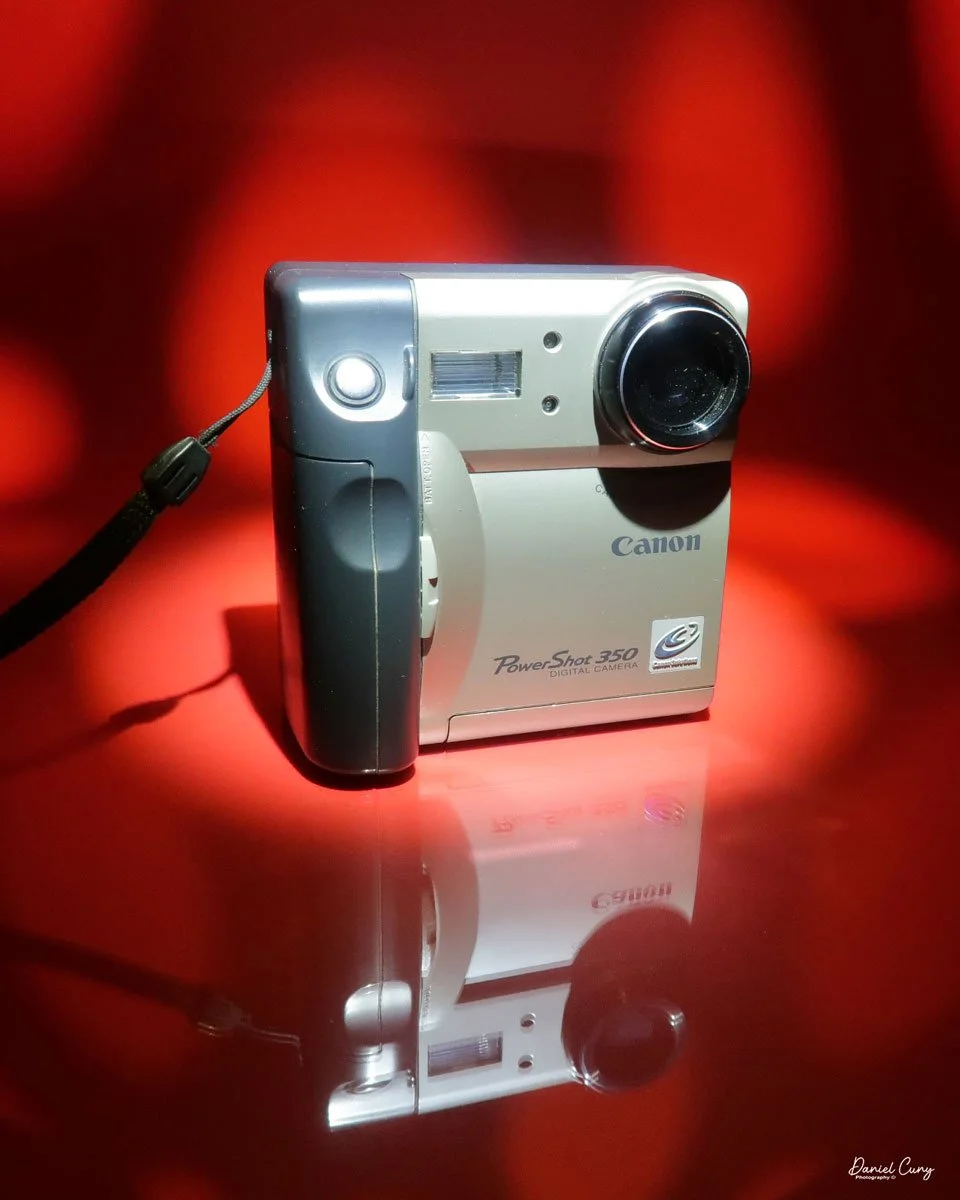
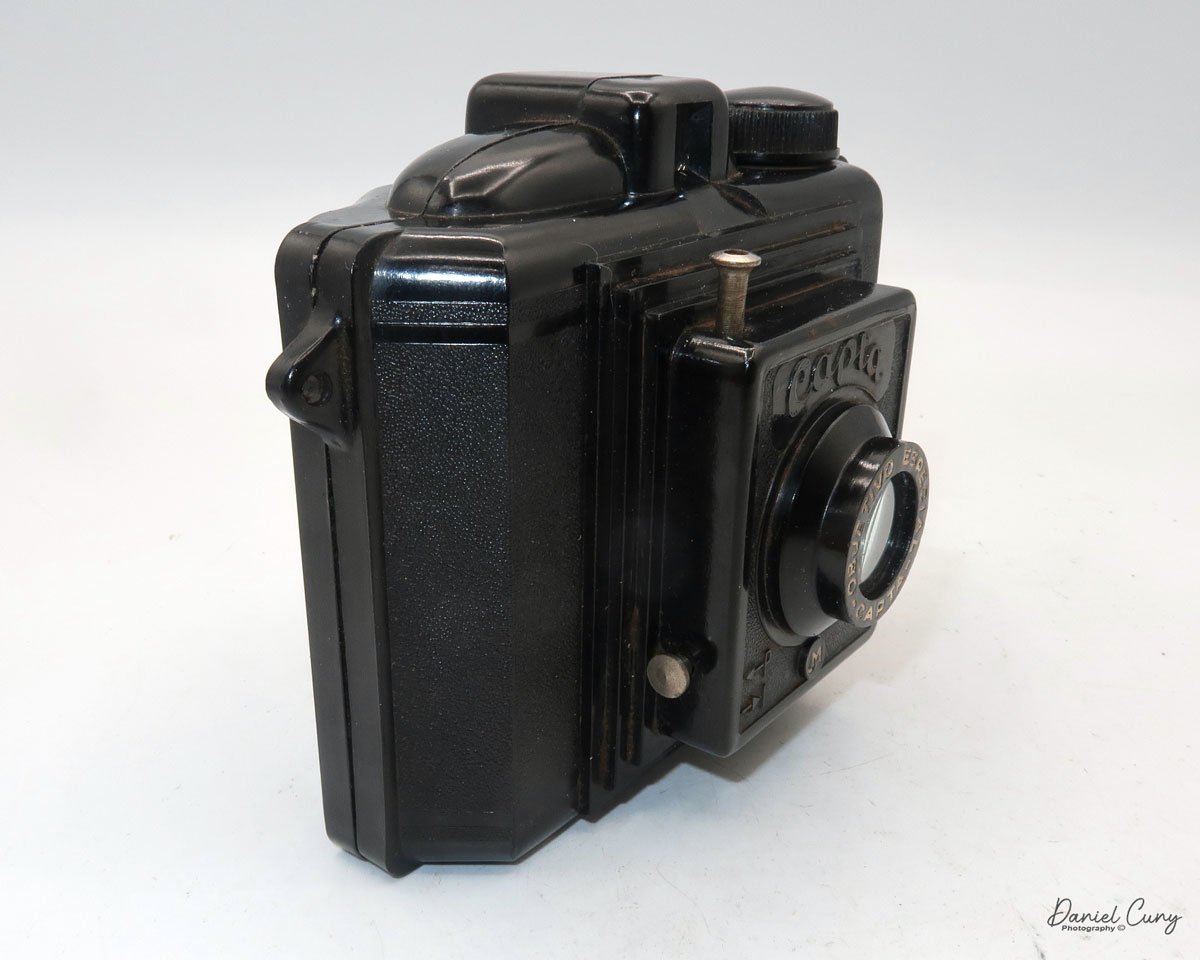
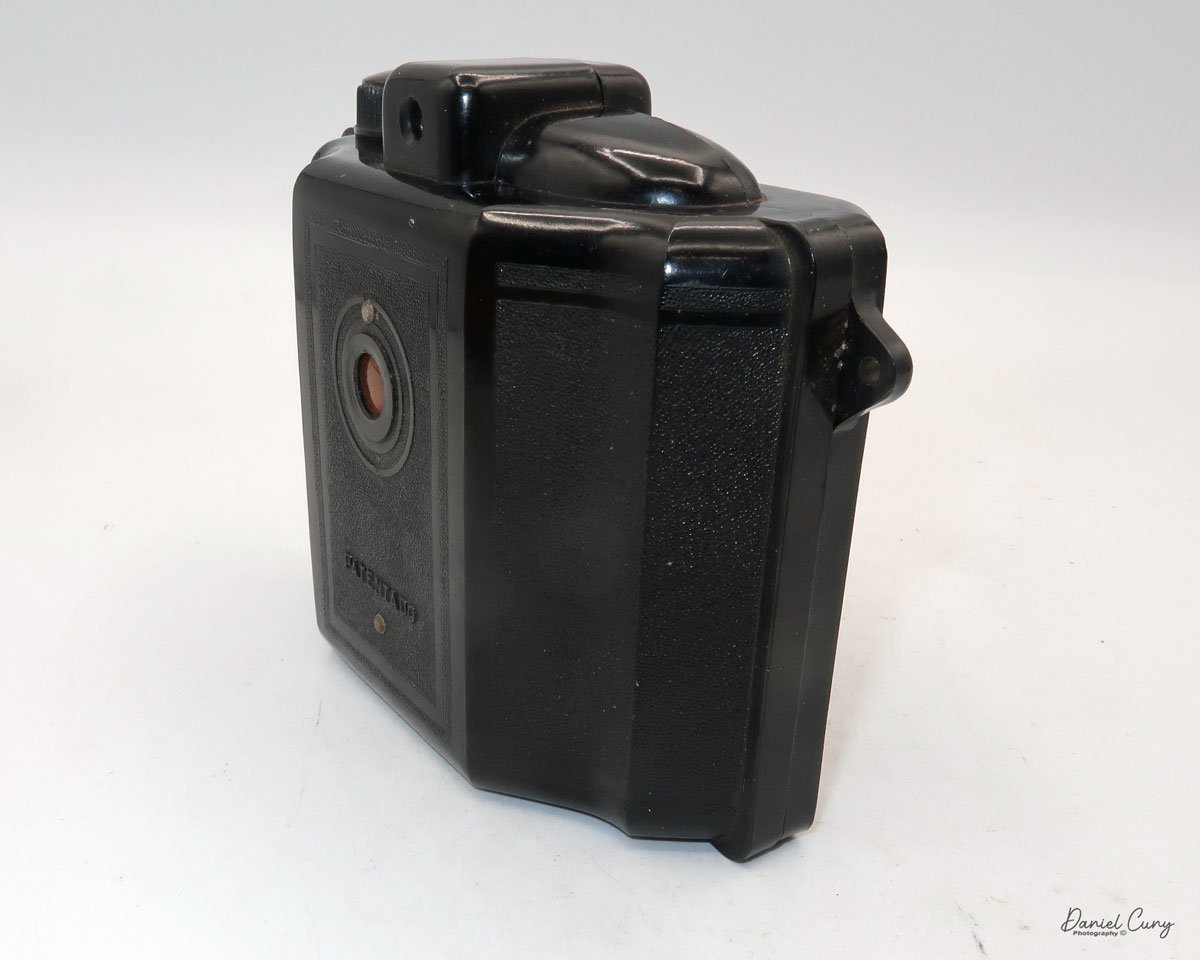
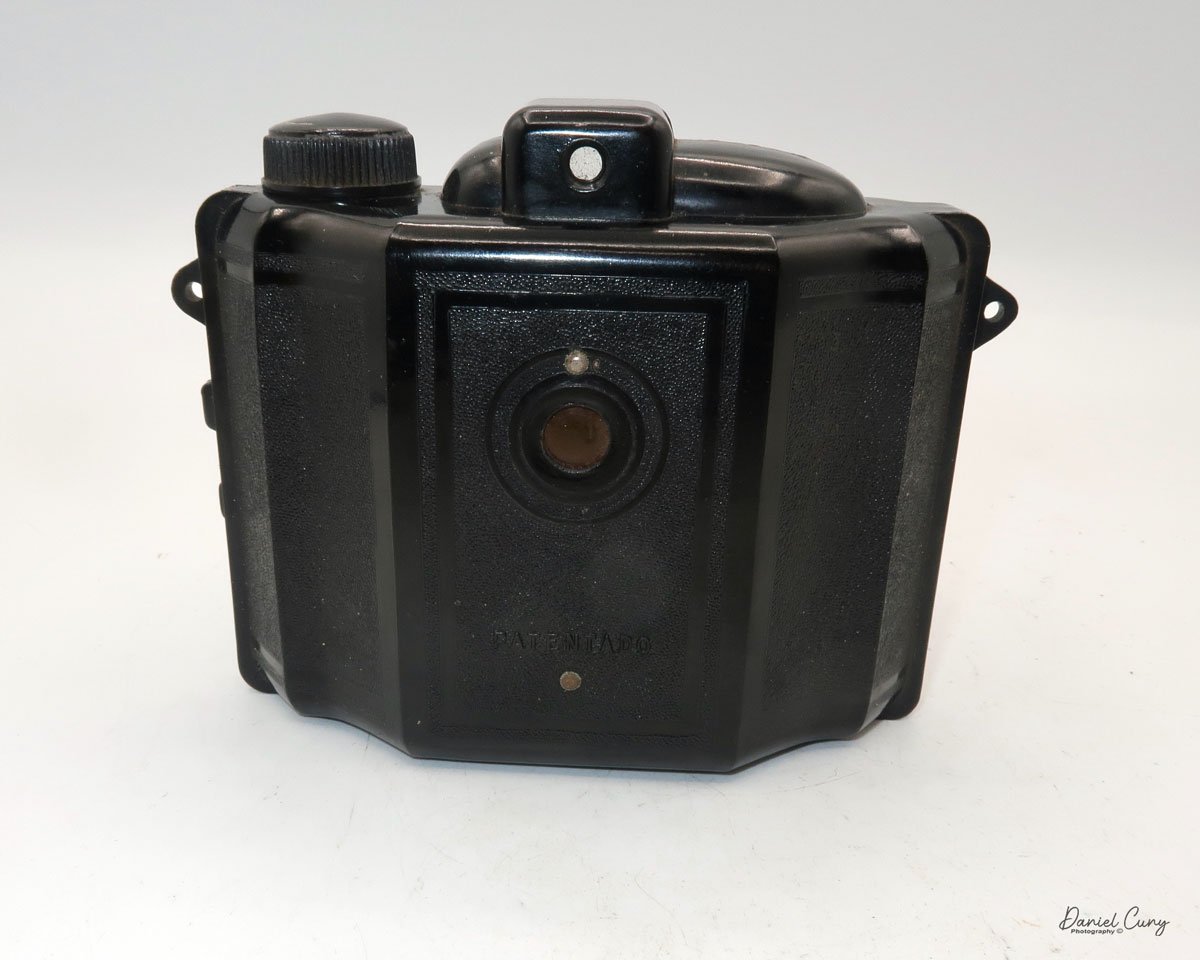
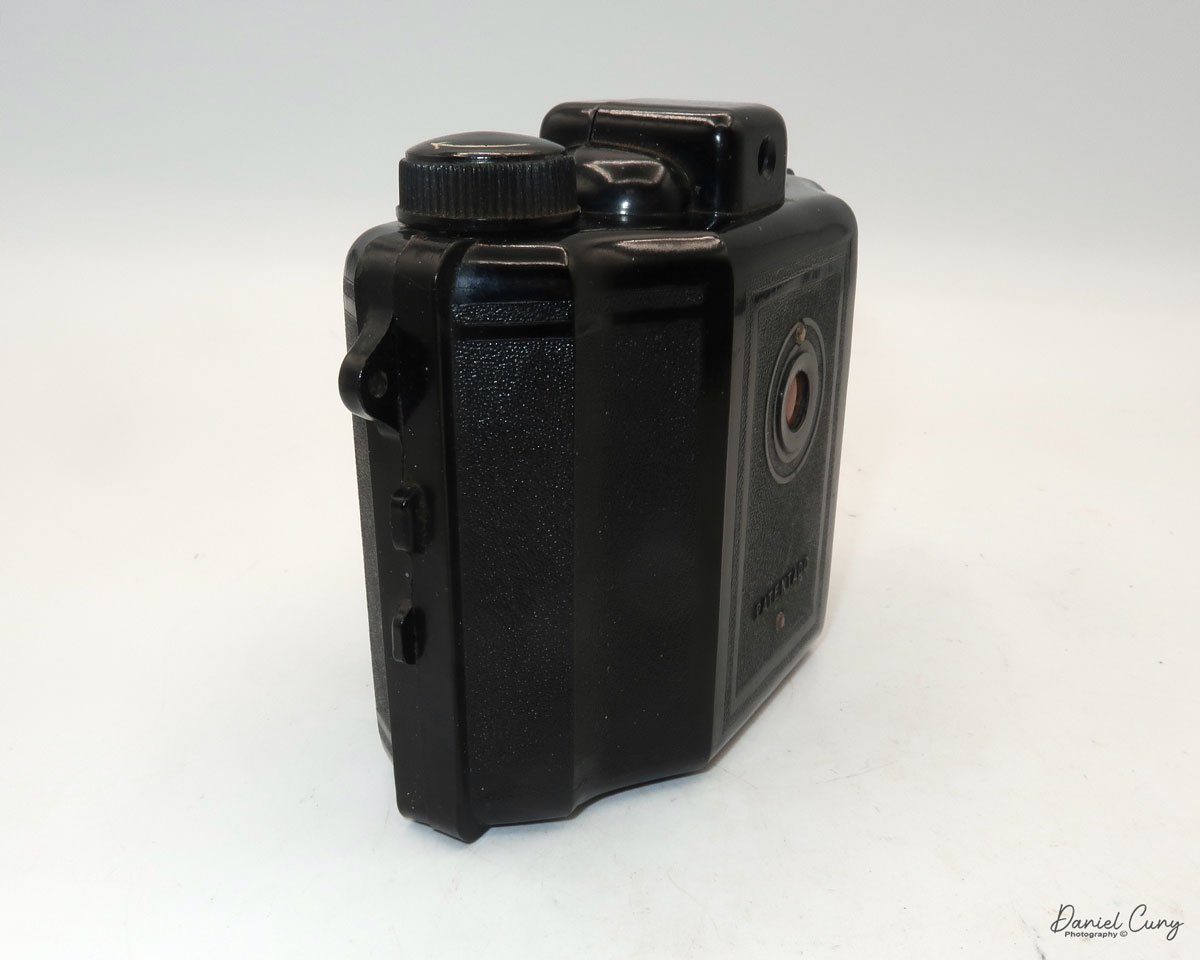
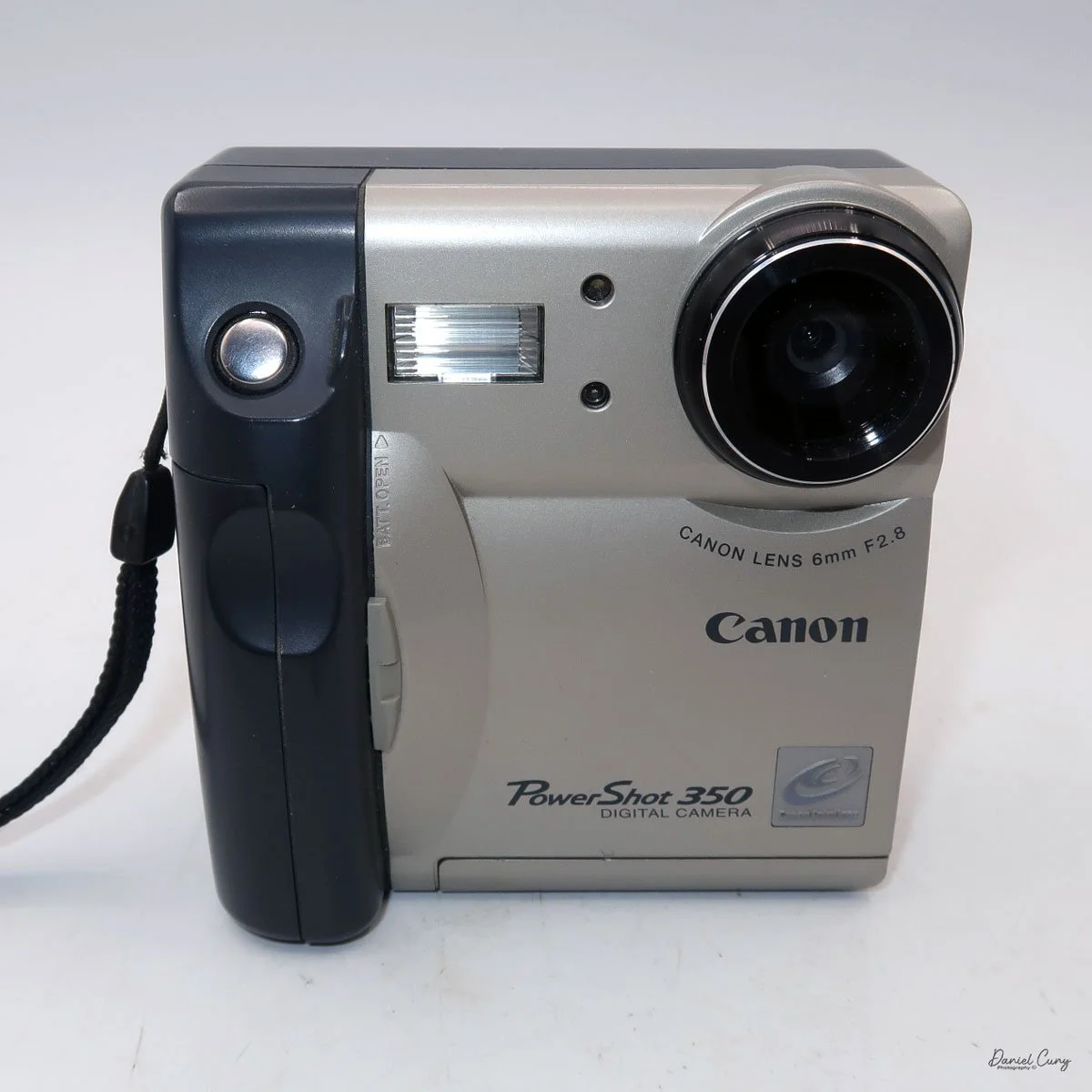
My Canon PowerShot 350 camera
It wasn't until after my almost twenty years working in a retail camera shop that digital cameras became increasingly popular. At the time, in the late 1990s, I was working in management for professional photo laboratories in the San Francisco Bay Area, a real hotbed for technology. Since I was still working within the photo industry, not in retail but with highly professional photographers, the conversations would be about what cameras and technology they were using.
Digital photography was in its infancy, and for a professional commercial photographer to go digital during this time cost around $100,000, so there were very few who did. For the commercial photo laboratories, there were conversations about the "death of film", which many laughed at, and if they did take it seriously, it wasn't for many years down the road, and nothing that would happen overnight.
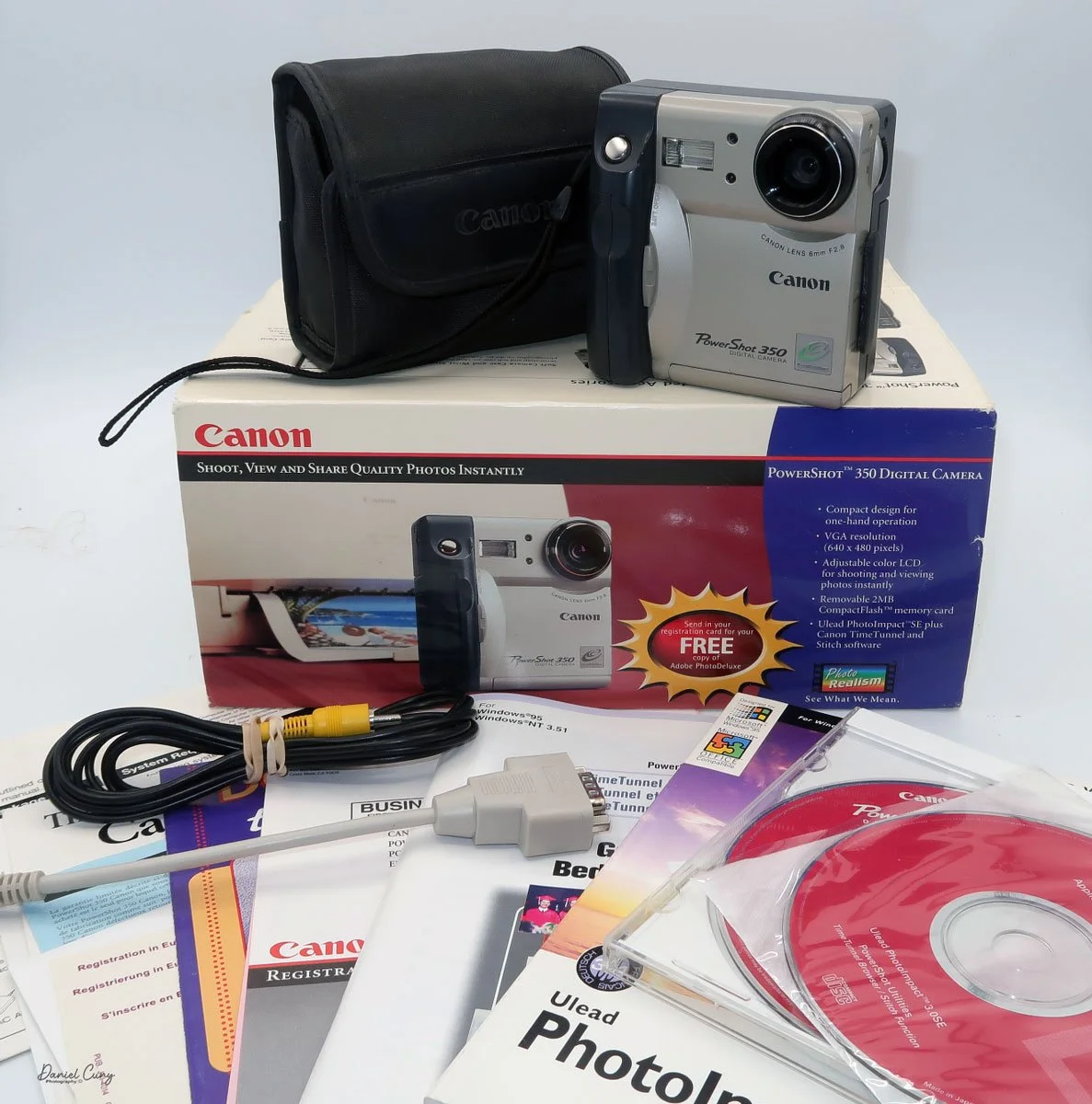
Not only was the digital craze happening for professional photographers, but also in the consumer market. One of the first digital cameras our family owned was the Canon PowerShot 350. The camera for this blog post is one I purchased recently. When it arrived in the original box, with the manual, software, and many of the original cables, I felt a wave of nostalgia and warmth, recalling family trips and vacations from the late 1990s.
Boxed Canon PowerShot 350, just missing a few items
As I picked up the camera to refamiliarize myself, my initial thought was that its design and features seemed amateurish compared to today's cameras. It was for the camera manufacturer! What features made sense for the family photographer who, at the time, had a home computer used for word processing, games, and other family entertainment? There was no online entertainment, as the fastest online connection was via a phone line at 28.8 or 33.6 kbps, or, if you were really advanced, 56 Kbps (kilobites per second). The internet was in its infancy, and companies like AOL's "You Have Mail" were dominant in the online world.
It's interesting to think back on those years. 1997 was also the year I signed up for this online selling platform. At the time, it was very similar to a message board, devoid of photos. You had almost to write code just to sell or purchase items. Everything was done via text, so you had to trust the description of the item only by what the seller was telling you. When the company added the ability to add photos in the early 2000s, it was a great benefit.
I can still remember that there were no names of people you'd buy from or sell to, but just a number. My number at the time was 1134, and today that company is eBay, the juggernaut of buying and selling mainly used items online.
I've written about Canon's history before, so in this brief history segment, I decided to focus more on its digital camera history.
History:
Canon's digital camera history dates back to the mid‑1990s and traces a steady evolution from low‑resolution consumer compacts to today's high‑performance mirrorless and professional systems. Building on decades of film‑camera expertise, especially its EOS SLR system introduced in 1987, Canon created a coherent digital ecosystem of bodies, lenses, and accessories that showcases impressive innovation.
1997 Brochure for Canon PowerShot 350
The first significant step into consumer digital stills came with the PowerShot 600 in 1996, a compact camera with a 0.3‑megapixel sensor that signaled Canon's commitment to mainstream digital imaging despite its modest specifications. This model launched the long‑running PowerShot line, which would expand into numerous point‑and‑shoot families aimed at travelers, families, and enthusiasts through the late 1990s and 2000s.
Canon's professional digital efforts grew out of its EOS film SLR platform, which debuted in 1987 as a fully electronic mount system and provided an ideal foundation for autofocus and electronic communication in digital bodies.
Early digital EOS models were often developed in cooperation with other companies. Still, in 2000, Canon released the EOS D30, its first digital SLR designed and manufactured entirely in‑house, pairing an APS‑C sensor with the existing EF lens mount.
Through the early 2000s, Canon rapidly expanded its DSLR lineup, targeting entry‑level, enthusiast, and professional users with a range of EOS digital bodies that shared a standard lens system. A landmark arrived in 2005 with the EOS 5D, widely noted as the first relatively affordable full‑frame DSLR, bringing a 35 mm‑sized sensor and strong low‑light performance to a broader audience than previous flagship‑level models.
Alongside DSLRs, Canon continued to refine compact digital cameras, including the stylish Digital ELPH/IXUS series that emphasized portability and automated shooting modes for casual photographers. These compacts helped popularize digital photography worldwide before smartphones began to erode demand for dedicated point‑and‑shoots in the 2010s.
In the late 2010s and into the 2020s, Canon shifted its emphasis toward mirrorless digital systems while continuing to support EOS DSLRs, reflecting an industry‑wide shift toward smaller bodies, electronic viewfinders, and advanced on‑sensor autofocus technologies. Across this progression—from the PowerShot 600 to full‑frame DSLRs and modern mirrorless lines—Canon's digital history is defined by continuous integration of new sensor, processor, and lens innovations into a unified imaging system.
My Camera:
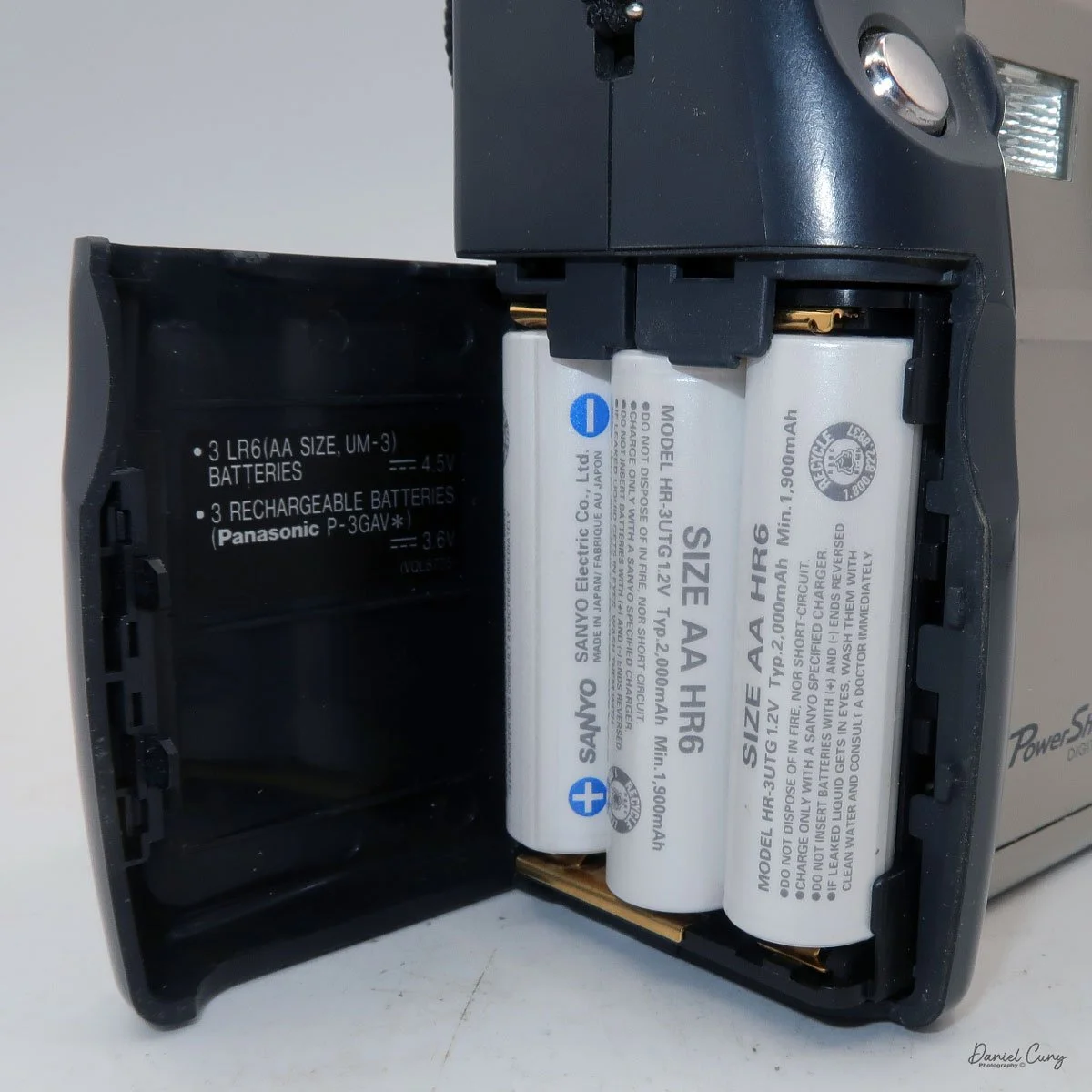
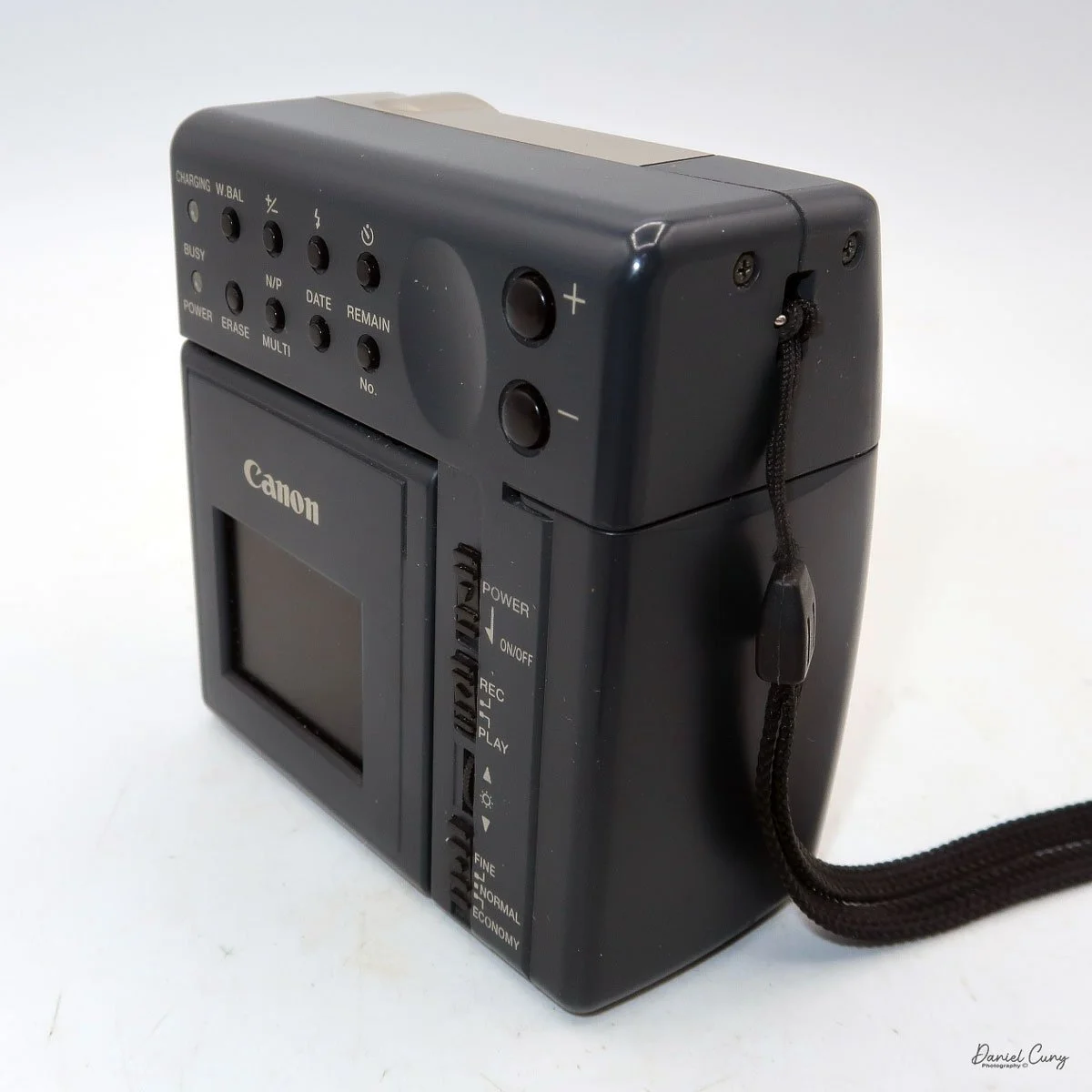
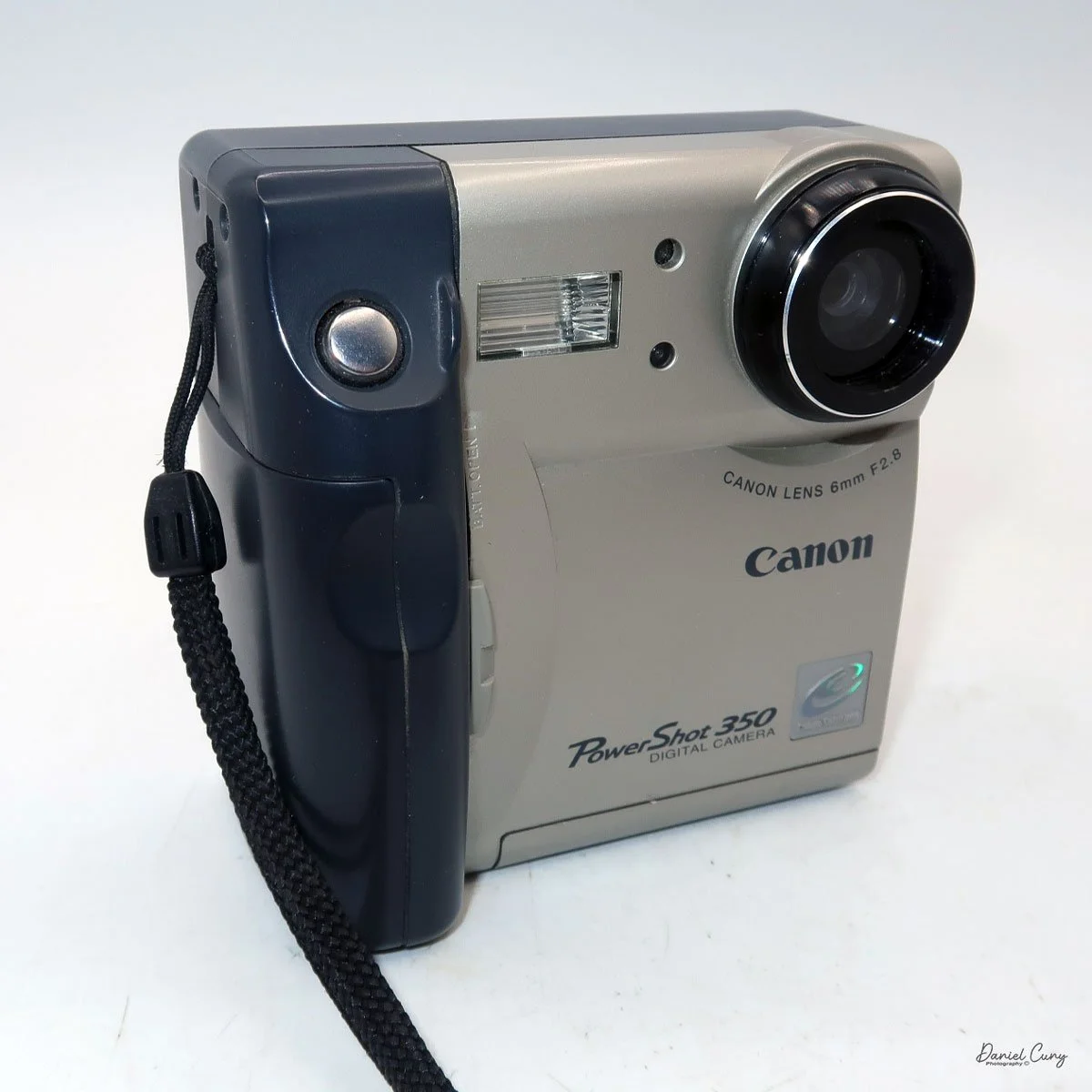
My Canon PowerShot 350 is a comfortable camera to hold in your hand and is 3.5" wide by 3.75" tall, and 2" deep, and weighs only 10.2 ounces without 3-AA size batteries to power the camera. You can use rechargeable batteries, or, if you prefer, Alkaline batteries. Initially, the camera came with a battery charger, but it wasn't included with the camera I recently purchased.
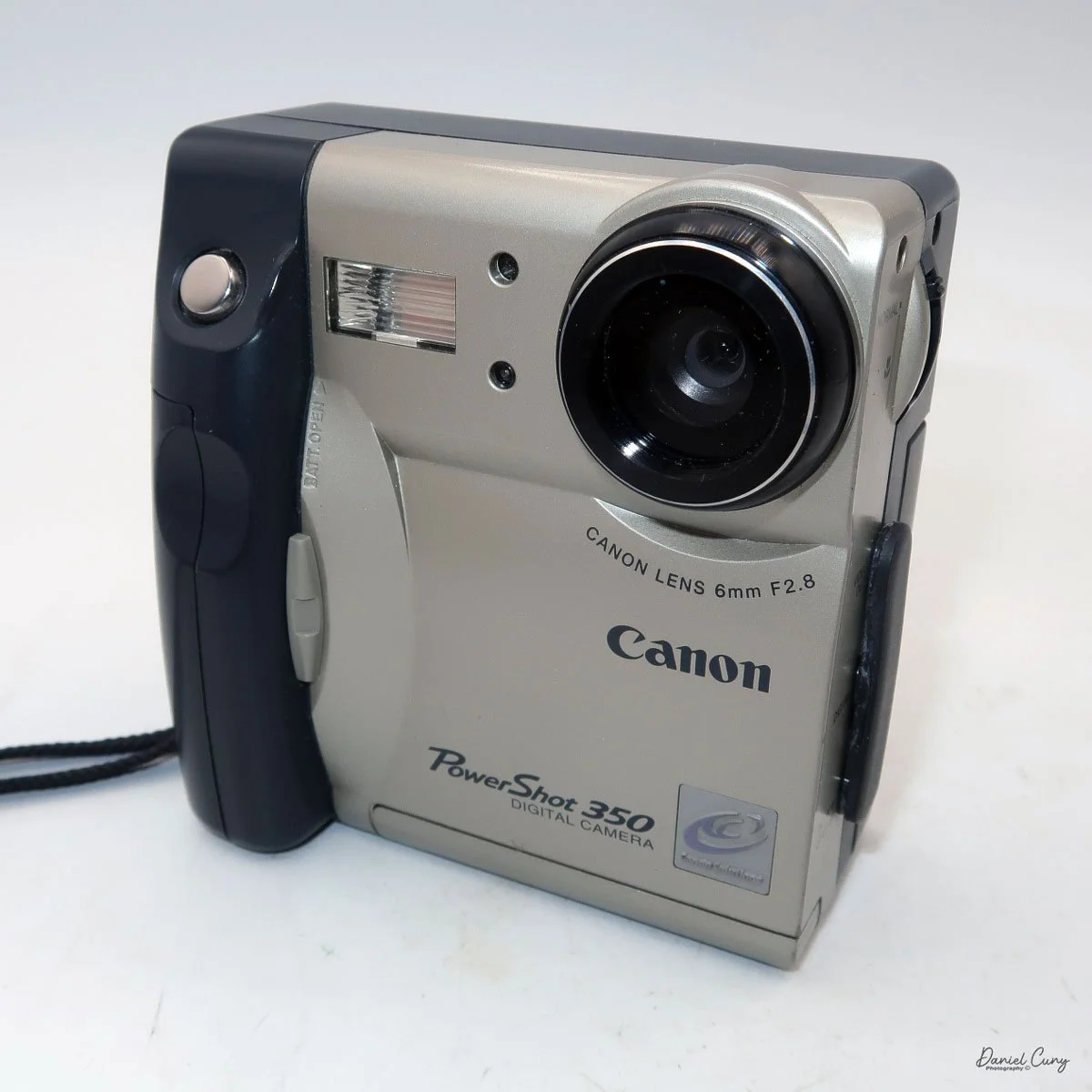
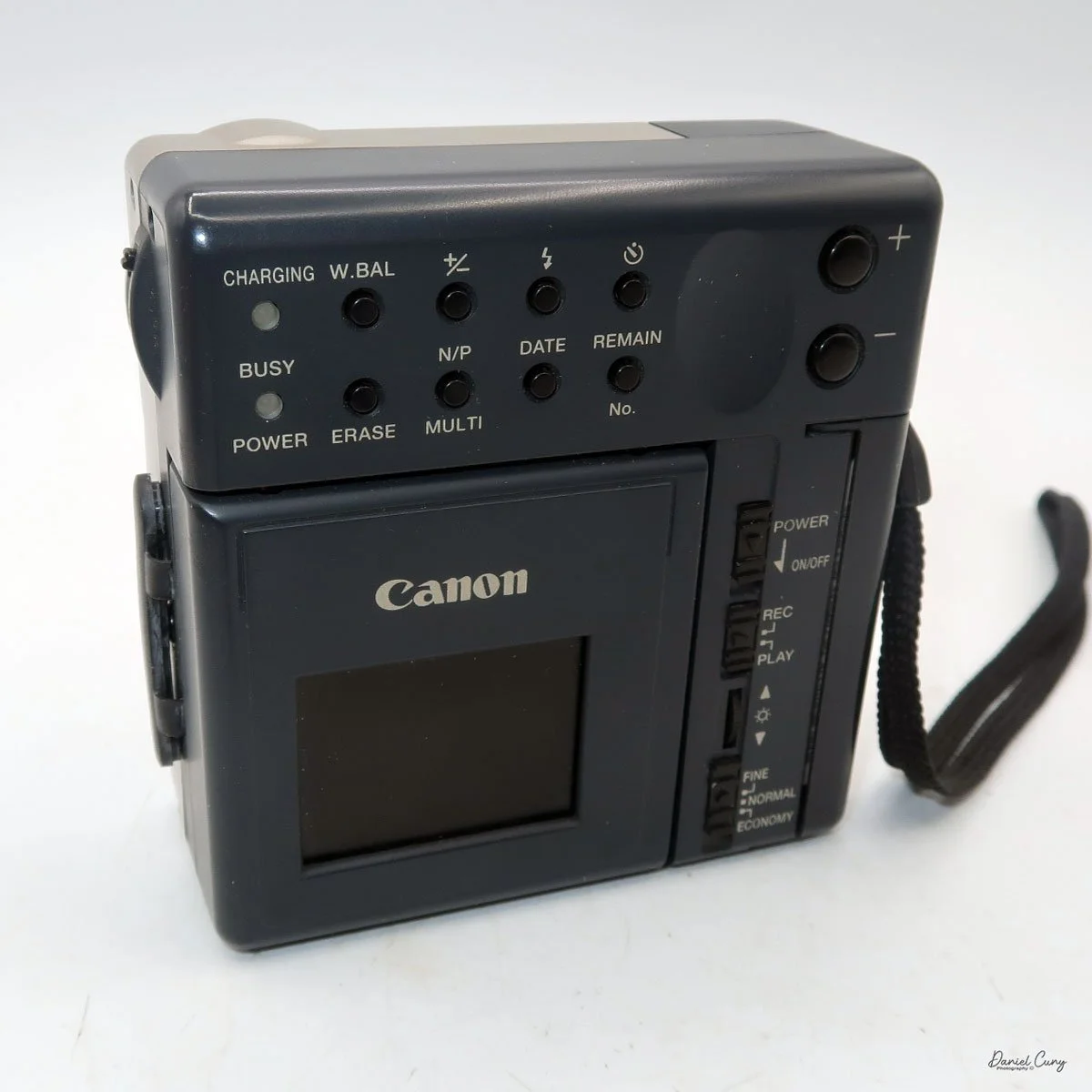
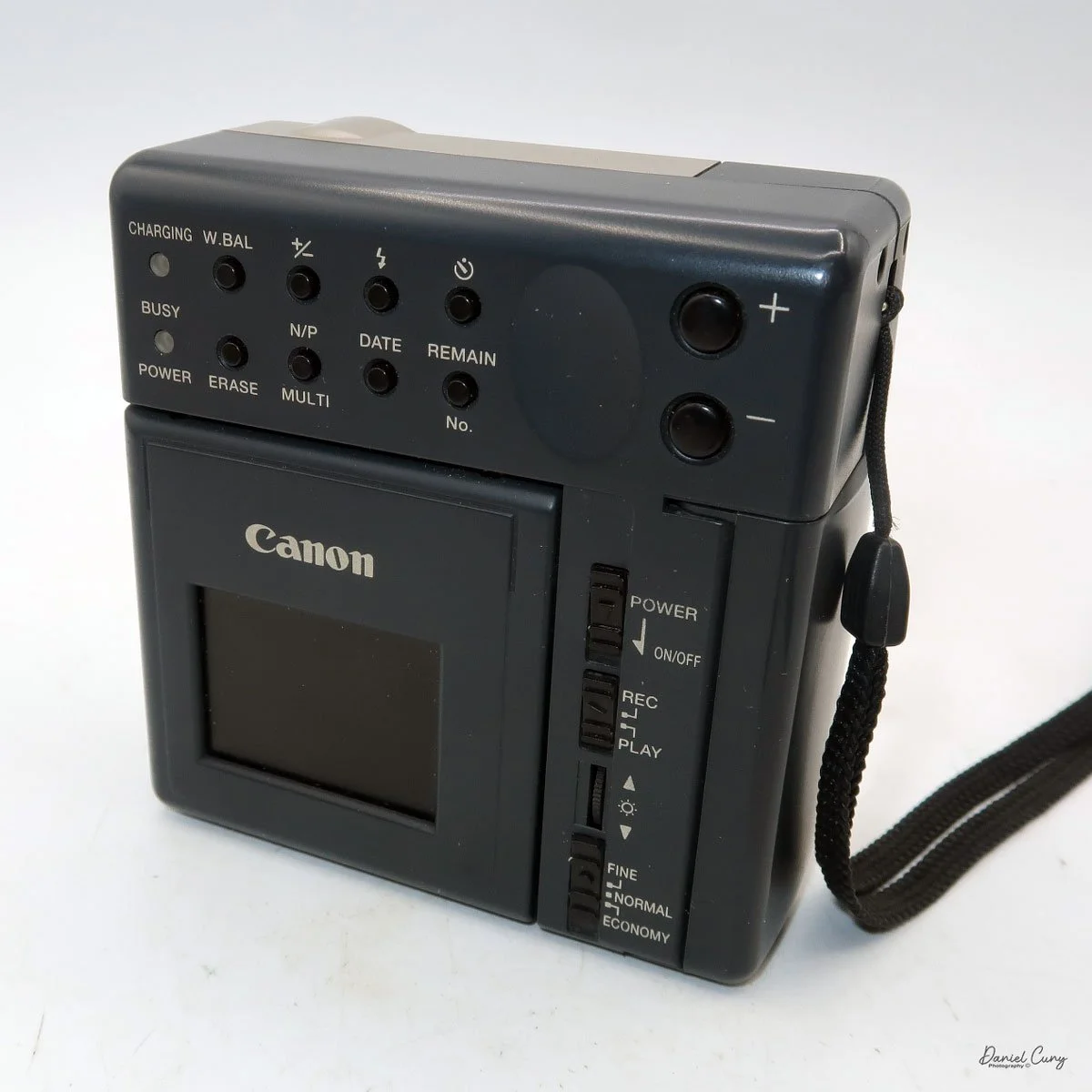
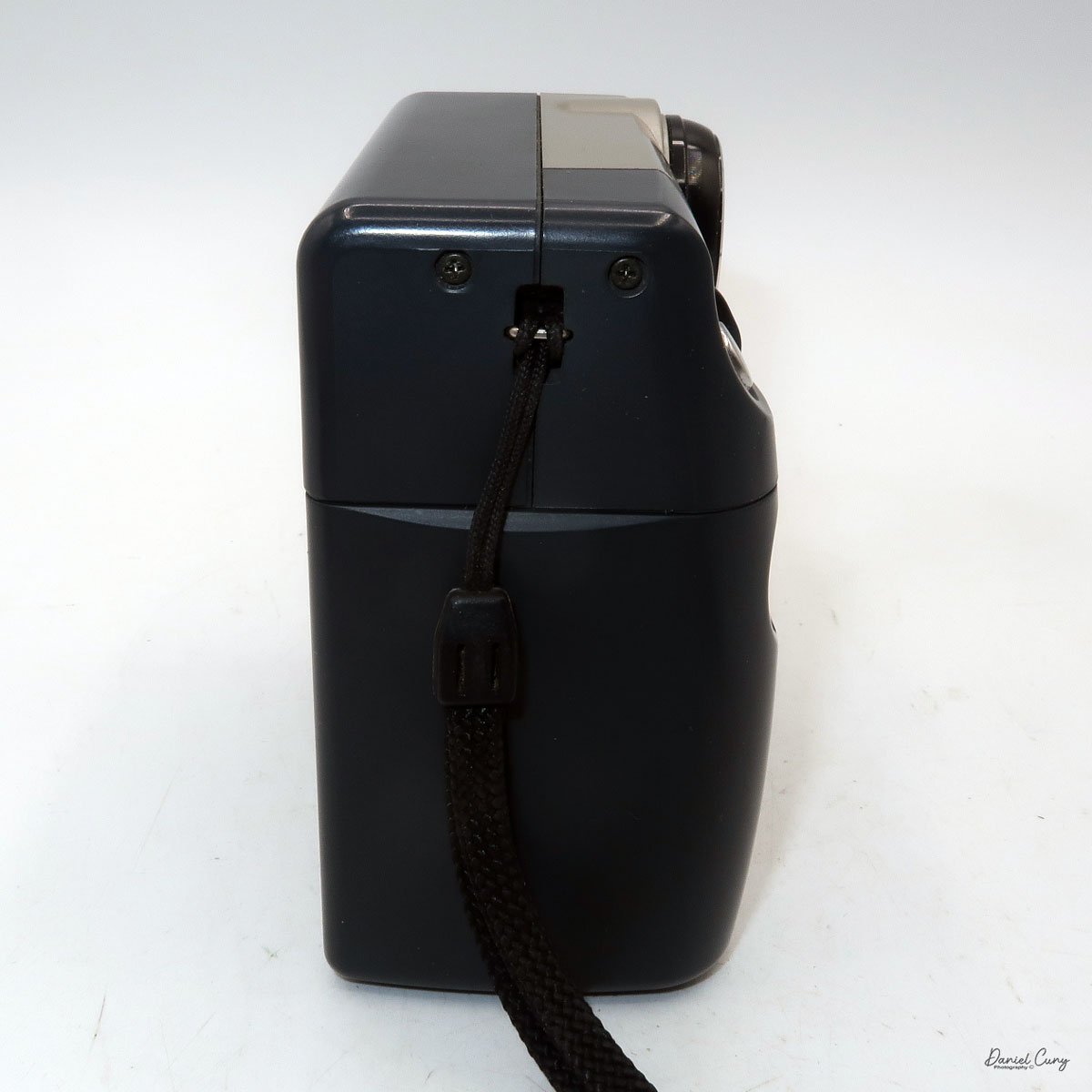
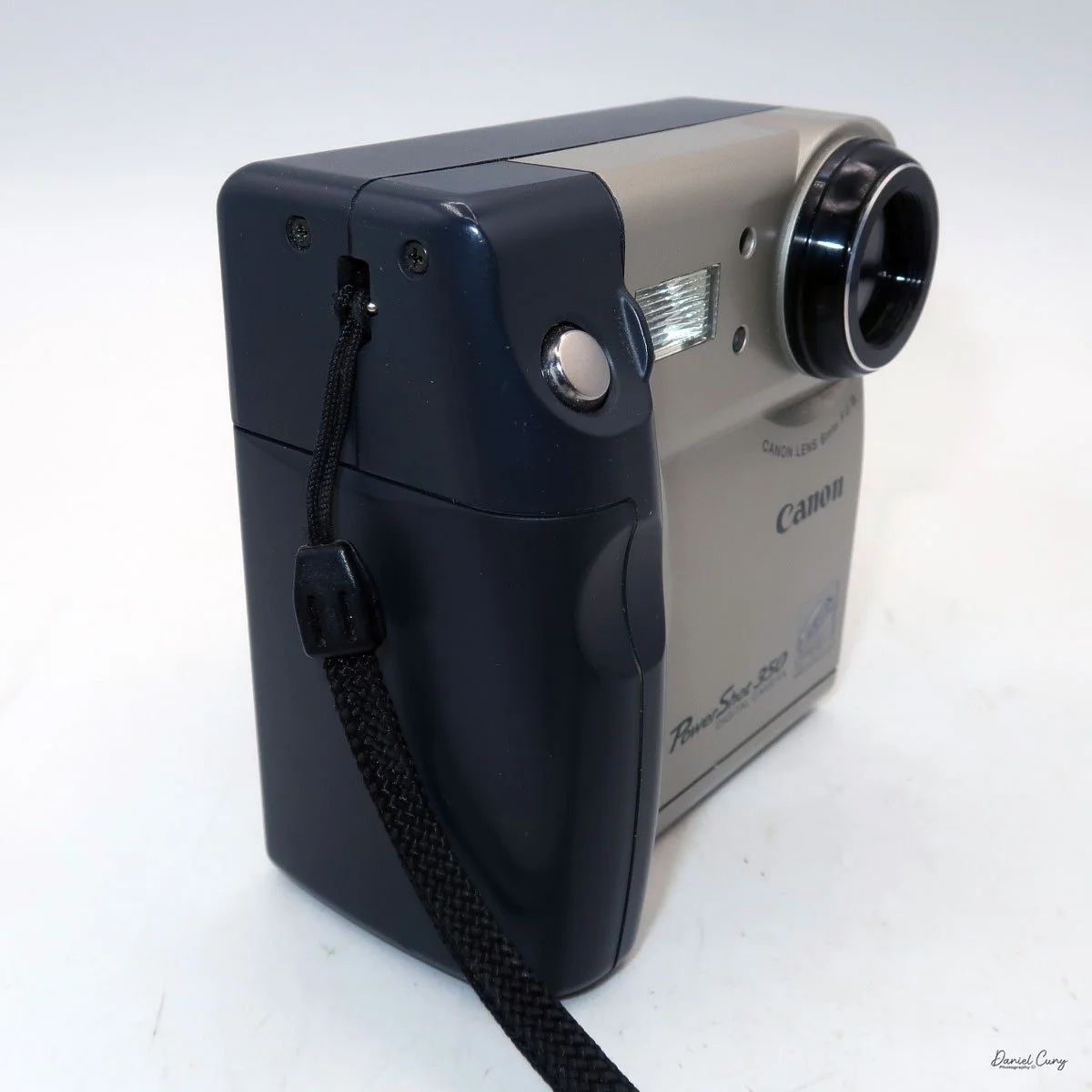












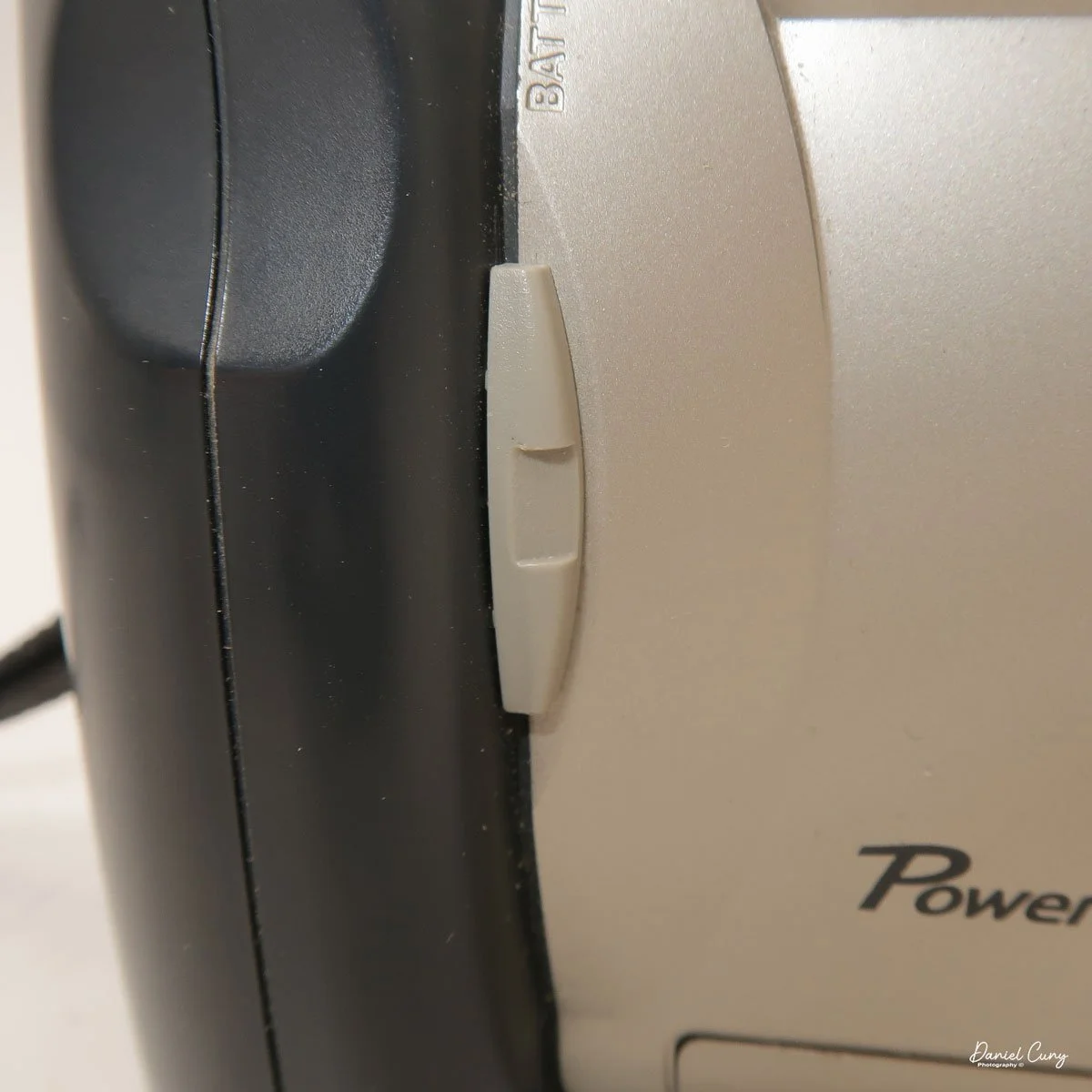
I generally prefer rechargeable batteries for this style of camera, as they perform very well. To put the batteries in the camera, on the inside of the camera's grip is a small lever you slide up to open the battery door. Once the three AA batteries are in the camera, close the battery door to start using the camera.
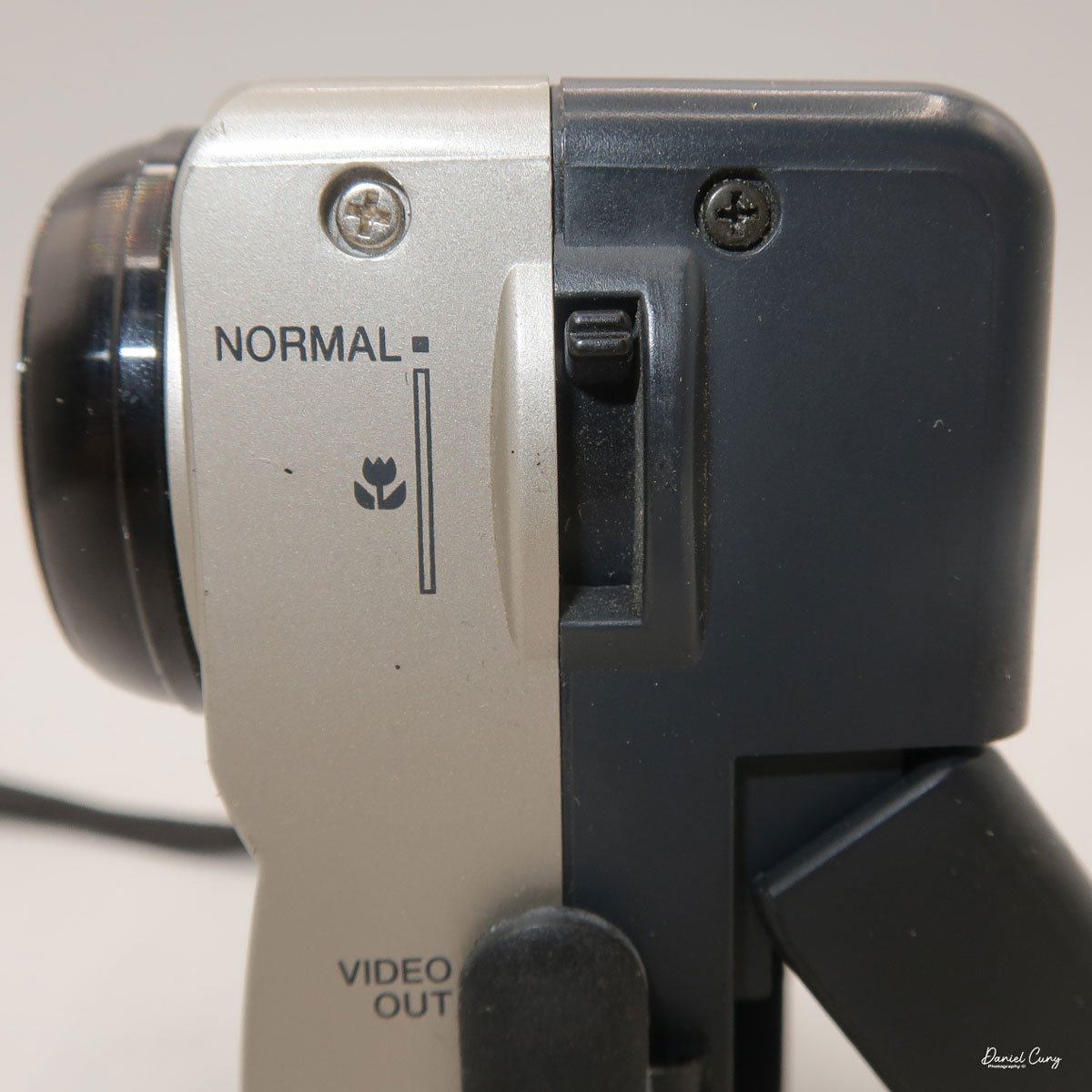
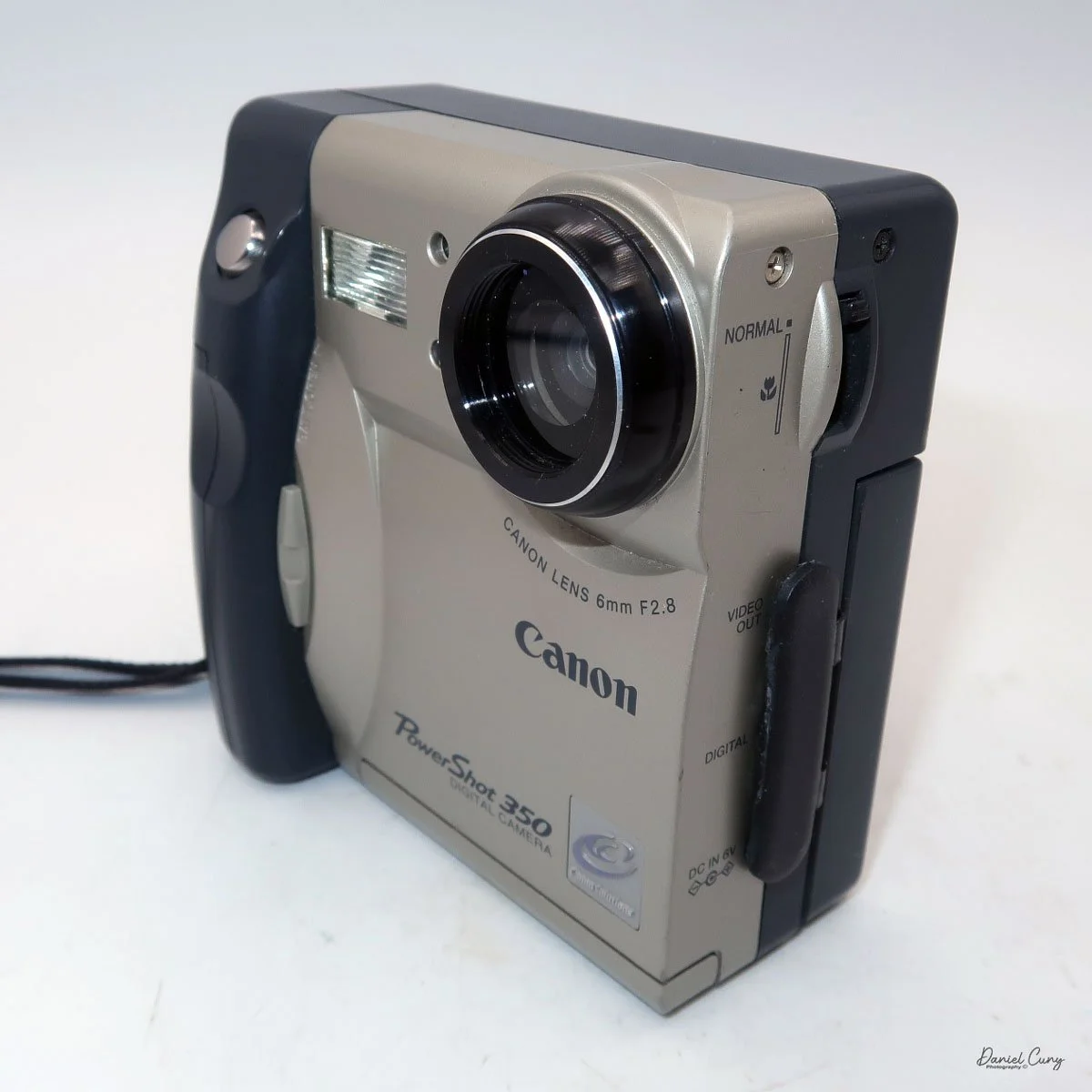
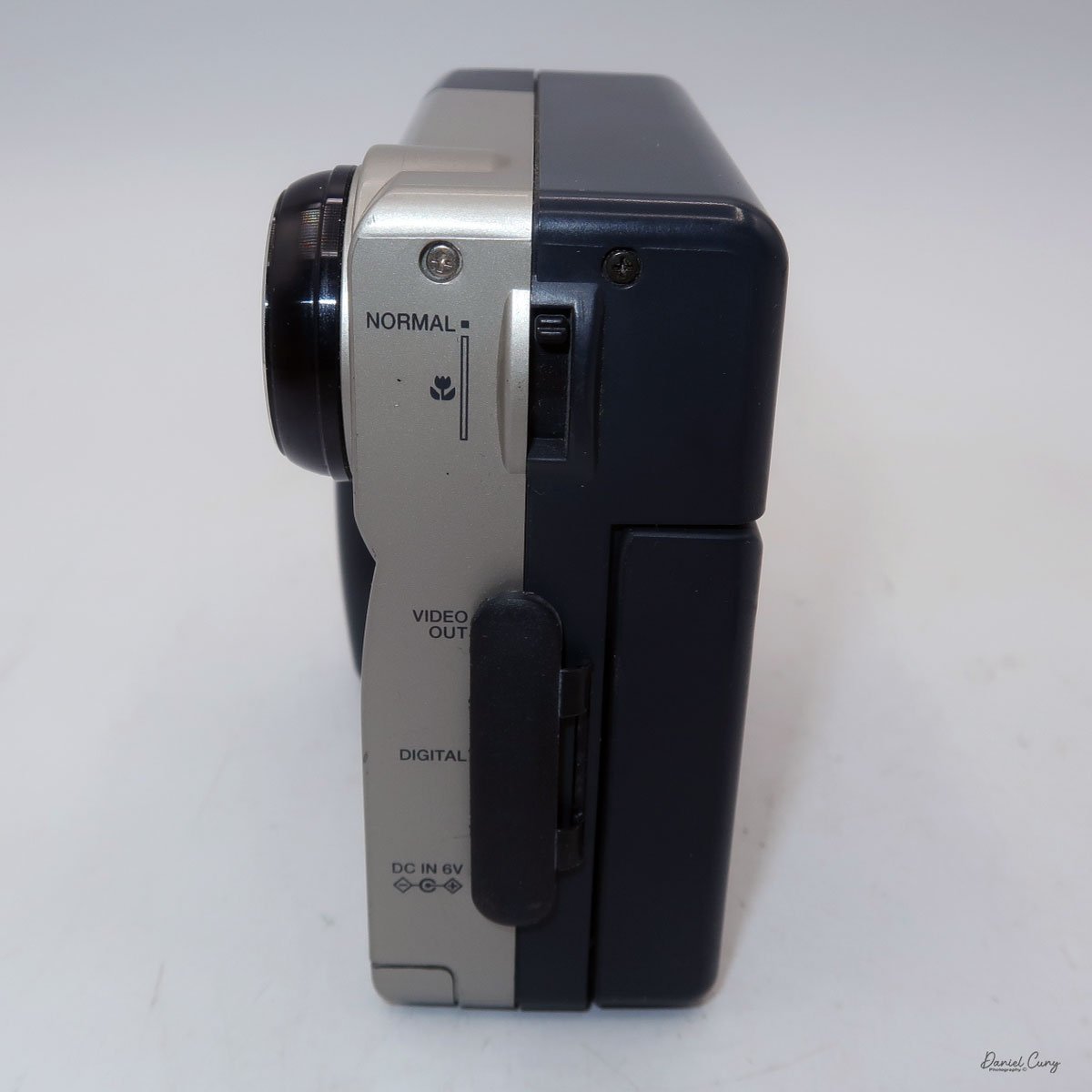
The Maximum resolution for the Canon PowerShot 350 camera was 640x480 with 24-bit color on a 350,000-pixel CCD sensor. The camera incorporates a 6mm f/2.8 lens and a 0.35-megapixel sensor. The lens is equivalent to a 43mm on a standard 35mm camera. The lens is a fixed focus, with Macro capability. In normal operation, the lens will focus from 26" to infinity. On the side of the camera, near where the lens is, is a slider for macro. Macro will focus from 1.2" to 26" by sliding the lever up and down to achieve focus which you can see on the 1.8" adjustable LCD screen on the back of the camera. The shutter speed range on the camera is from 1/4 to 1/2000, all using an internal TTL, programmed metering system with over/under exposure compensation, which I'll discuss later.
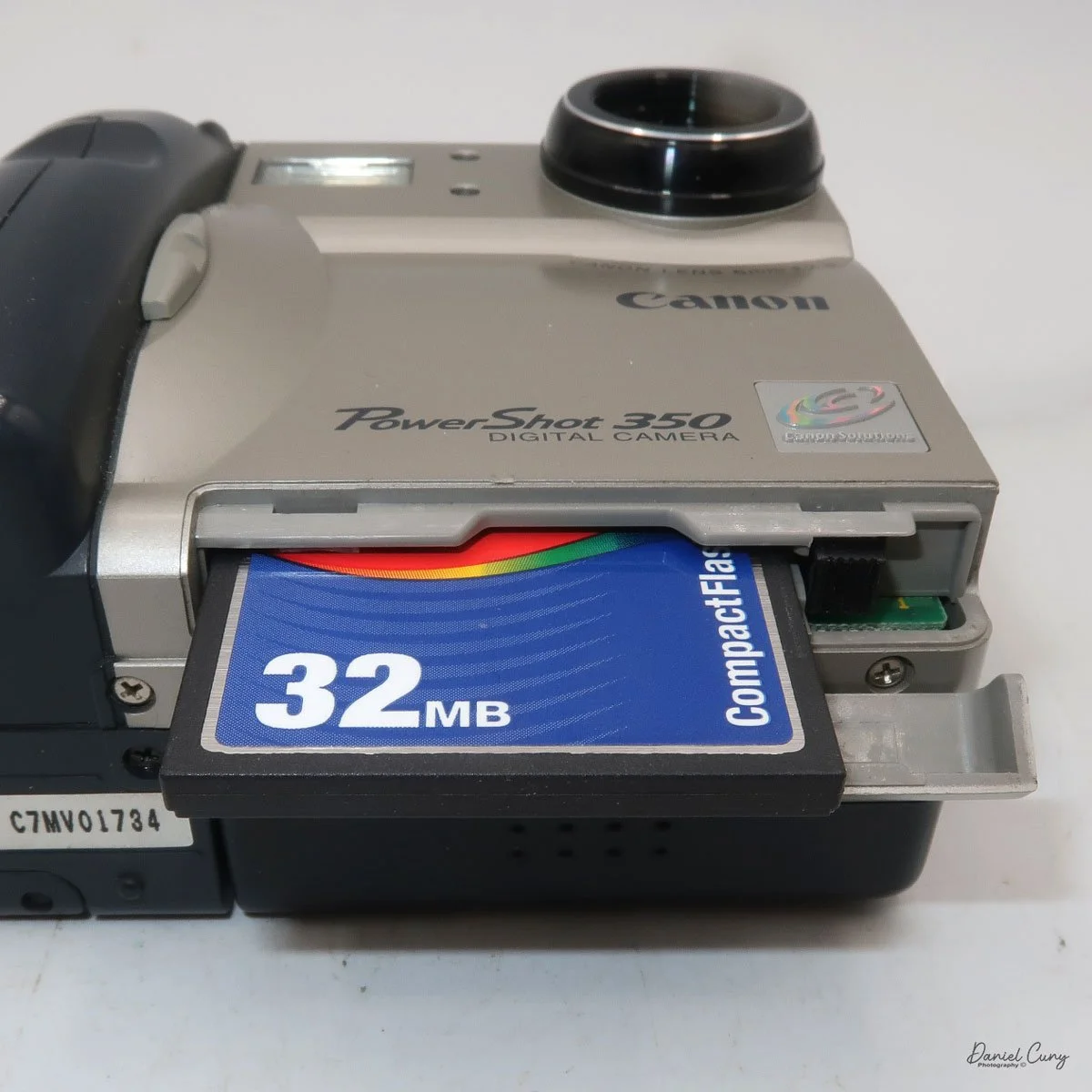
The images are written to a removable CompactFlash card, which fits into the bottom of the camera. At the bottom of the camera is a small door that you slide towards the front of the camera to open. Once opened, you'll see the slot for the 2 MB card that came with the camera. I don't have a 2 MB card anymore, so I had to use the 32 MB card, which is the smallest I currently have.
To remove the CF card, on the side of the slot is a small button that is folded to the side. Pull the button up and press in which will slide the CF card out of the camera. After inserting the CompactFlash card, fold the button to the side to close the card door.
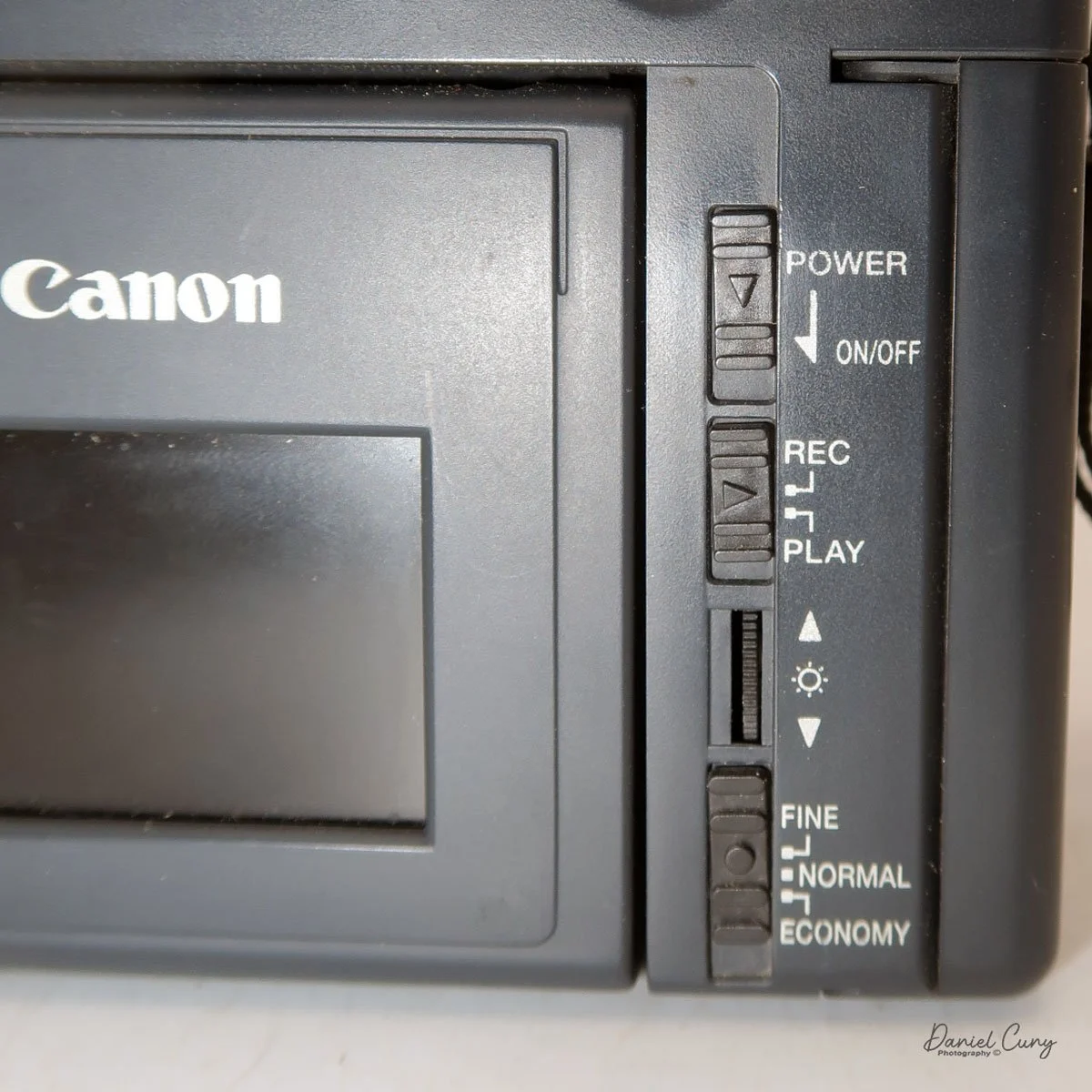
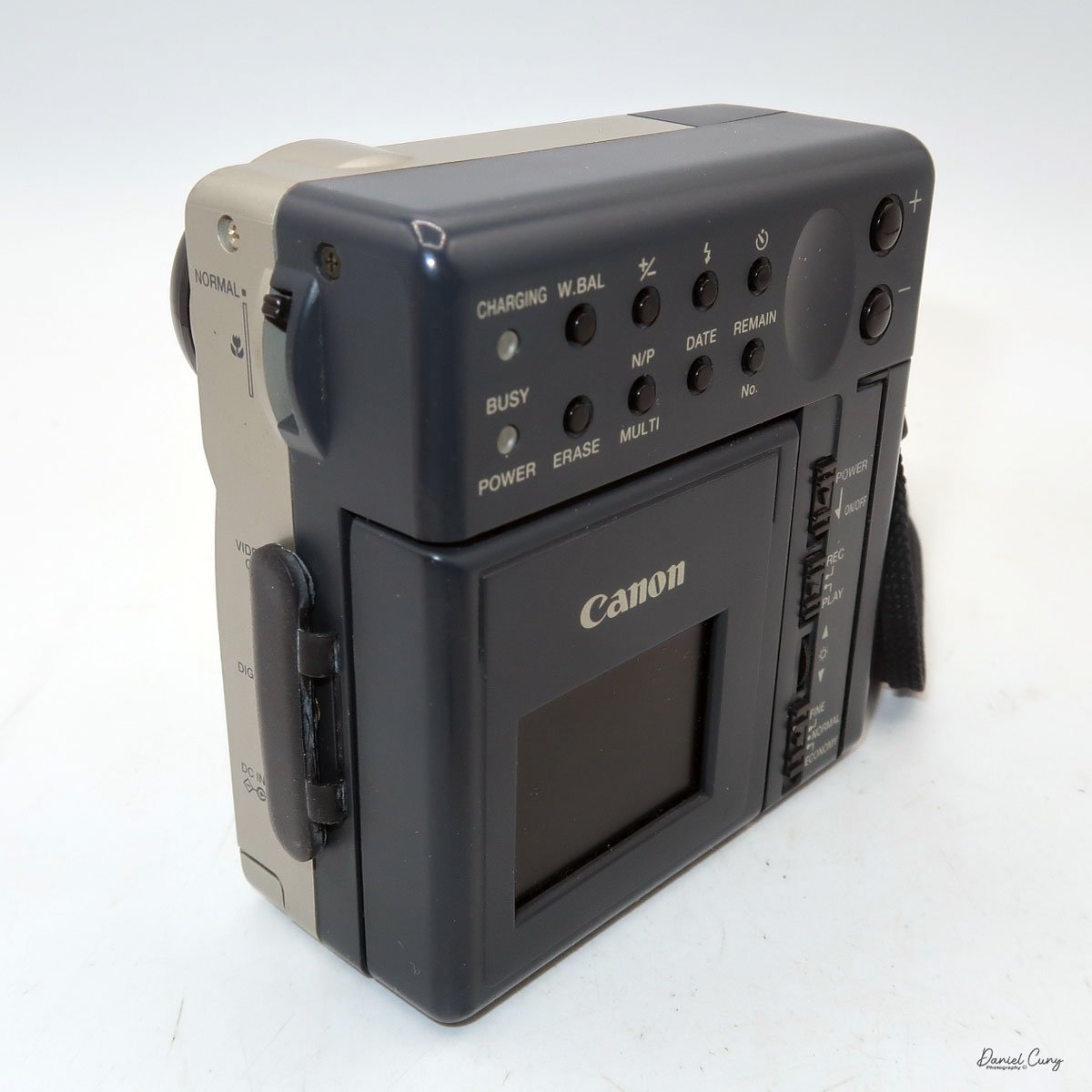
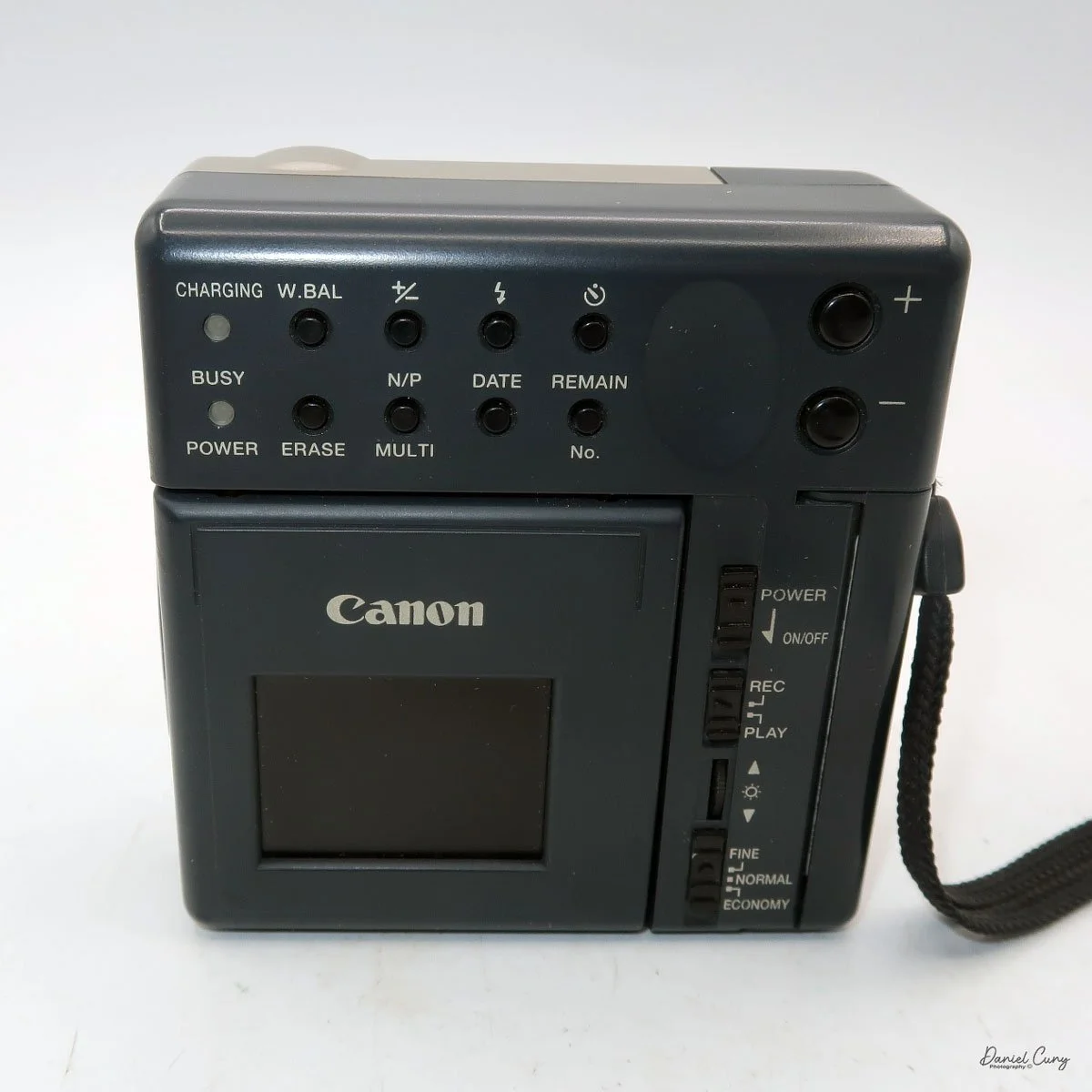
On the back of the camera, along the right side of the adjustable screen, are four controls. The top is the power on/off button. Below that is the switch to "record" or "playback" these images on the CompactFlash card. Next is a wheel with +/- controls to adjust the rear screen brightness, and at the bottom is a switch to select image quality: Fine, Normal, or Economy. On a 2 MB card included, you could fit 11 images in Fine, 23 in Normal, or a whopping 47 in Economy.
When you turn the camera on via a switch on the back of the camera, you do see a "live view" on the adjustable screen on the back of the camera. Next to this very small 1.8" screen by today's standard, there is a wheel that will brighten or darken the image on the screen. Unfortunately, when there is any light outside, the screen is almost impossible to view images, and you'll need to shade it to even see a faint image.
The same is true when you view the images you've recently taken, which pop up on the screen after the image was taken. Once you shade the screen, you'll be able to see the image better. In low-light or indoor situations, images appear better on the rear screen in both "live view" and playback mode. It's interesting to see the lag time in the "live view" images on the screen and how long it takes for the camera to write the image to the CF card. While photographing the back of the camera for this article, I took a short video showing the lag time of this camera. Here's the short video.
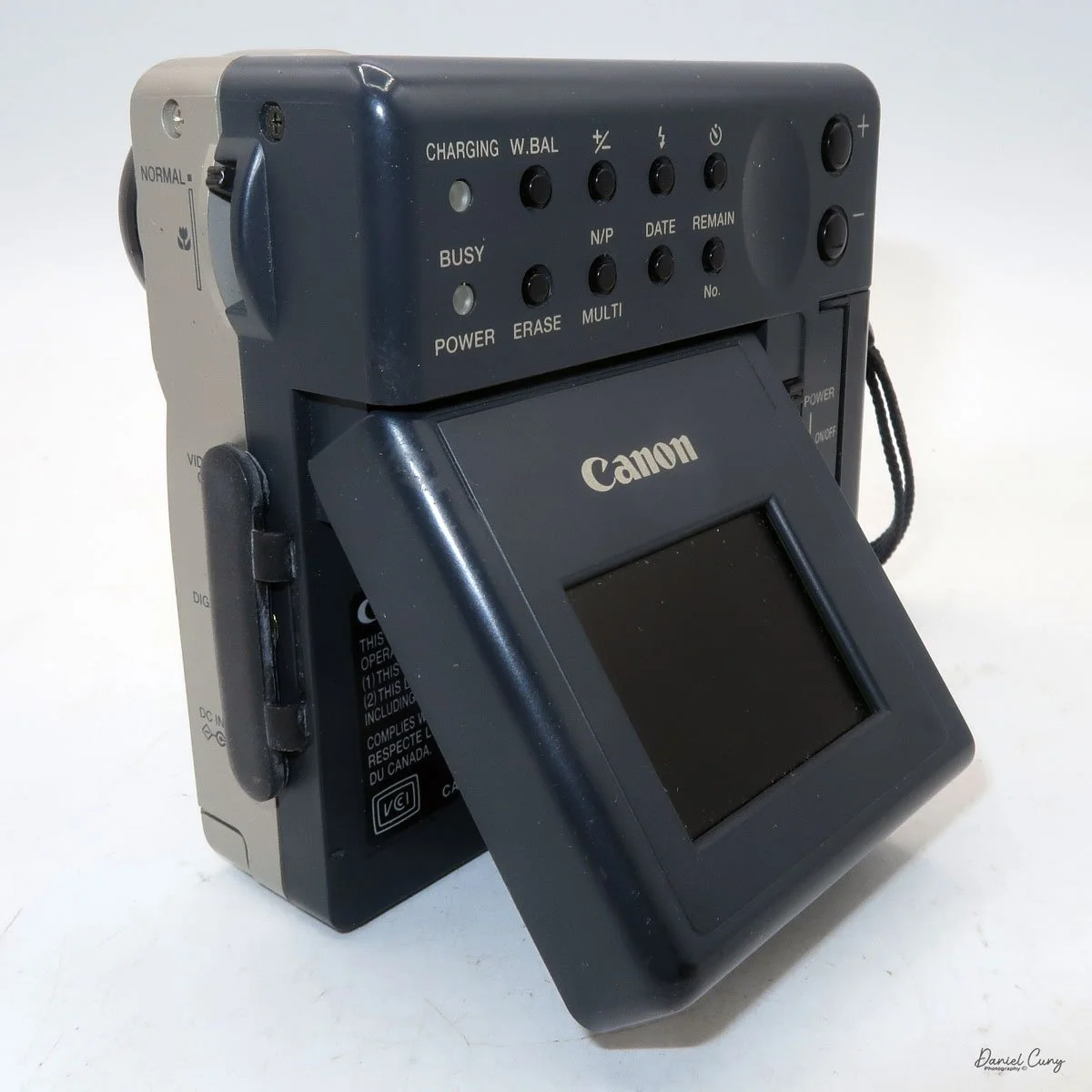
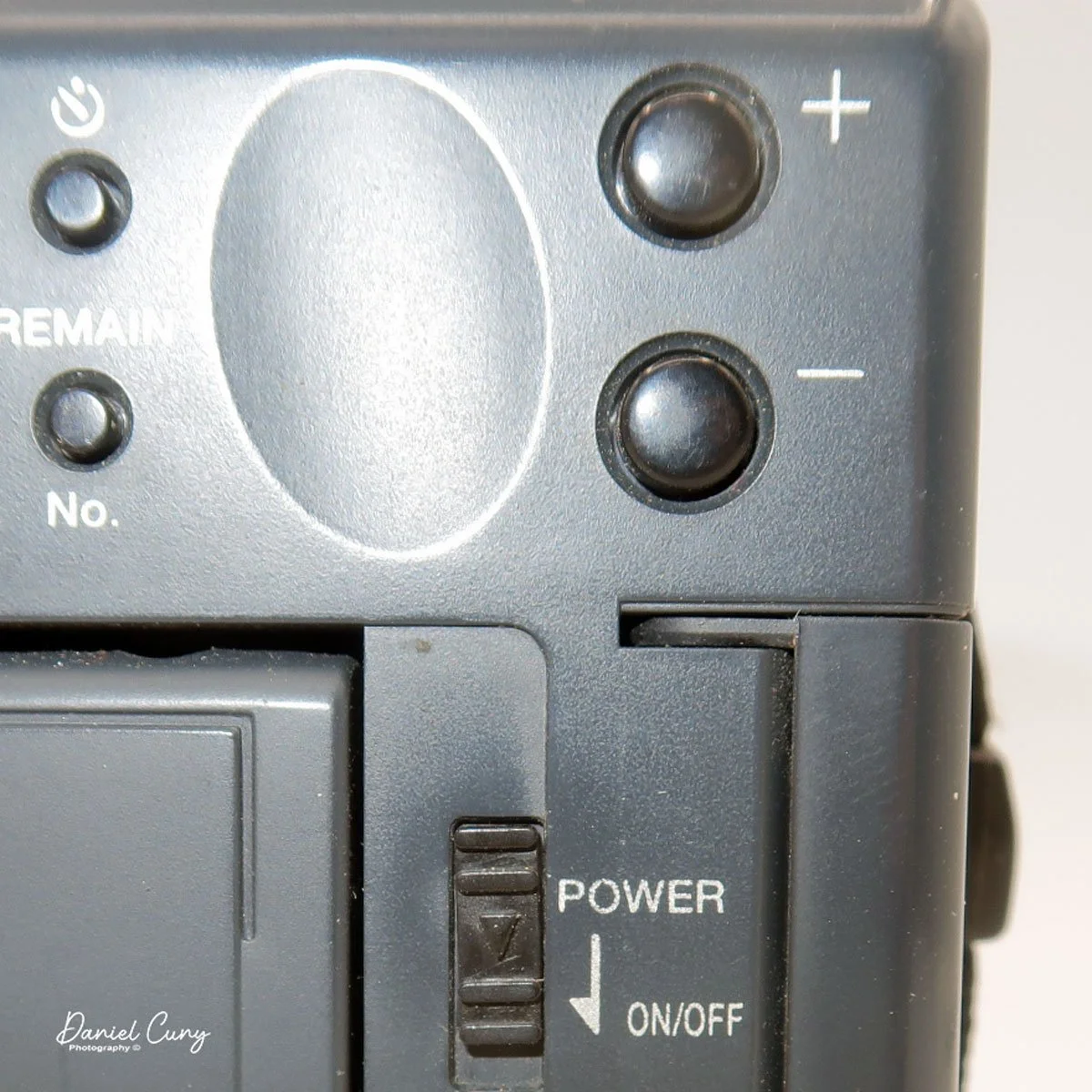
Most of the camera's controls are located on the rear of the camera body. There are two lights on the far left: one for charging the batteries and one for power/busy. They will light up when the camera is on and blink when the camera is "busy" or writing the image to the CF card.
The four buttons along the top are "W.Bal", setting the white balance for the images. "+/-", the ability to over or underexpose the images by up to four stops in either direction. "Flash" sets the flash modes: On, Off, Auto, and Red Eye Reduction. In "Self timer" mode, the camera will delay the photo by 10 seconds.
Along the bottom, the four buttons are "Erase", allowing the photographer to erase the photo taken, "N/P" in the top position is for Positive or Negative images to be taken, and on the bottom, "Multi", which allows you to see multiple photos on the screen on the back of the camera. When I put the camera in this mode for image playback, I could see the photos, but they were so small that it was hard to tell which ones they were, especially on such a small screen with low resolution compared to today's standards. Next to that is "Date," which lets you set the camera's date, and the last button is "Remain," which shows the number of images remaining on the CF card.
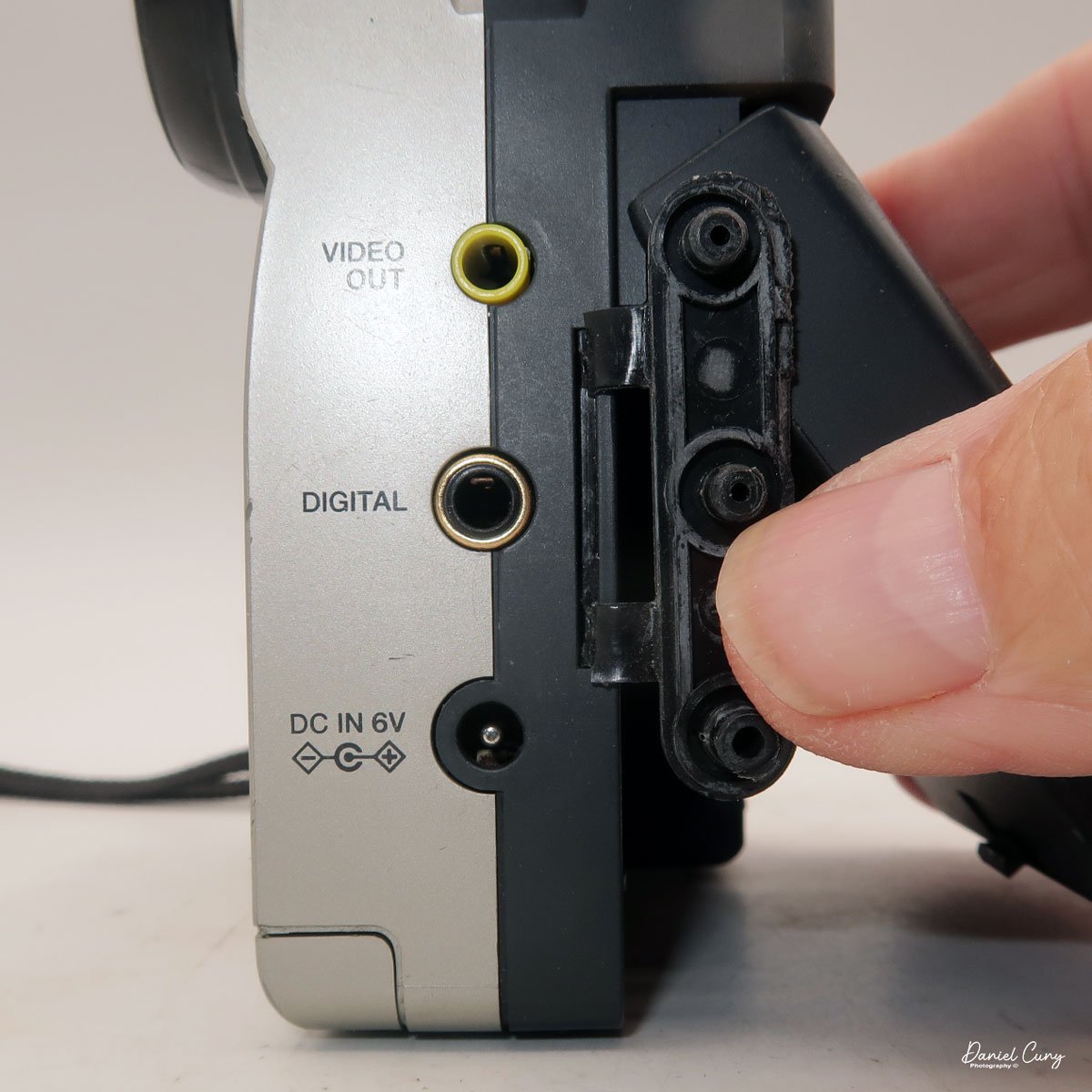
Along the side of the camera, under the lens's focus slider, are three ports labeled "video out" and "digital," so you can connect the camera to a television or computer to display its images. The bottom was for the charger to recharge the batteries within the camera.
My Images:
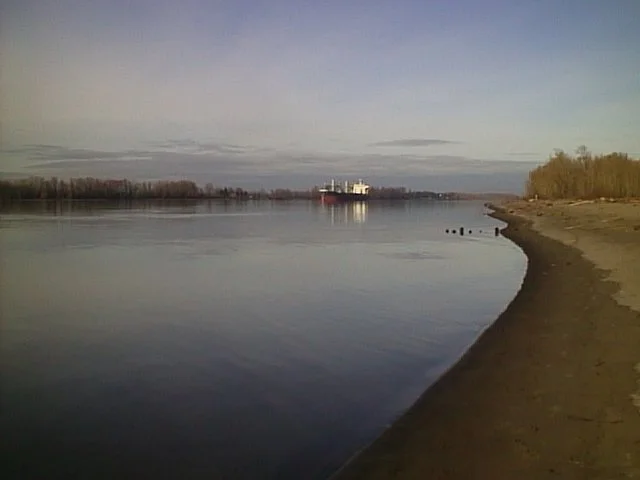
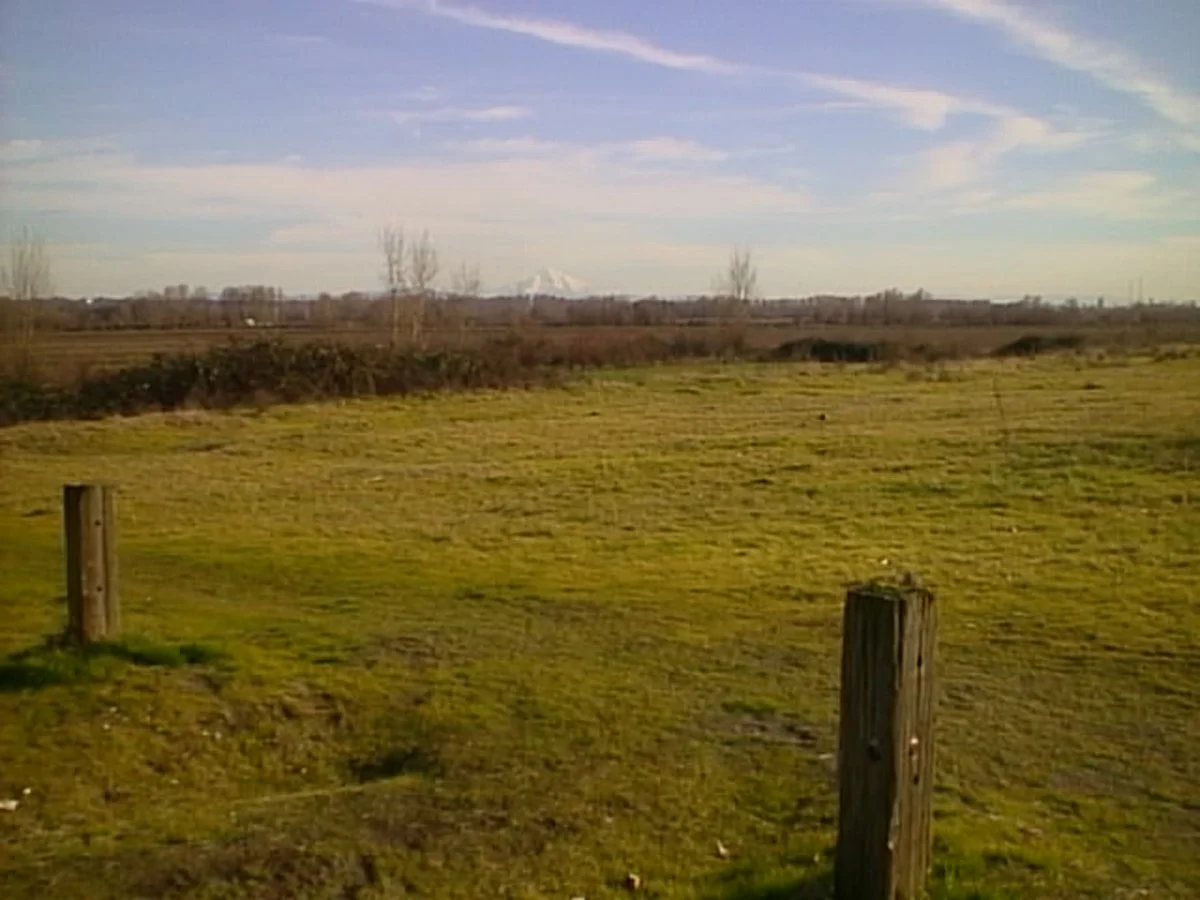
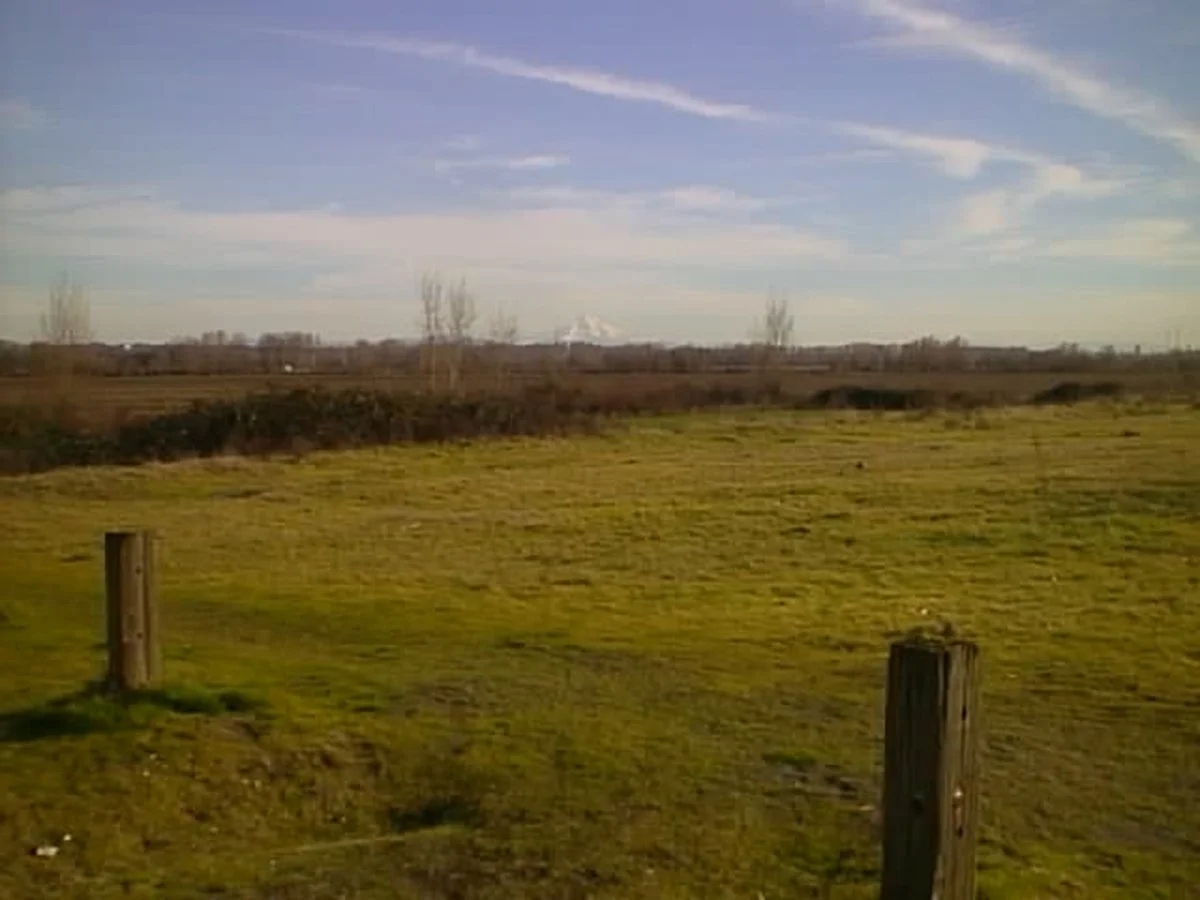
I took the camera to Frenchman's Bar, a local park just on the Columbia River where I live, to take the dog for a walk and to take photos with the Canon PowerShot 350. It was a surprisingly sunny January afternoon, with incredible scenes of the river and Mt. Hood.
What an excellent chance to take the camera out to see what it could do. When I got home, I offloaded the images to look at the file sizes. To my surprise, each image had the normal file, along with an incredibly small (2kb) matching thumbnail file used for preview purposes on the rear screen after taking the photo. The file sizes were 150kb for the Fine resolution, 71kb for the Normal, and 31kb for the Economy.
Here are some sample images I took during the walk.
Conclusion:
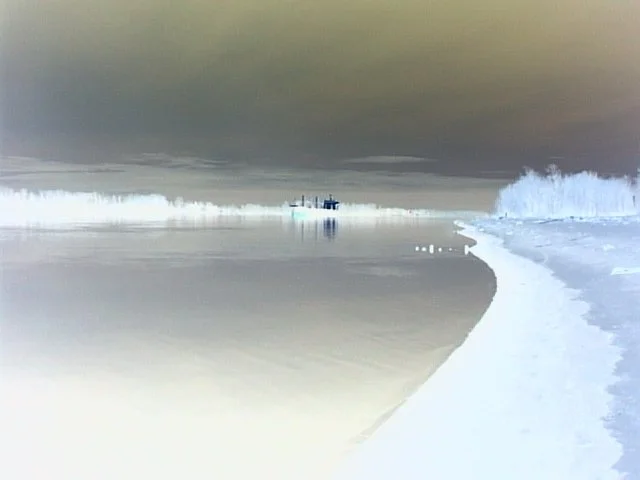
Since this camera used CF cards for image input, I didn't have to jump through many hoops to get images in and out of the Canon PowerShot 350. Since it was a familiar camera I had owned in the past, it was pretty straightforward, and the one thing I found interesting was the ability to photograph in the negative color range. It was more for gimmickry than functionality.
Nonetheless, it was fun to pick up and shoot with, but the writing time compared to what we have now is funny. Still, I'm happy to have such a complete camera, aside from a couple of cables.
Here's a link to my other Camera Reviews.
I also have a store on eBay, Cuny's Cameras and Photos, where I sell some of the cameras I've reviewed, along with other photographic odds and ends. If you see something you like, send me an email, and I'll offer a discount.
Thank you for taking the time from your busy schedule to go back almost 30 years to the technology in cameras before 2000. It's impressive how far cameras have come in this short time.
Until next week, please be safe.