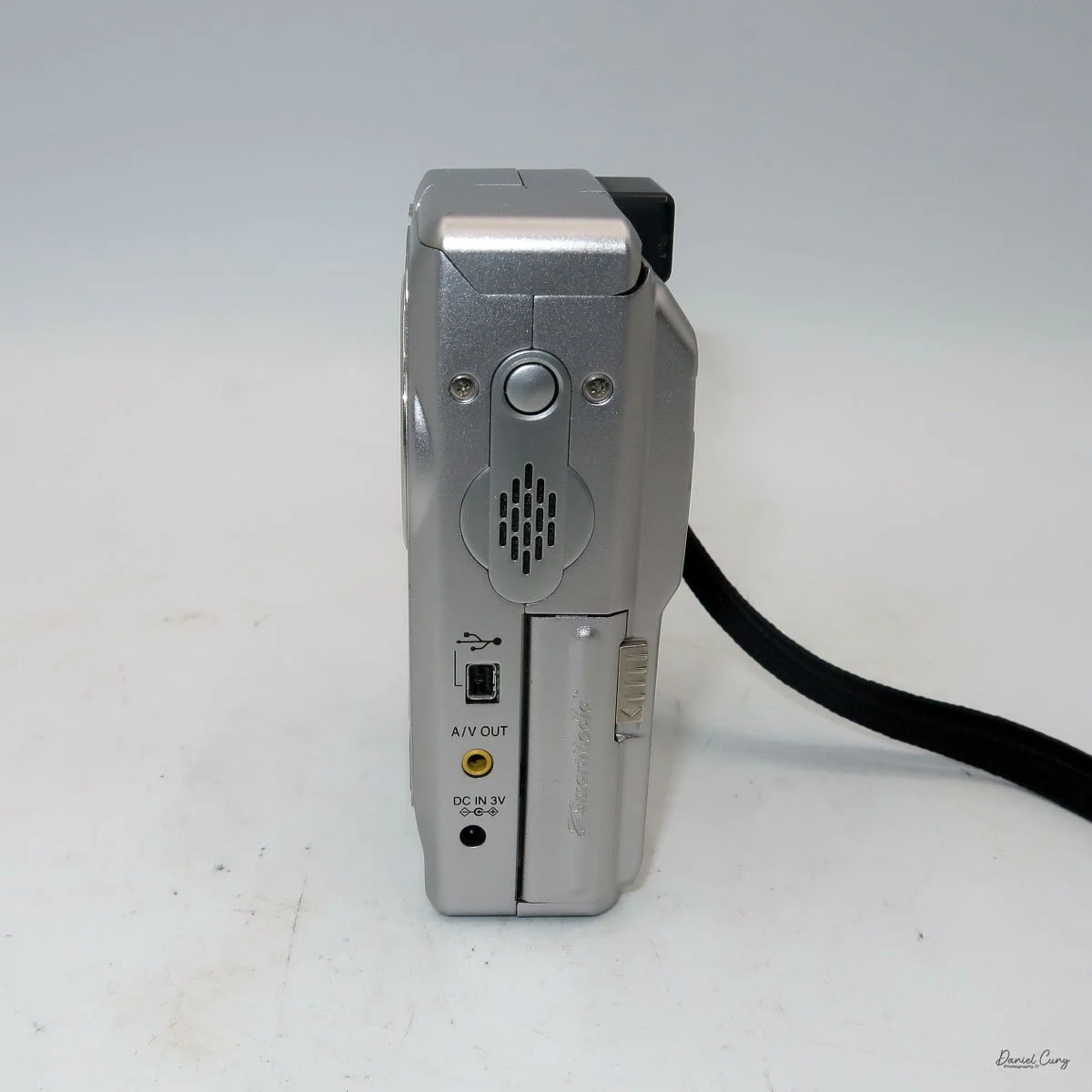
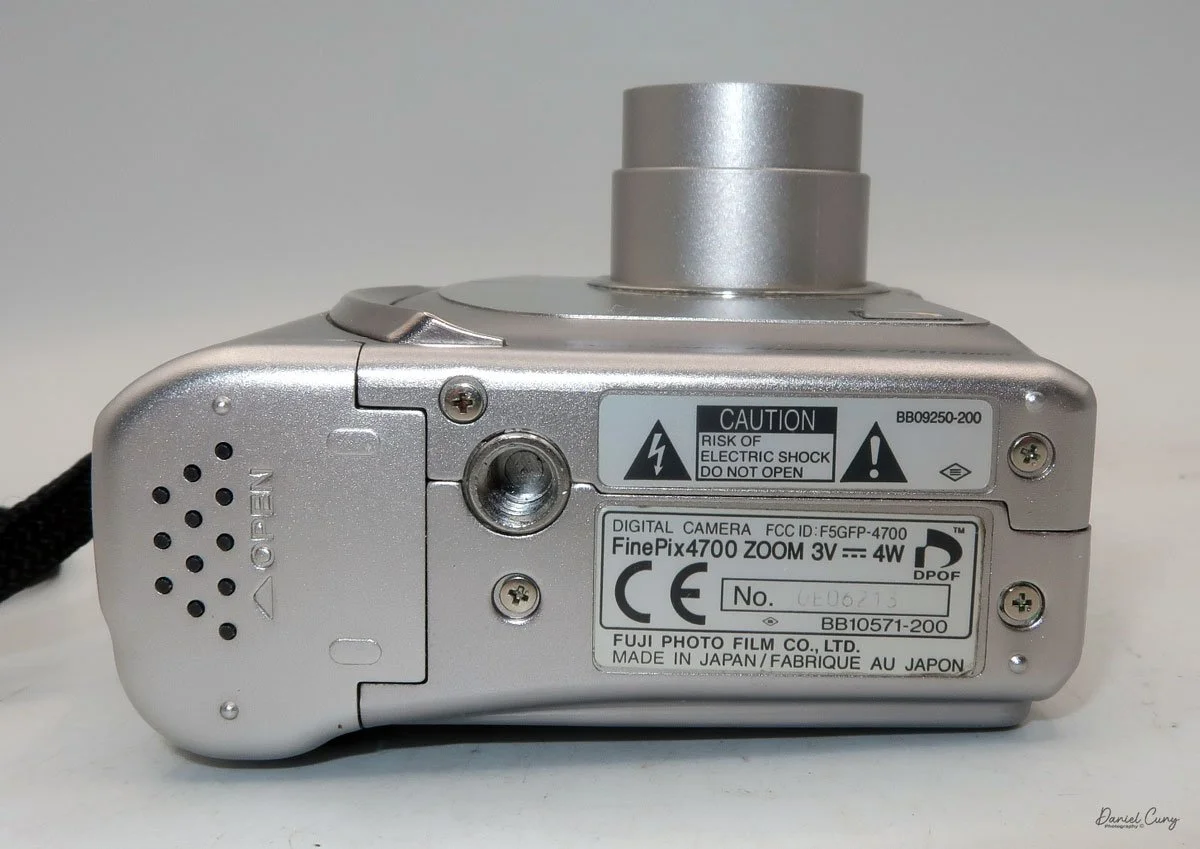
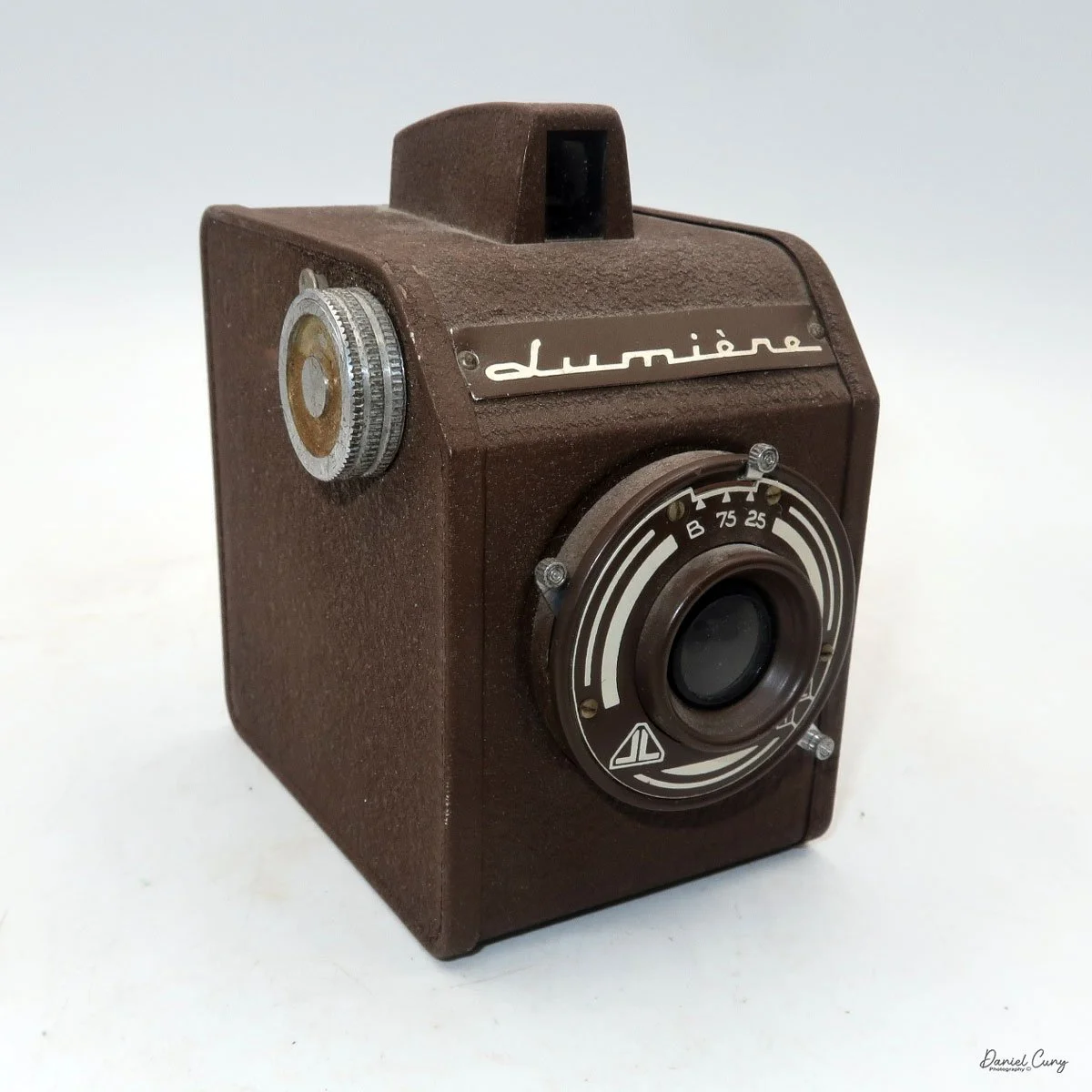
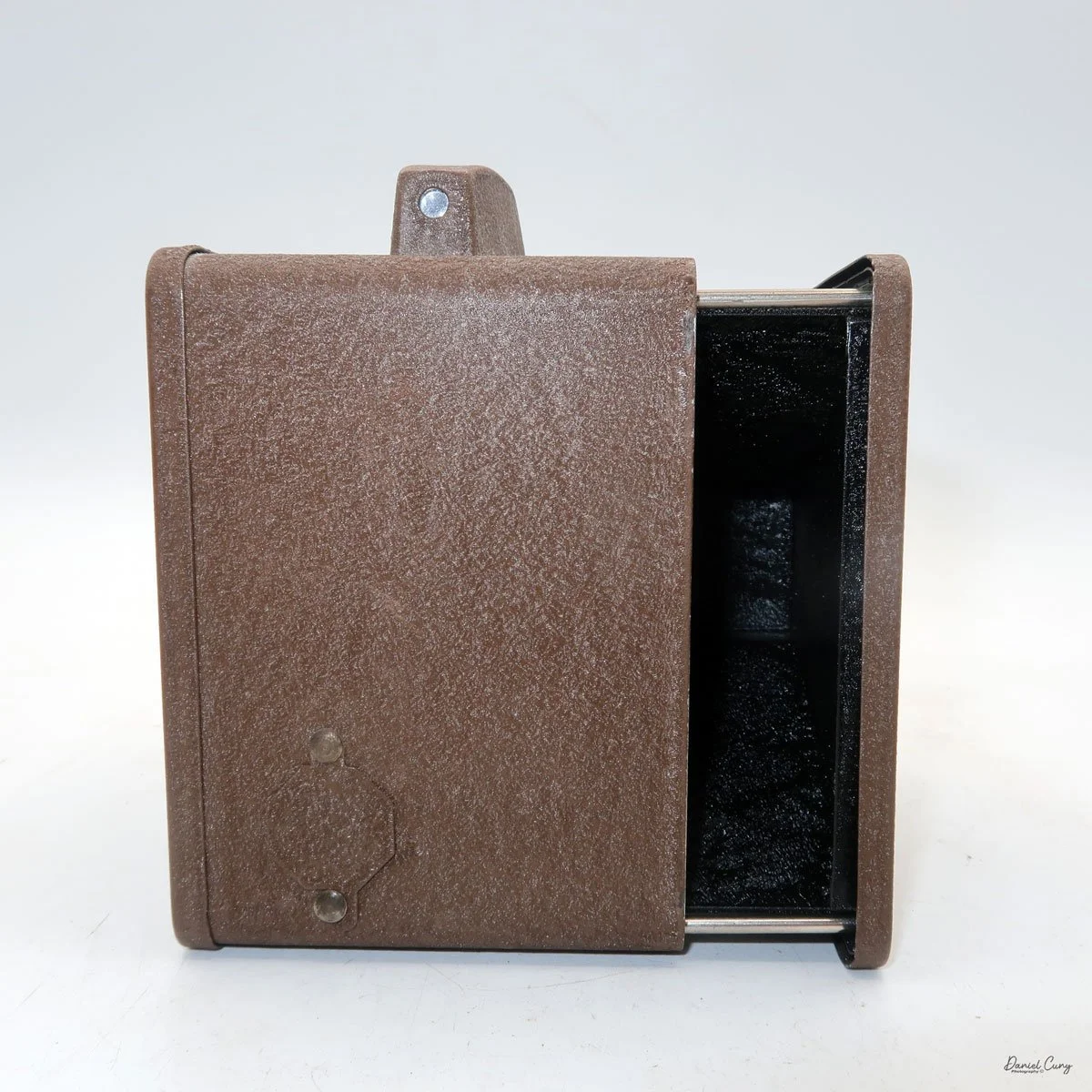
Physically, the Duca is tiny: only about 4 inches tall by 3.25 inches deep and just over 1.5 inches wide, and it weighs 10.1 ounces with the cassettes in place. The body is nicely rounded and fits well in the hand—definitely a camera you could drop in a coat pocket and forget about until you need it.
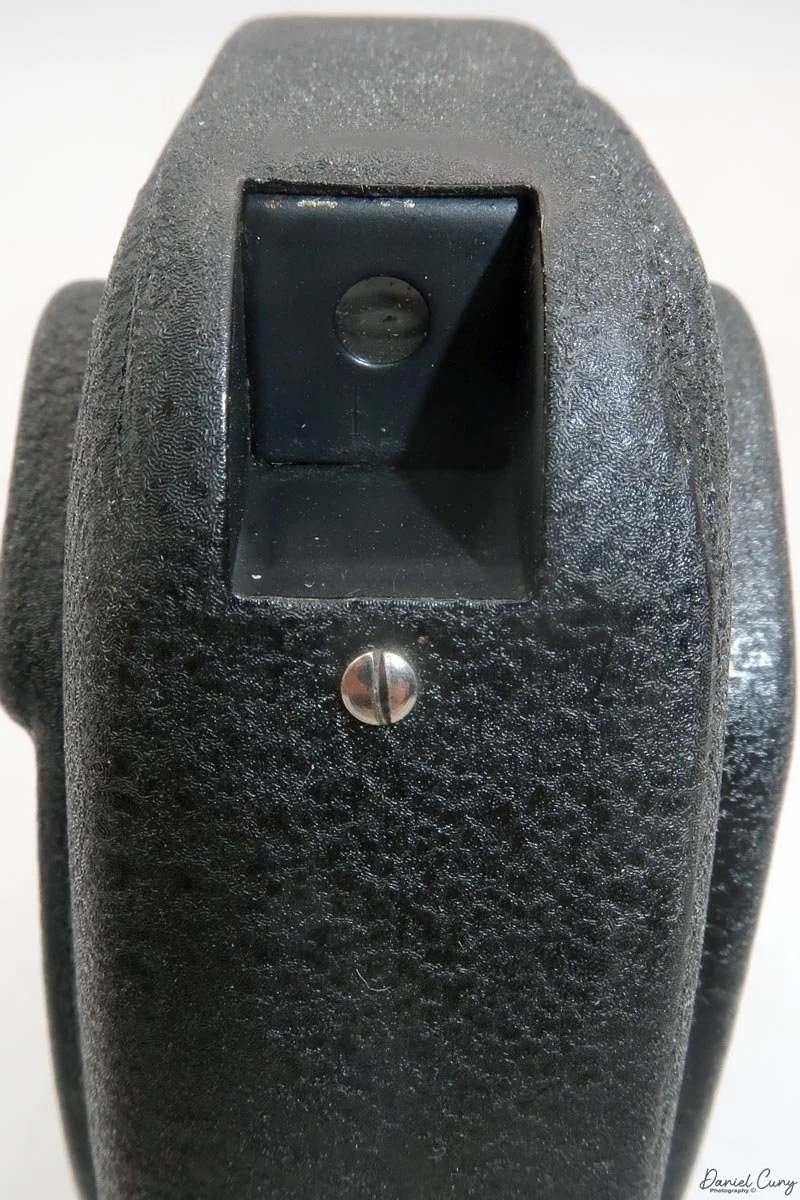
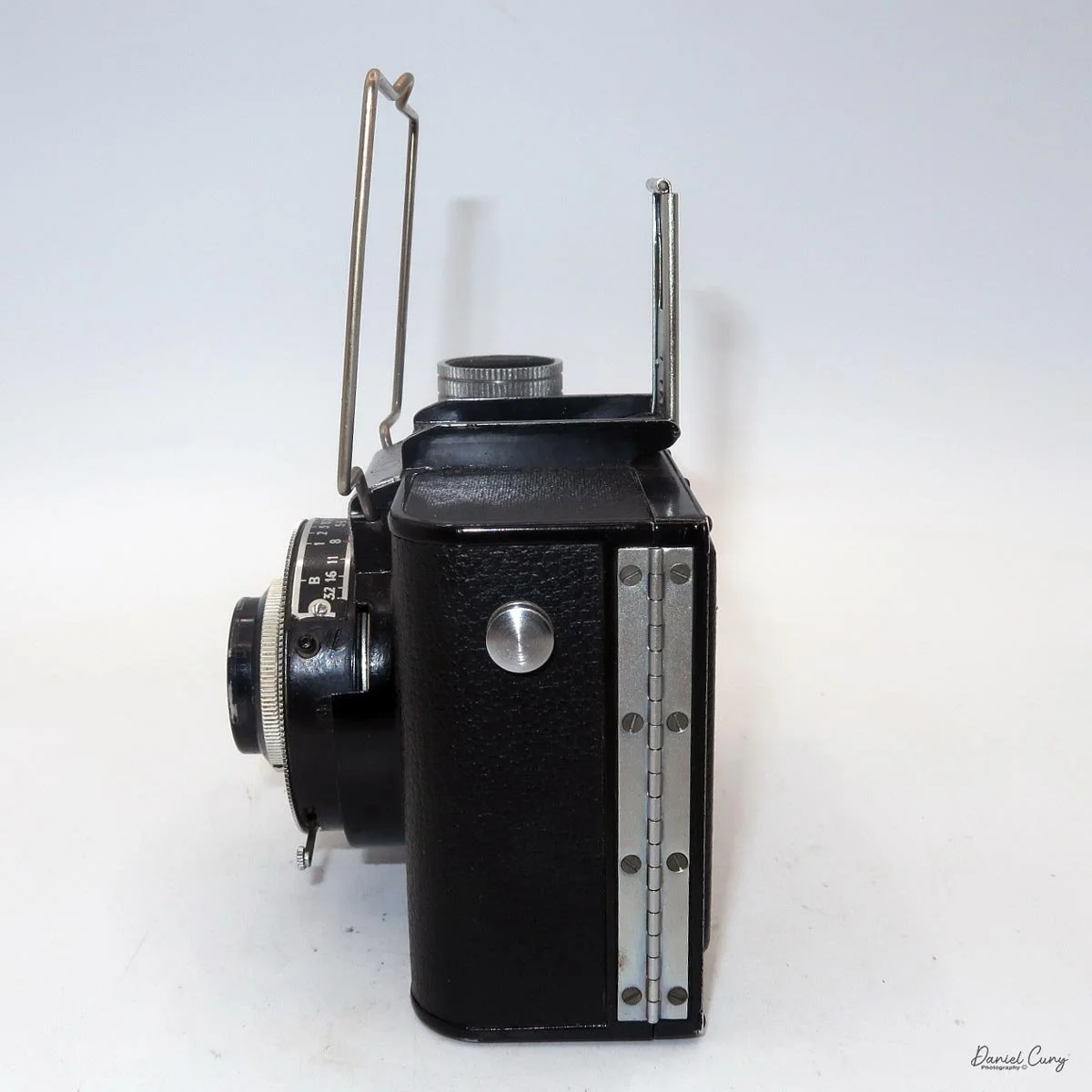
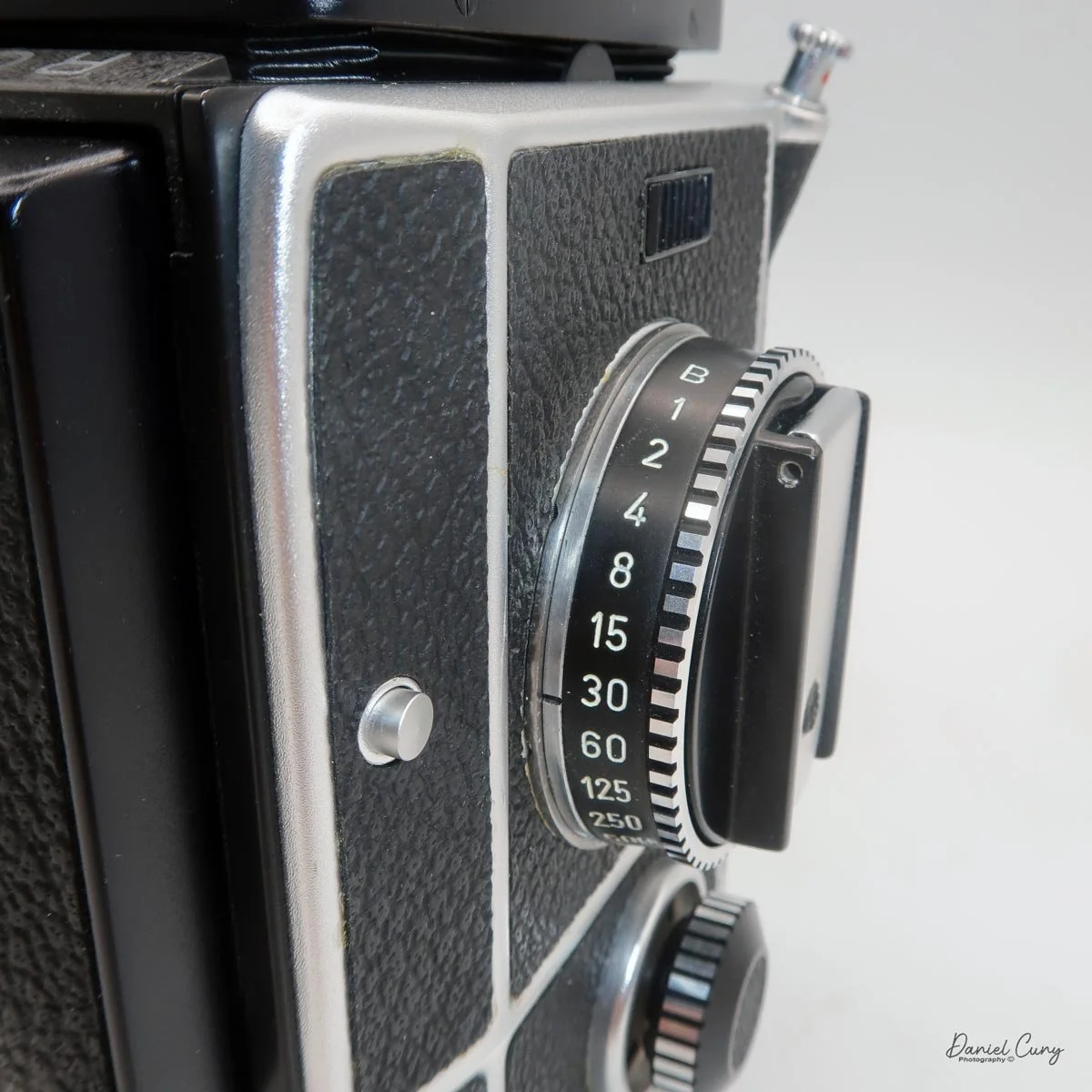
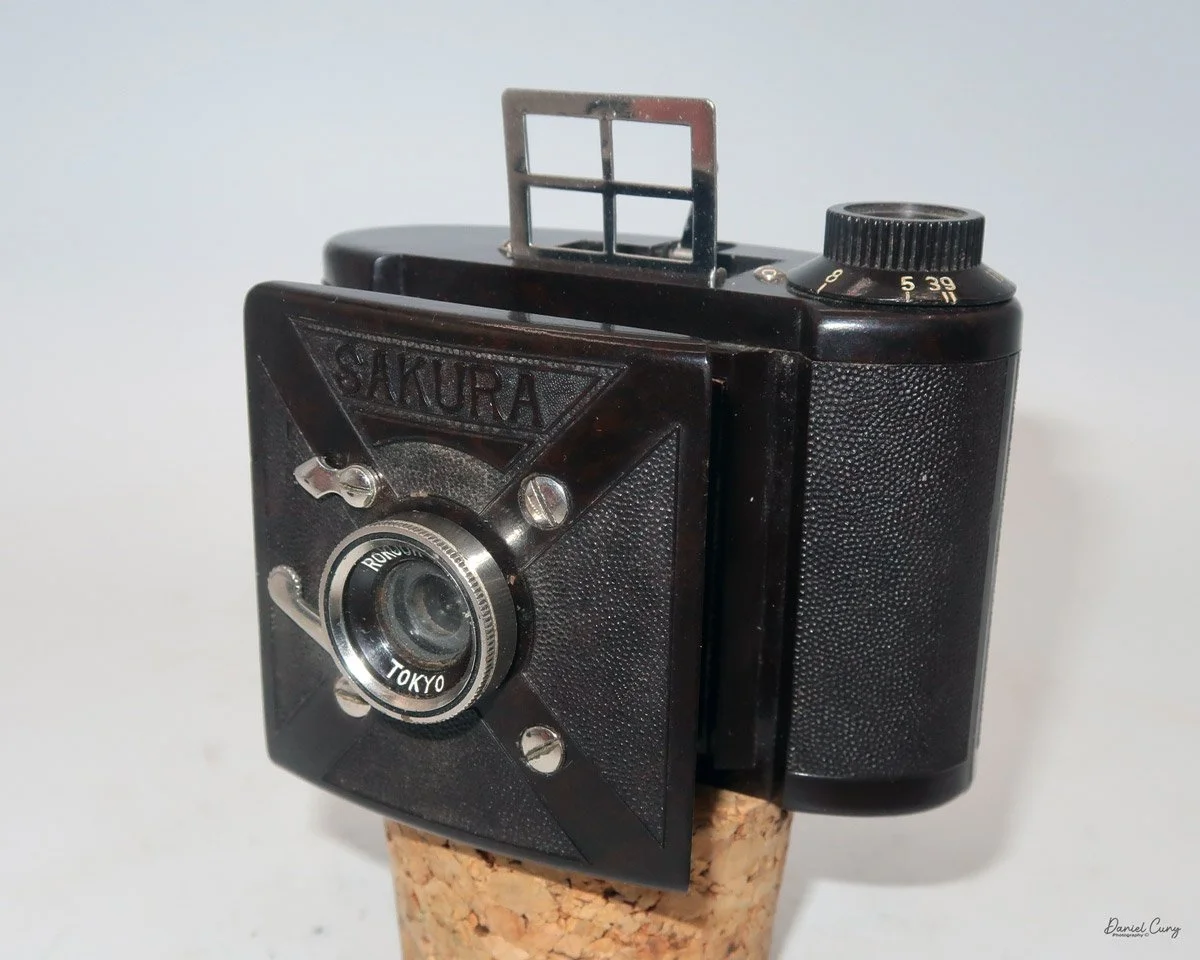
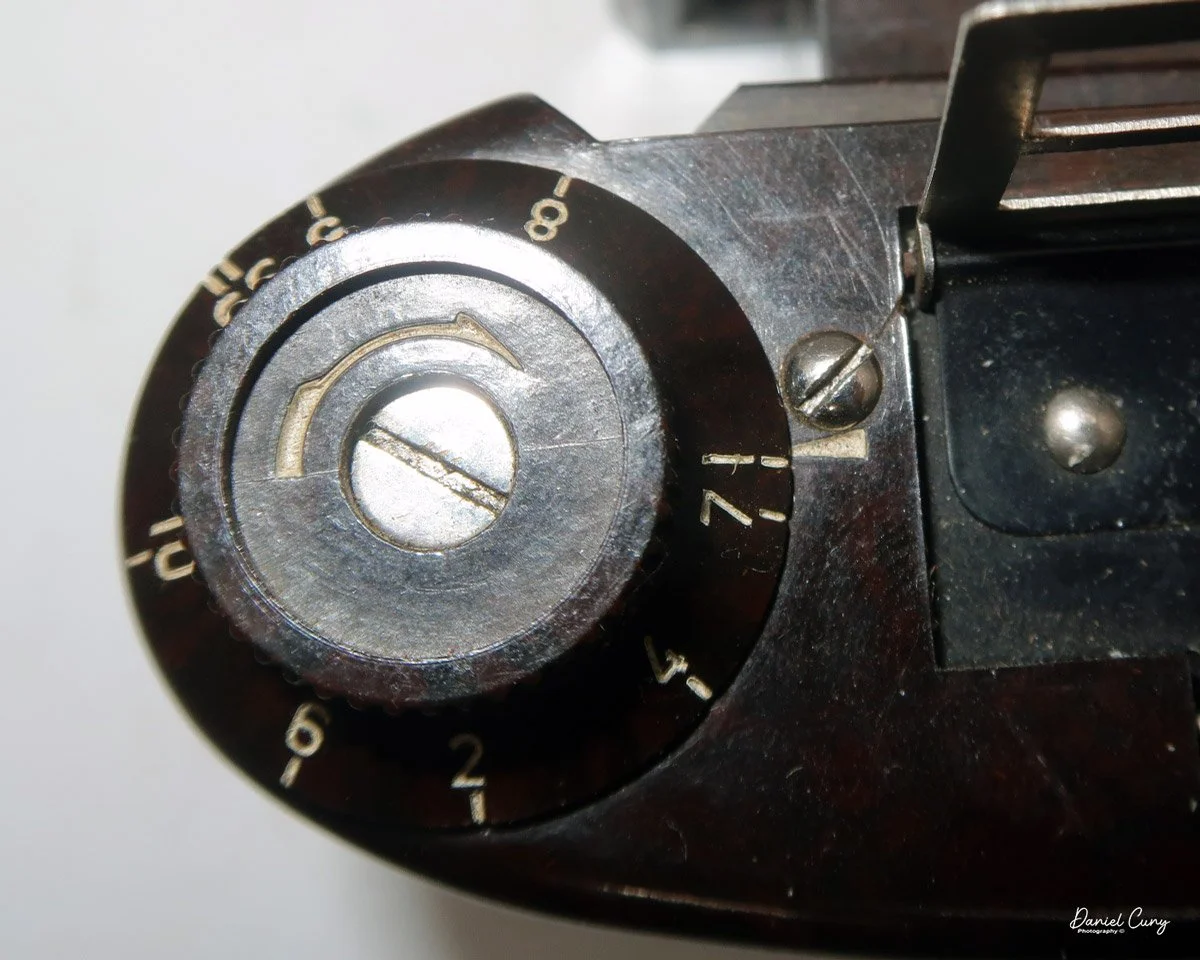
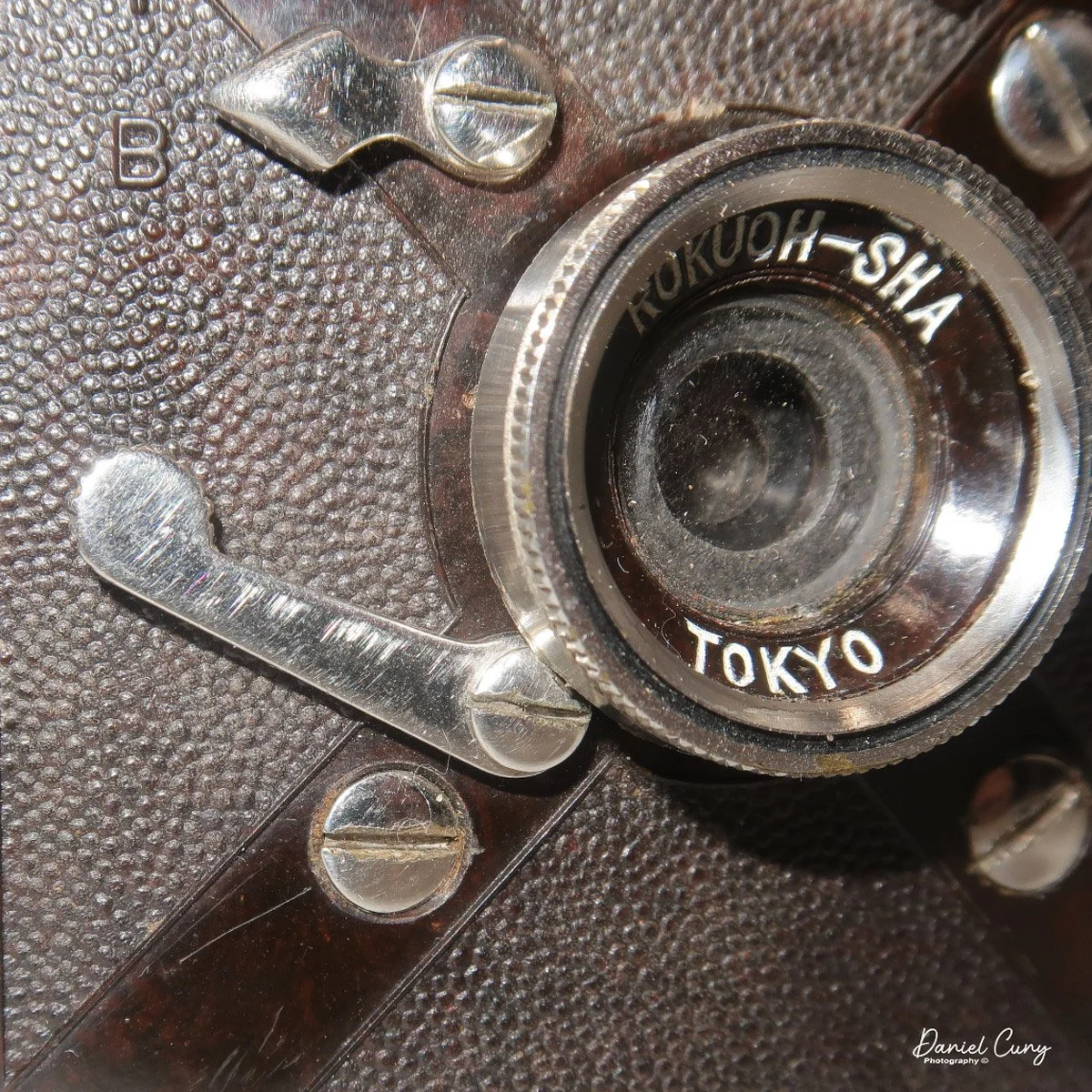
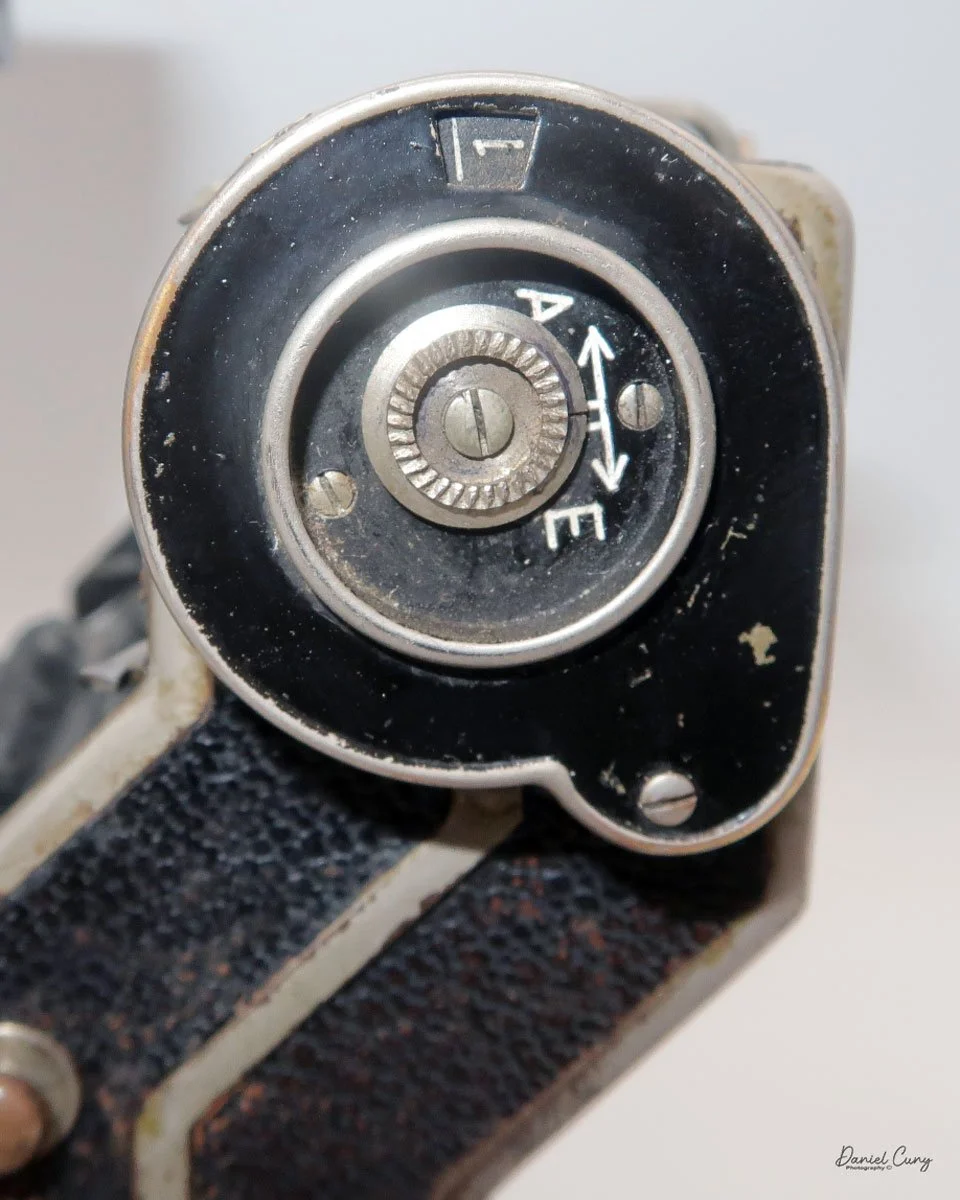
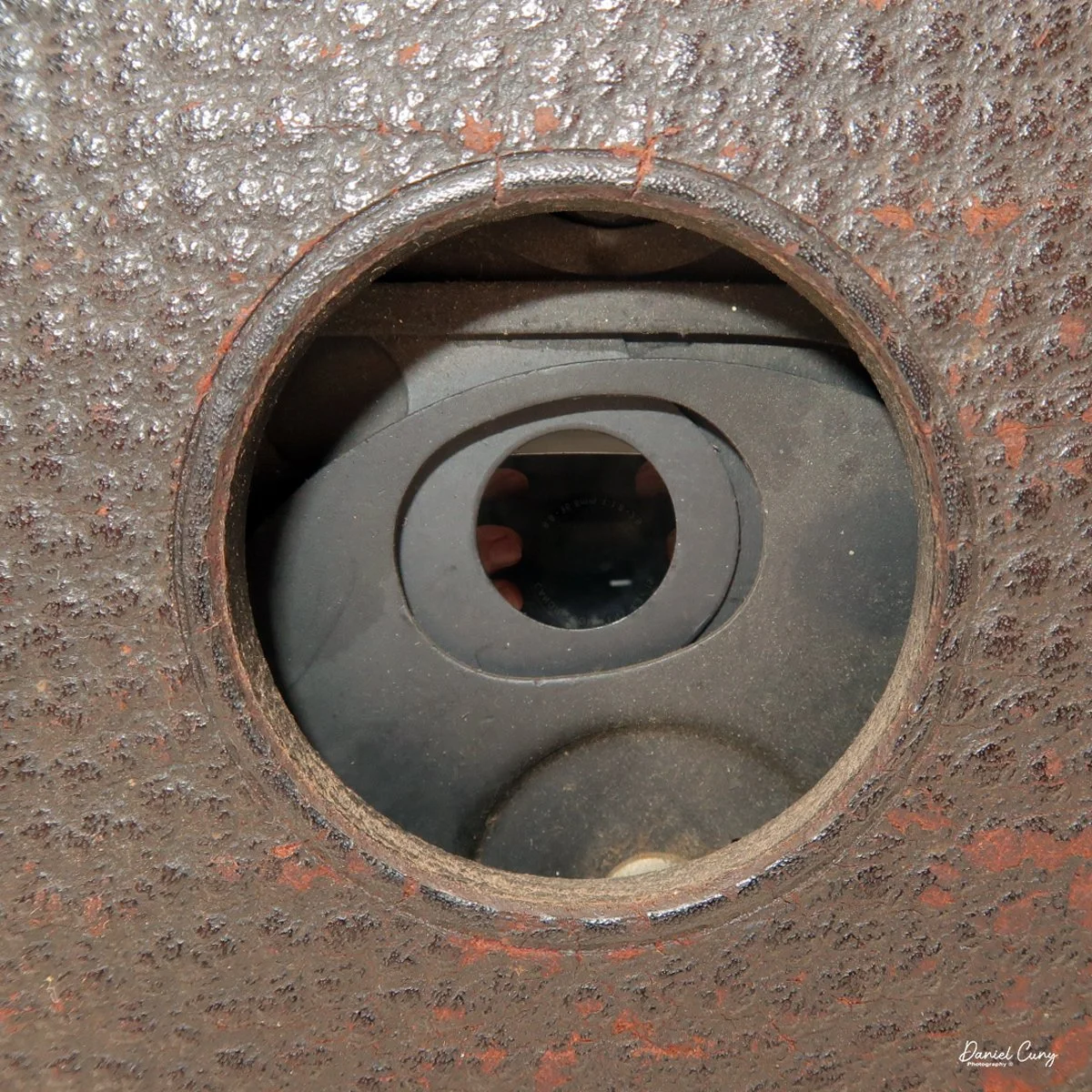
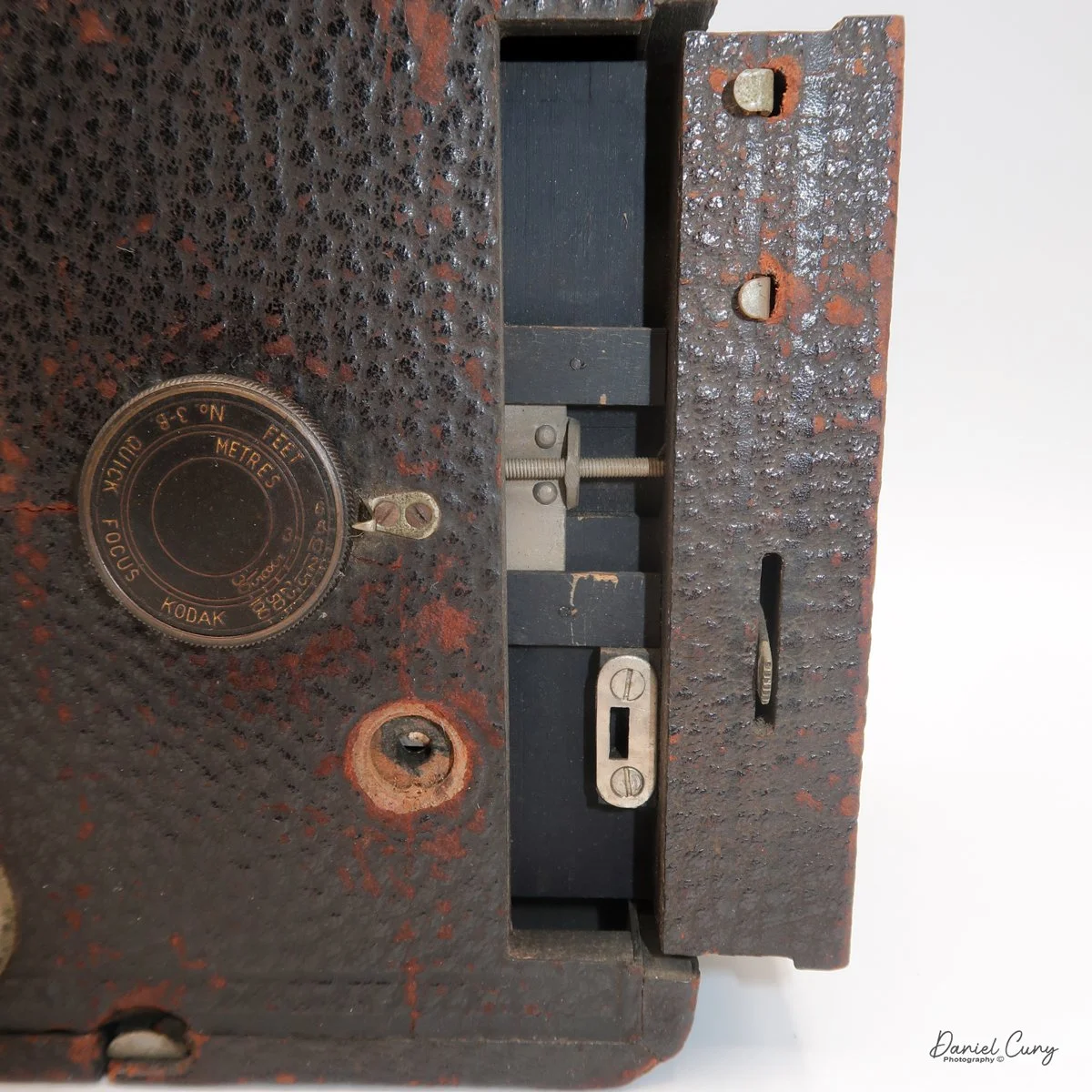
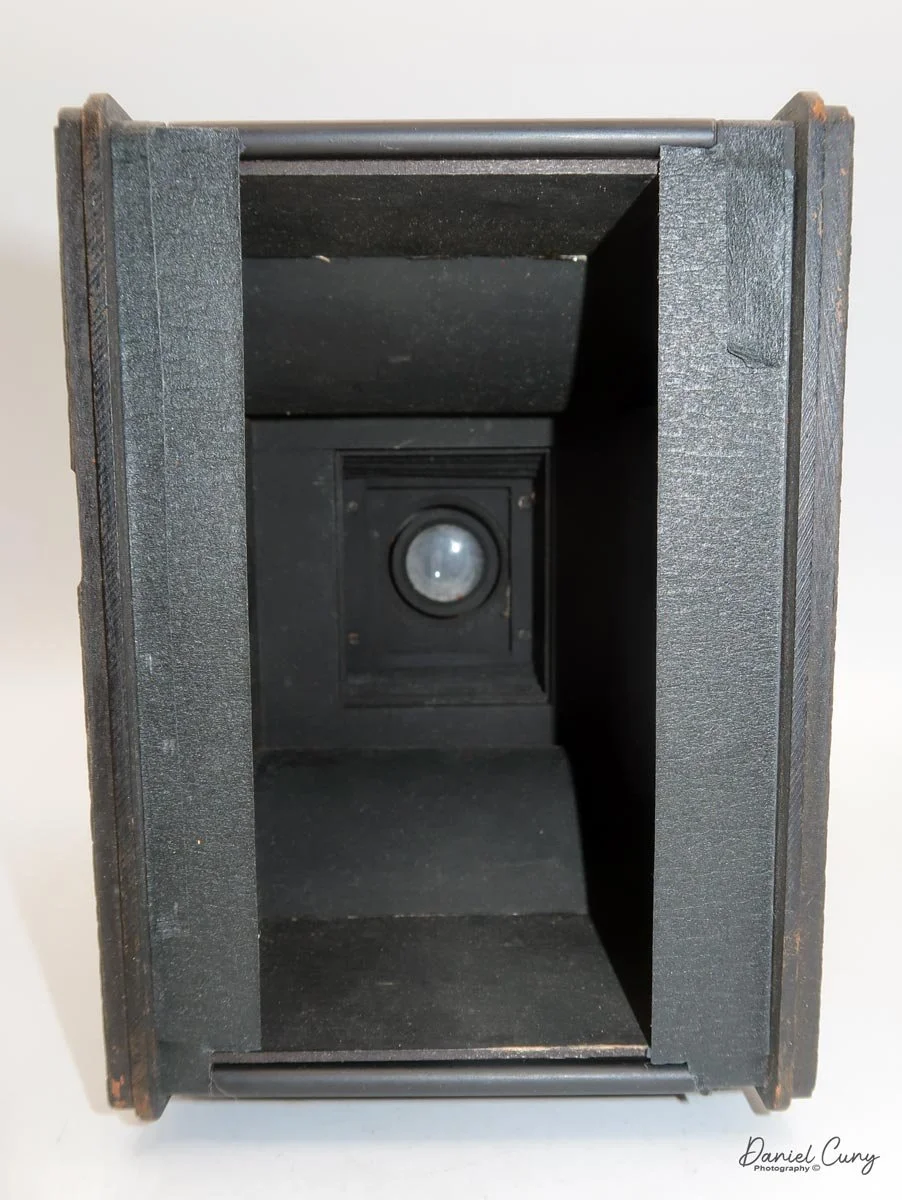
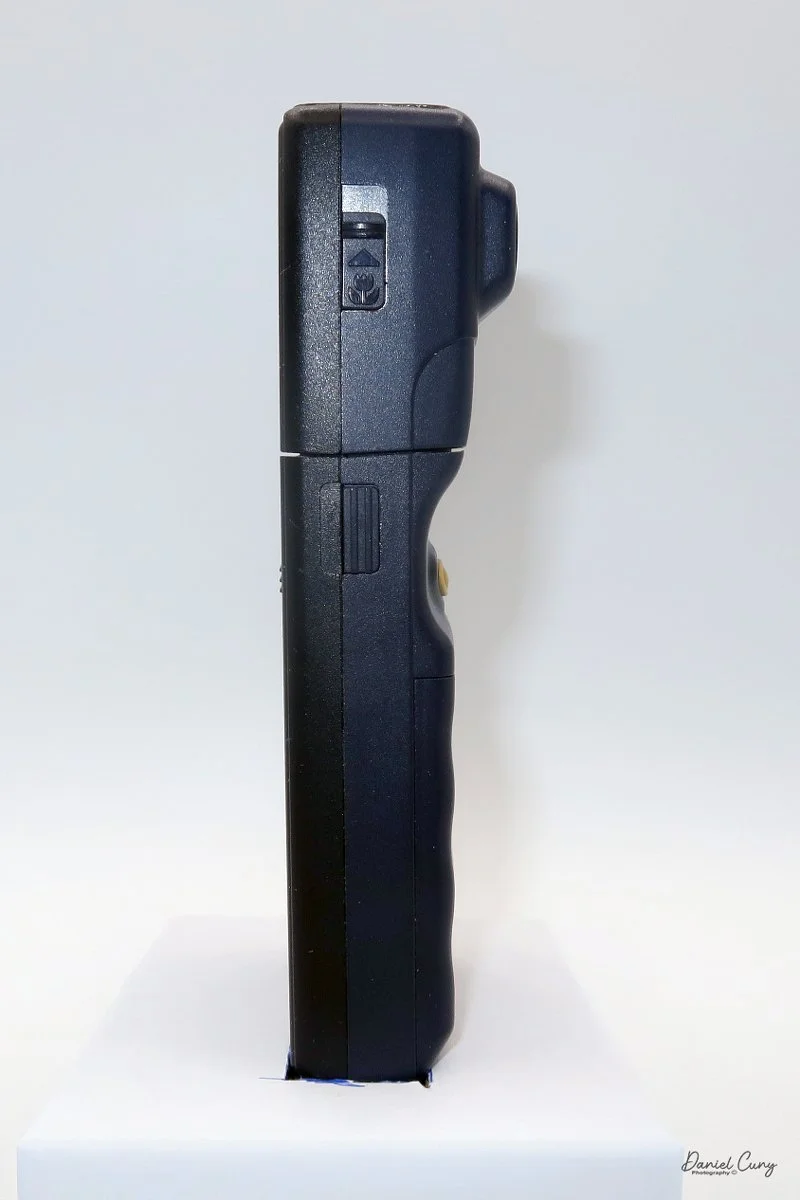
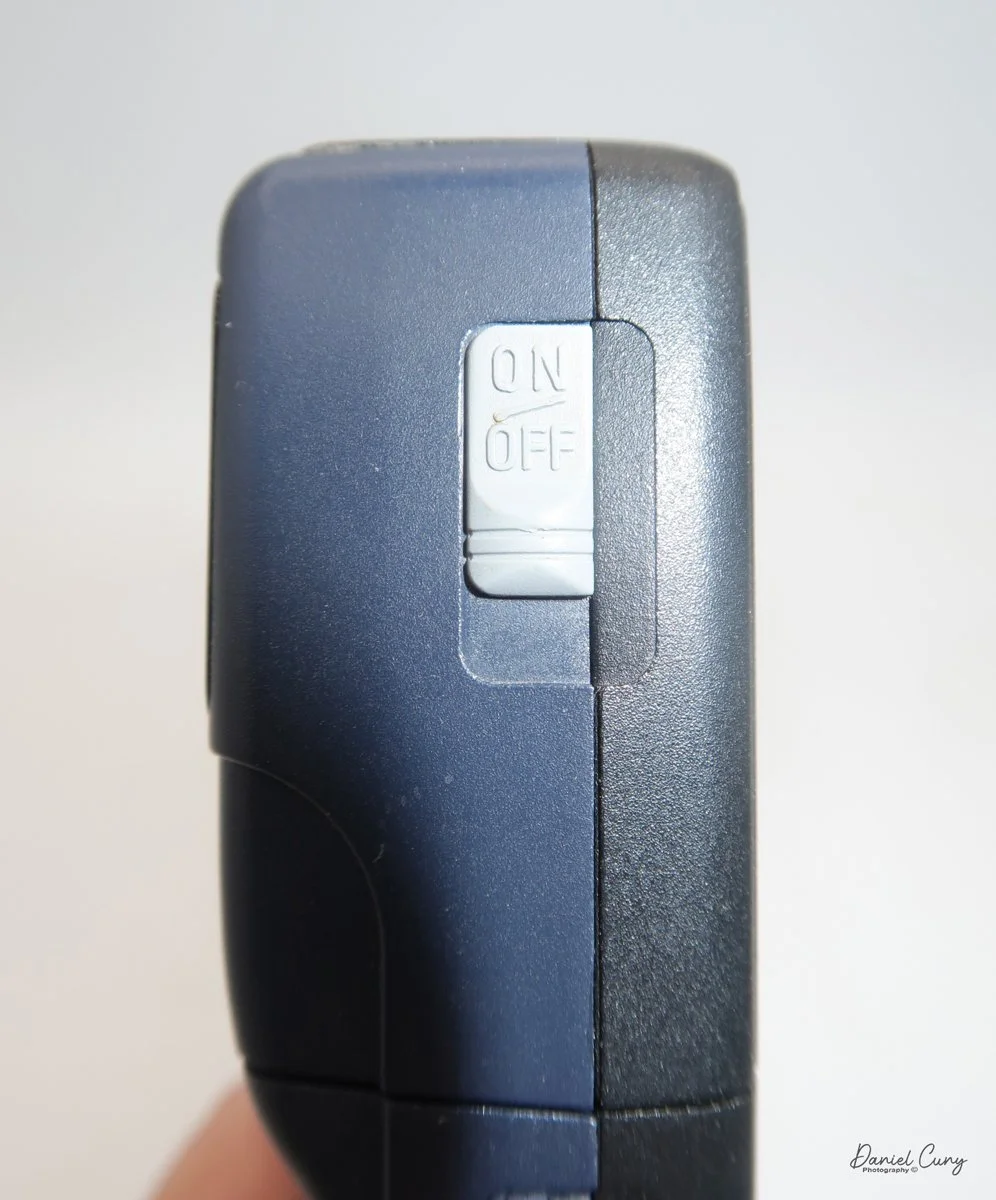
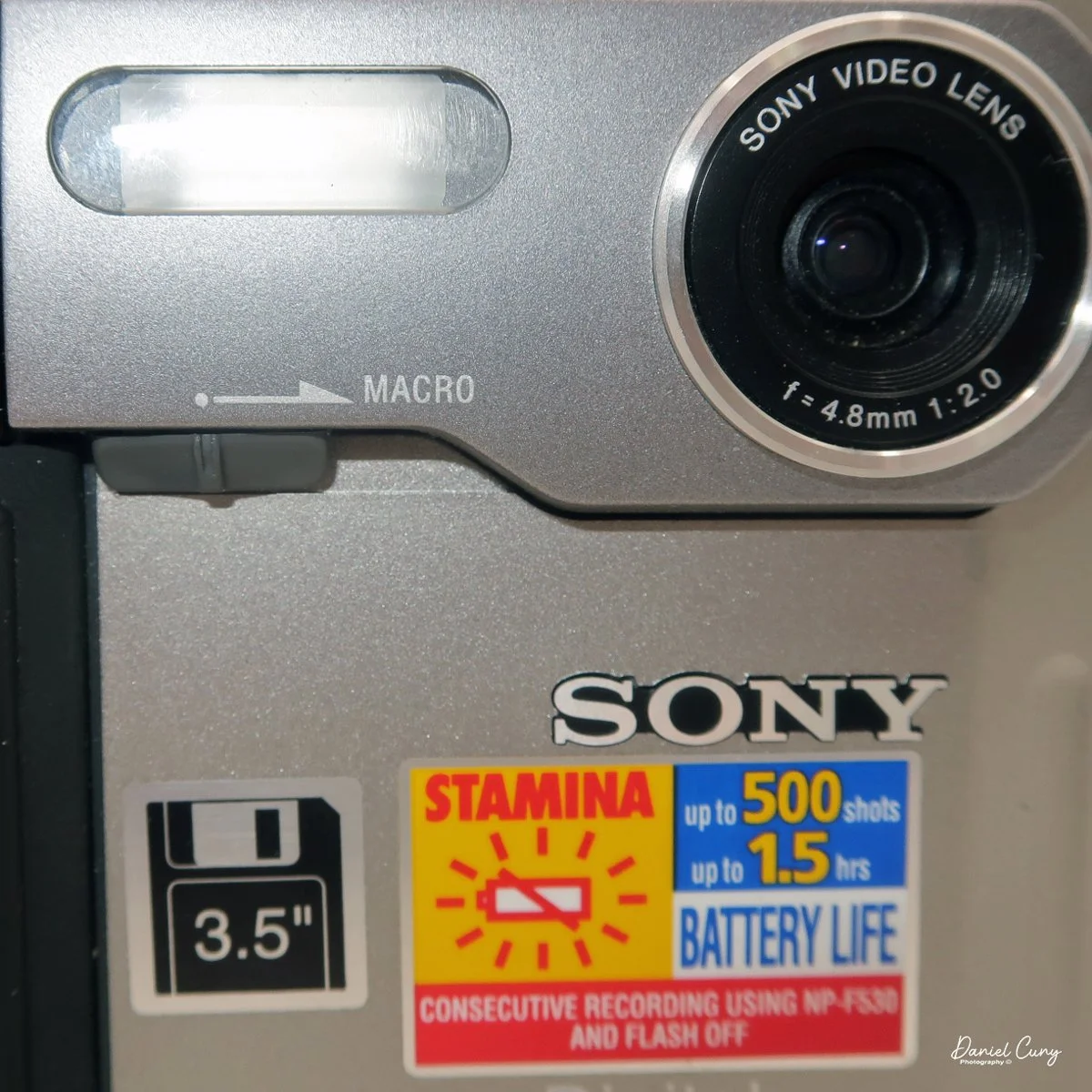
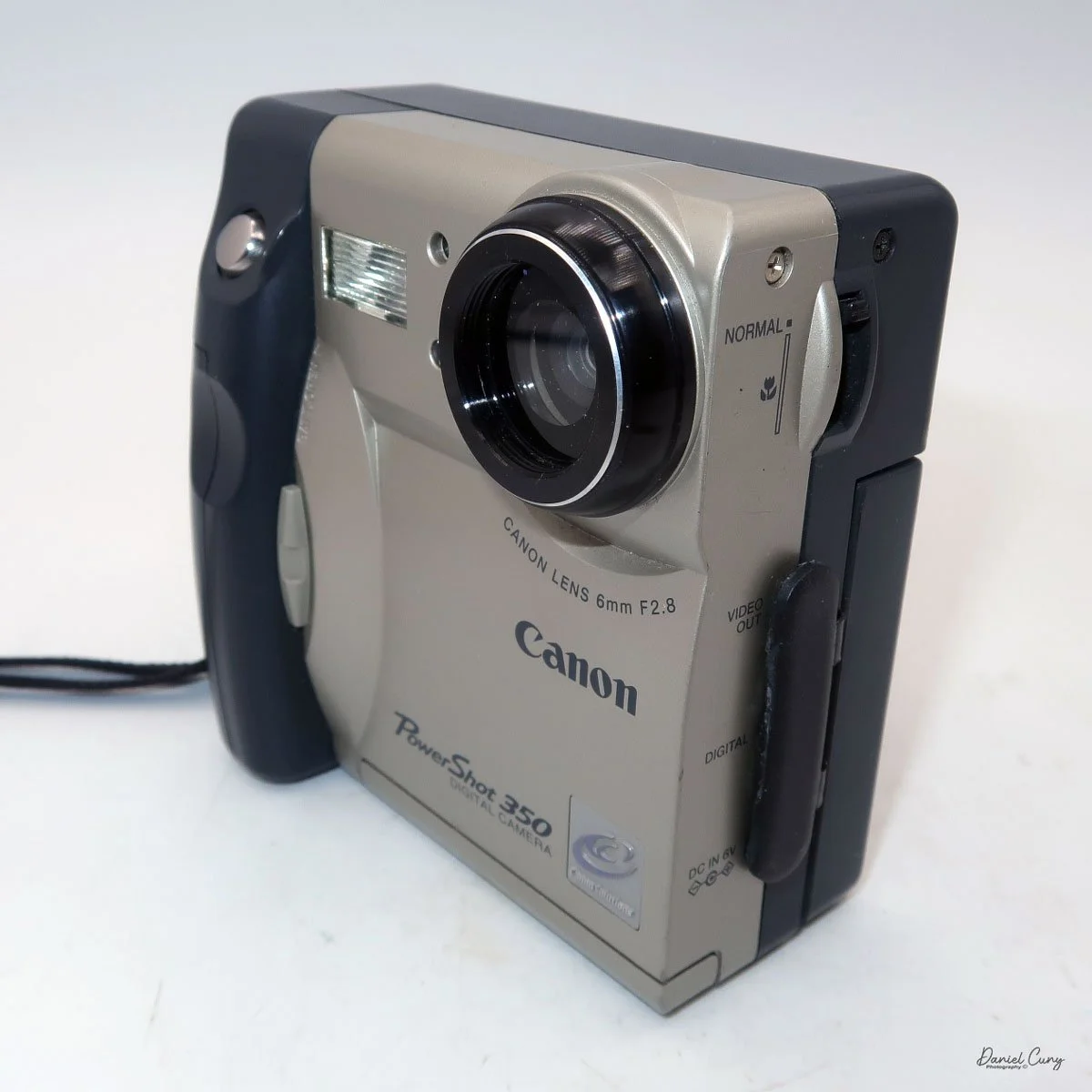
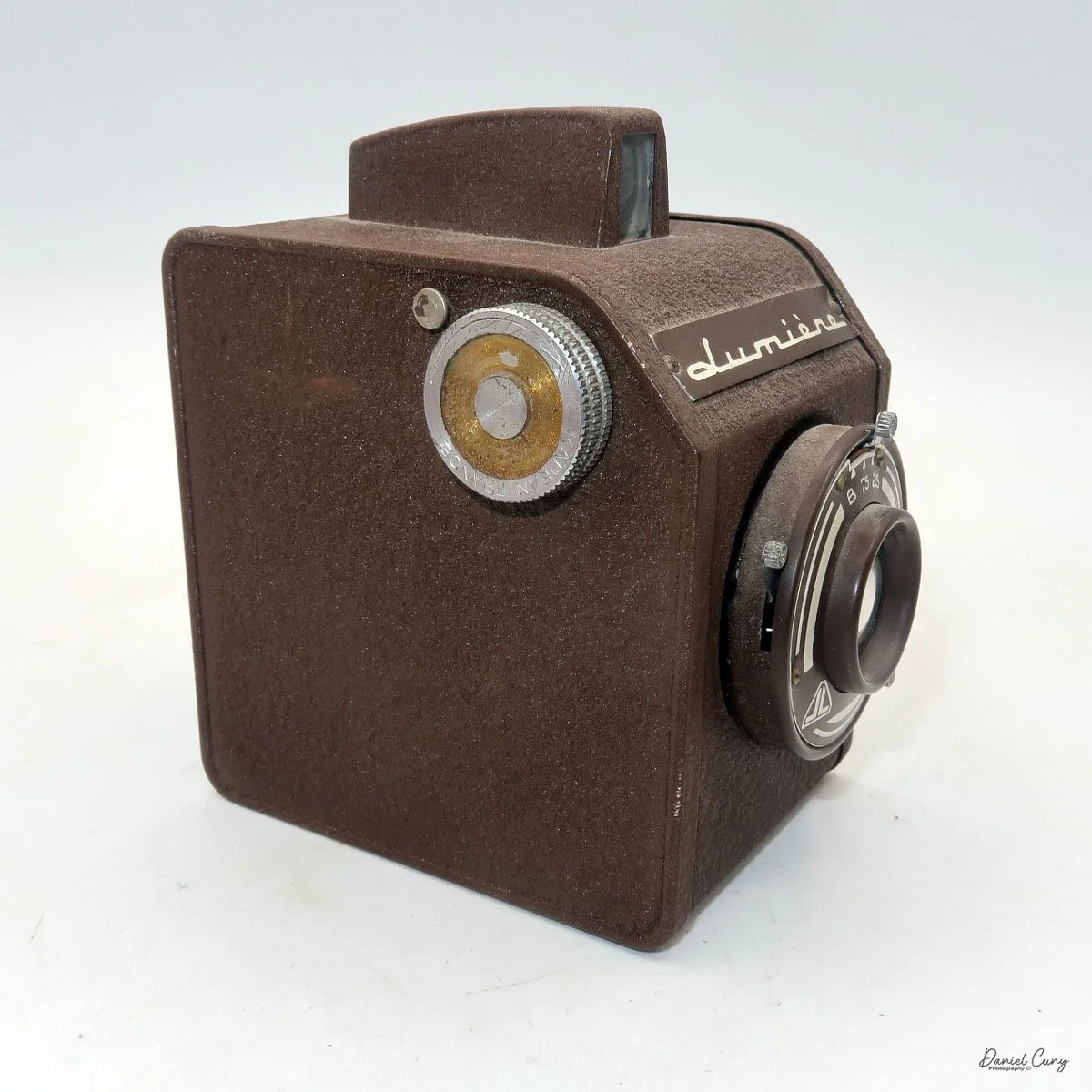
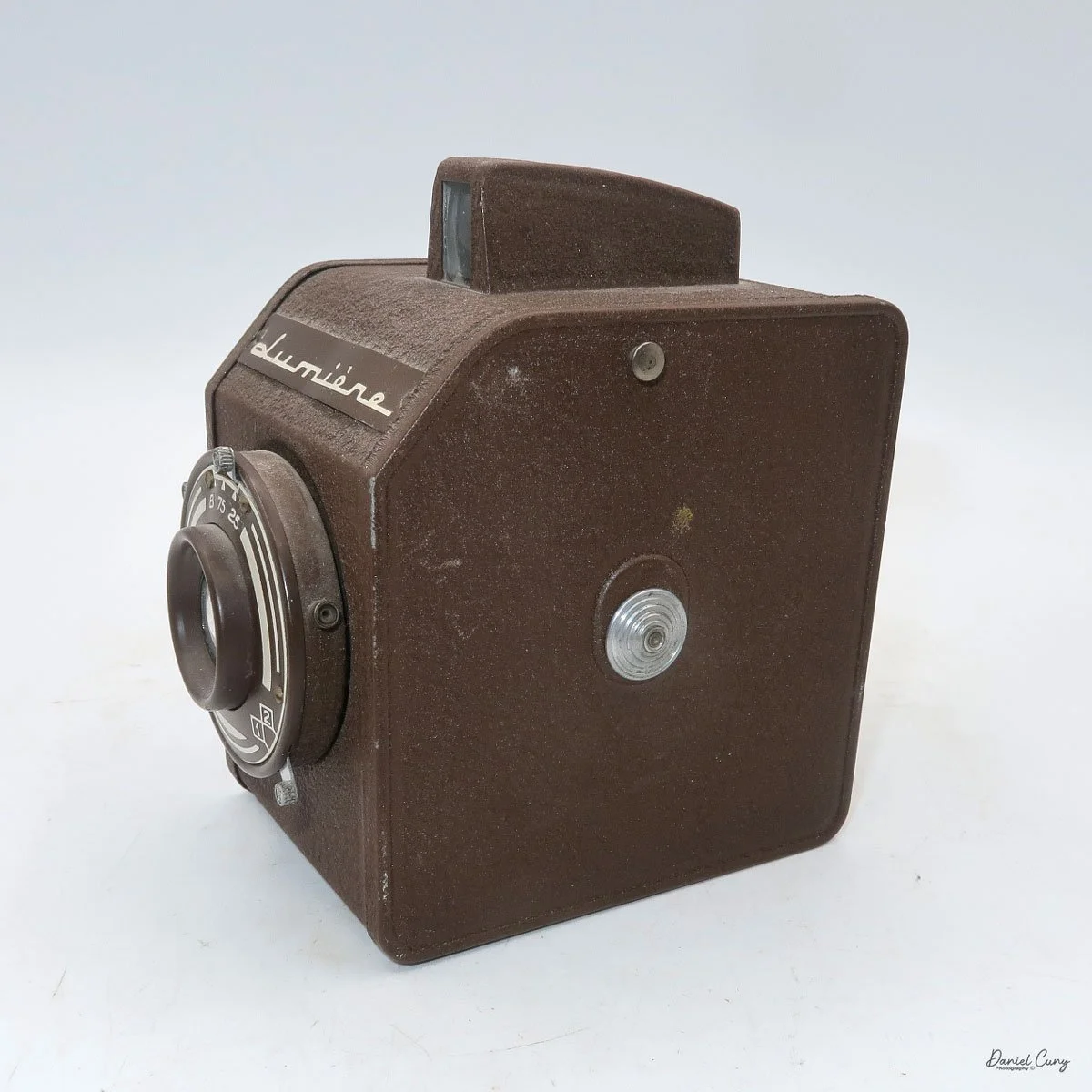
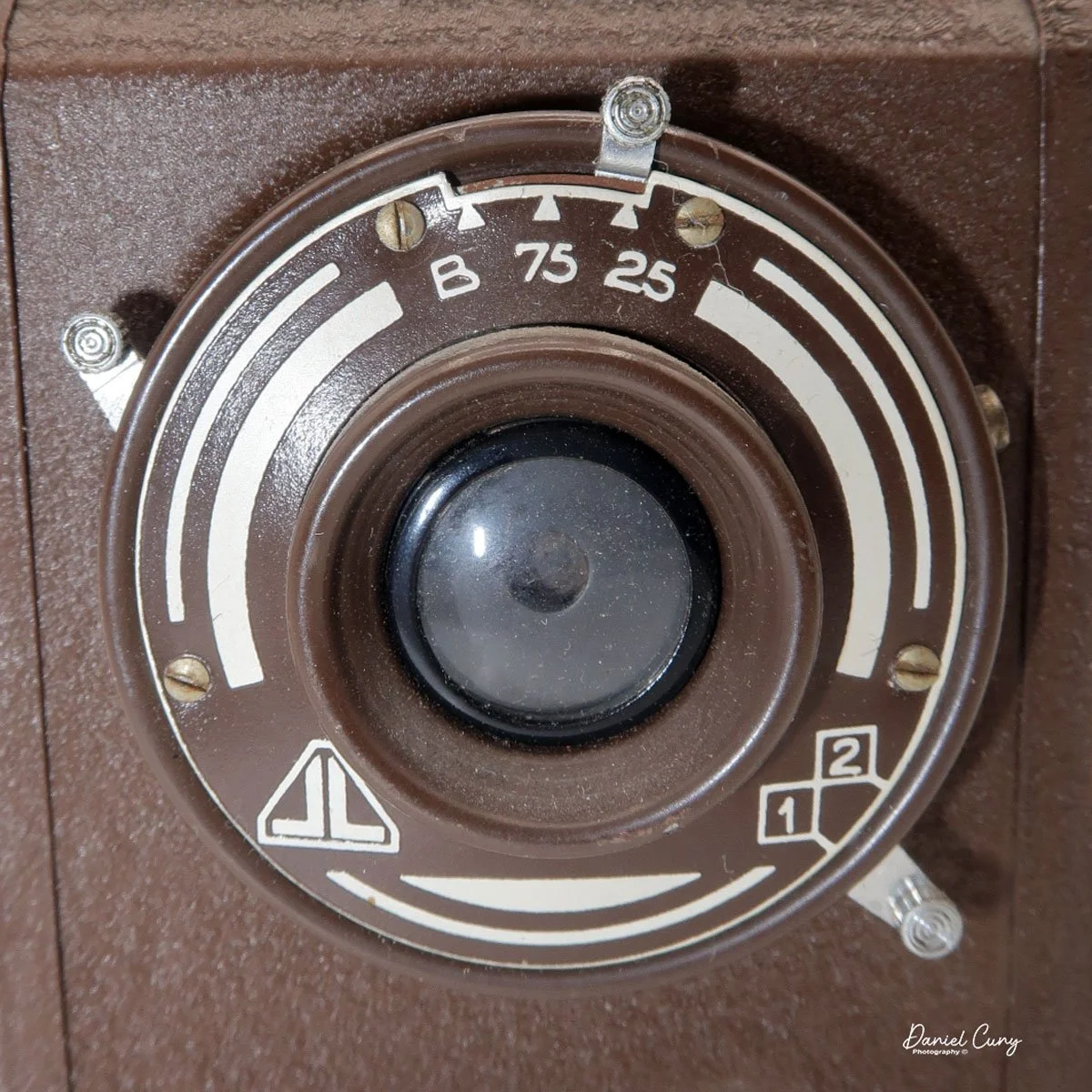
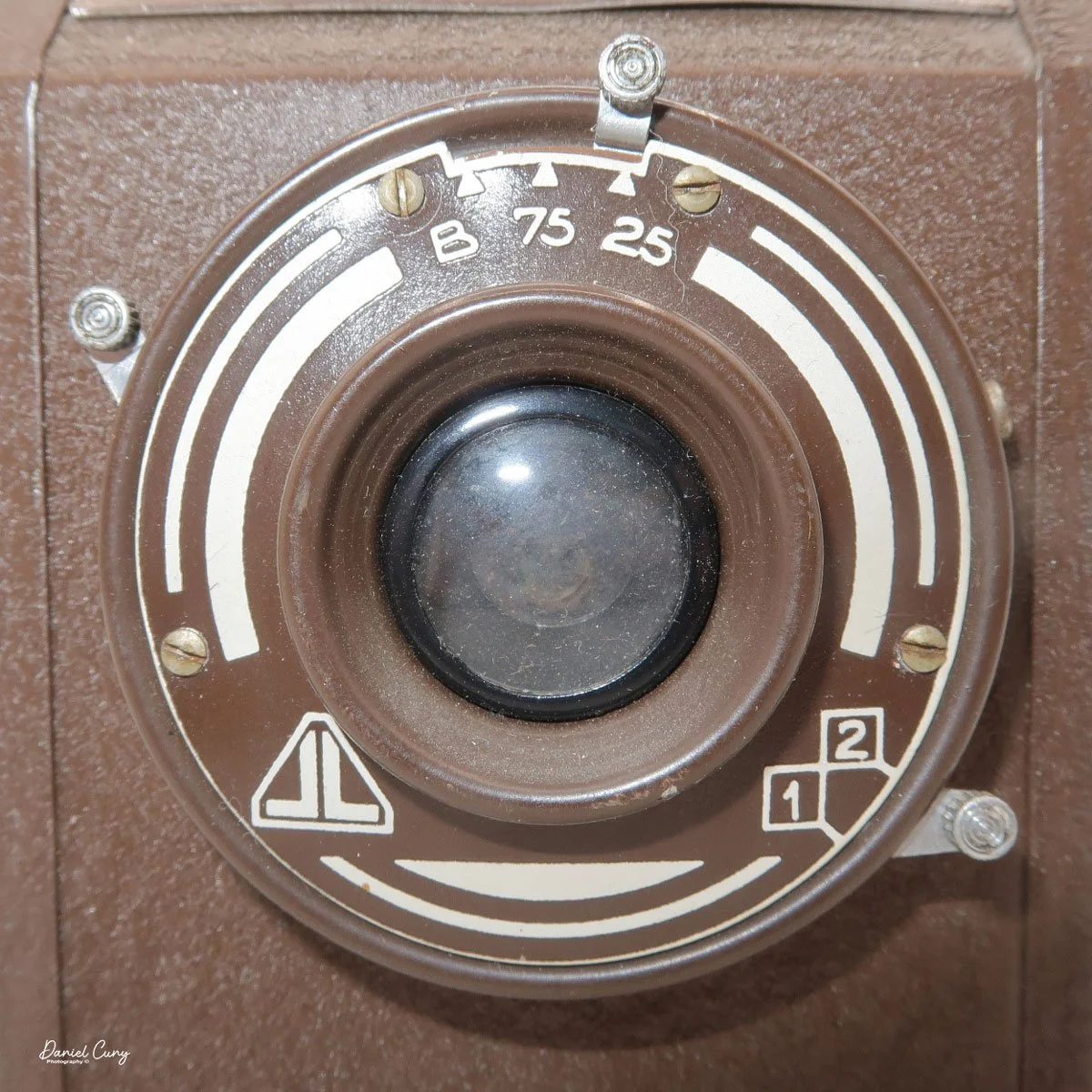
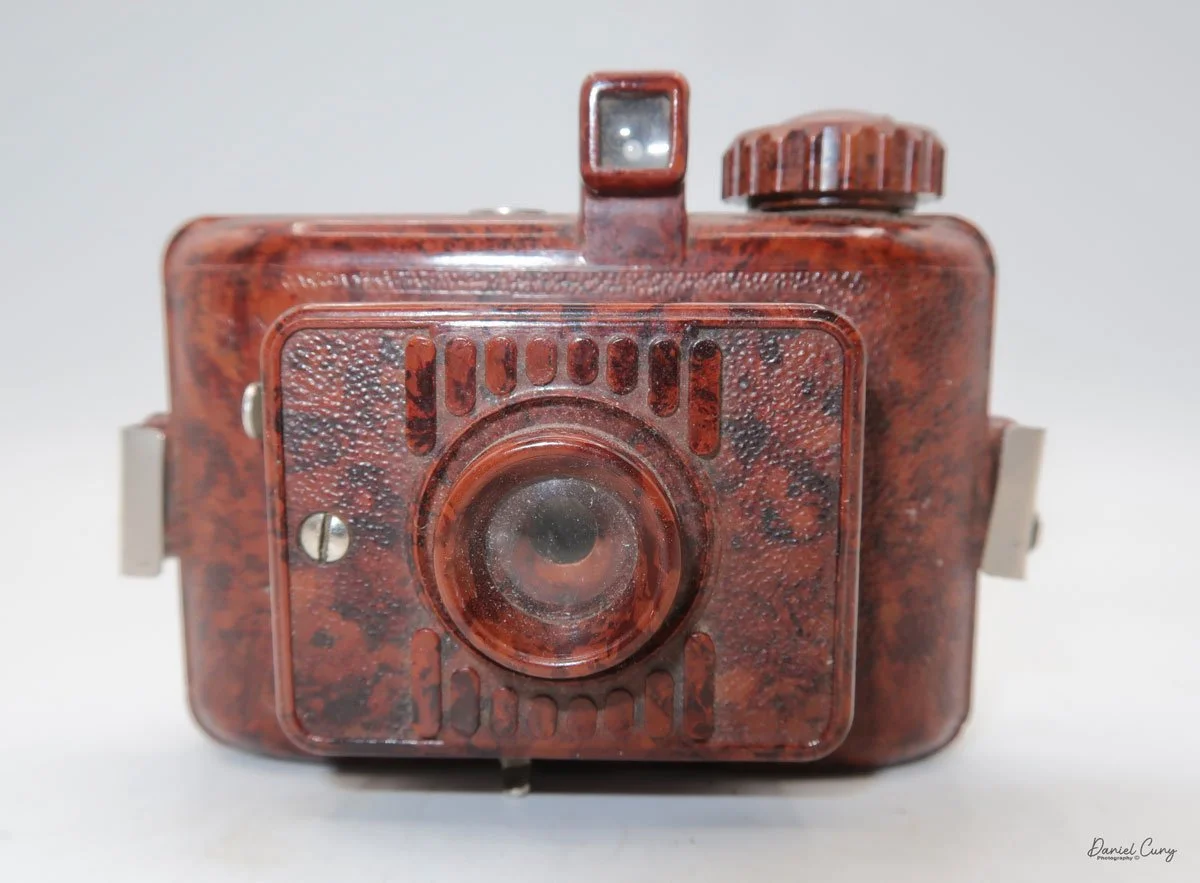
The camera is very basic. The lens is a fixed 5 cm, f/11 meniscus design, though a rarer f/8 version is supposed to exist. Shutter speeds are limited to just two settings: 1/30 of a second and "P" for timed exposures. A small switch on the camera's faceplate, just below the viewfinder, sets the speed. I've also seen a version where the speeds are marked "I" for instant and "T" for timed. My guess is that mine is a later version, but I can't say that for sure.
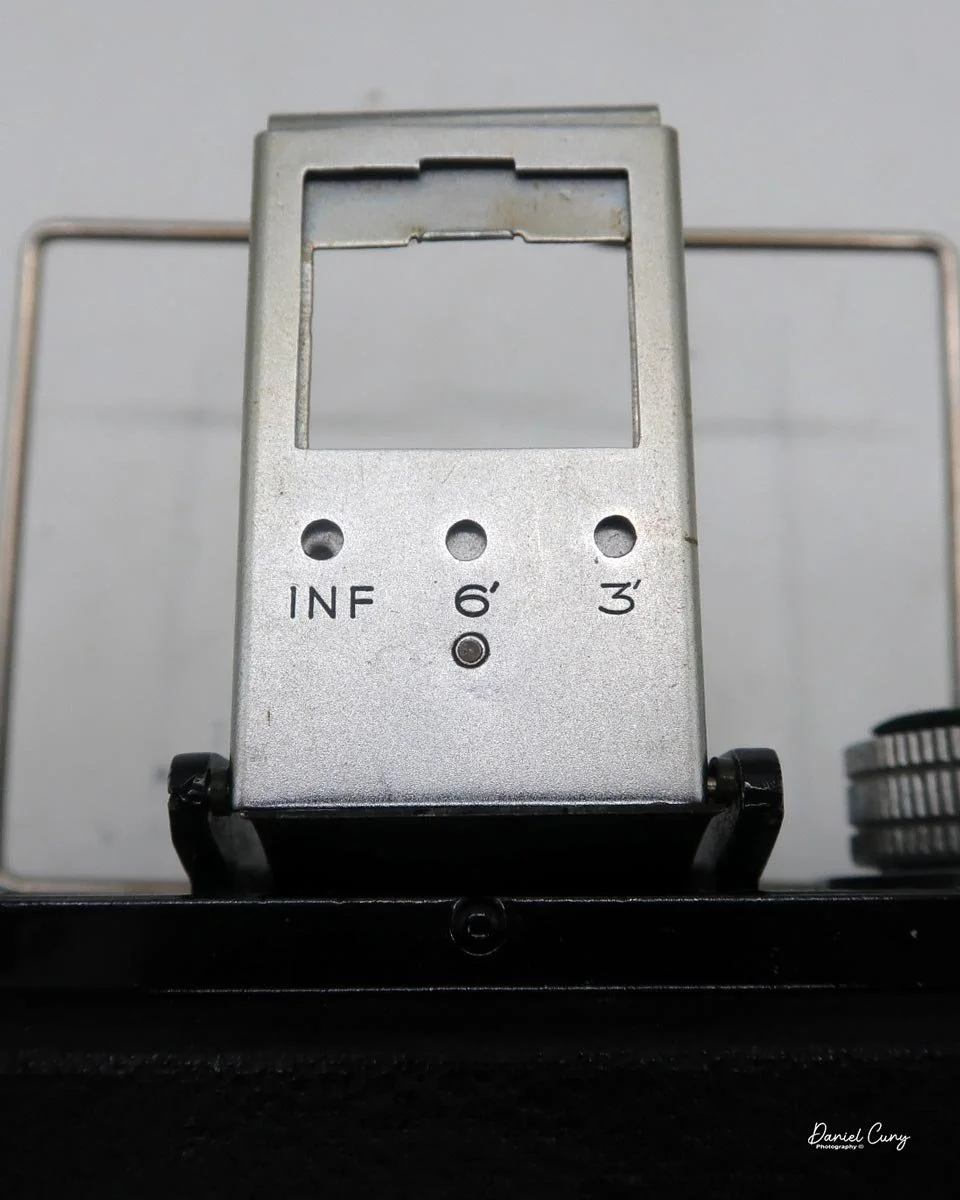
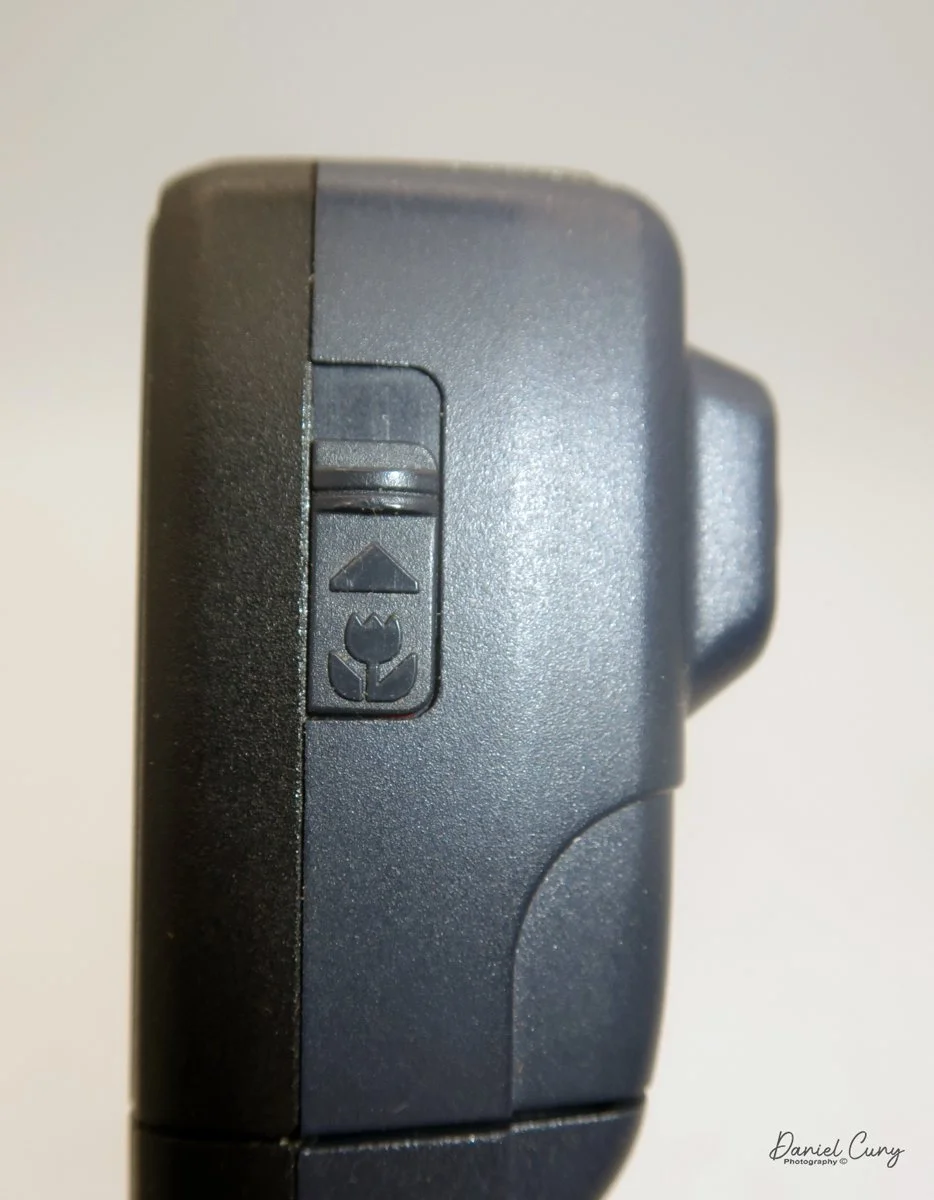
Focusing is done in only two zones. You can set the lens for 1–3 meters or 3 meters to infinity. To focus, you turn the outer ring of the lens until the red line points to the distance you want.
Loading Film and Getting the Duca Ready
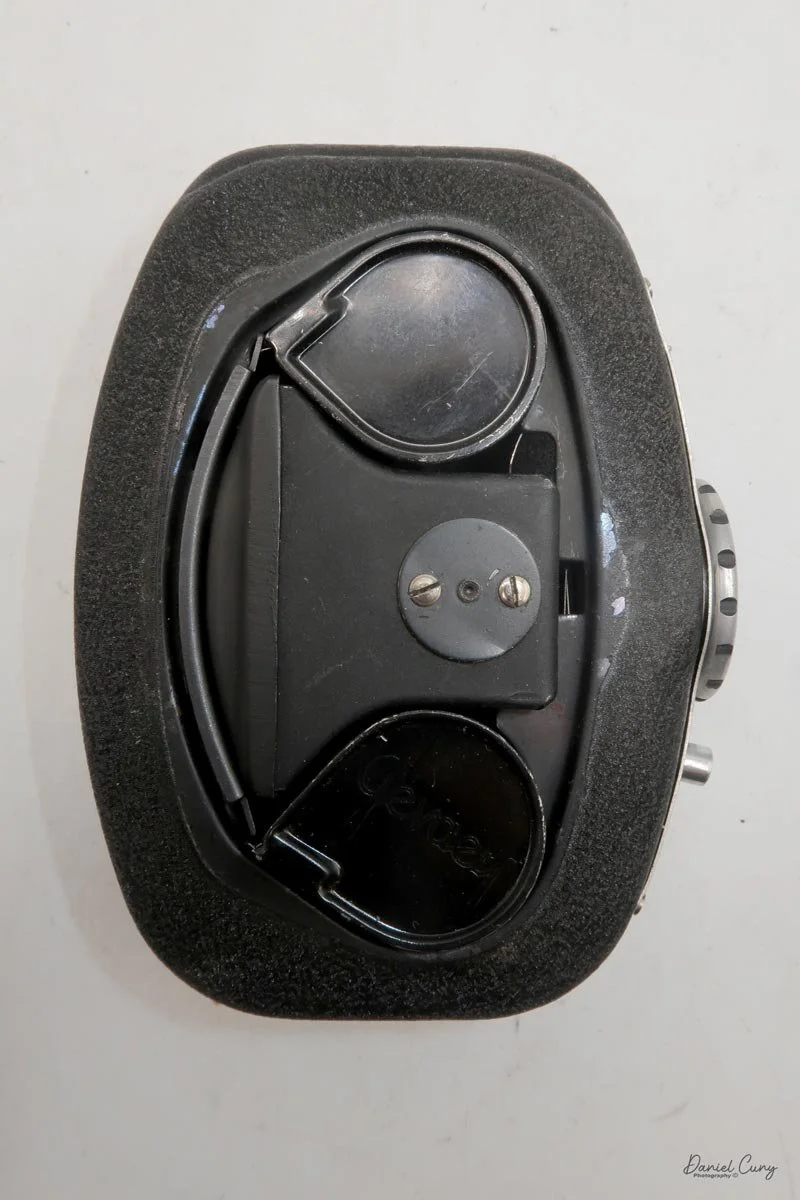
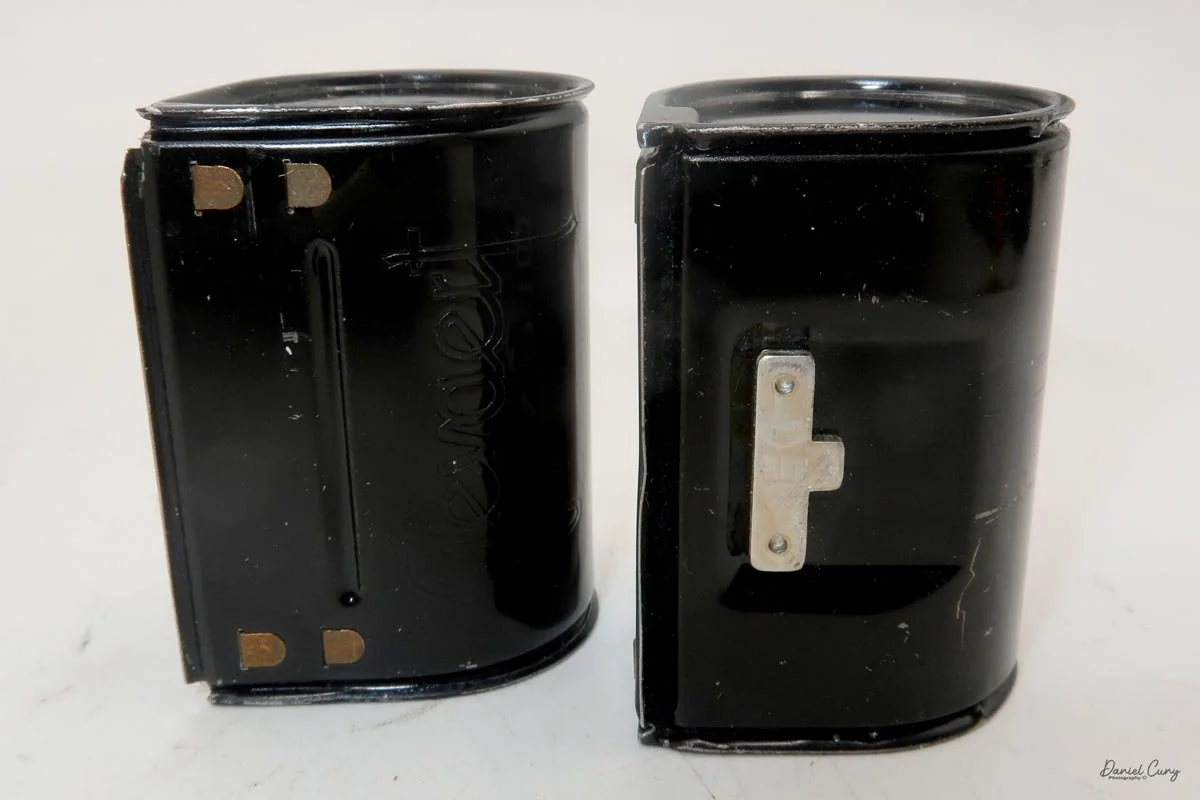
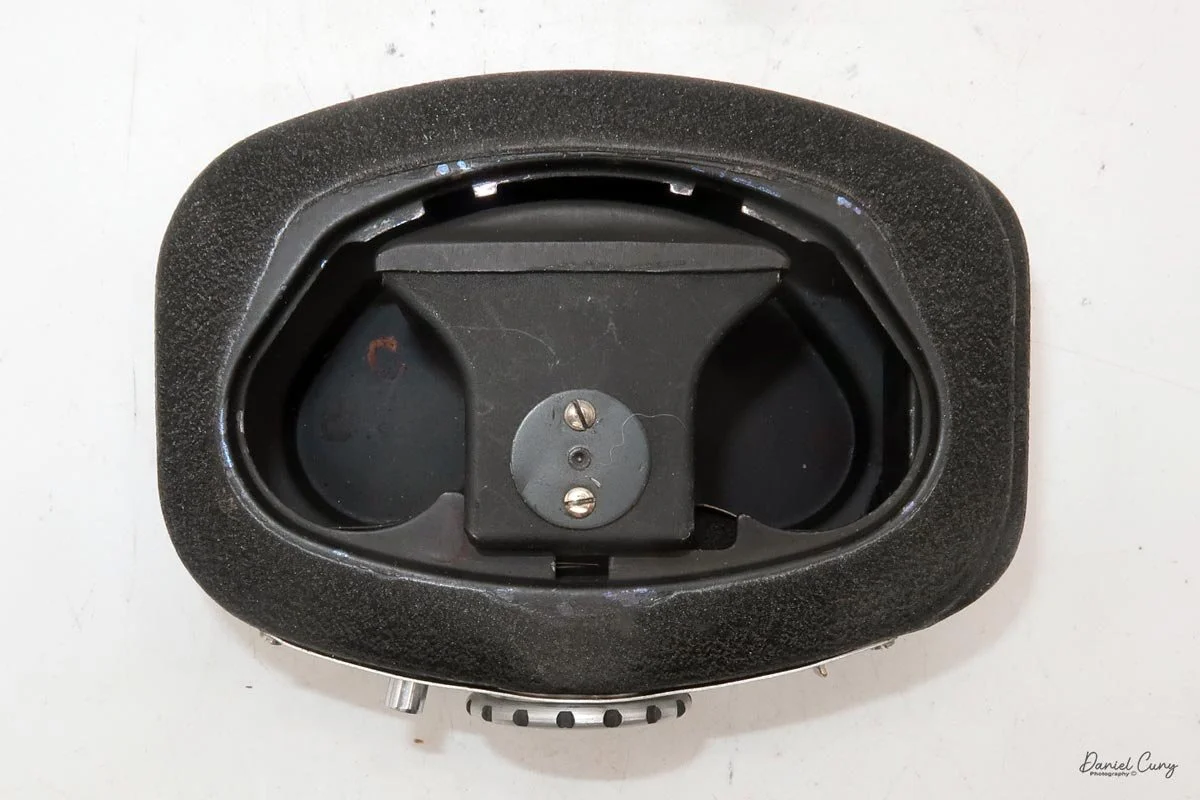
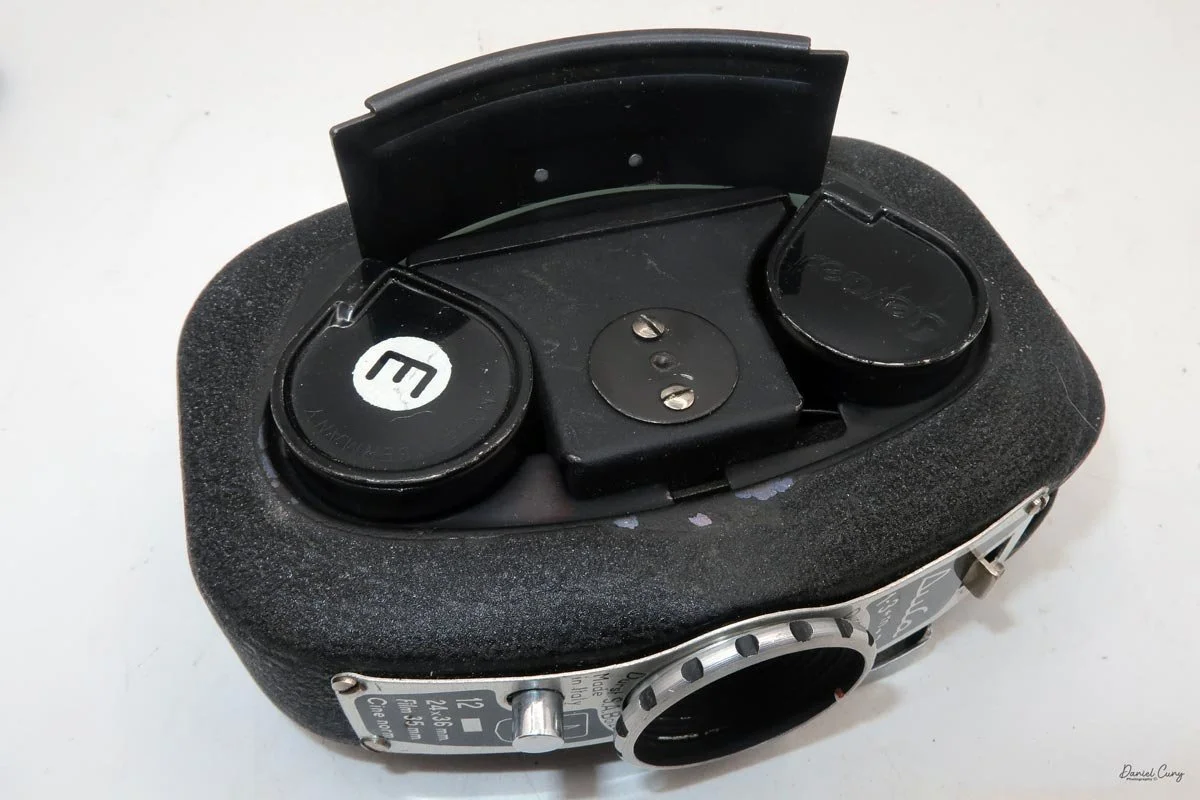
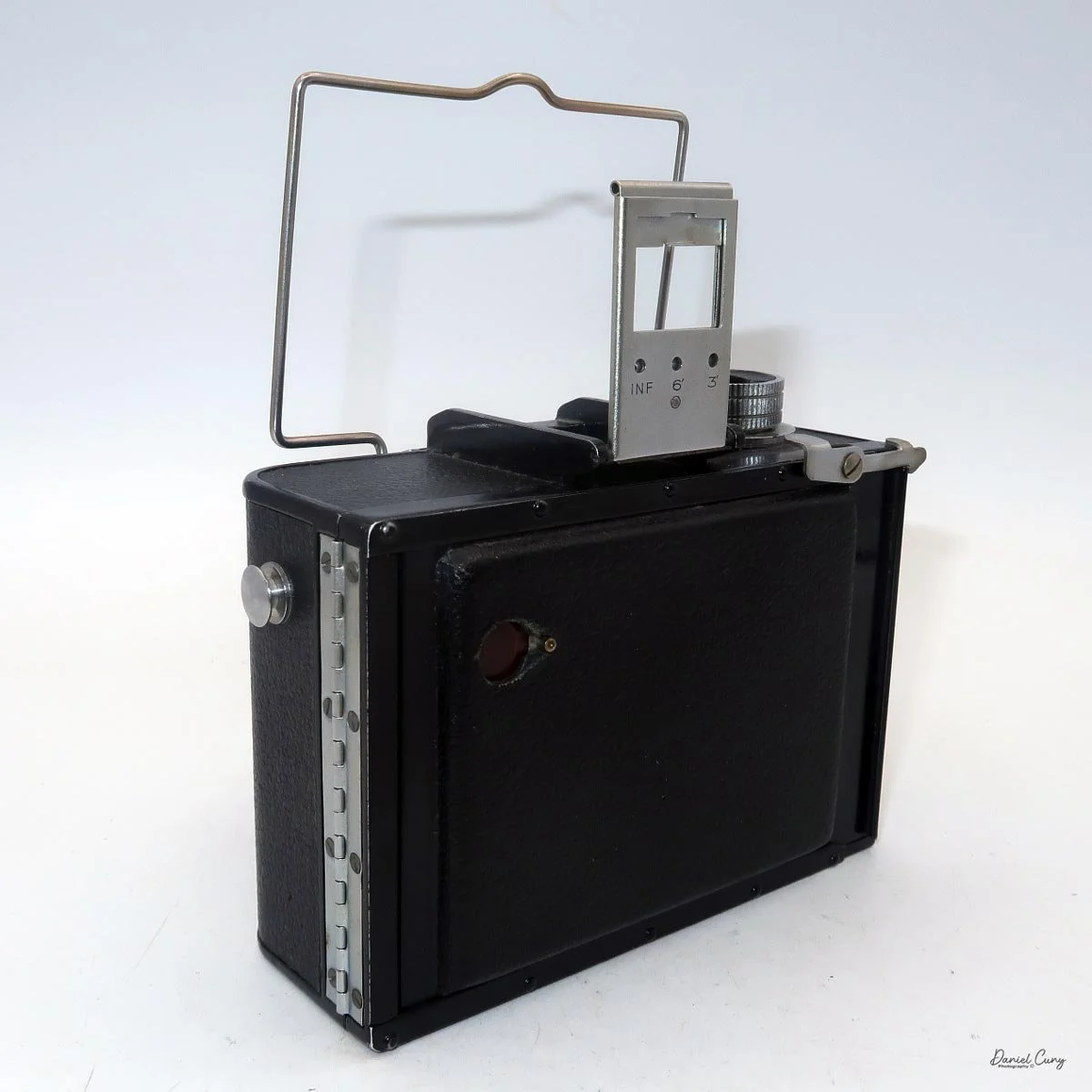
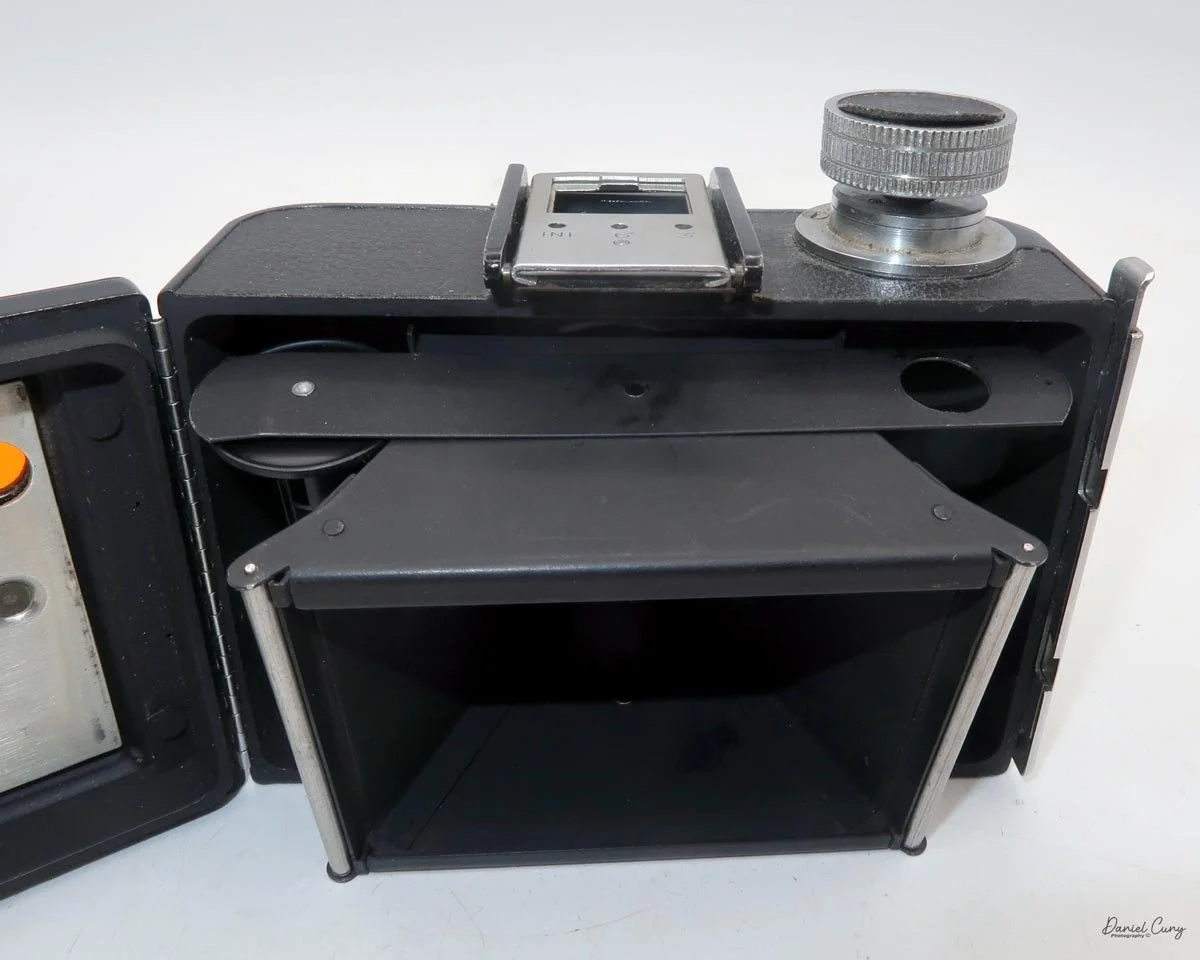
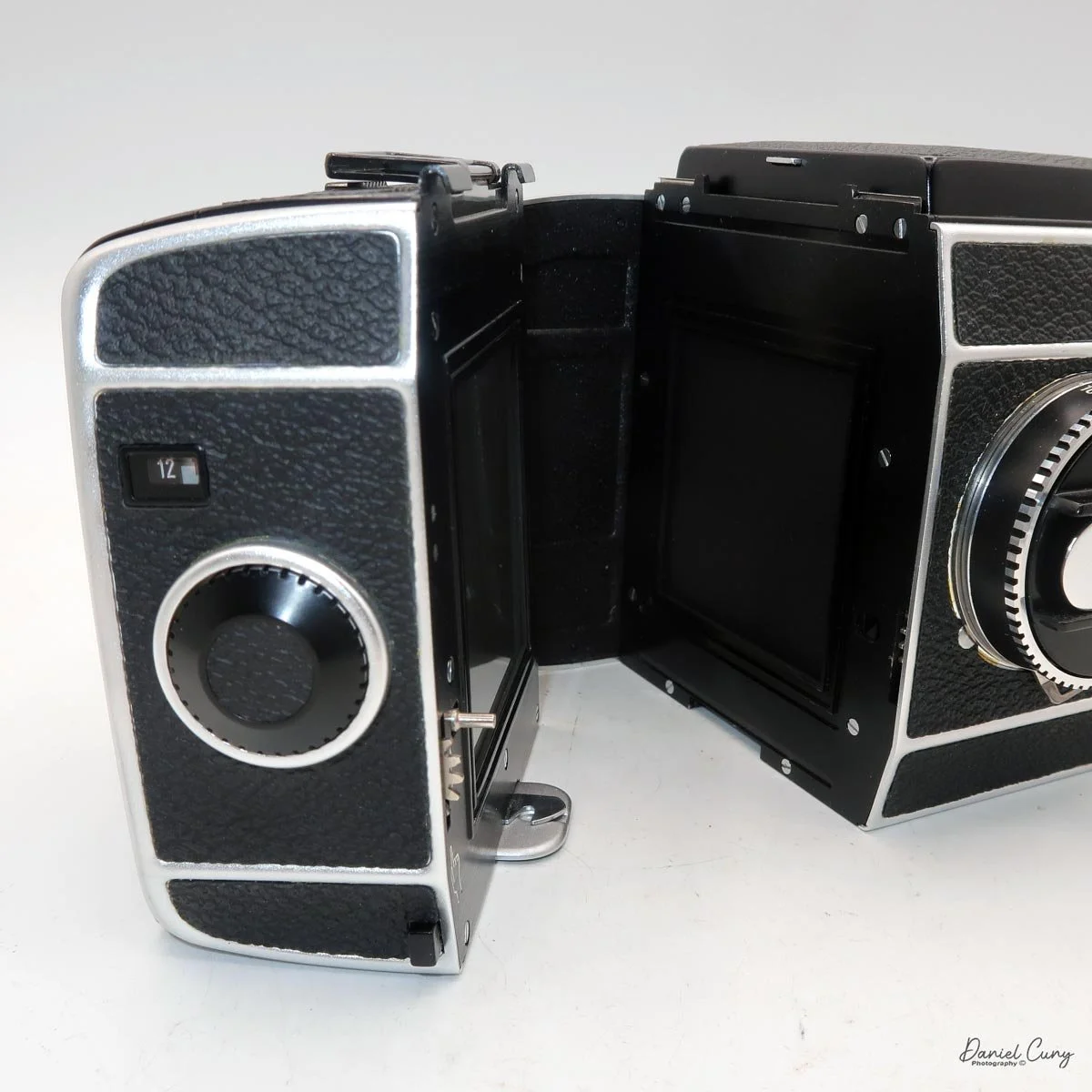
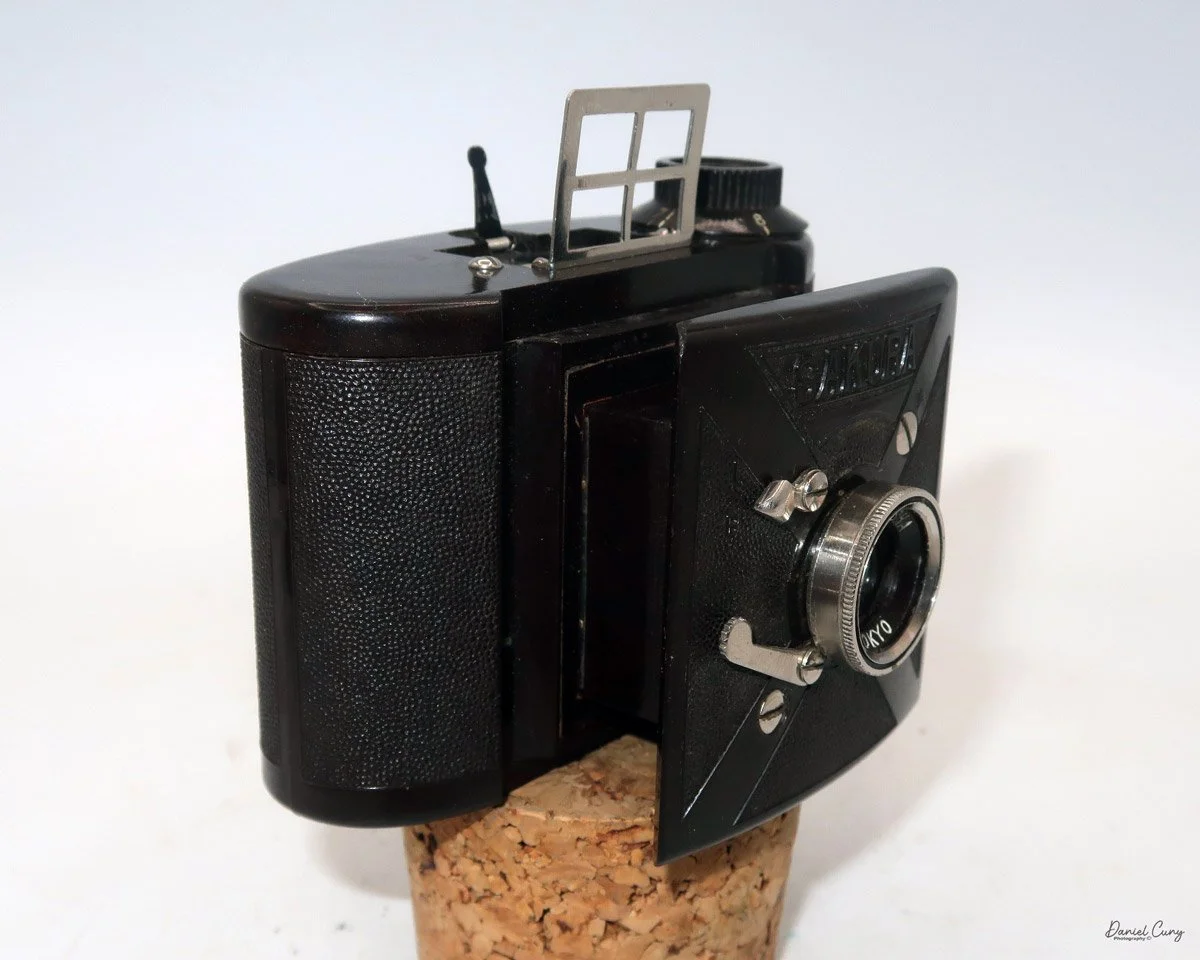
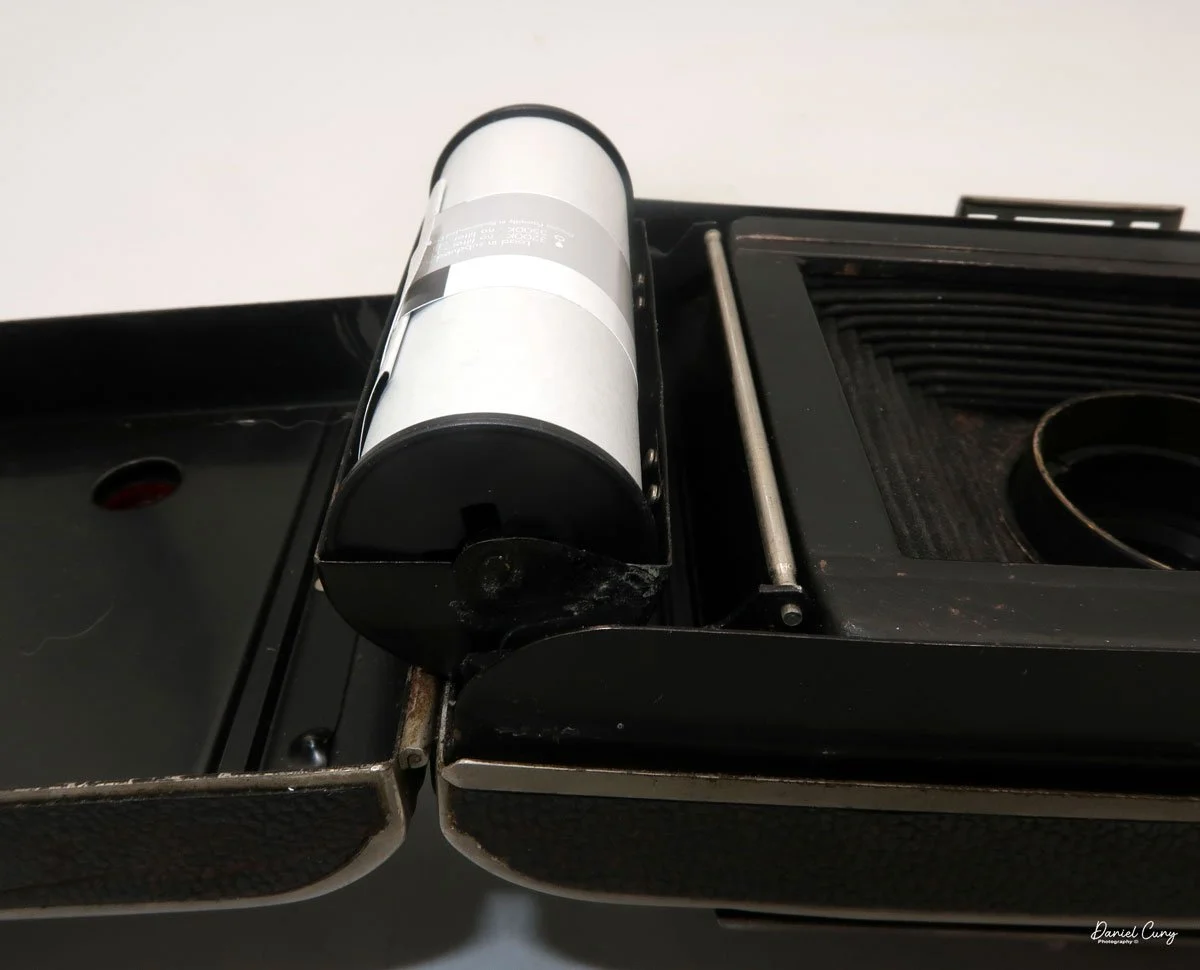
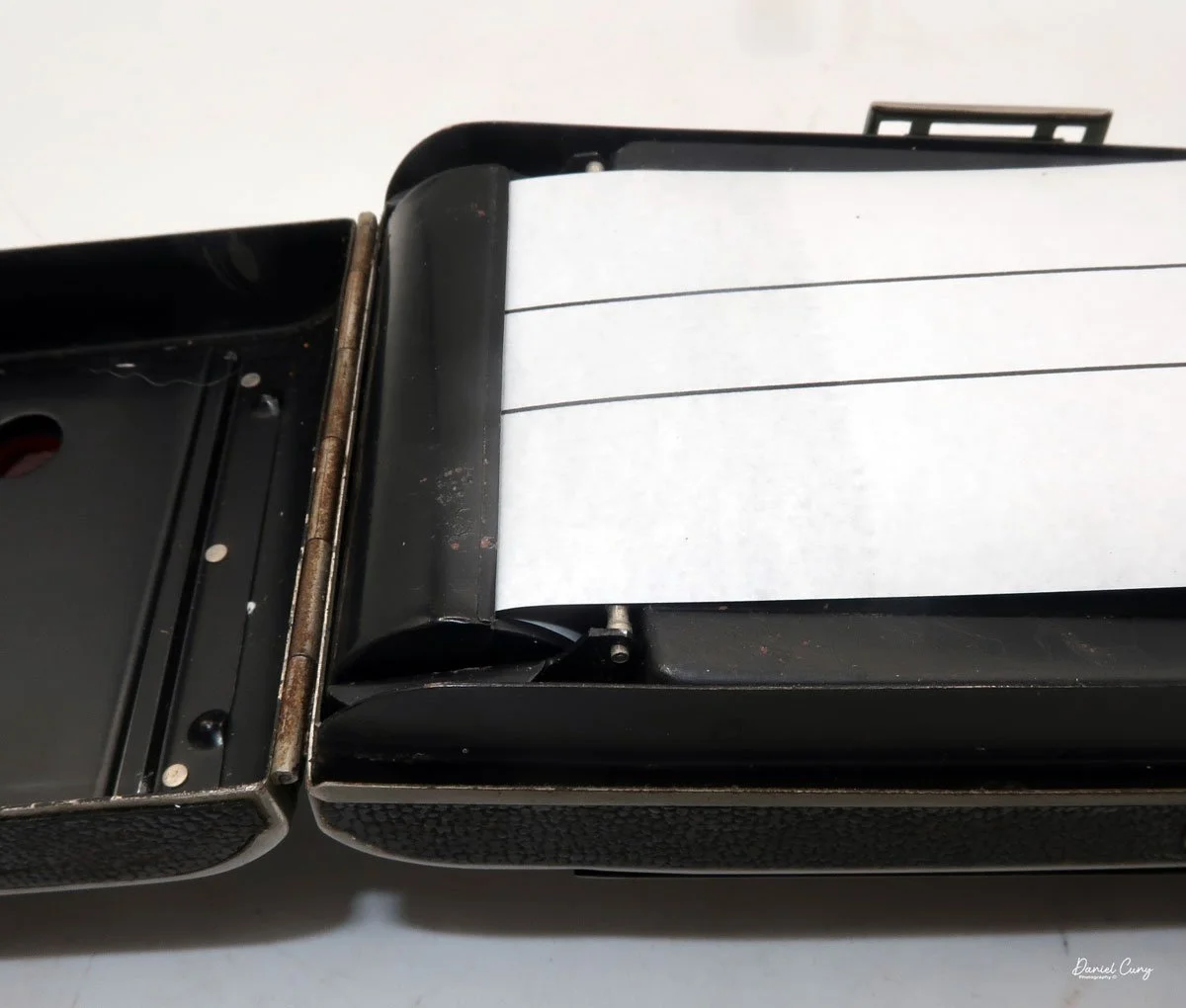
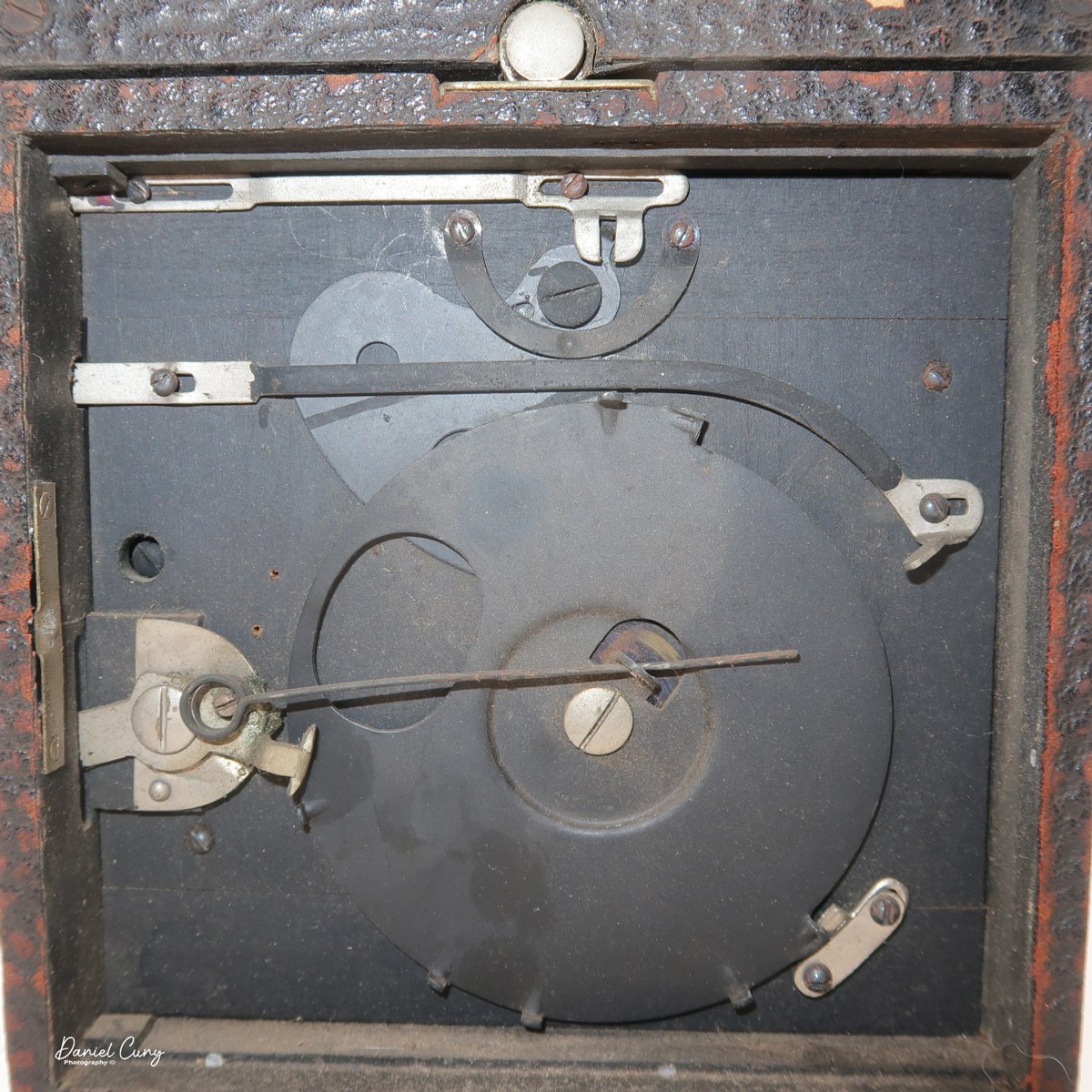
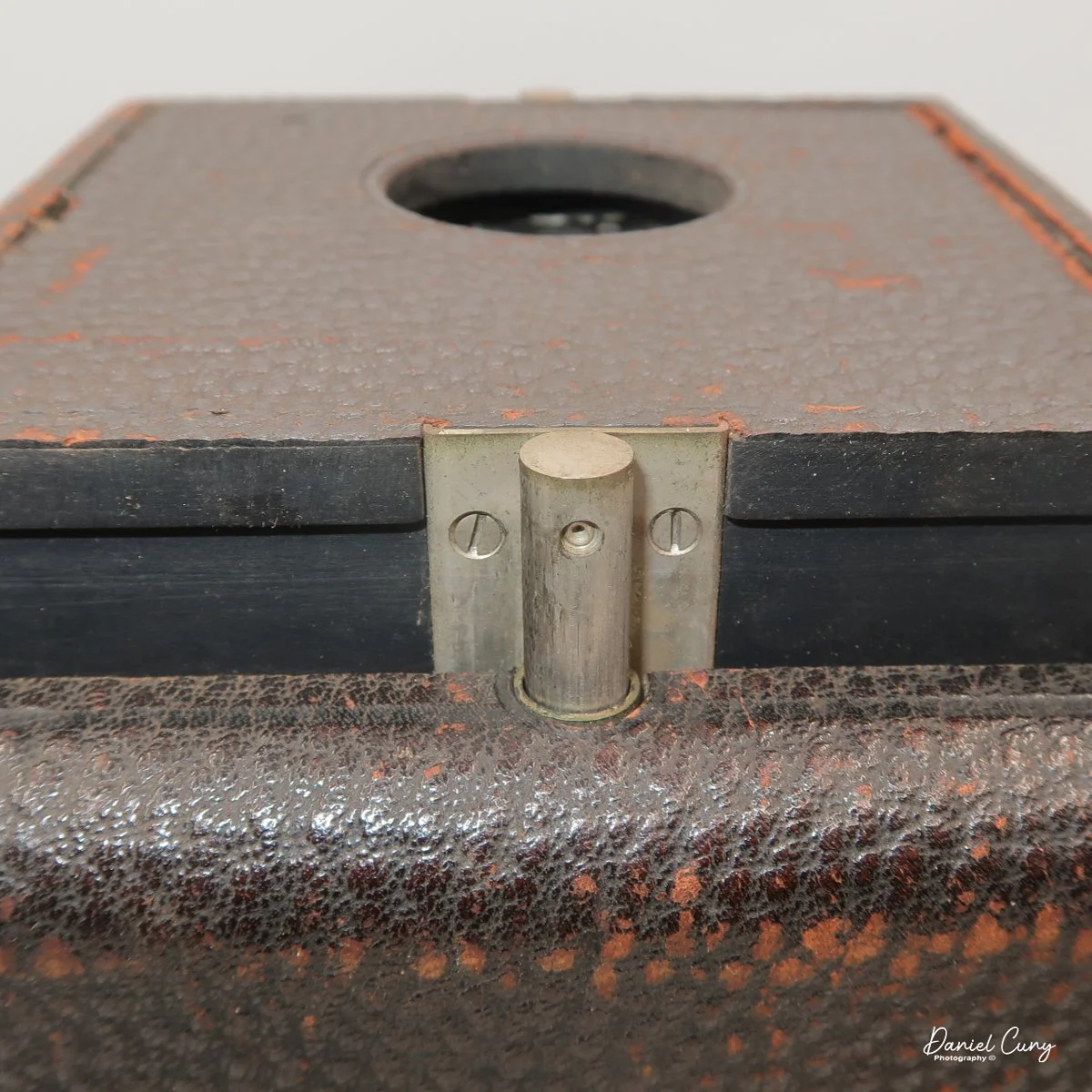
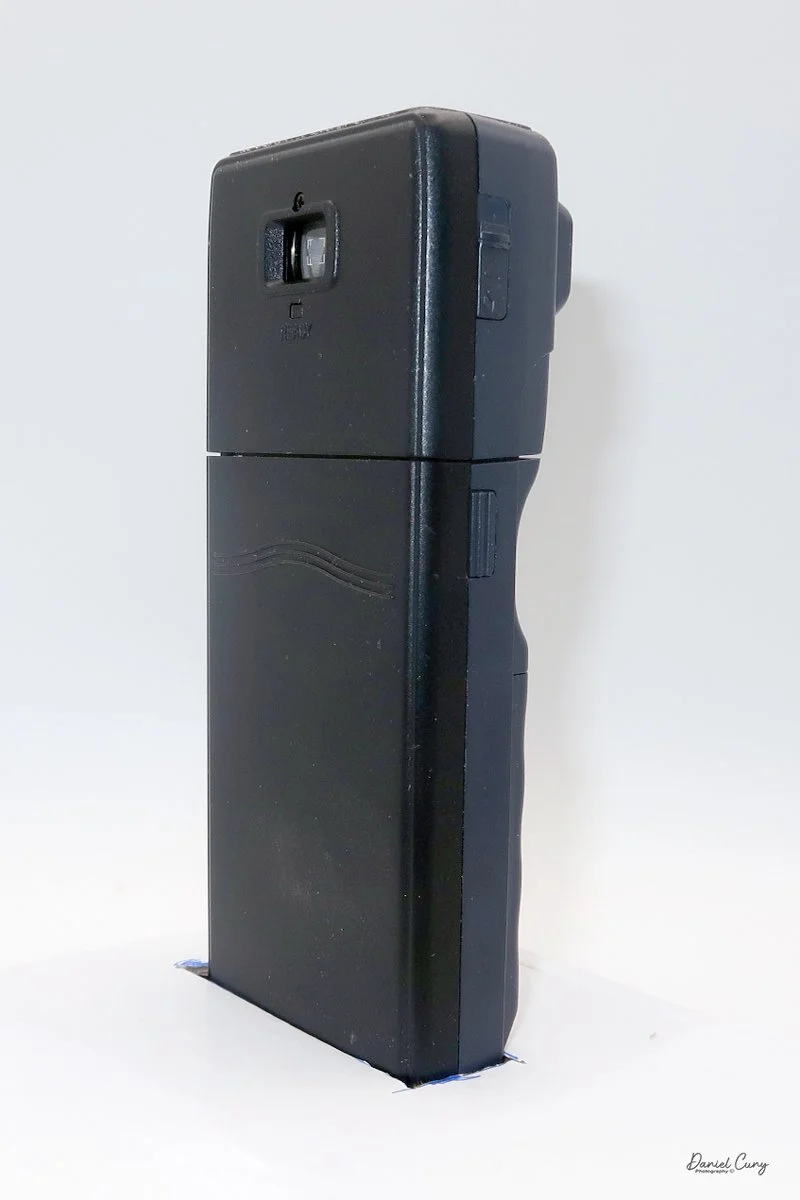
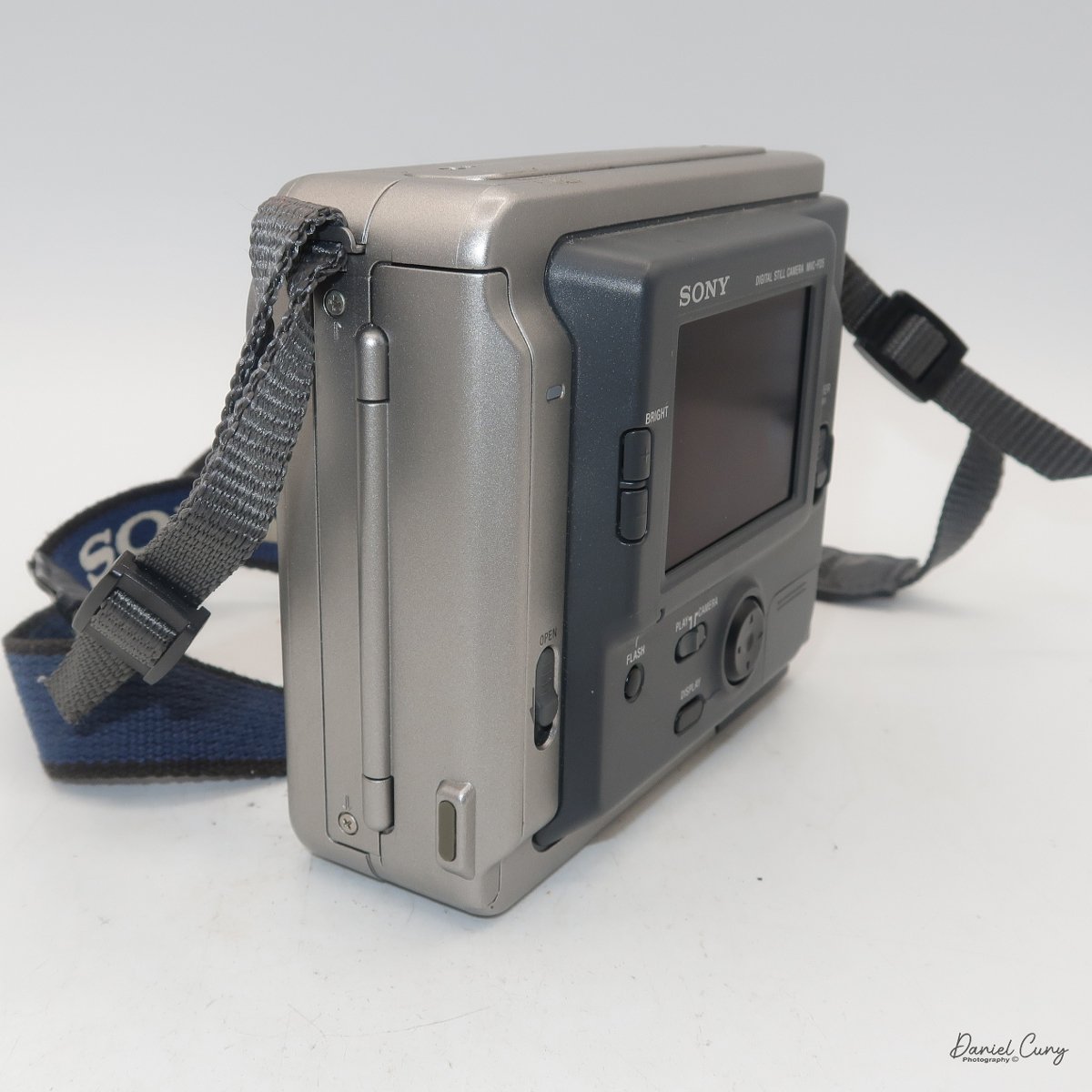
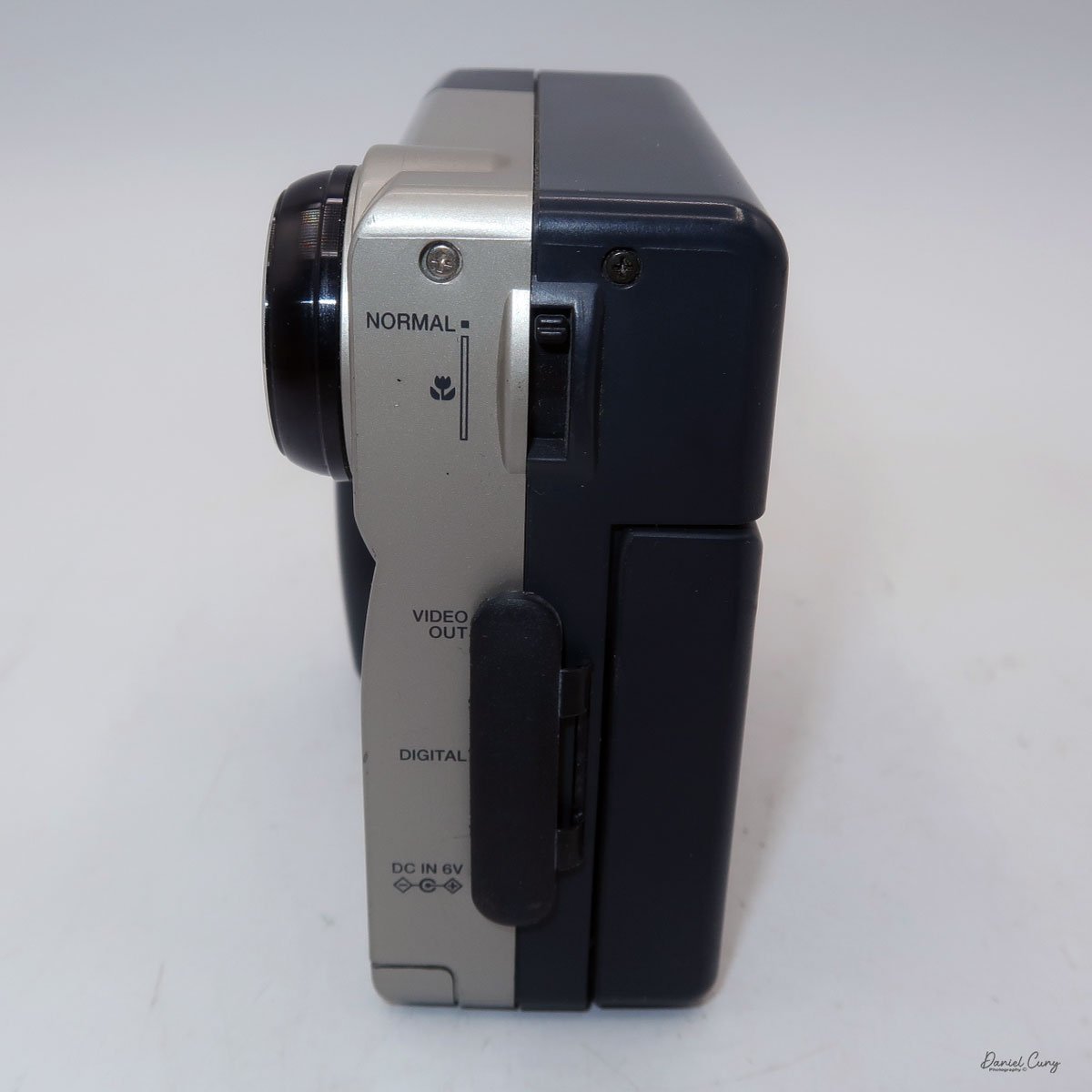
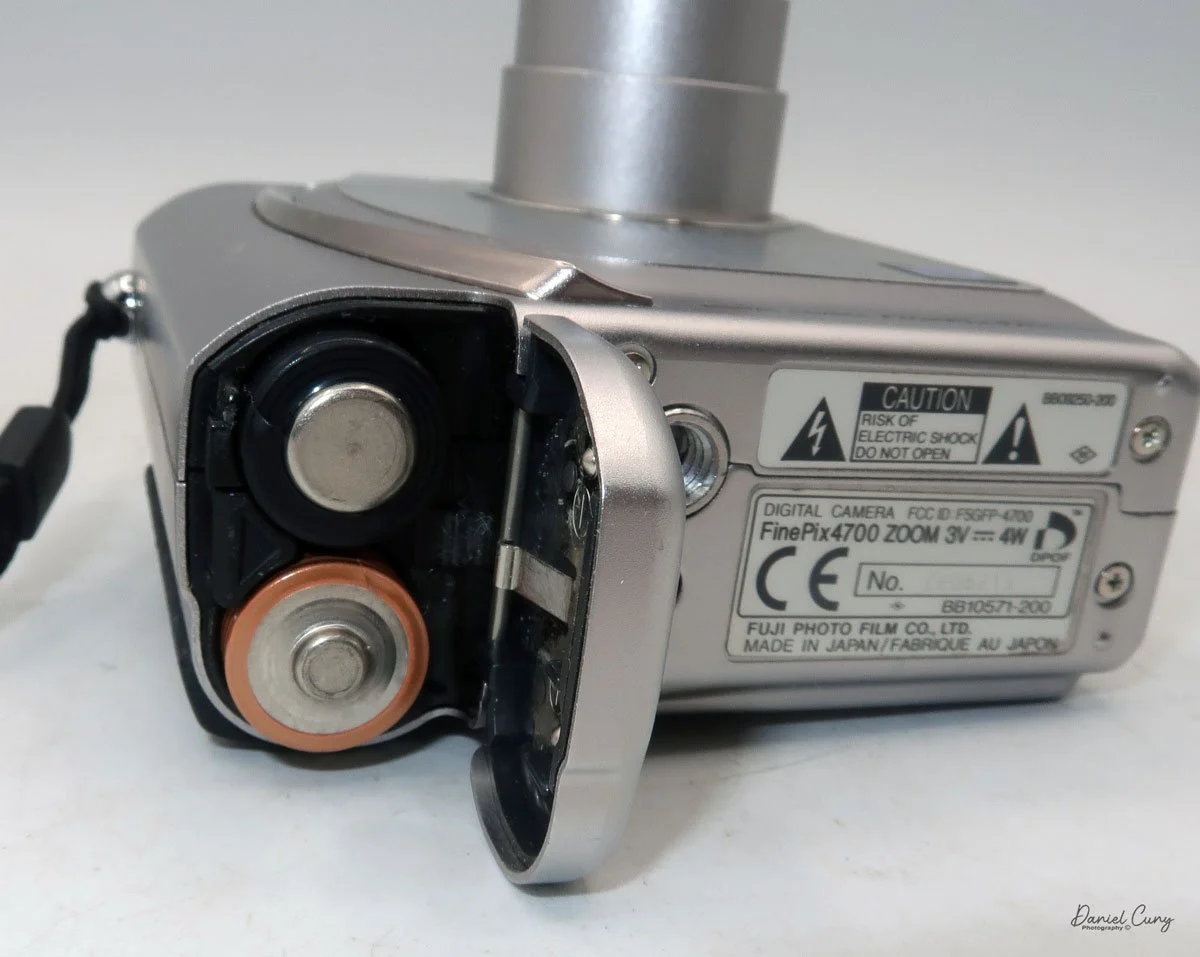
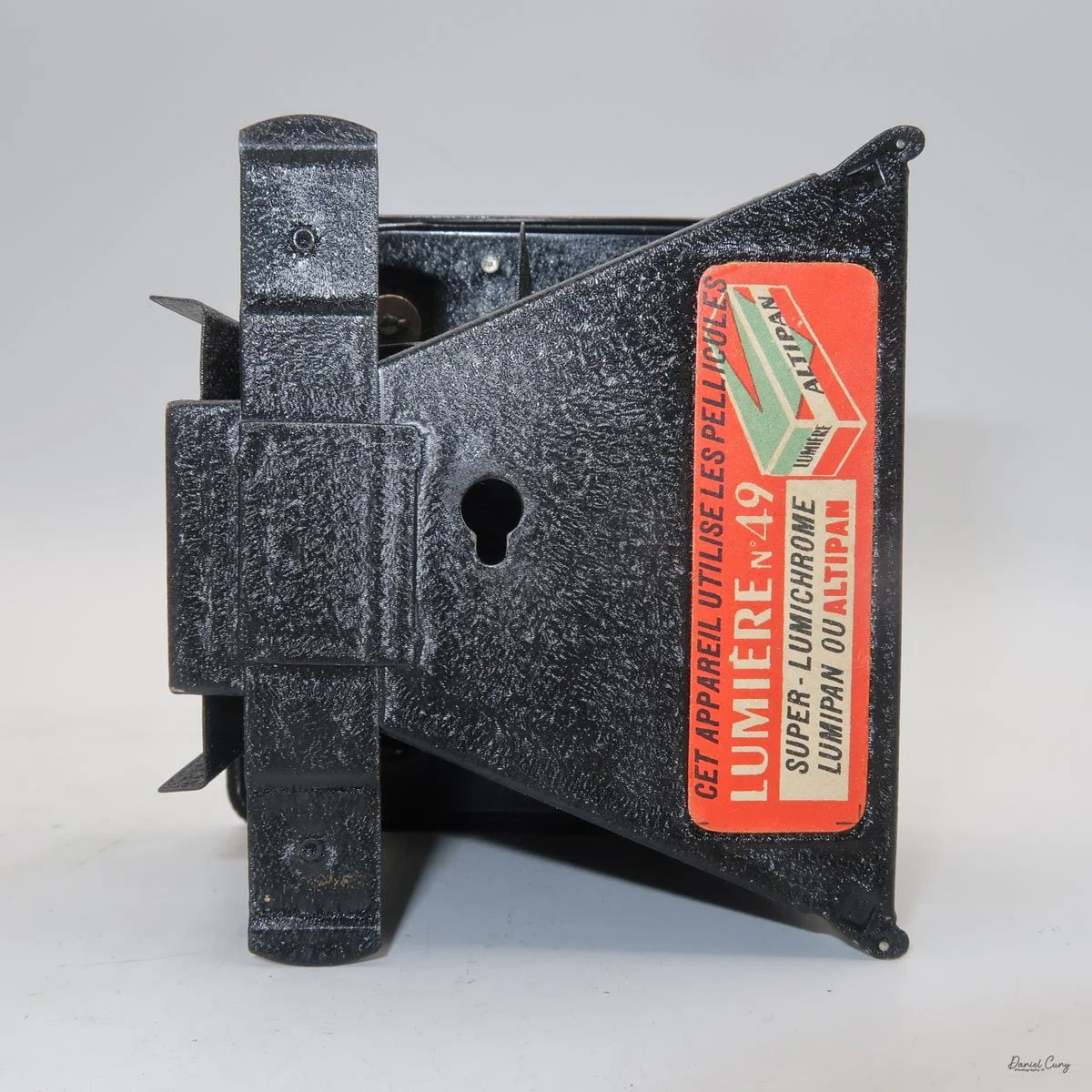
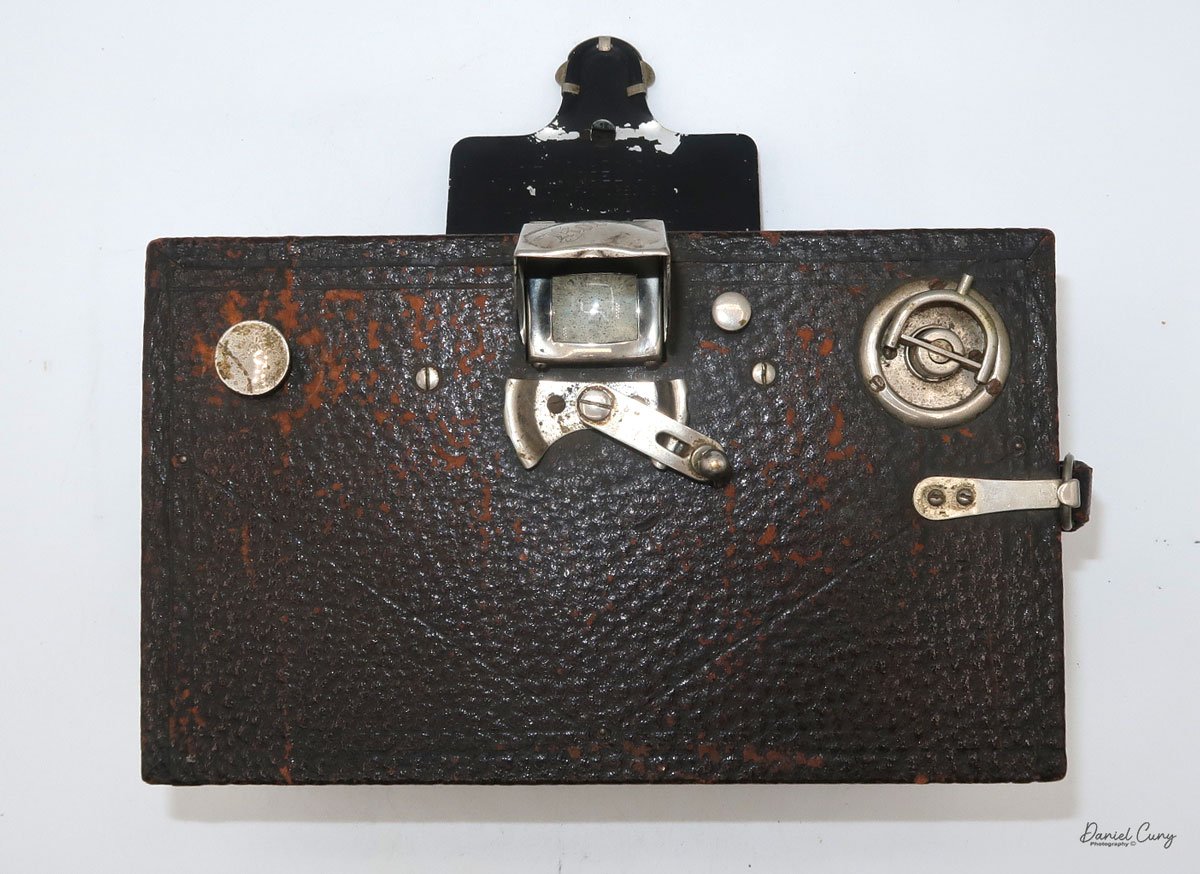
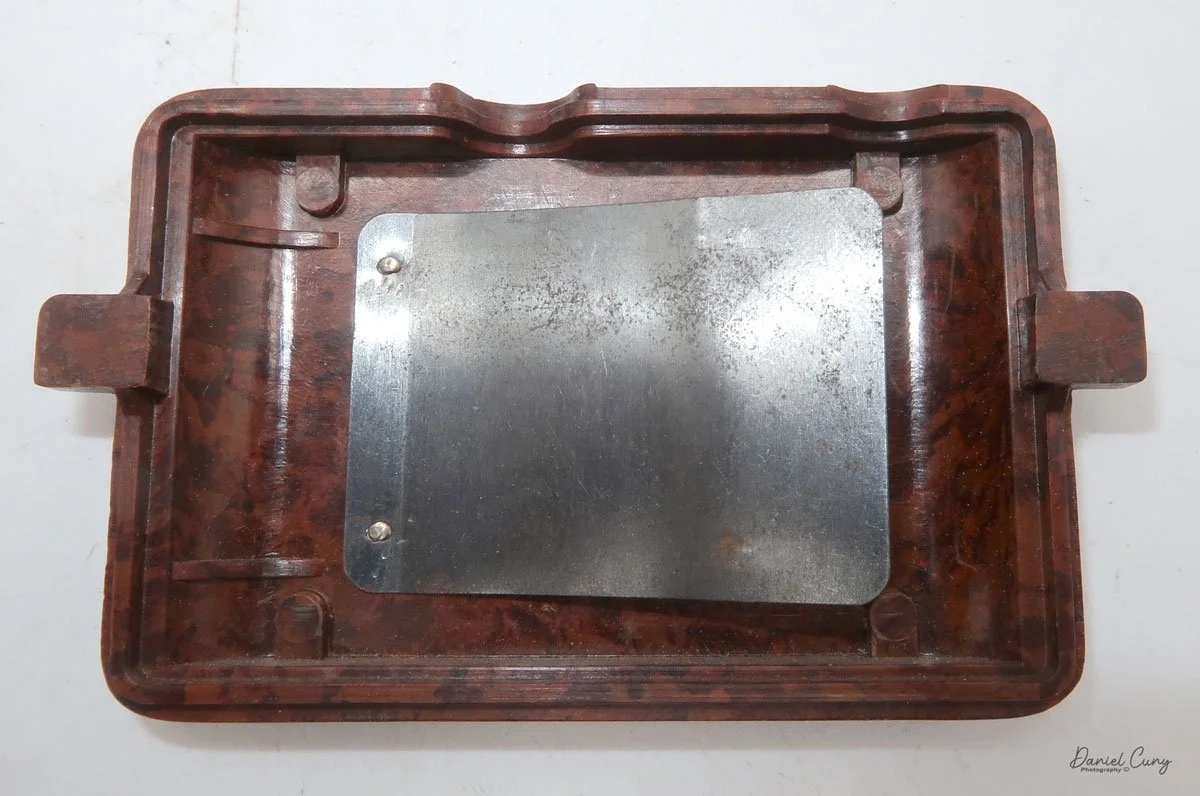
To open the camera for loading, there's a small curled‑up lip on the right side of the body that you lift to swing open the film door. Inside, you'll see the two Agfa Karat cassettes. They pop out along with the pressure plate, which sits just behind the film gate and pulls straight up and out for loading.
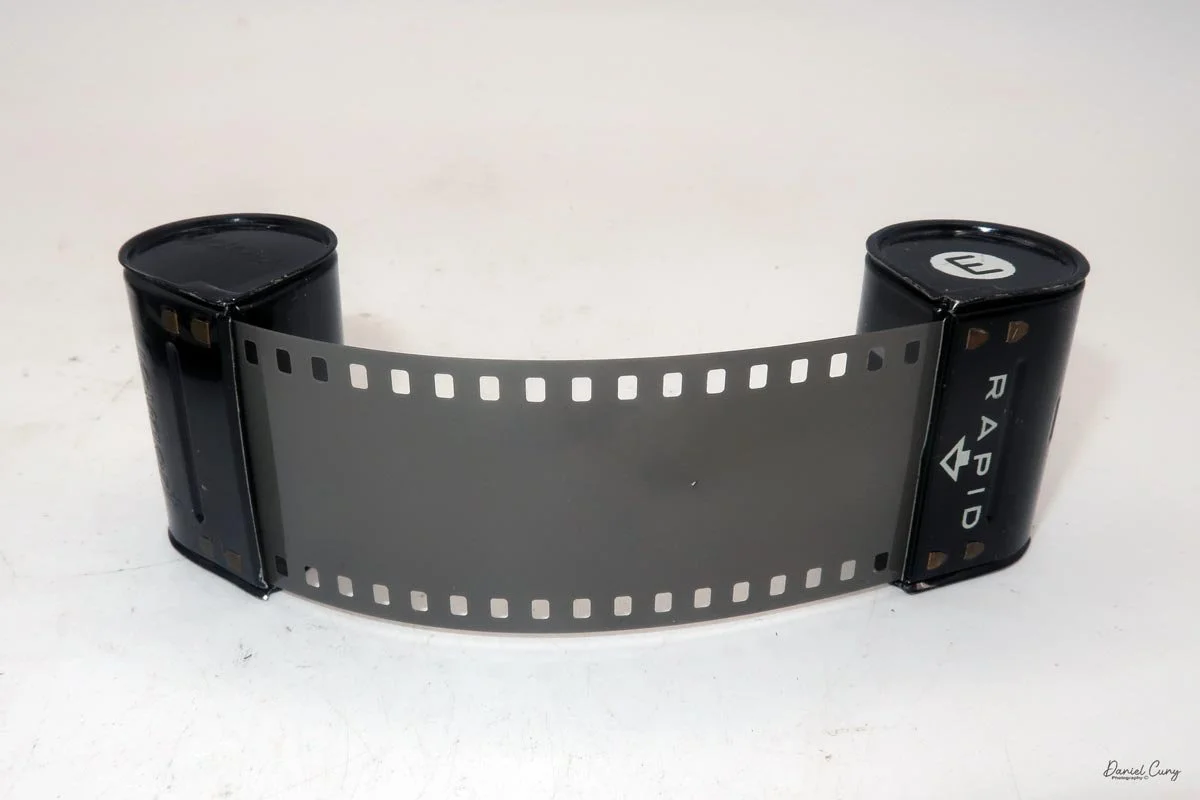
As mentioned, the camera takes Agfa Karat cassettes. When these were sold new, each roll of 35mm film was cut for 12 exposures, and the front of the camera proudly states that it takes 12 photos per roll. Since I have bulk 35mm film and two cassettes, I loaded my own.
I put one of the cassettes and my bulk loader into a dark bag. Inside the bag, I opened the loader, pulled out what I guessed would be enough film for 12 exposures, and added a bit more to be safe. I fed the film into the first cassette and closed up the loader, leaving a short length to thread into the second cassette. Then I unzipped the dark bag and removed the loaded cassette.
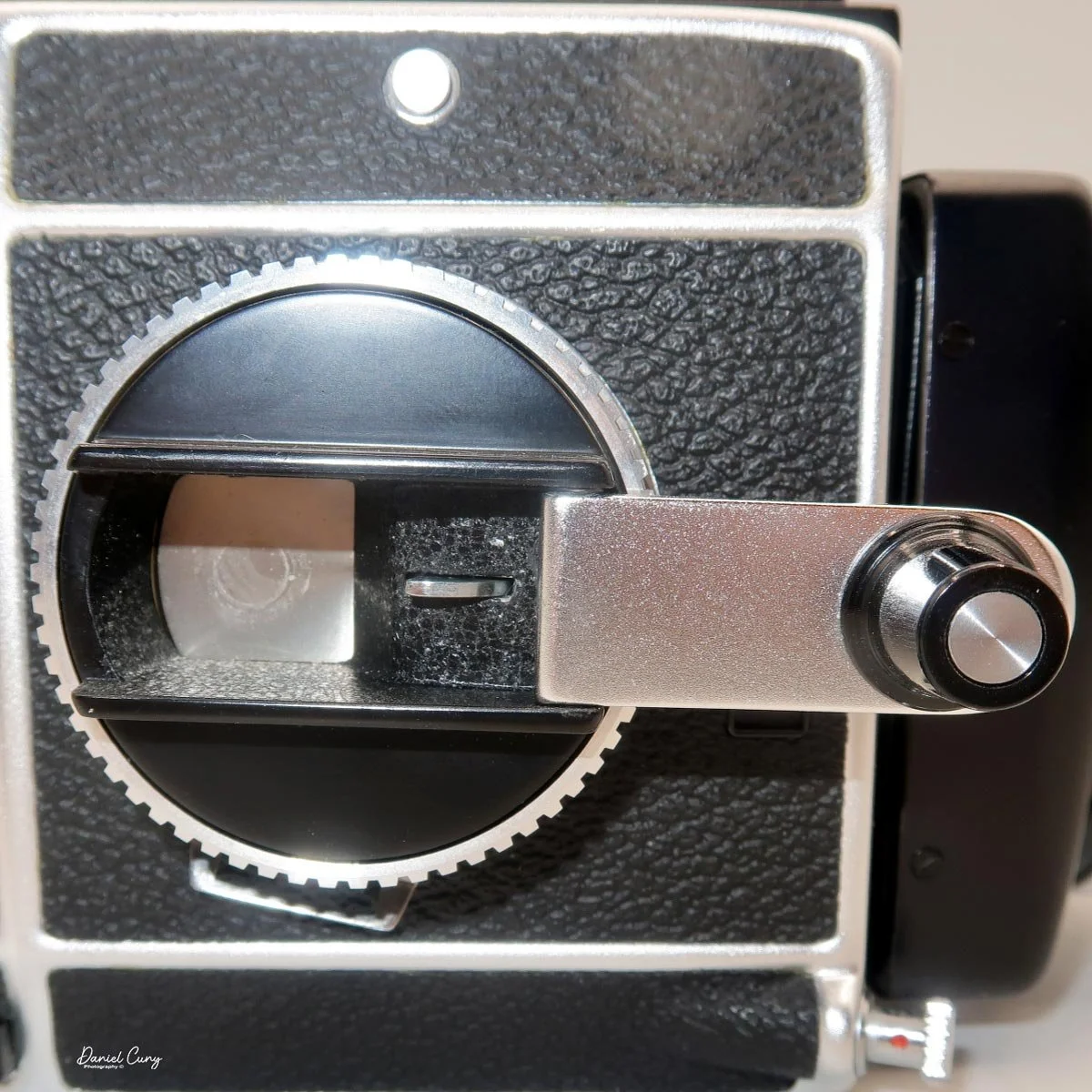
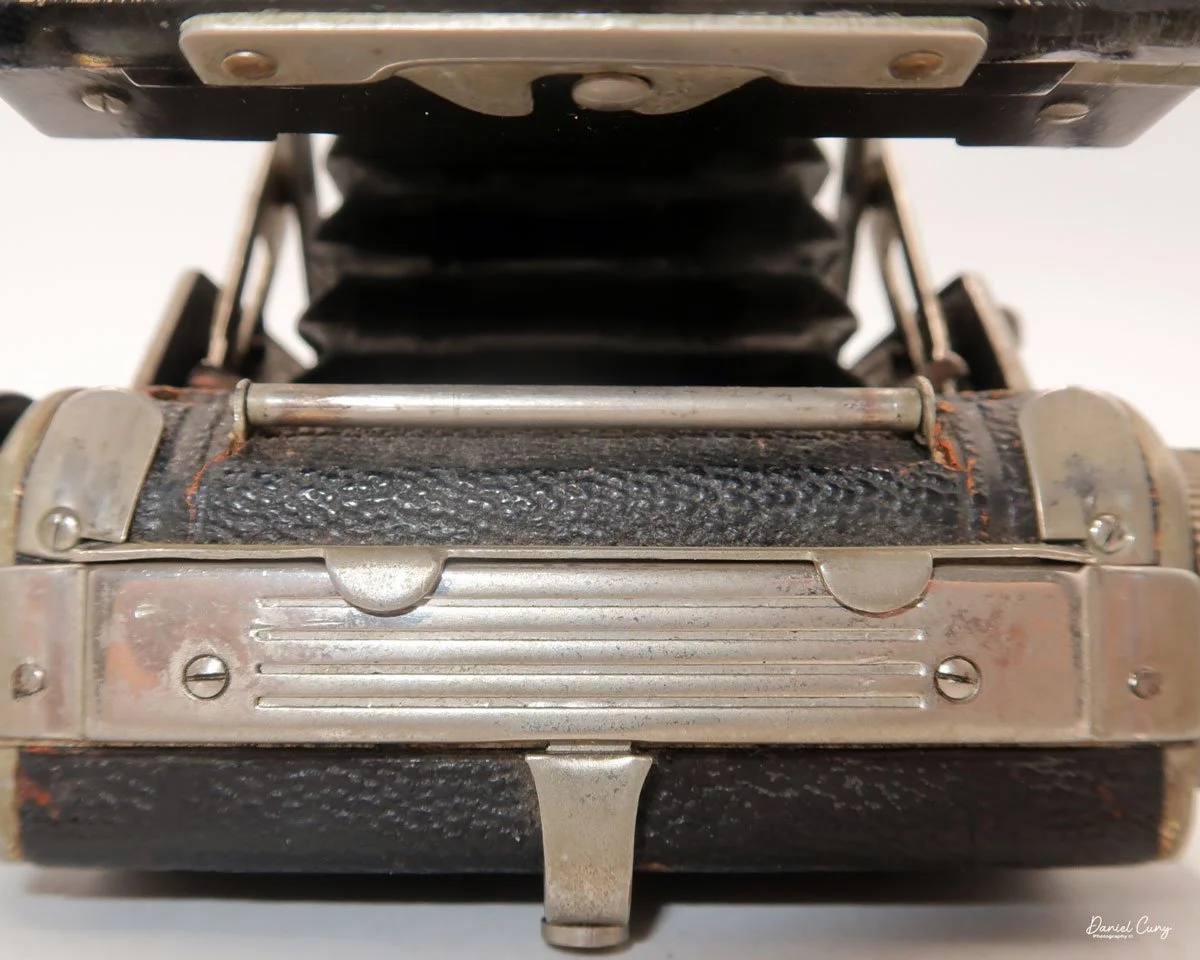
In the light, I could now feed the end of the film from the first cassette into the second one, slide both cassettes into the side of the camera, and drop the pressure plate back into place, making sure the film sat flat against the gate. Before closing the door, I advanced the film a bit to confirm that it was transporting. With the cassettes and pressure plate removed earlier, I'd noticed a small brass pin—very similar to the one in the Ansco Memo—that pops out, grabs a film sprocket, and moves up to advance the film.
Once everything looked right, I swung the back door into position and pressed it firmly against the body. Two small notches on the back have to line up with the body; if they're off even a little, the door won't sit snugly.
Before heading out, I took a look at the lens and saw that the front element was pretty grimy. With some lens cleaner and tissues, I managed to clean the front, but because the camera is built the way it is, I couldn't get to the rear element at all. With the film loaded and the transport confirmed, I was ready to go for a walk through the neighborhood.
Shooting with a Vertical 35mm
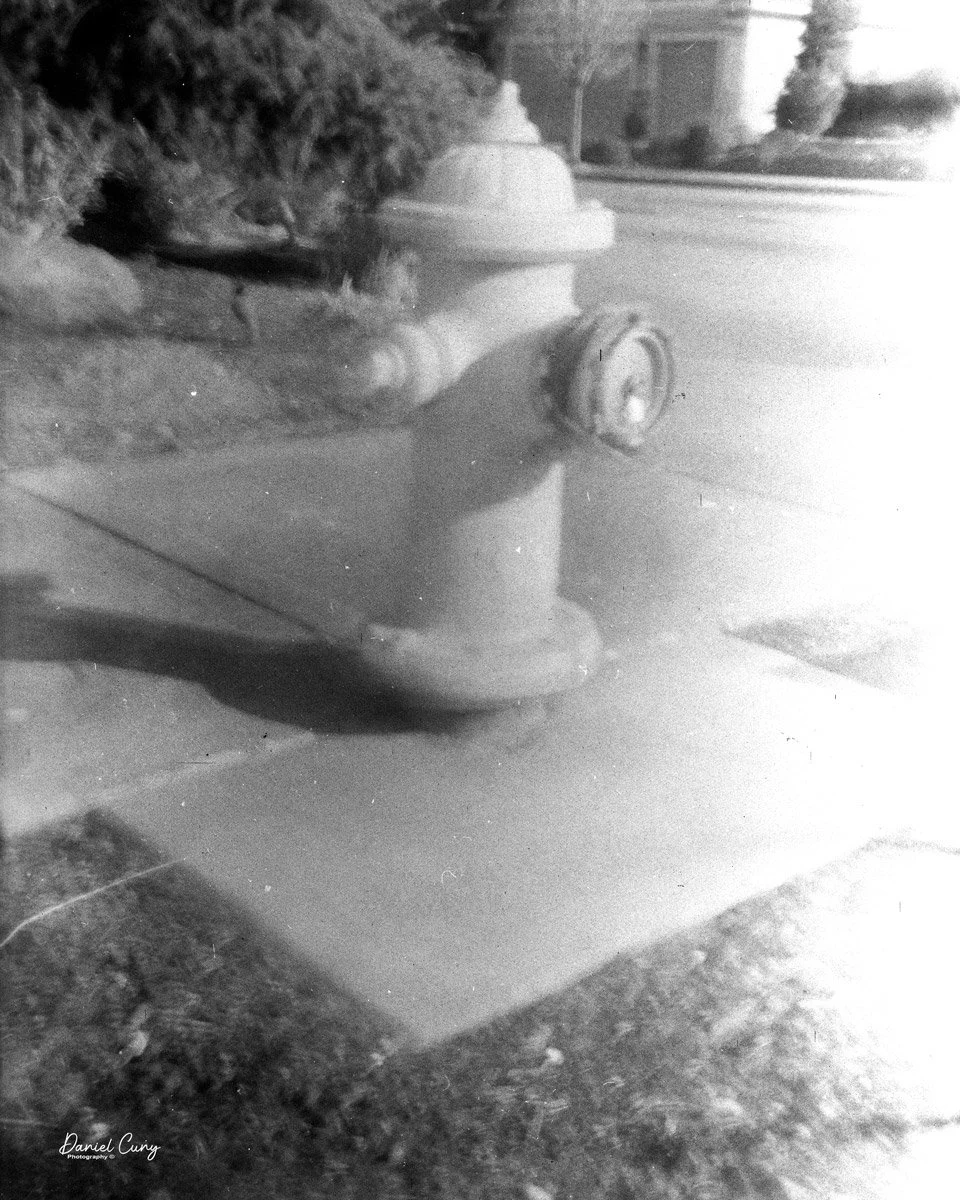
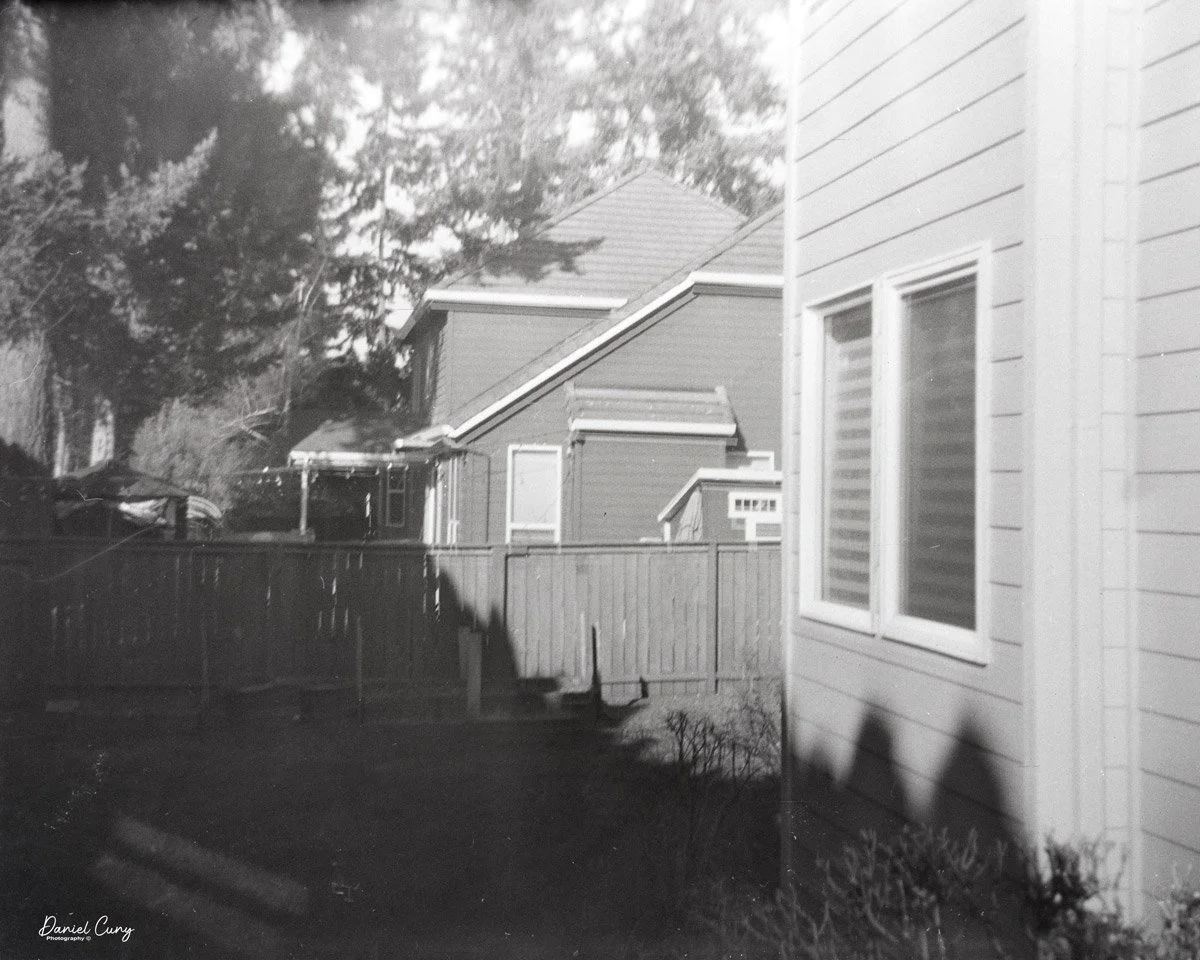
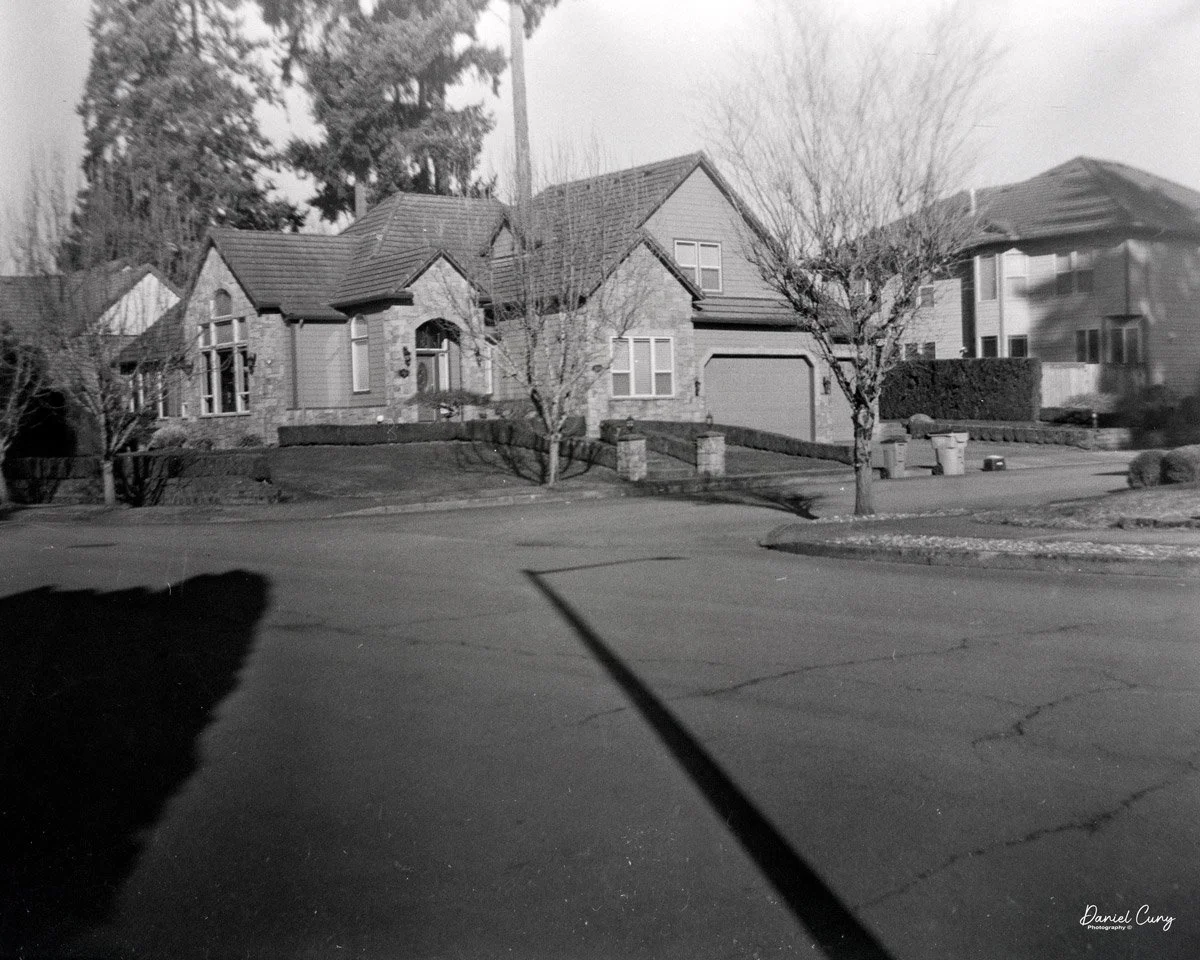
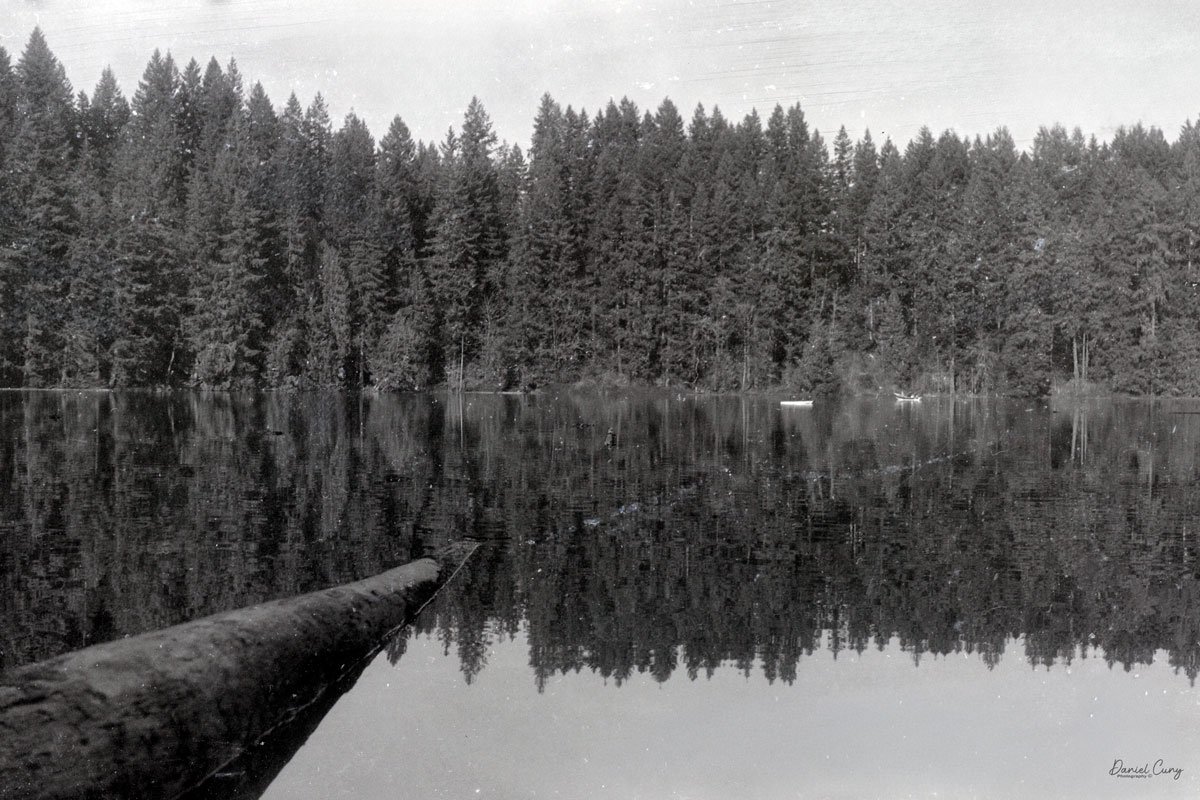
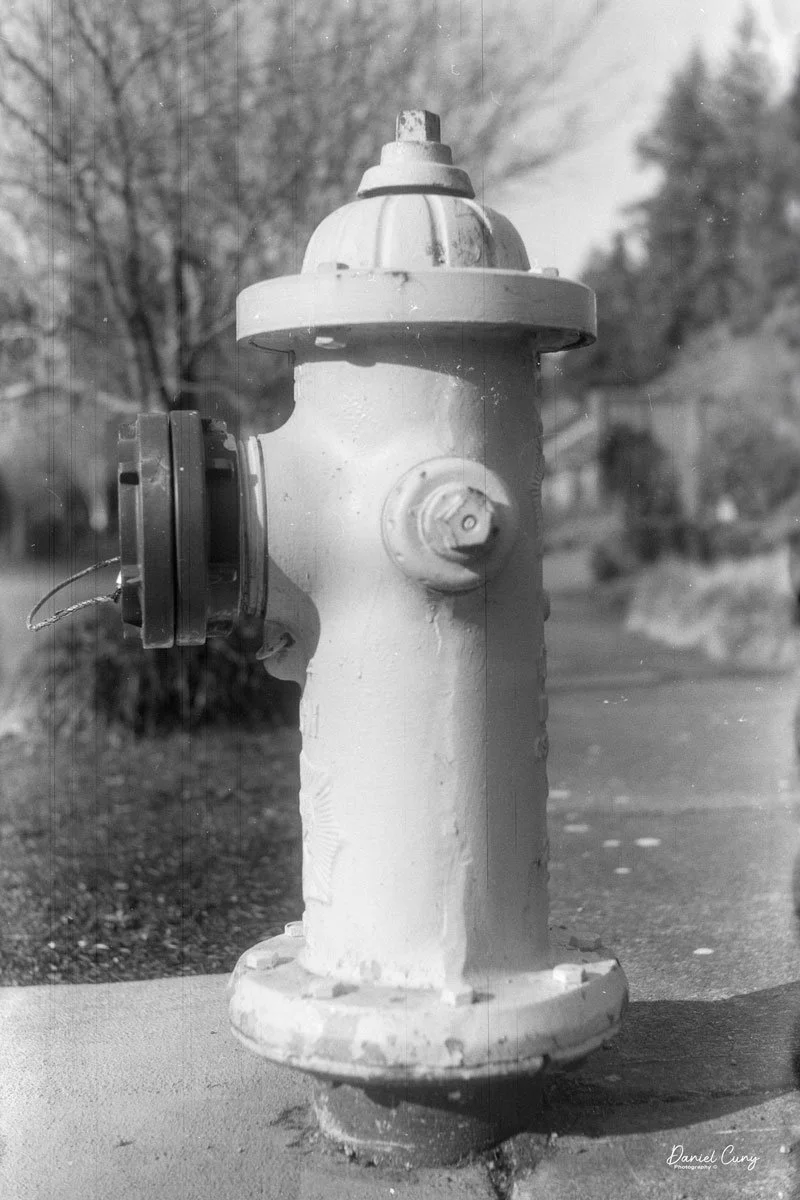
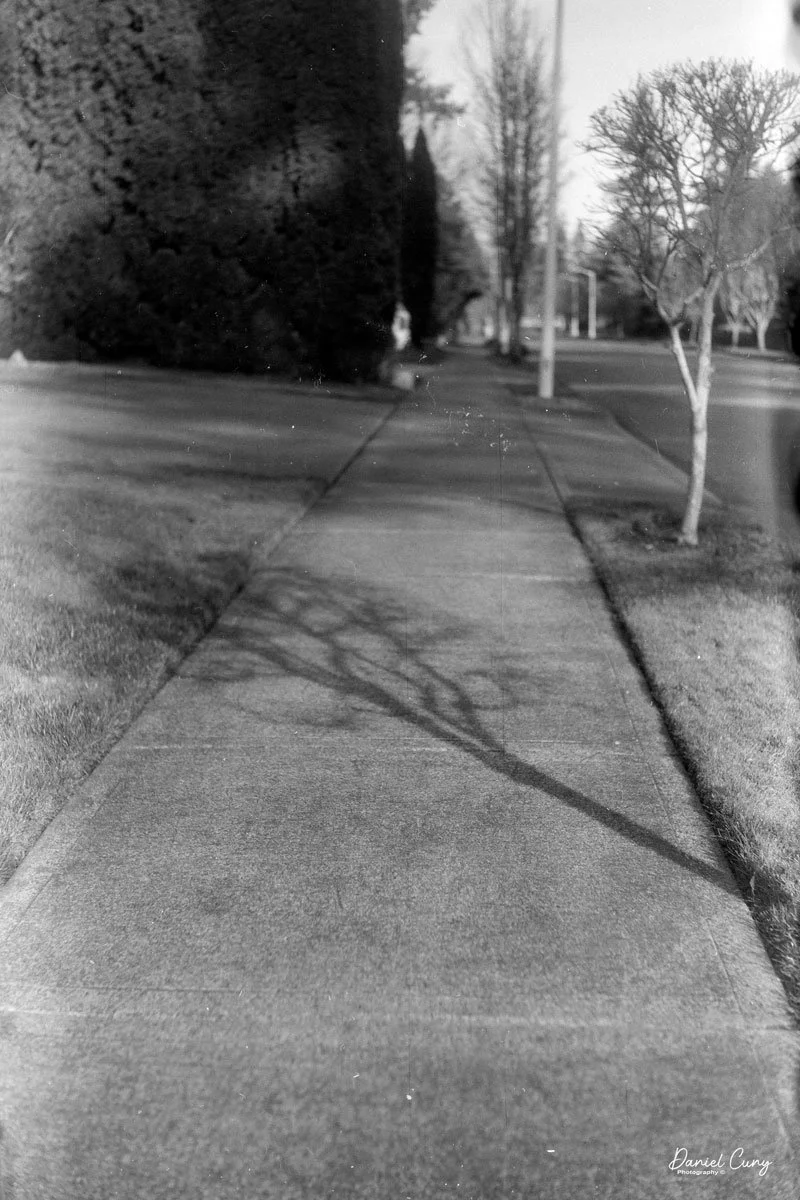
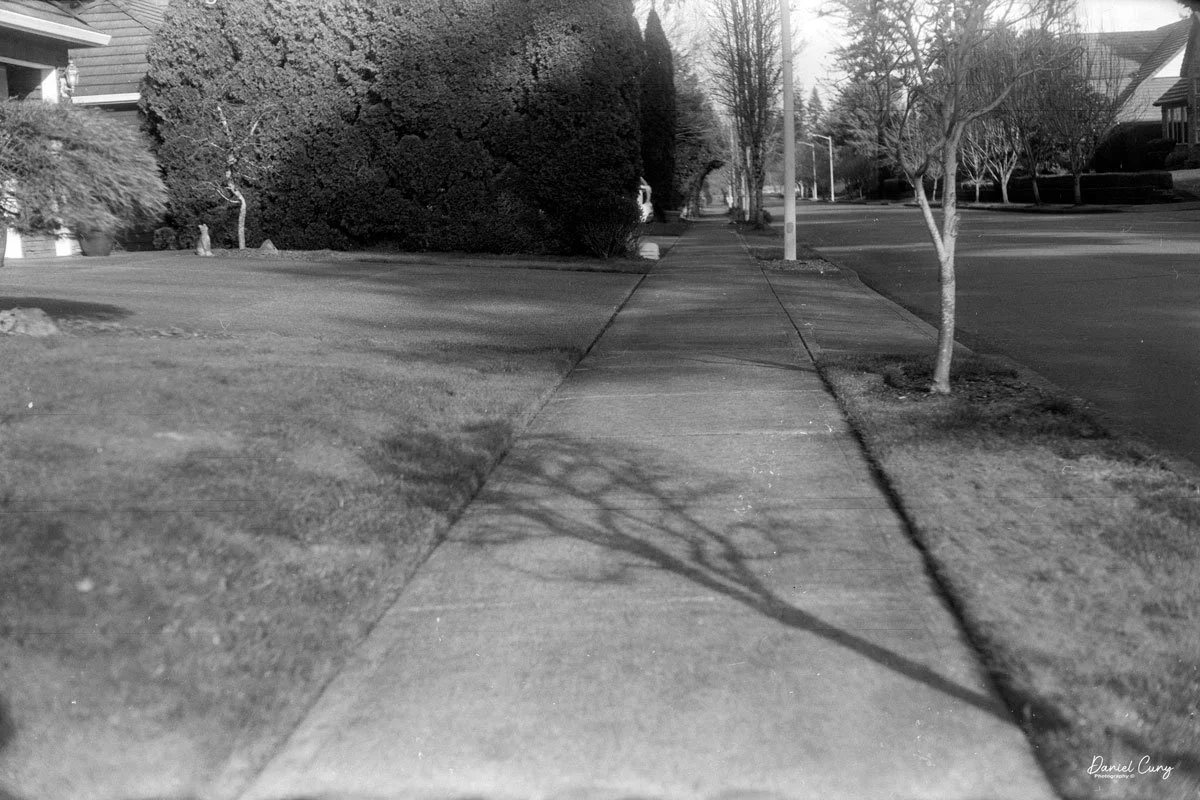
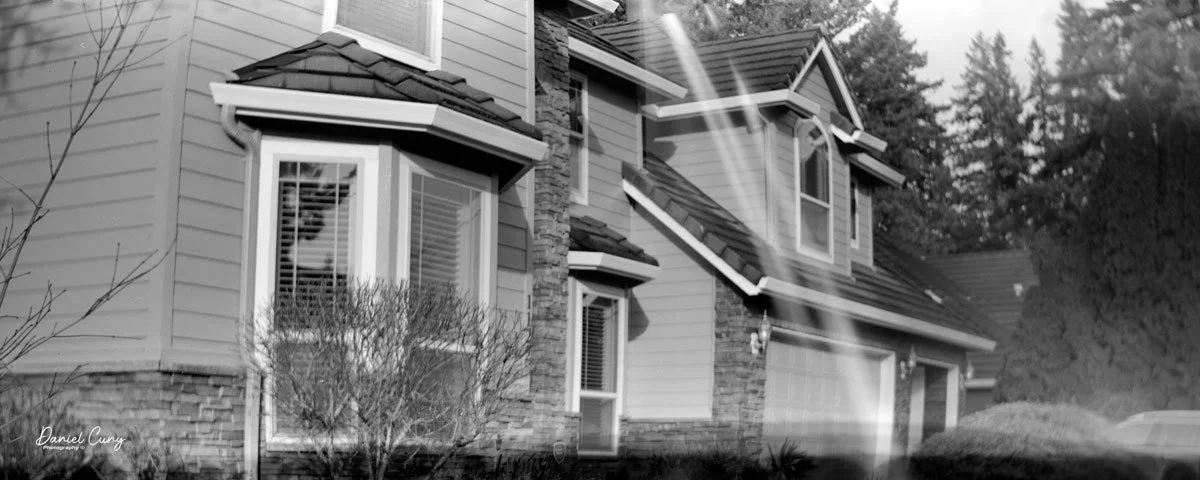
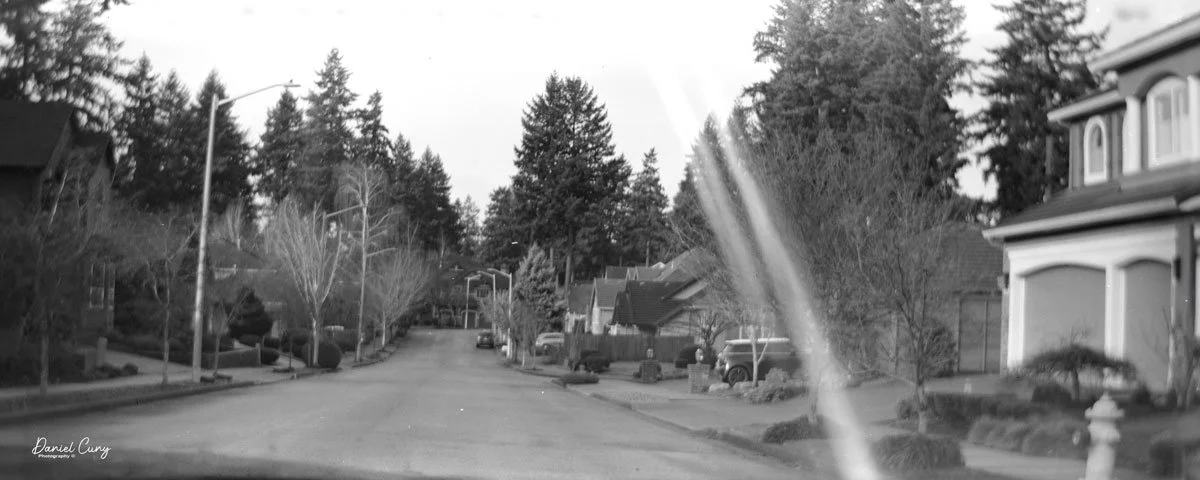
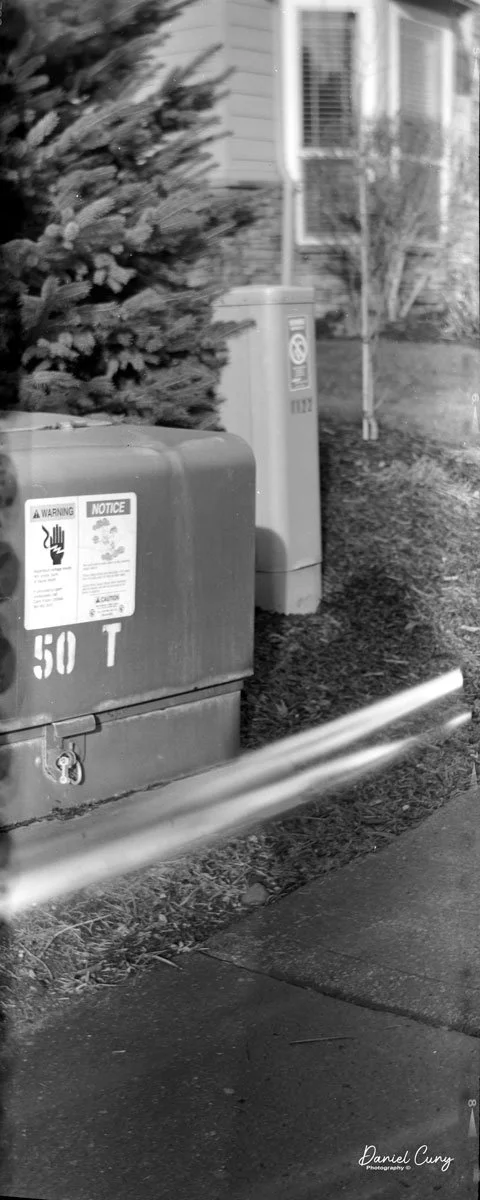
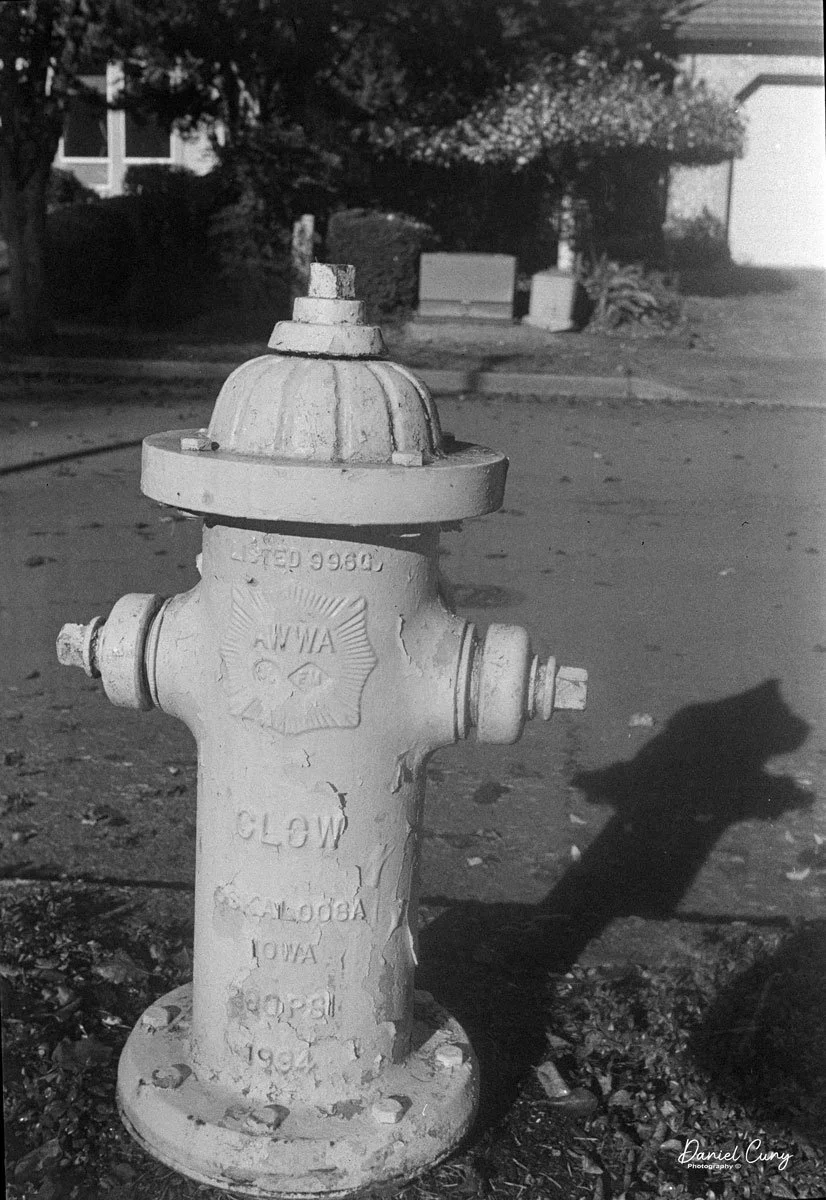
With film in the camera, I headed out around the neighborhood, trying to photograph some of the same subjects I usually shoot—houses, parked cars, trees, little details I run across on my walks.
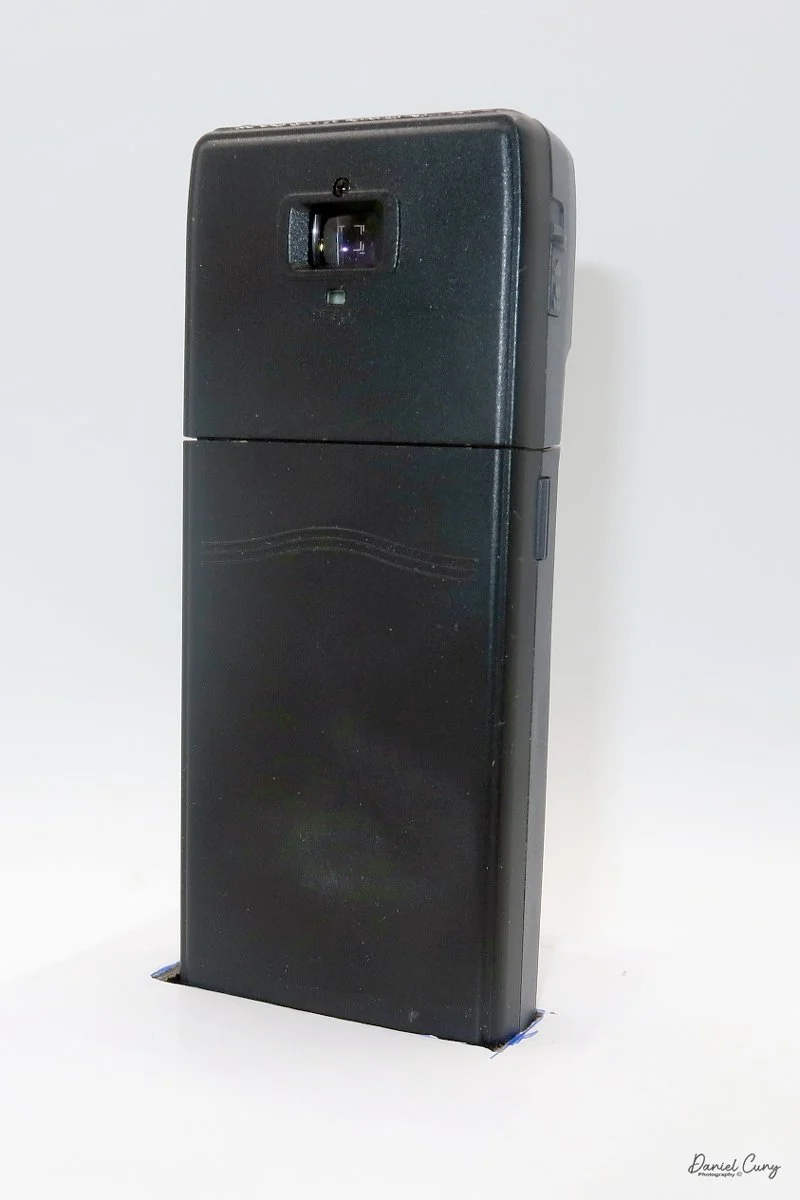
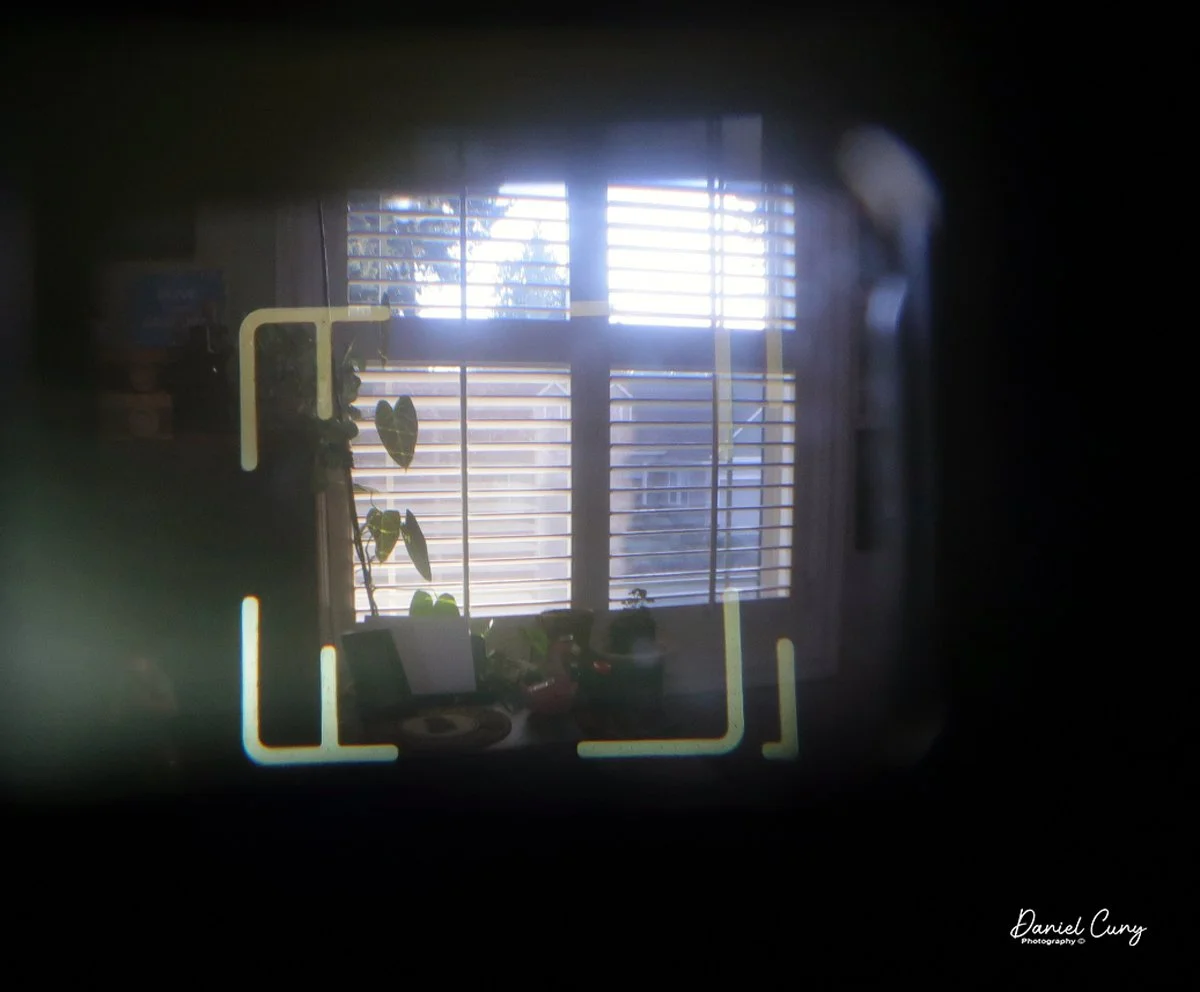
The camera's faceplate shows a horizontal rectangle next to the number 12, while the viewfinder is vertical. I found that confusing at first. Was this meant to be a horizontal or a vertical camera? With only 12 exposures per roll, it seemed logical that they'd be in a horizontal orientation to match most 35mm cameras. Still, the vertical viewfinder was telling me otherwise. I wasn't sure, so I shot in both orientations early on, turning the camera back and forth.
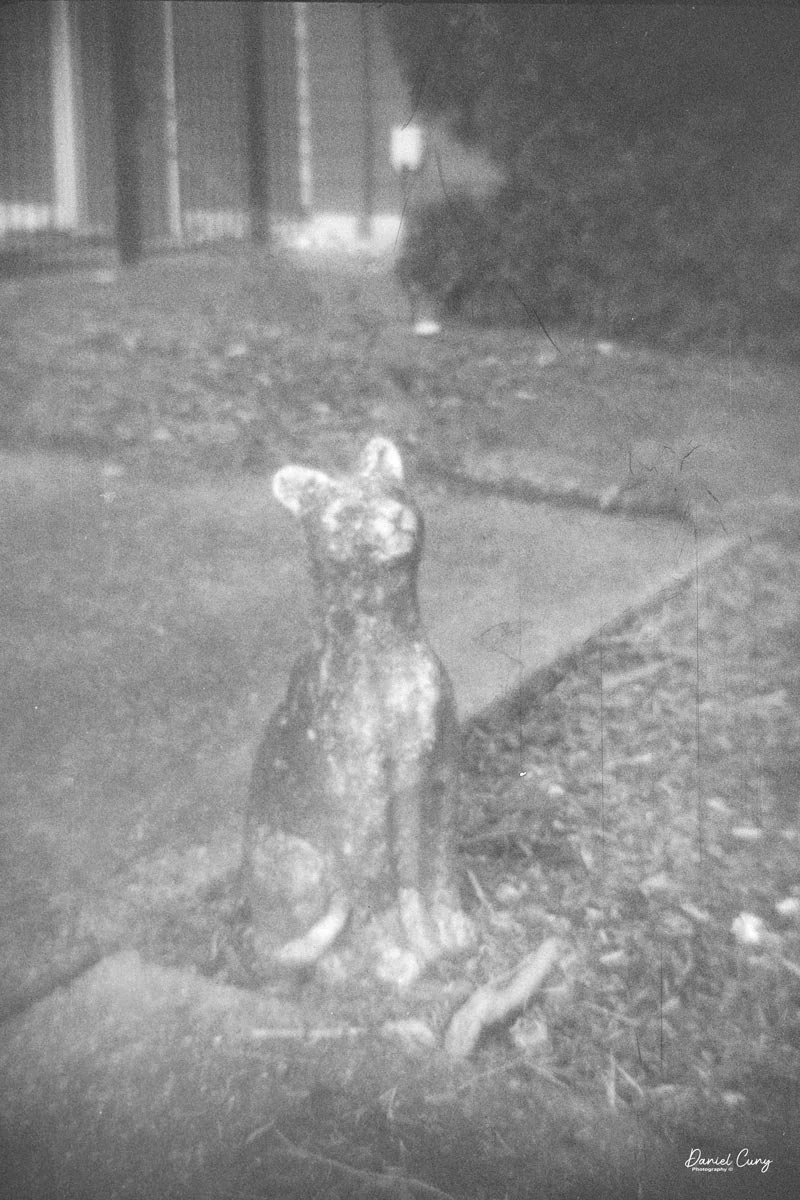
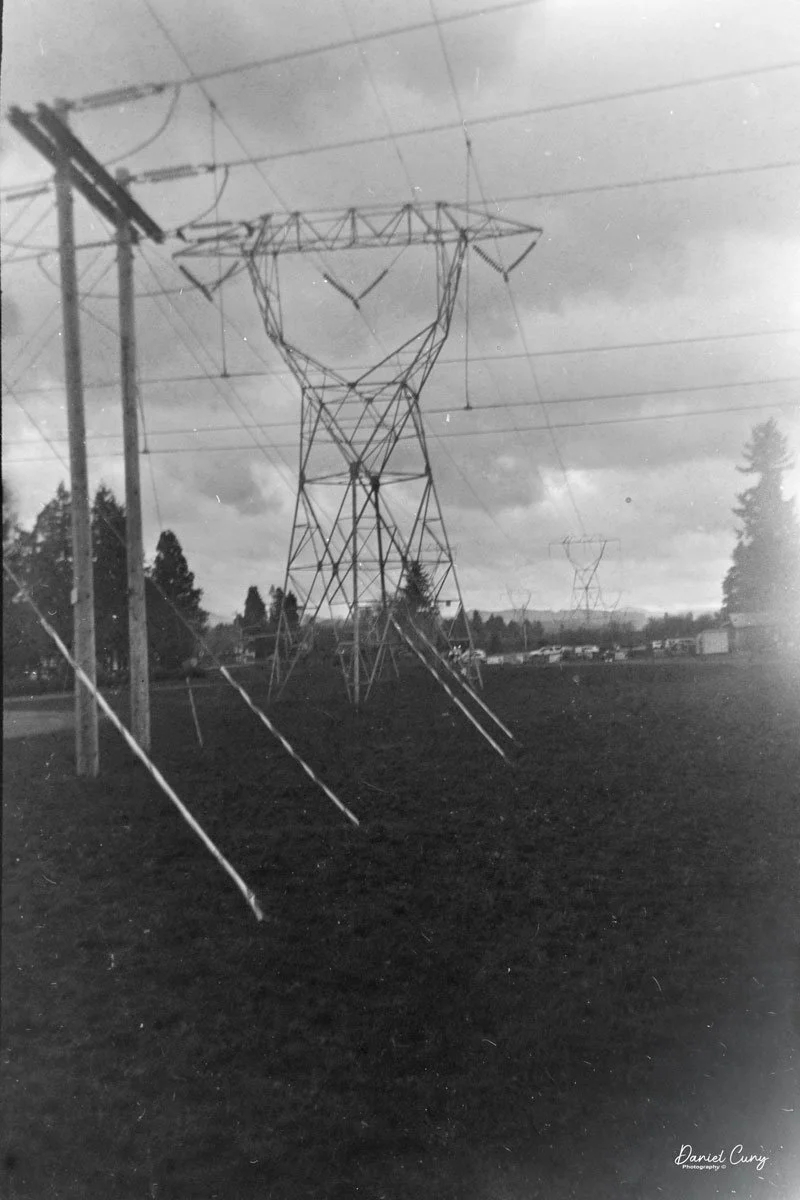
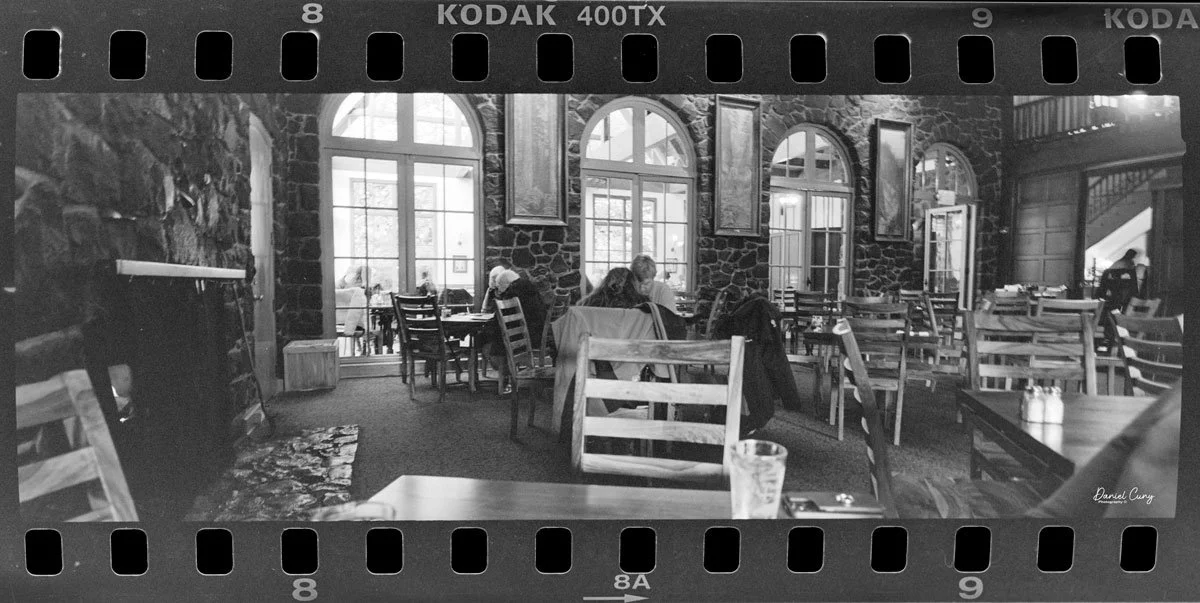
Once I processed the film and looked through the negatives, it was obvious: the Duca is a vertical‑format camera. If you want a horizontal image, you turn the whole camera on its side. It's not complicated, but it does take a little mental adjustment when you're used to most 35mm cameras being the other way around.
Results and Thoughts
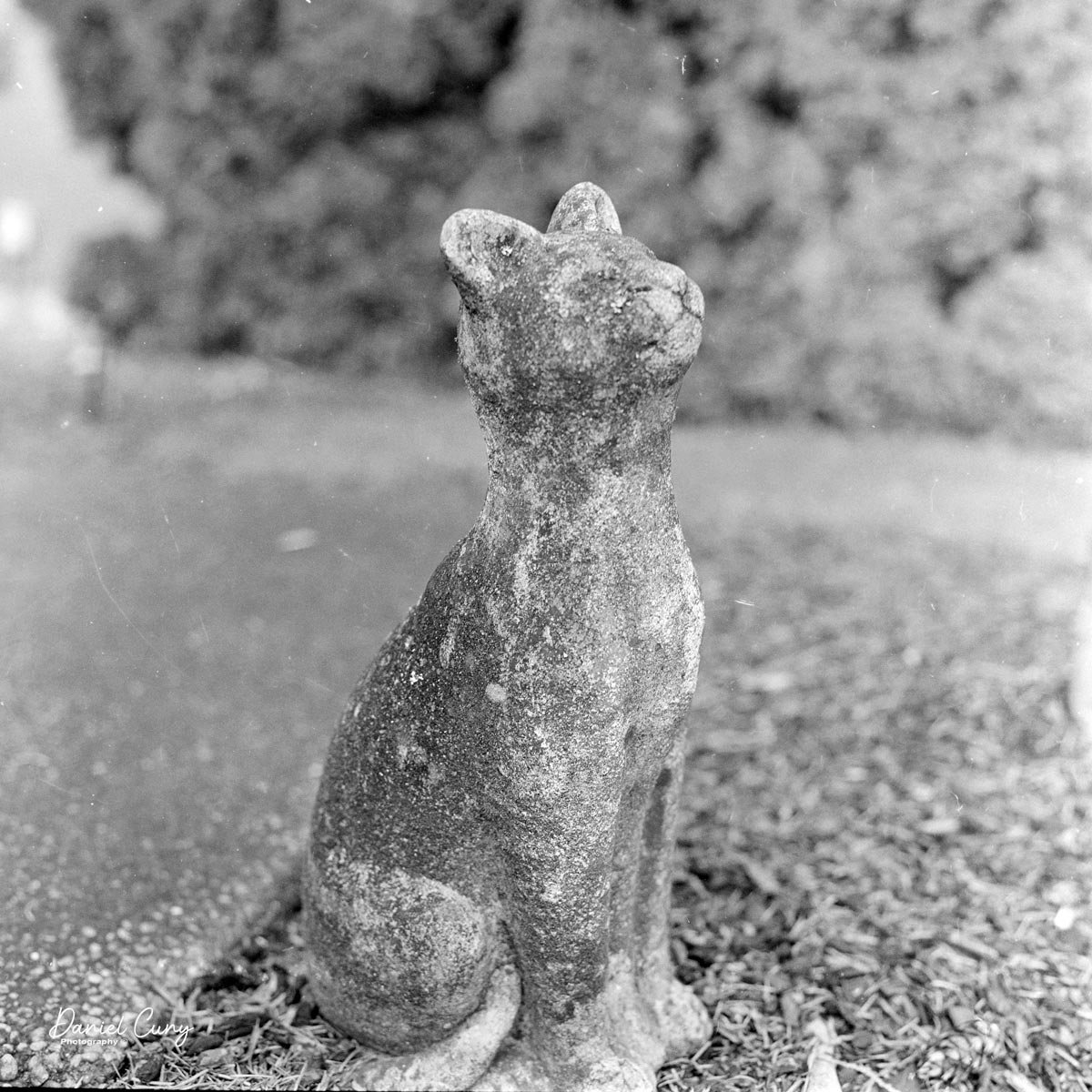
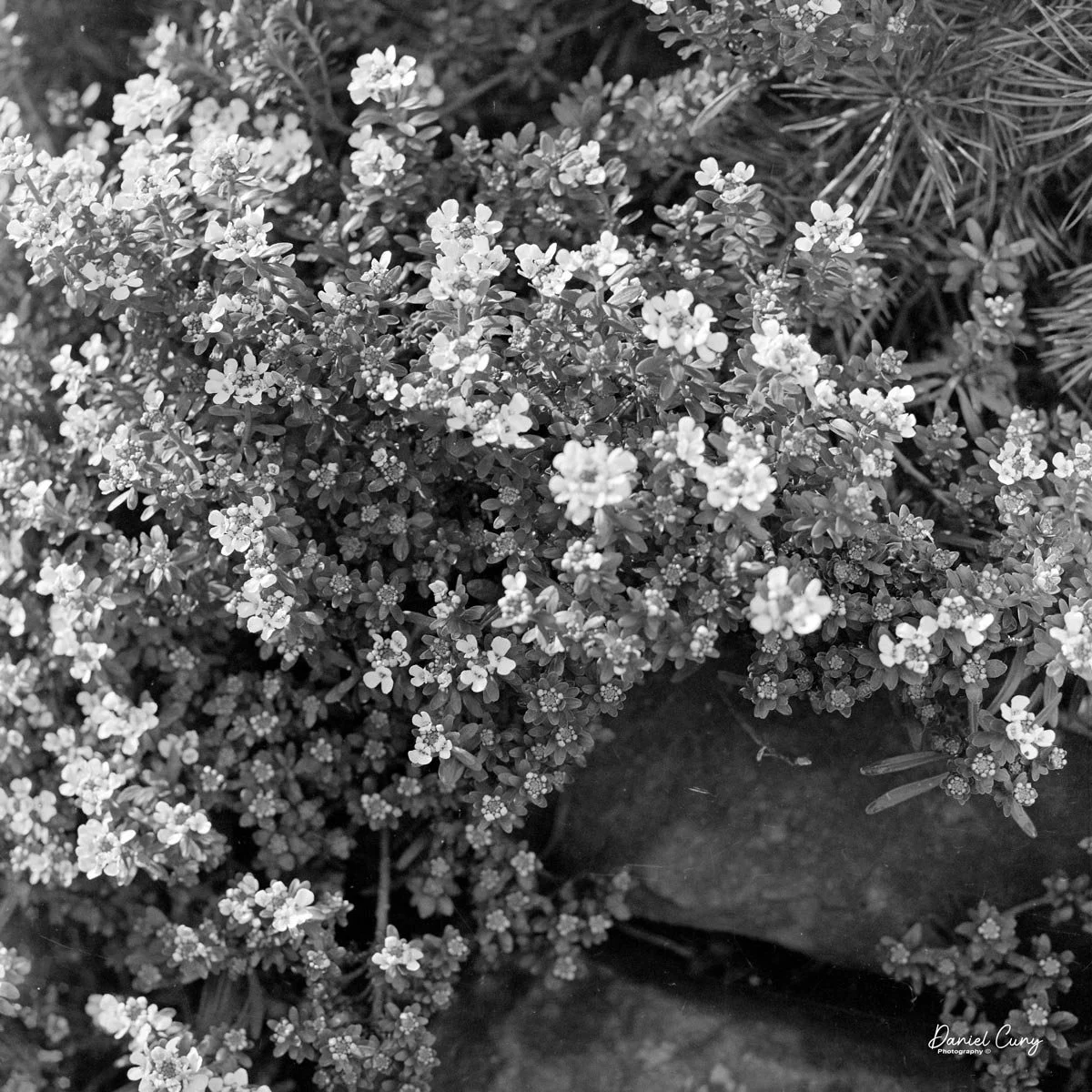
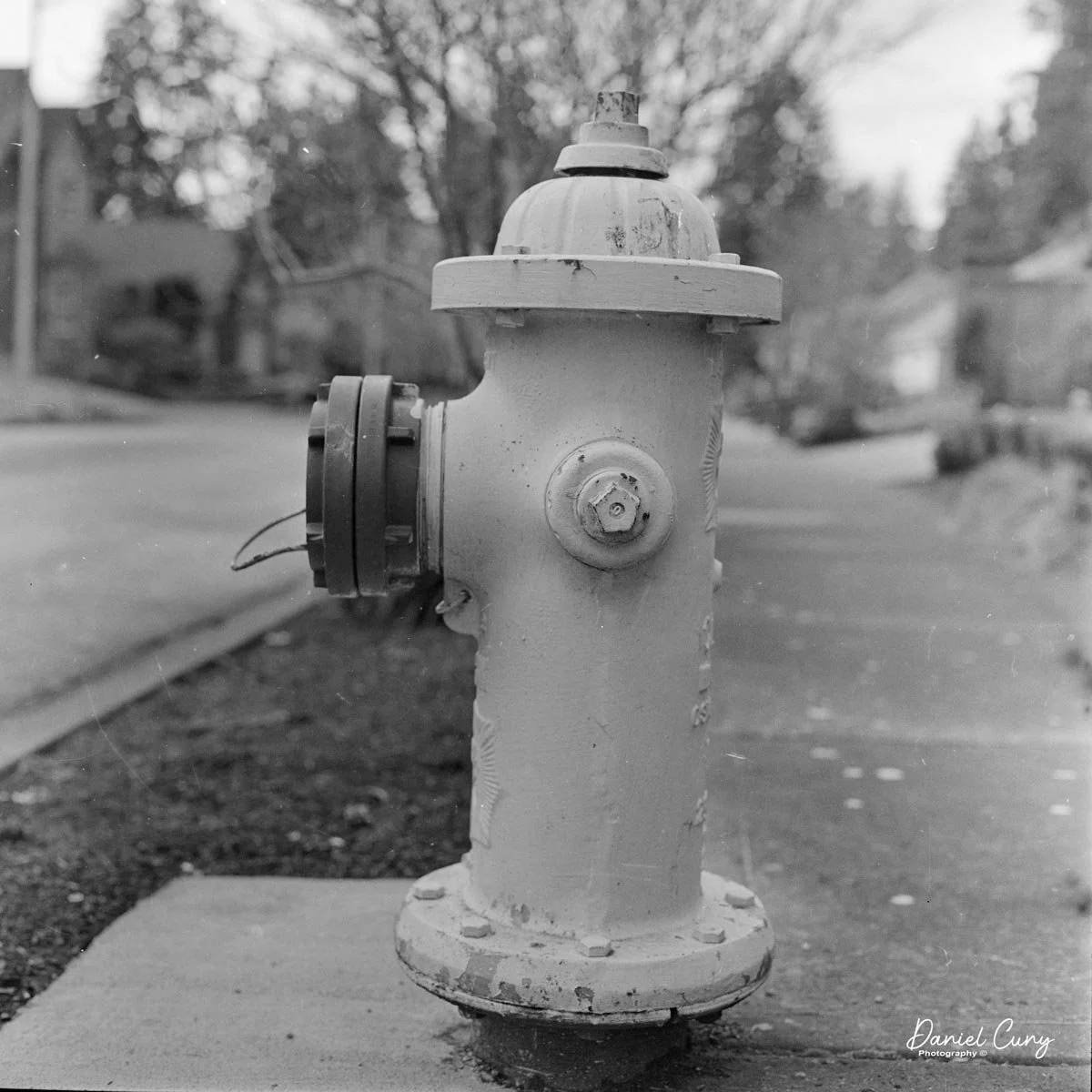
Some of the images turned out great, and some didn't. There are a few reasons for that. One is focus—I didn't always remember to switch between the two focus zones when I changed subject distance. The other is exposure. With only one shutter speed and one aperture, you're basically at the mercy of the light. The negatives showed some variation, but nothing I couldn't deal with in post‑processing. It reminded me a lot of shooting with an Instamatic: pick a film with a wide exposure latitude and let it do the heavy lifting.
I got 14 frames on the roll before the film refused to advance into the second cassette, which tells me my length estimate in the dark bag was close. The camera itself handled well. The viewfinder is on the small side and can be difficult to look through, especially if you wear glasses, but it's usable once you get used to it.
The transport worked smoothly, and the shutter opened and closed as it should. The lens, however, is still dirty on the rear element, and there's really no easy way to clean it without taking the camera apart. That shows up in the photos as a general softness, almost like shooting with a soft‑focus filter. On some subjects, the look can actually be pleasant; on others, it just makes things a bit mushy.
Overall, the Duca was a fun camera to use, and I'll definitely shoot it again. The whole process—from loading the Karat cassettes, to working with the vertical format, to seeing the results—was enjoyable. It's the kind of camera you could toss in a pocket when you head out on a trip and forget about until something catches your eye. I like that it's doing all of this as a full‑frame 35mm camera in such a tiny body.
Thanks for taking the time to read about my experience with this little Italian wonder of a camera.
If you'd like to see more of my camera adventures, here's a link to my other camera reviews. And if you're interested in cameras, lenses, or other photo gear I'm letting go of as I thin the collection, you can visit my Cuny's Cameras and Photos online store.
Until next week, please be safe.