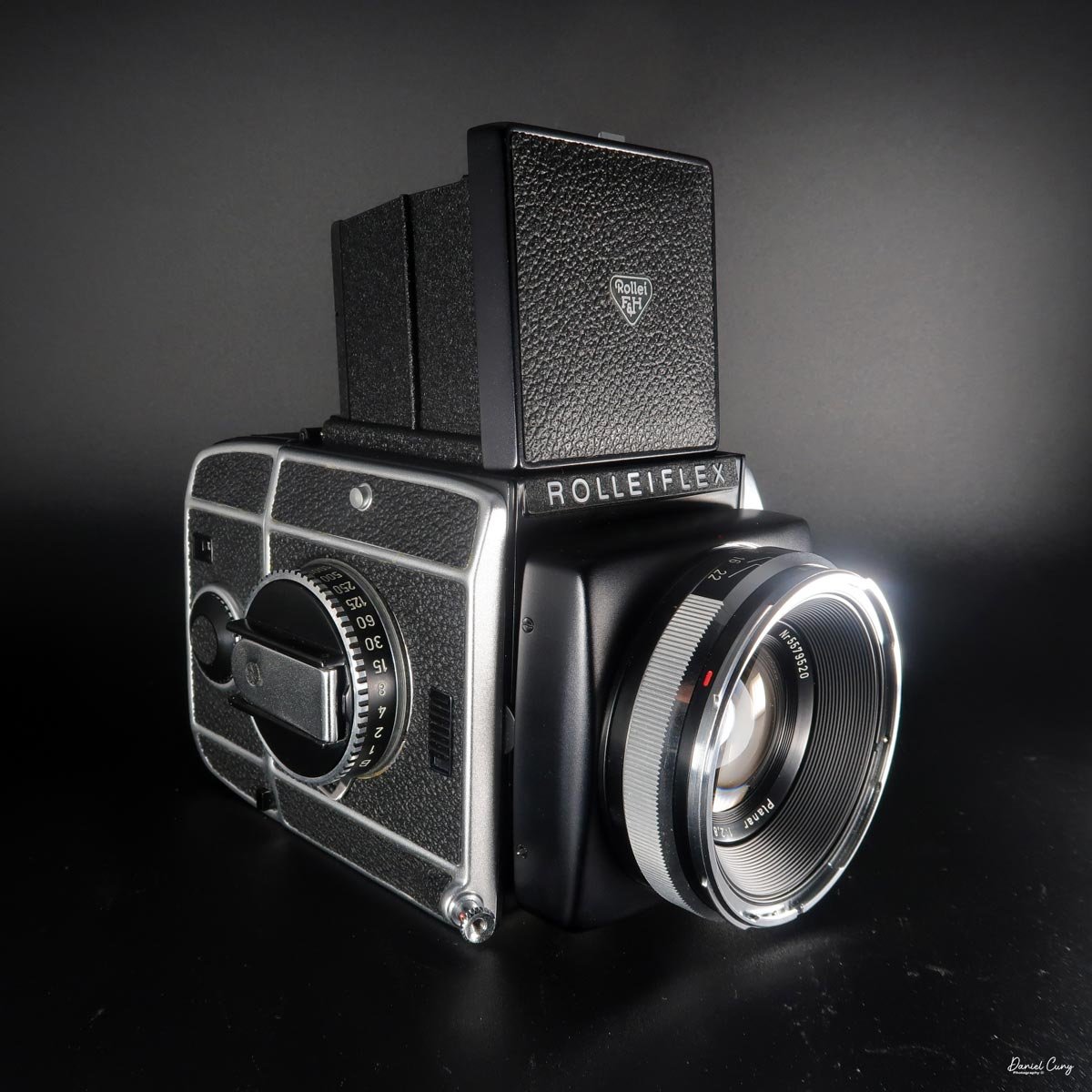
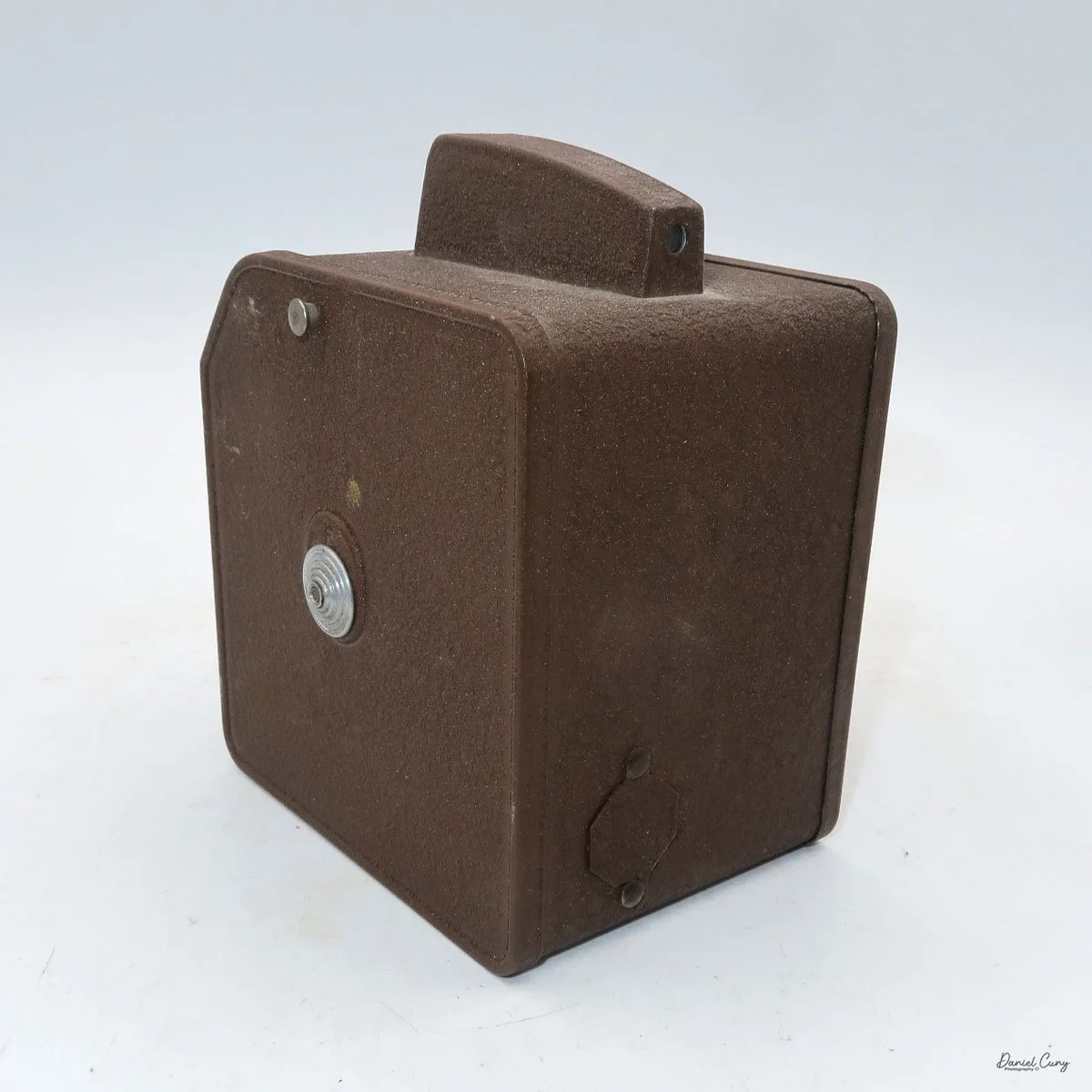
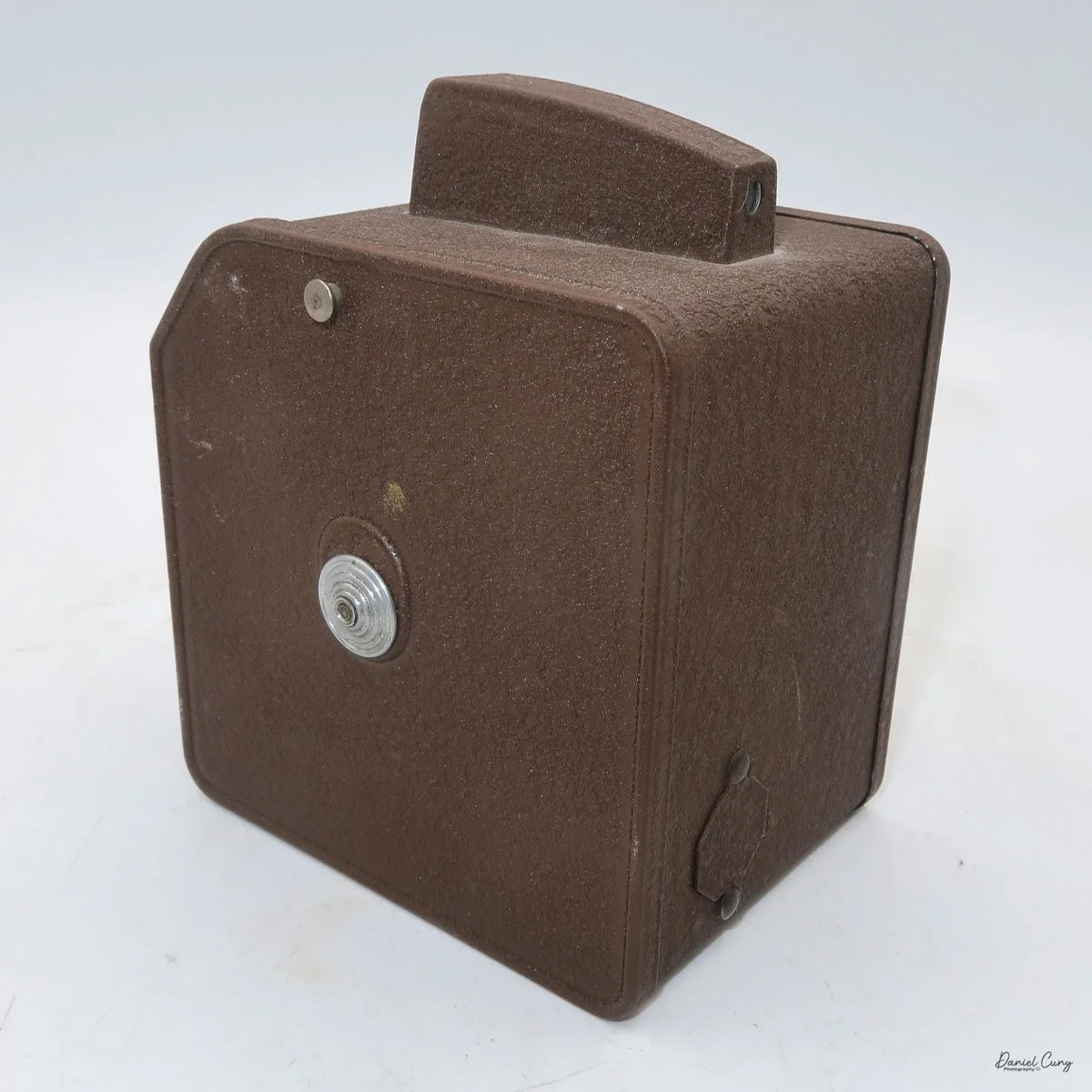
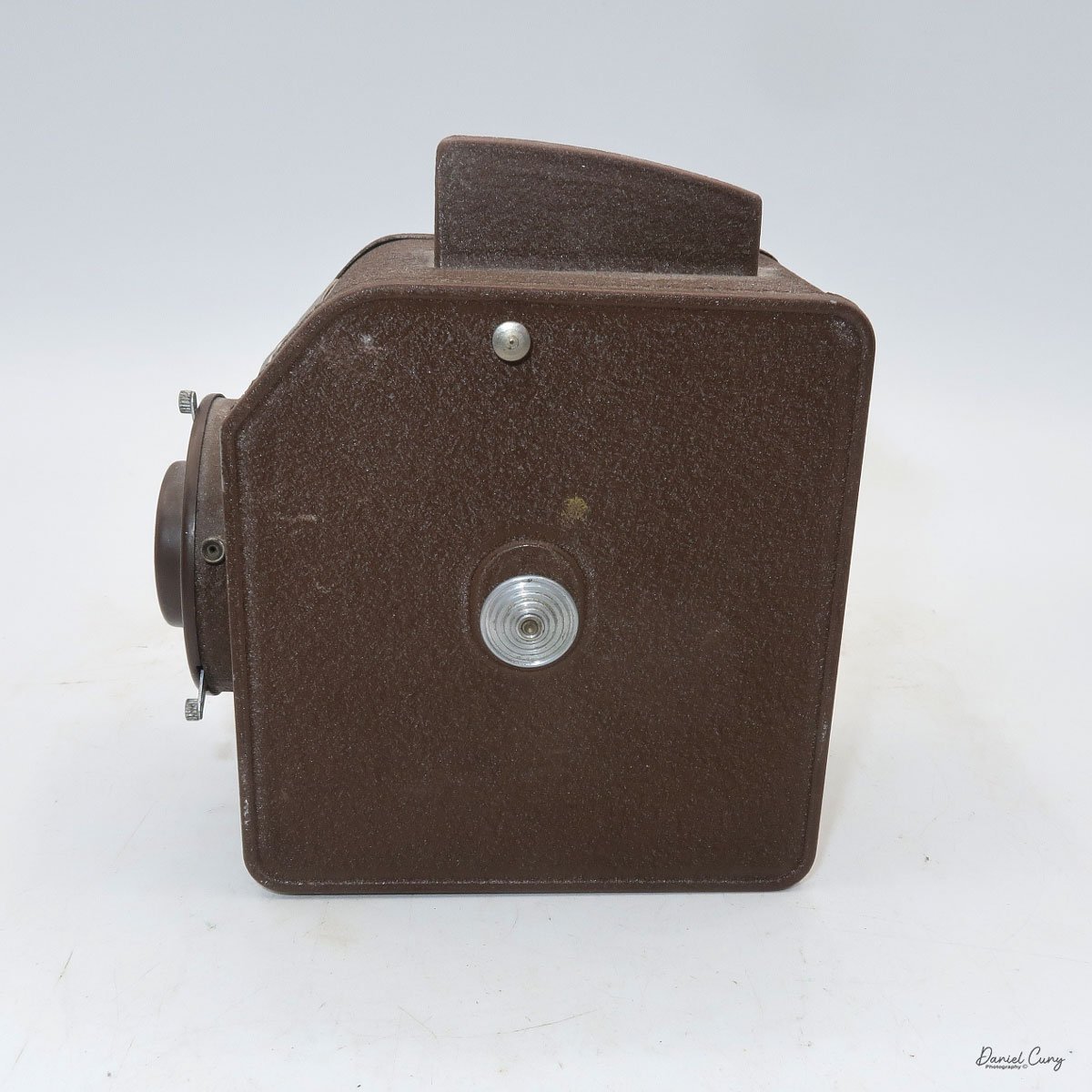
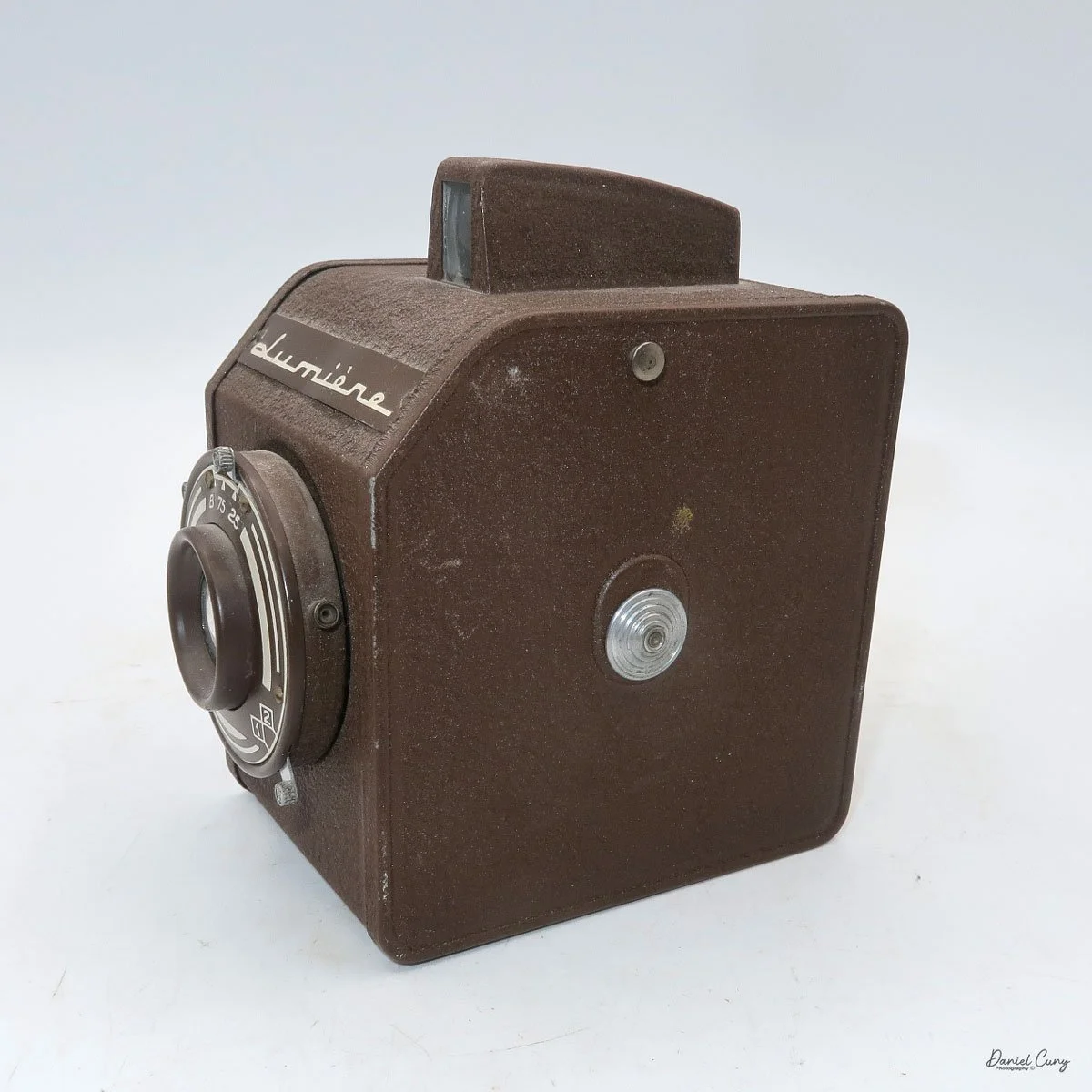
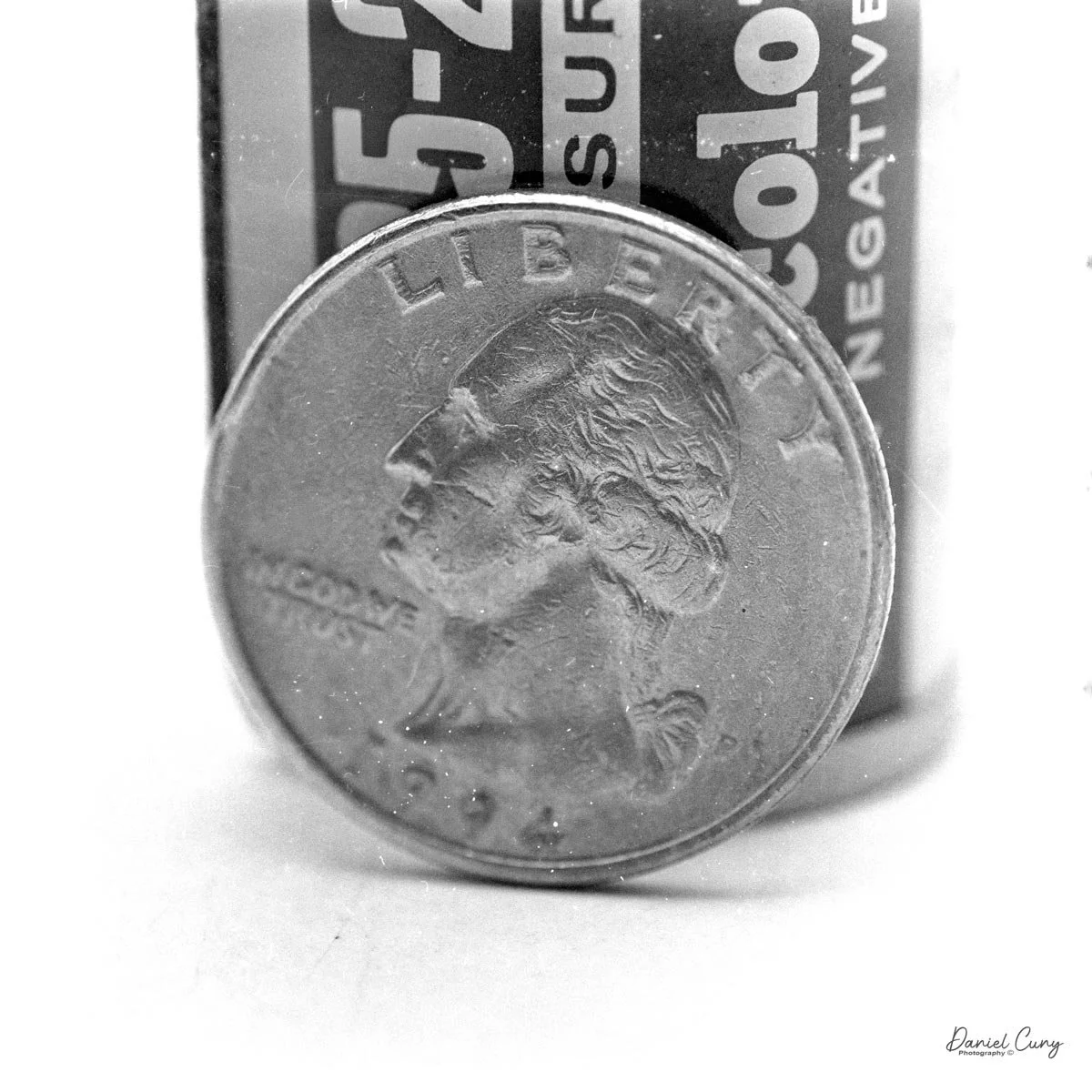My Rolleiflex SL66
As a photographer and photo industry professional for well over 50 years, I've had the privilege of working with just about every kind of camera you can imagine. From everyday 35mm SLRs and rangefinders to Hasselblad systems, I've logged a lot of miles with medium‑format gear as well.
In the late 1990s, I represented Sinar, which meant regular time behind some of the finest large‑format cameras available. Later, repping Leaf digital backs put me in front of Mamiya RBs and 645s, Hasselblad V and H systems, Fuji GX680s, and the Contax 645. With all that variety, there was still one big gap in my experience: I had never actually photographed with a Rolleiflex SL66.
About a year before I retired—so roughly three years ago—I finally had my chance. An SL66 with 80mm, 50mm, and 250mm lenses came up for auction online. I wasn't sure about the condition, but I rolled the dice and bid anyway.
When I won the lot at a surprisingly low price, my first reaction wasn't joy; it was suspicion. Inexpensive cameras often have a story. To my surprise, the body turned out to be mint‑to‑near‑mint, and the lenses were in equally excellent shape. The real question, of course, was whether it worked.
I pulled off the lens cap, removed the dark slide, cocked the shutter, and pressed the release. At a fast speed, the camera rewarded me with that beautiful, crisp shutter sound. Then came the real test: I set it to 1/2 second. The shutter opened, paused, and closed exactly as it should. At that point, I had a big grin on my face—I knew I had a mechanically healthy SL66 on my hands.
And then, like so many good intentions, the camera went on a shelf.
Background: Rollei's Leap into SLRs
Rollei Advertisment
For decades, "Rolleiflex" meant twin‑lens reflex. That changed with the introduction of the Rolleiflex SL66 at Photokina 1966, Rollei's serious move into the professional 6×6 SLR world. Designed as a studio‑oriented system to challenge Hasselblad, the SL66 combined a focal‑plane shutter, modular film backs, and interchangeable finders with familiar Rollei ergonomics: left‑hand focusing and right‑hand film advance.
Rollei had explored the idea of a medium‑format SLR as far back as the mid‑1950s, but strong TLR sales kept those projects on the shelf until demand shifted and Hasselblad began to dominate professional work. When it finally arrived, the SL66 was a true "engineer's camera": bellows focusing, the ability to reverse‑mount lenses for close‑up work, and front‑standard tilt for plane‑of‑focus control—features that gave it some of the movements you'd normally associate with a view camera.
Built from 1966 to 1982, the SL66 used 120/220 roll film in 6×6 backs and typically wore Carl Zeiss Planar glass, firmly placing it in the high‑end studio category. Later SL66E and SL66SE models added through‑the‑lens metering and improved electronics. Still, the core concept stayed the same: a heavy, extremely capable, close‑focus‑friendly studio machine in a world increasingly moving toward lighter, more electronic medium‑format systems.
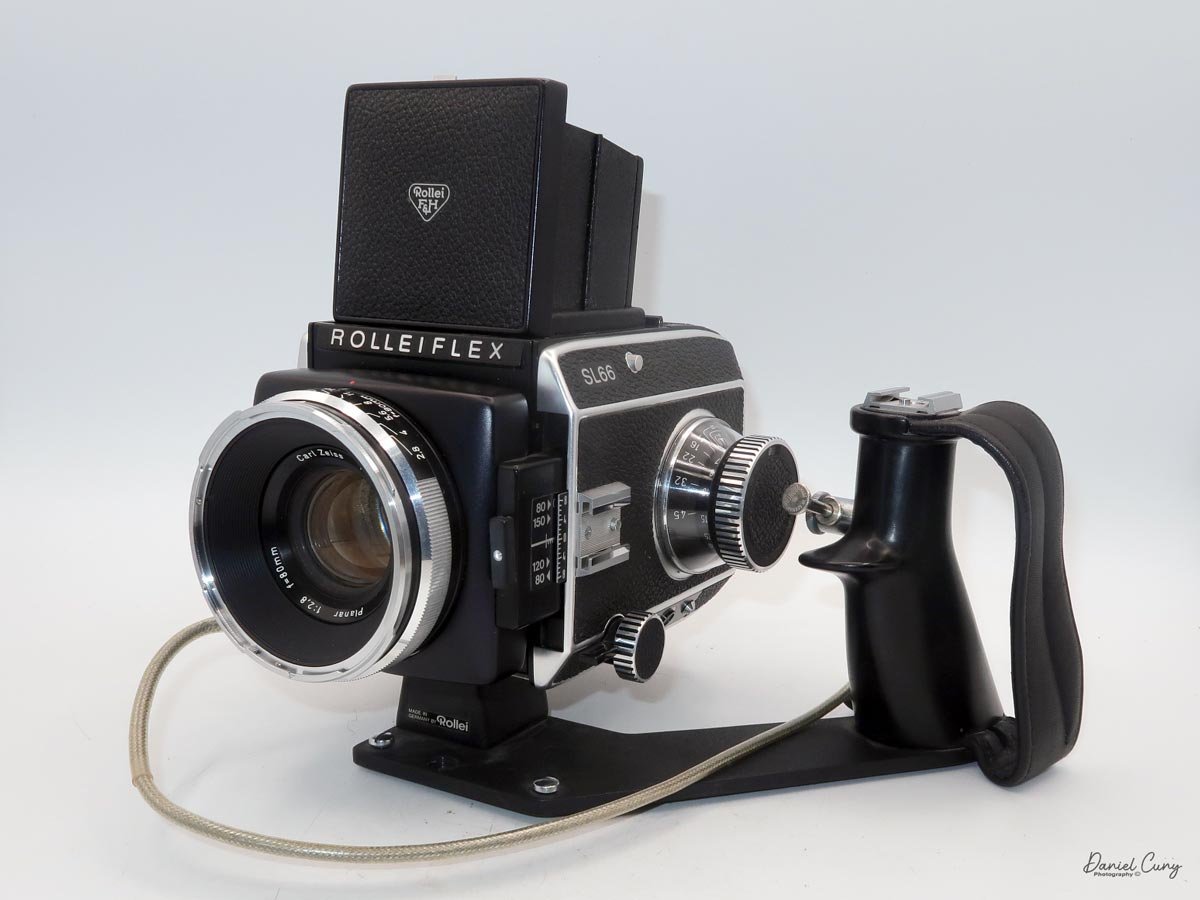
My Camera
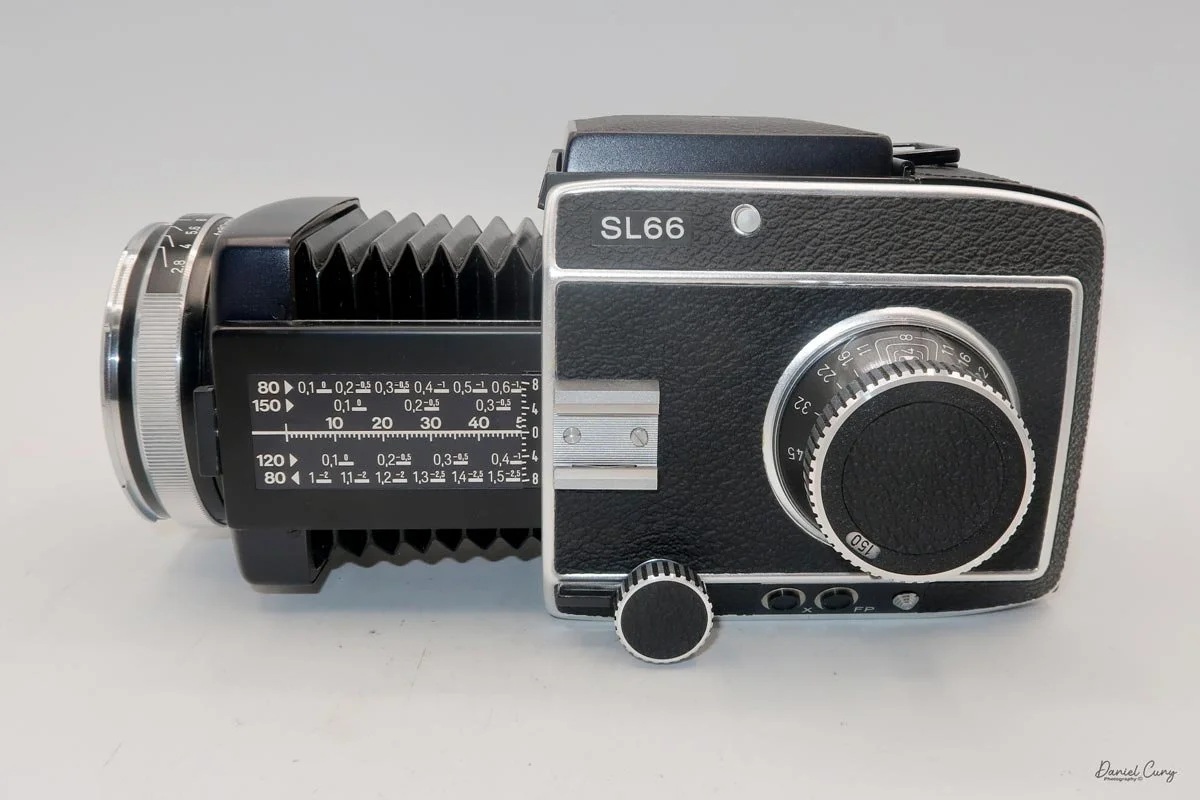
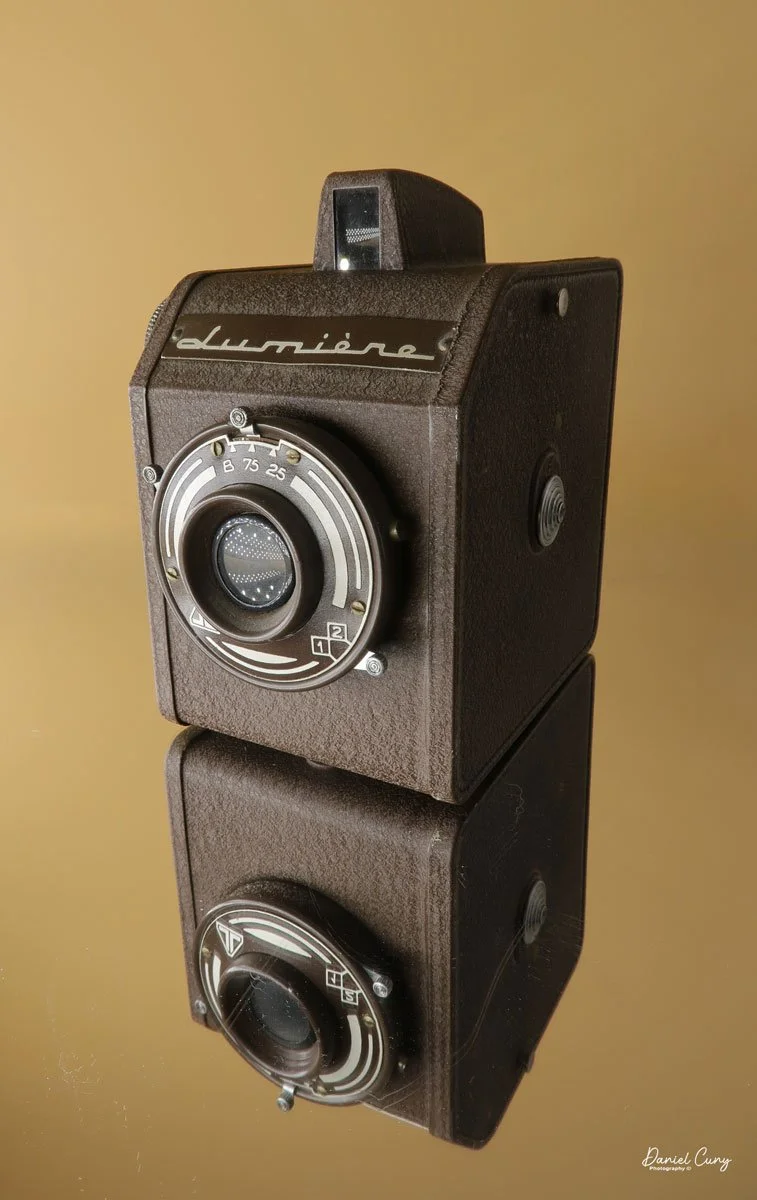
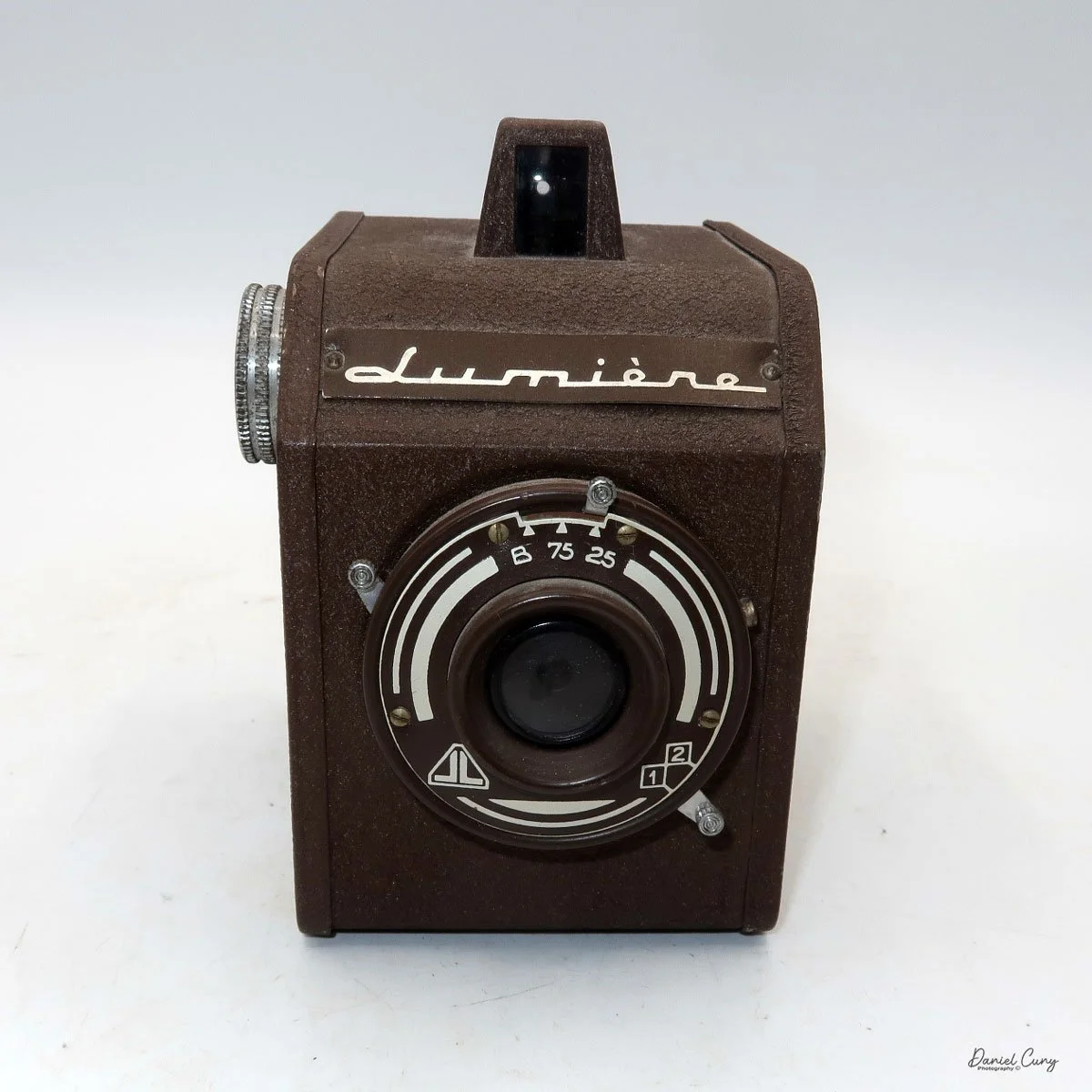
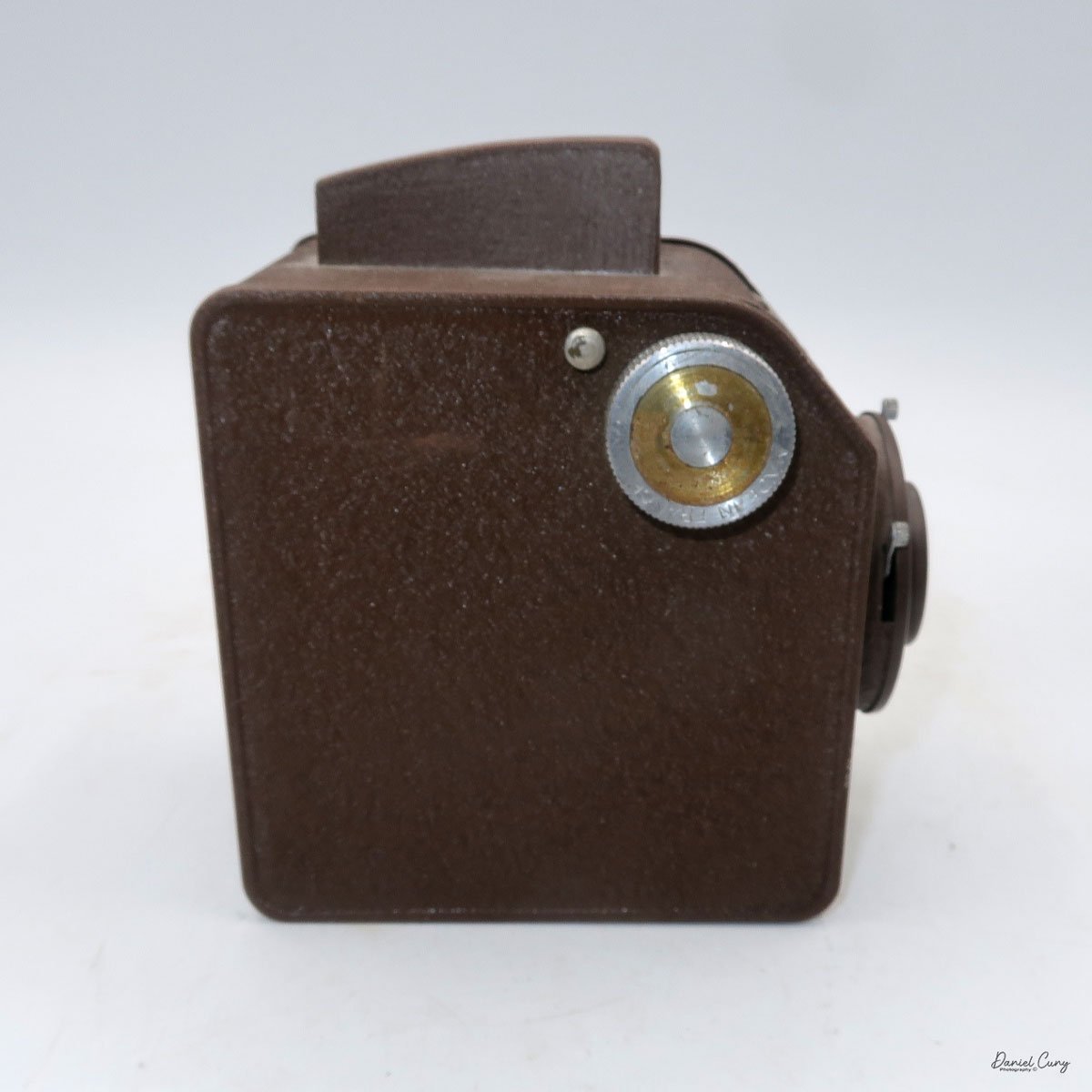
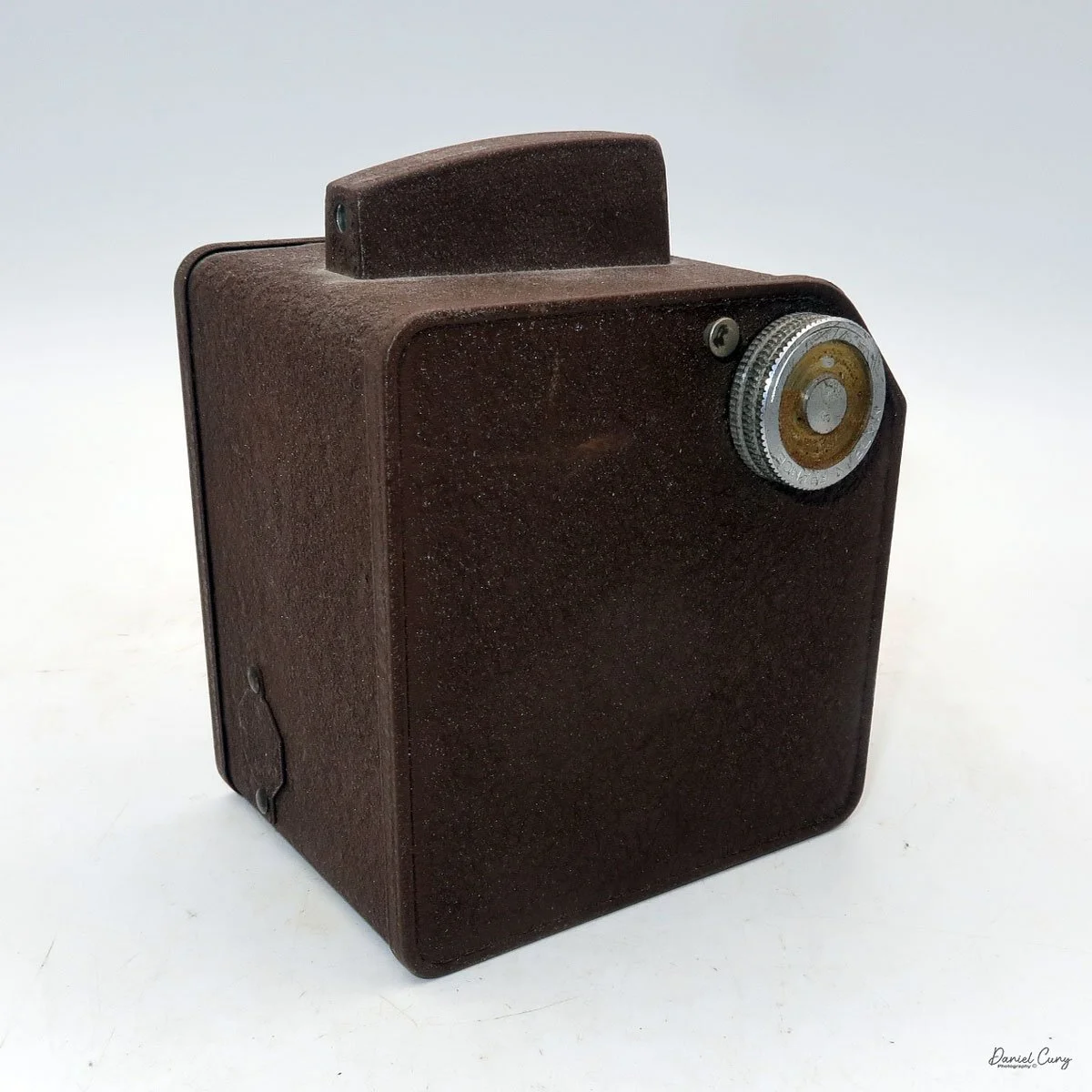
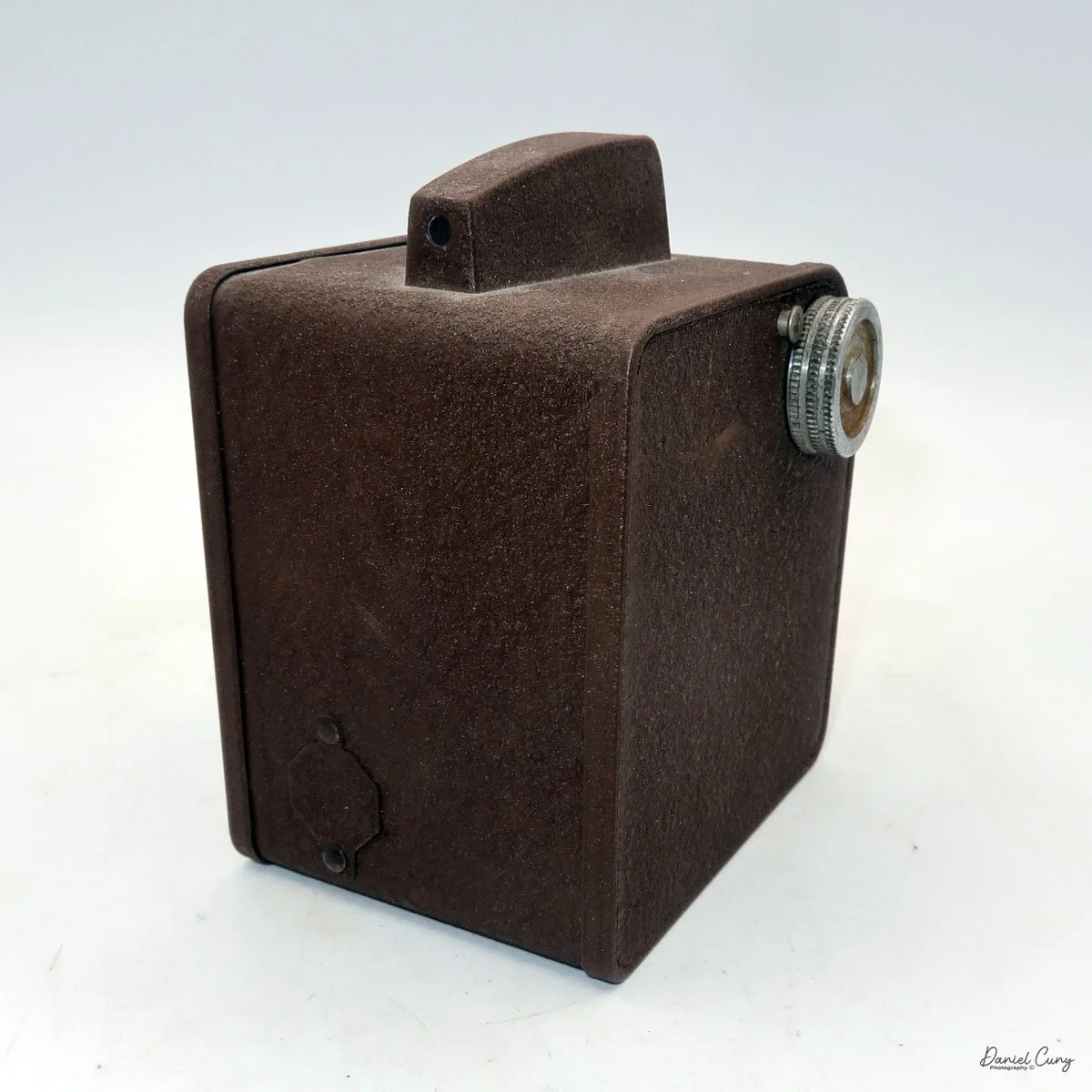
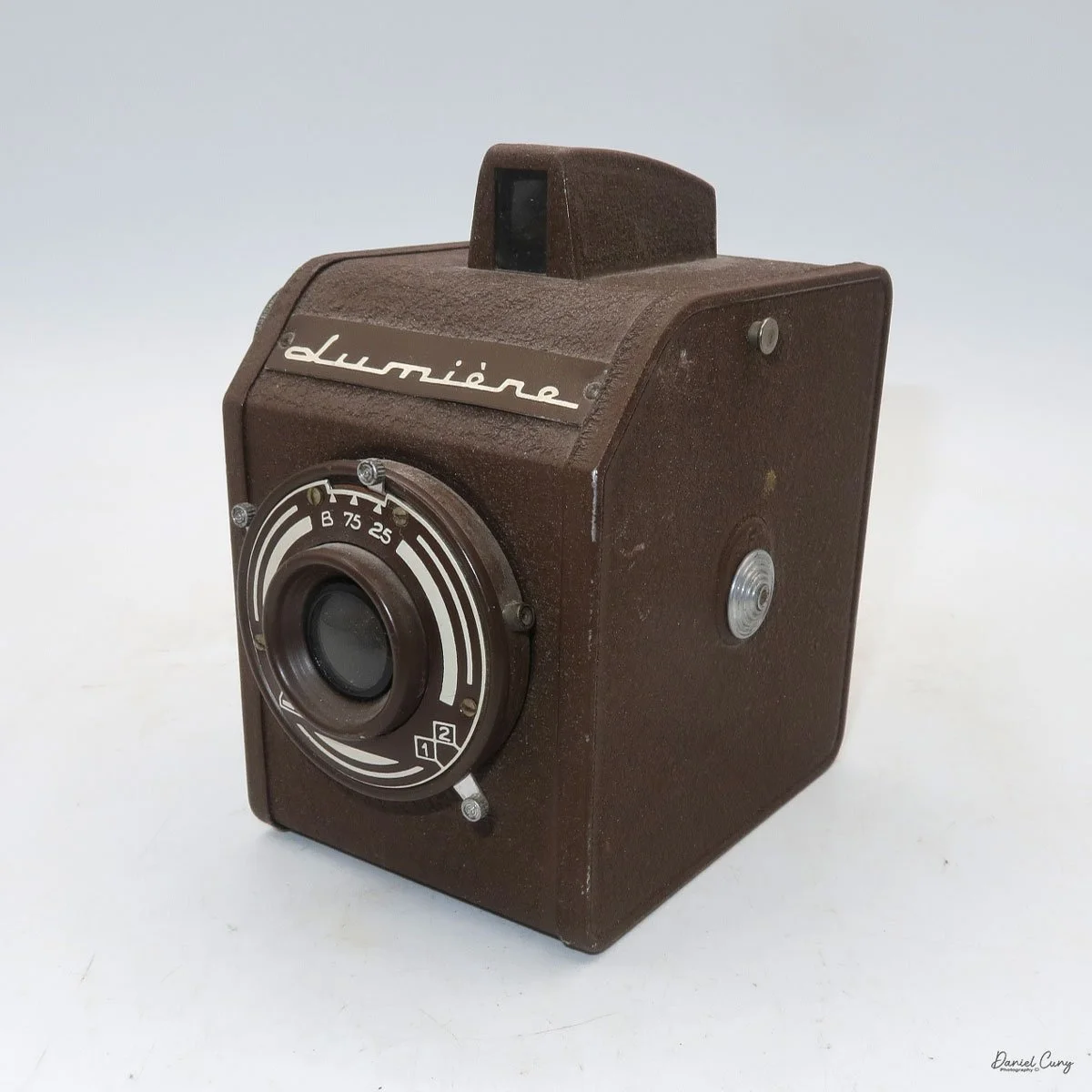
My Rolleiflex SL66 is a substantial camera. With the 80mm lens retracted, it measures about 7" front to back; with the bellows fully extended, it's closer to 9". It's roughly 6" wide thanks to the oversized focusing knob, about 4.5" tall with the waist‑level finder closed, and around 7" tall when the chimney is open. On the scale, the body with a back and an 80mm lens comes in at about 4 pounds, 4.5 ounces—this is not a casual walk‑around point‑and‑shoot.
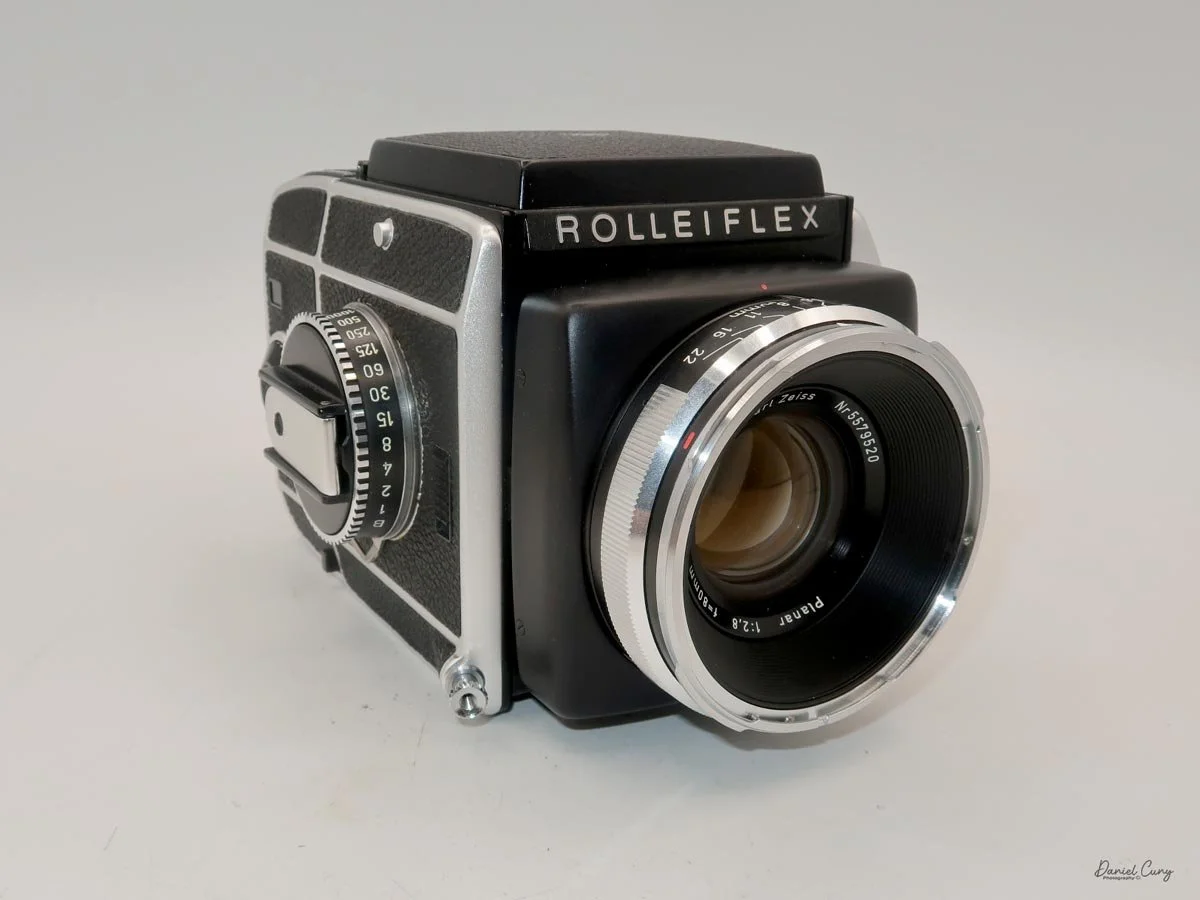
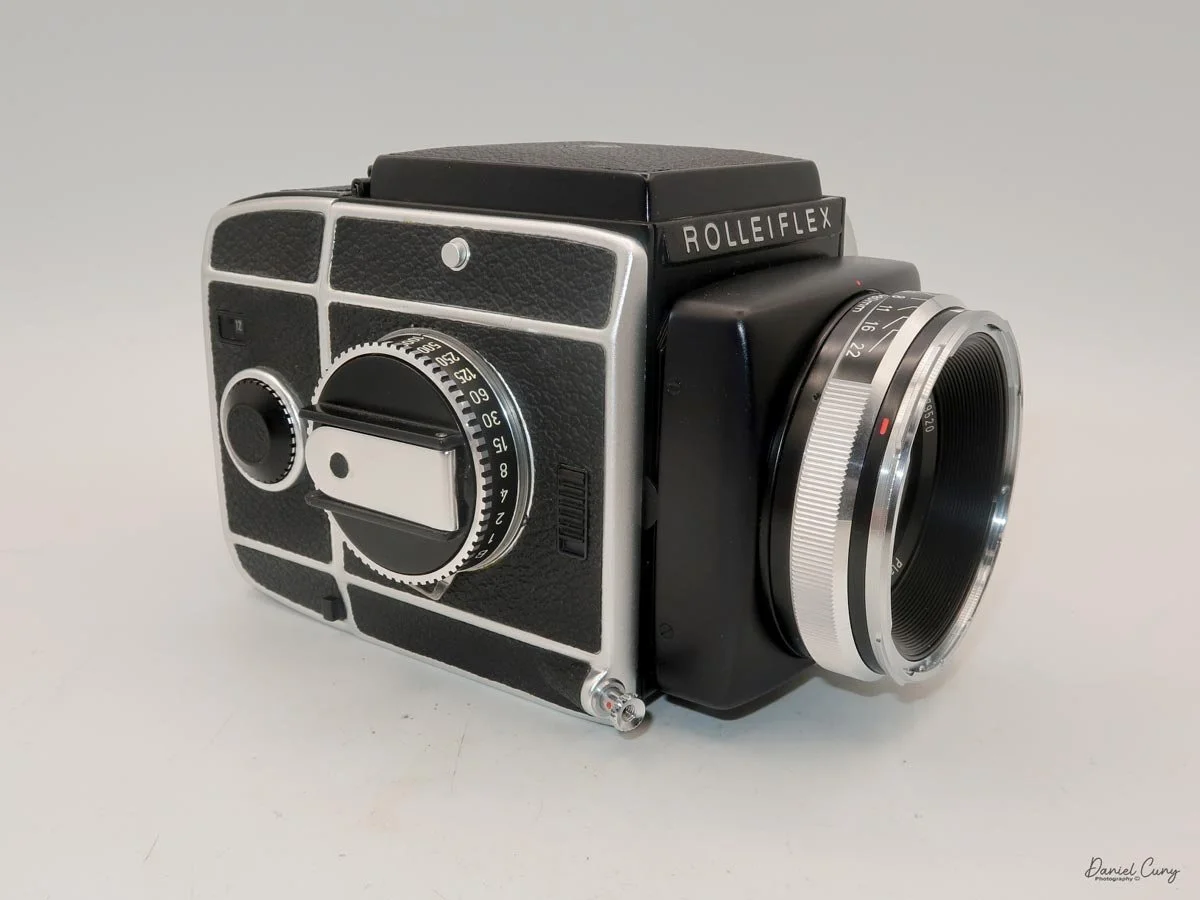
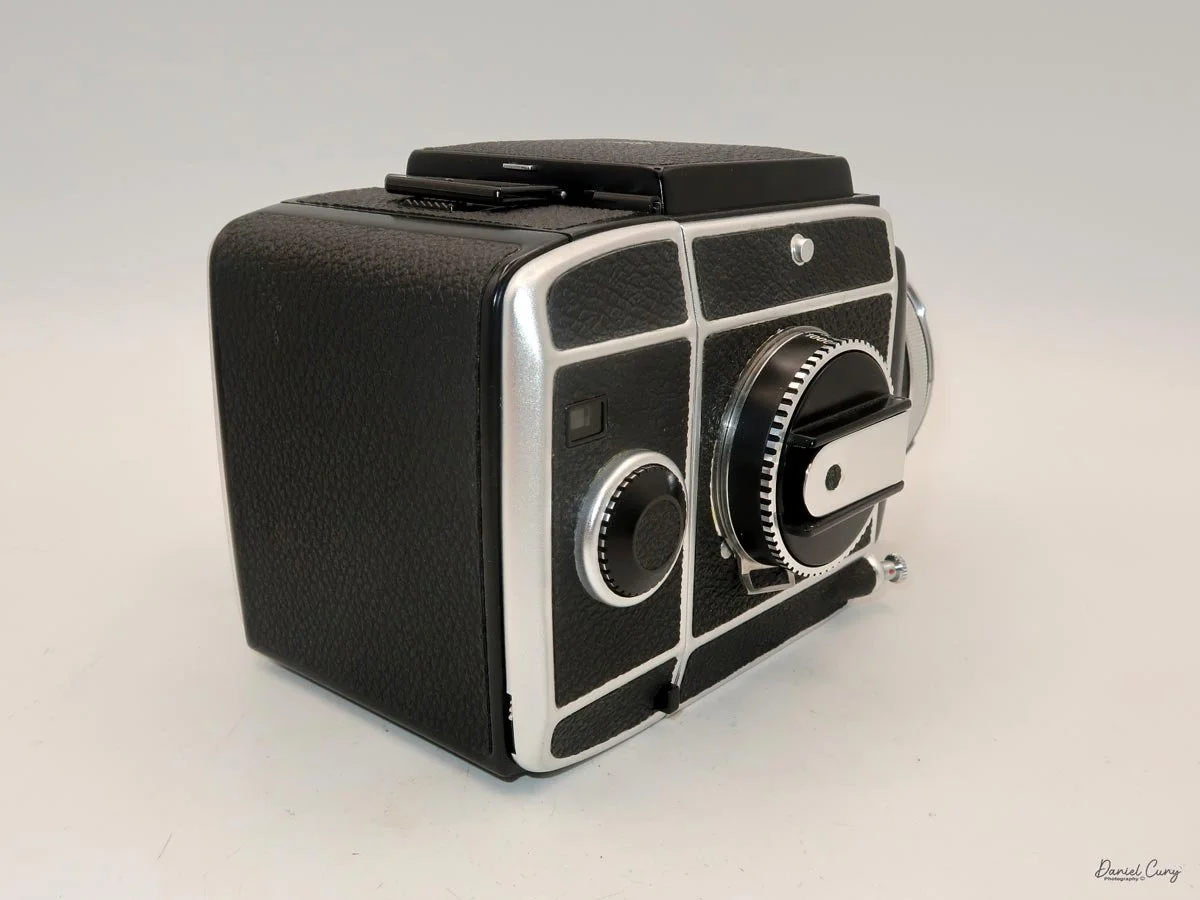
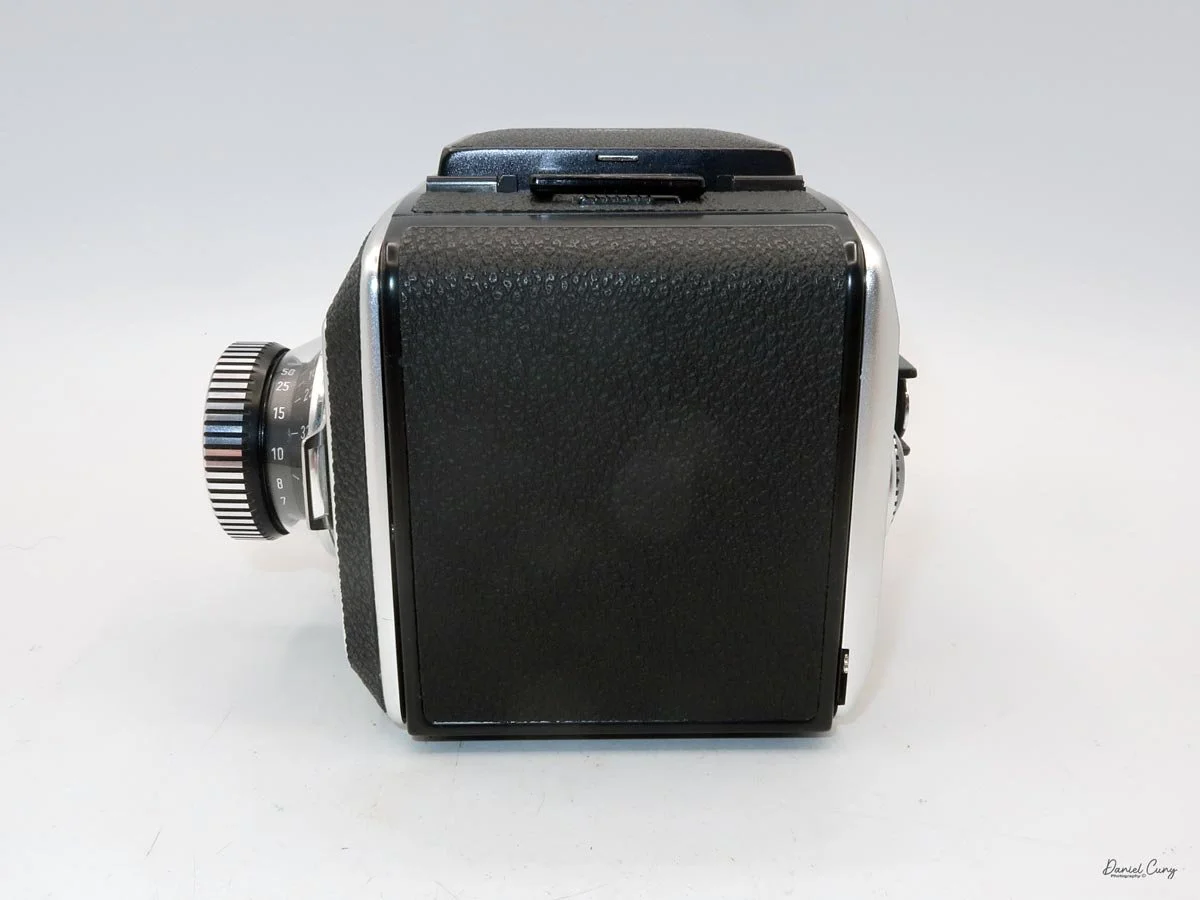
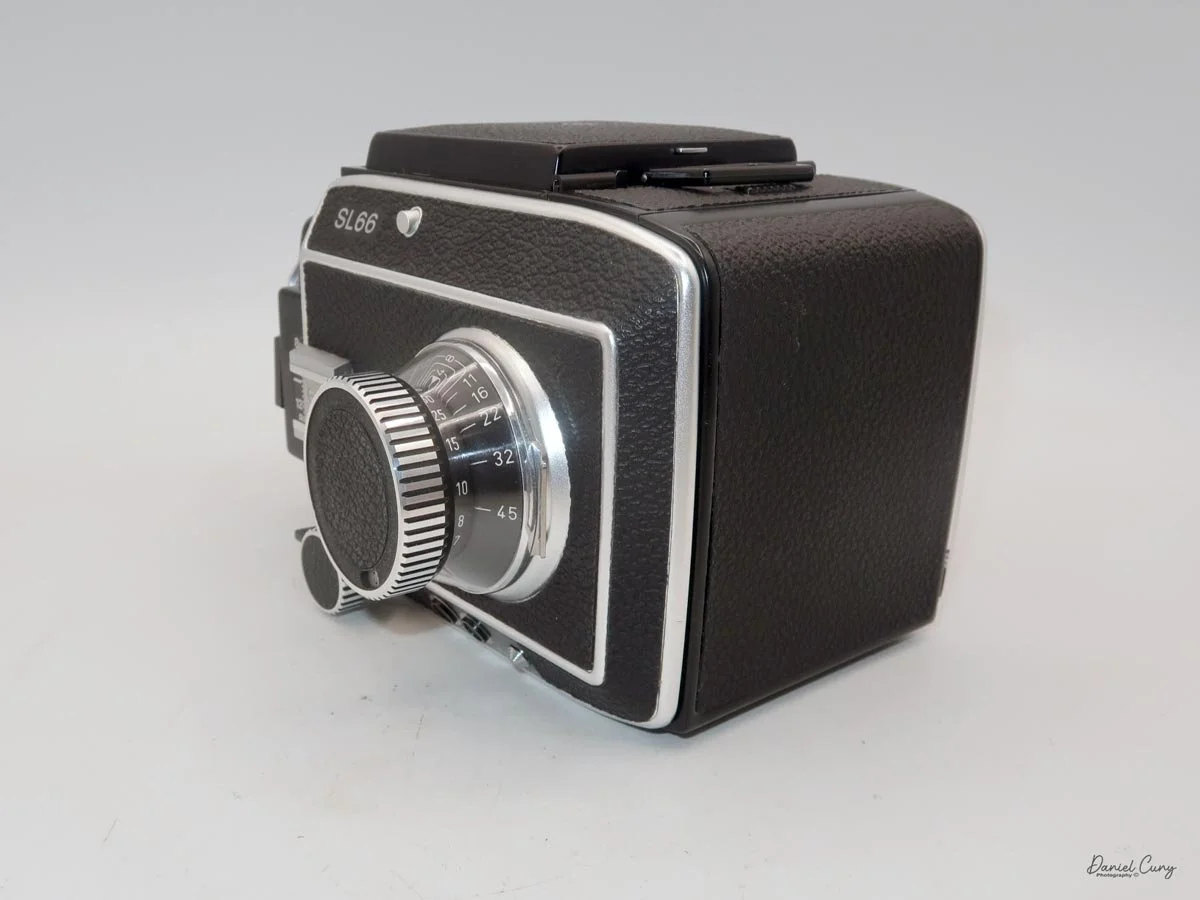
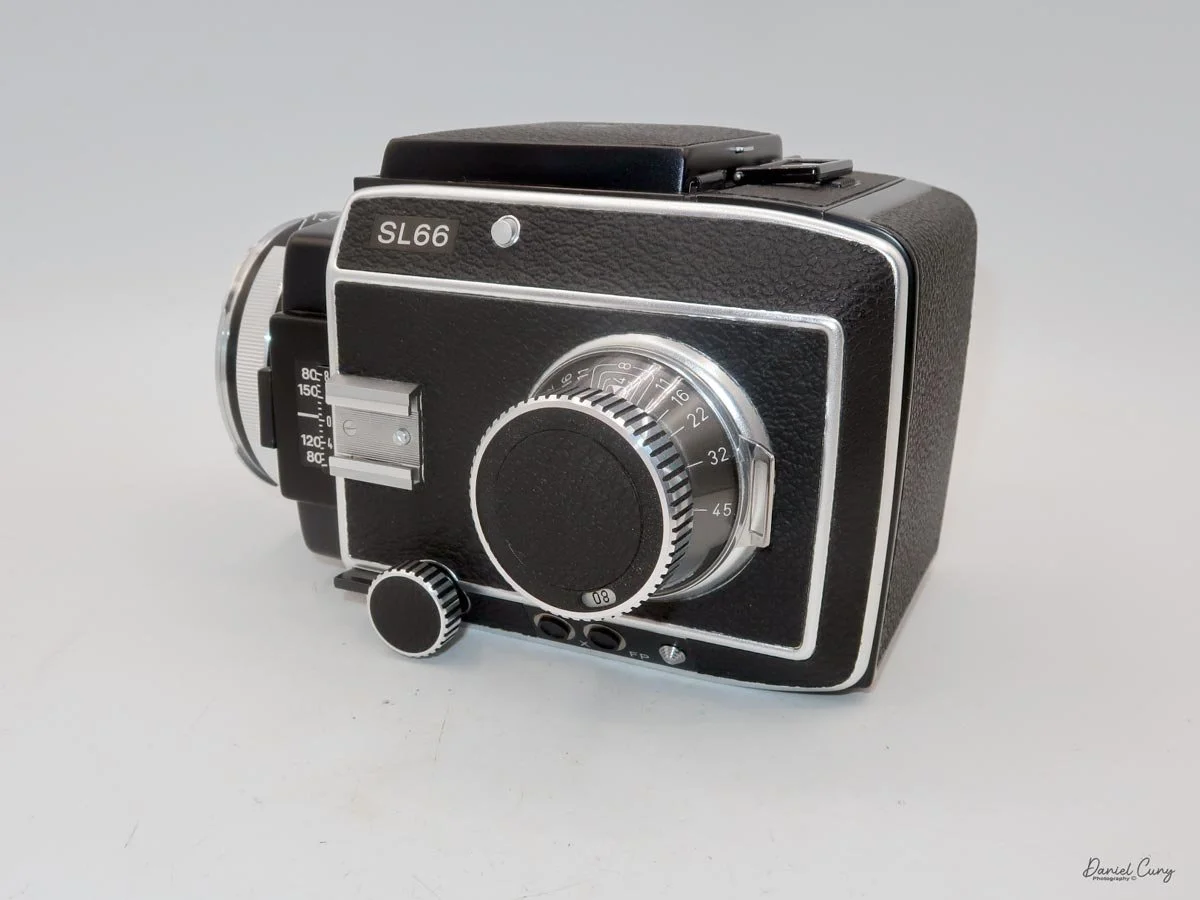
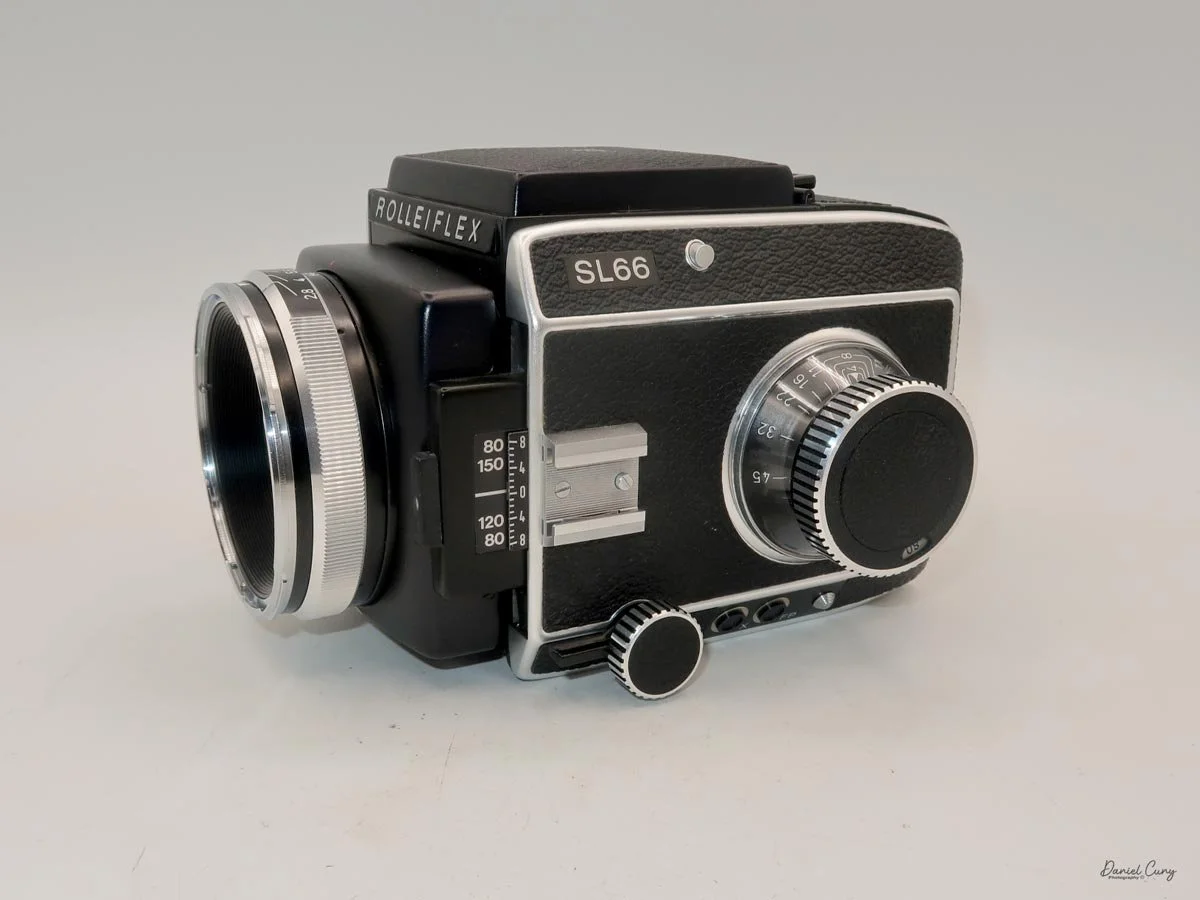
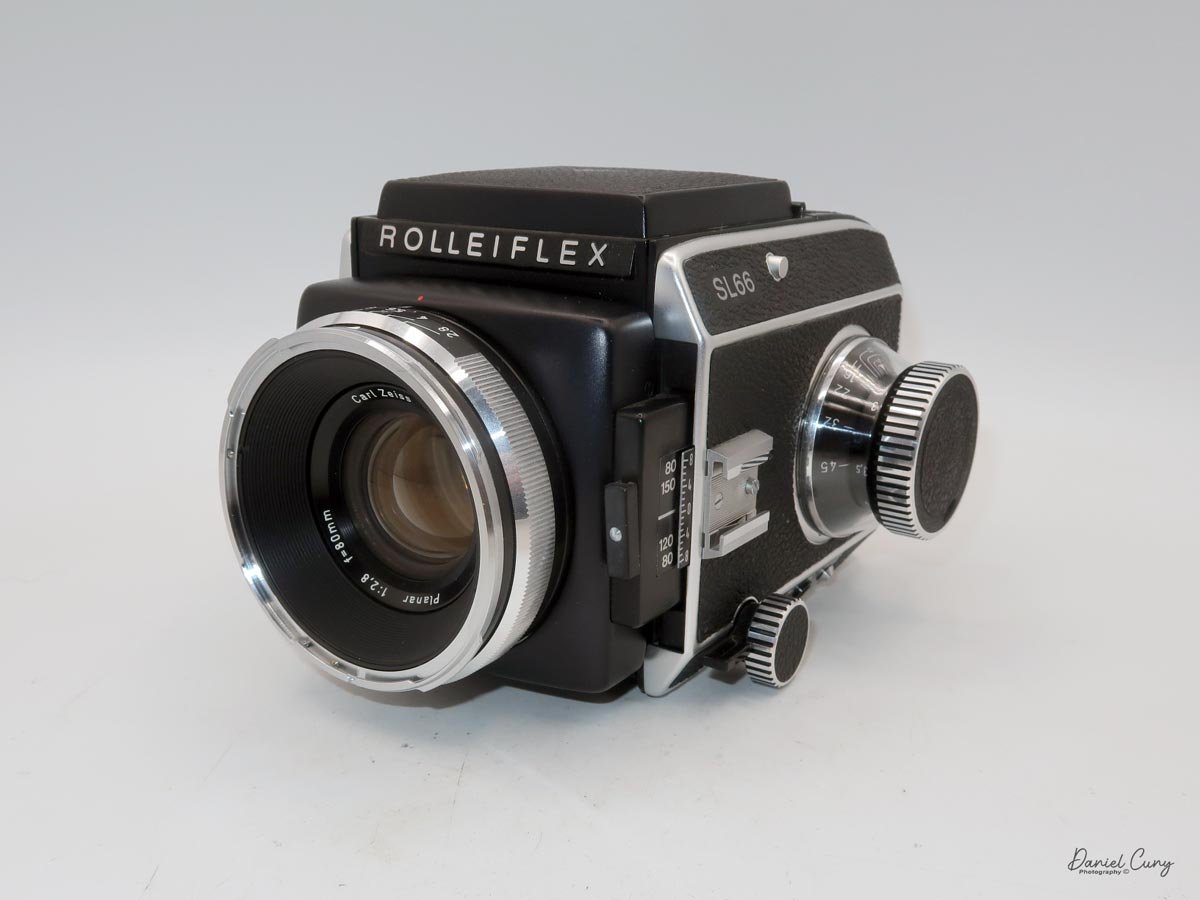
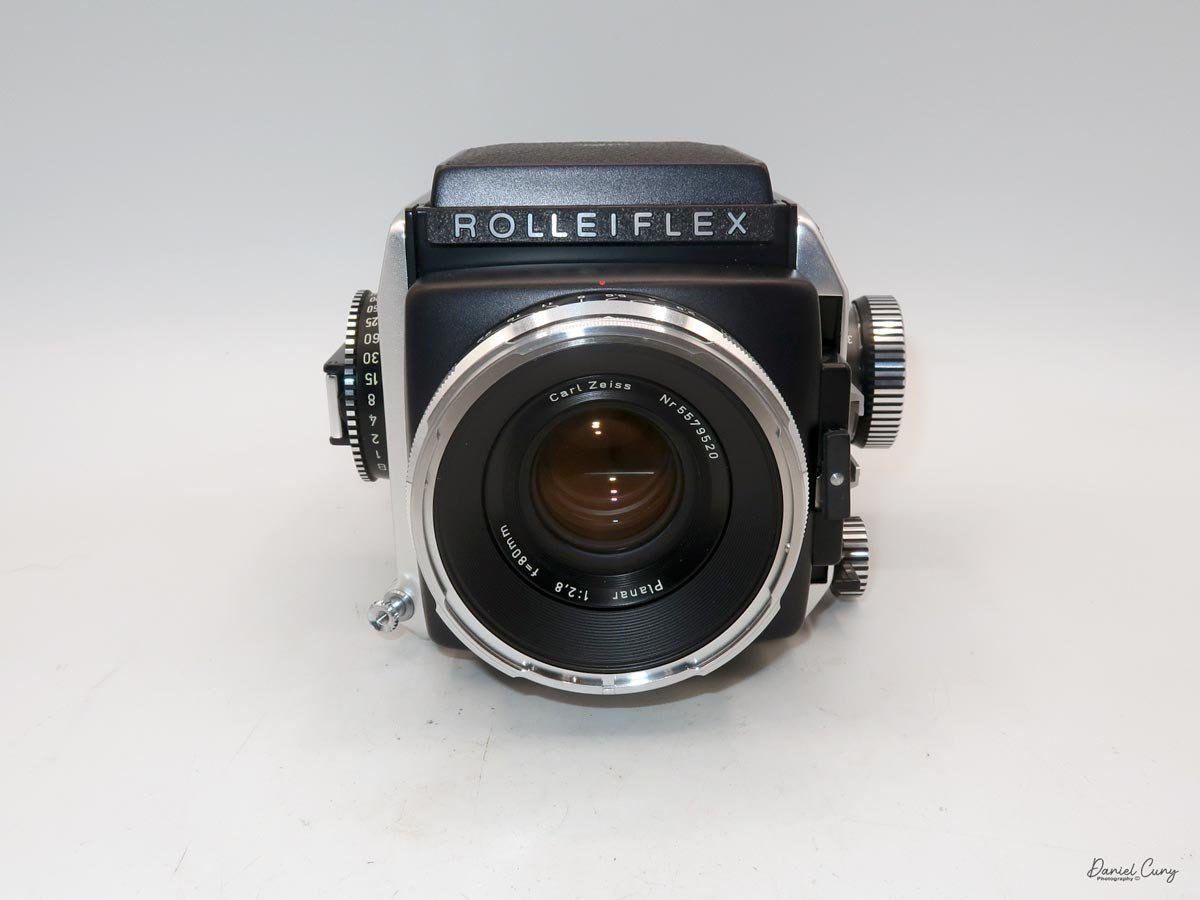












That weight buys you some very unique capabilities. The standout feature is the built‑in bellows, which allows the SL66 to focus much closer than most medium‑format SLRs I've used. Mamiya RB/RZ cameras also use bellows and can get in tight, but the SL66 manages similar close‑focus versatility in a slightly more compact, much lighter and a better‑balanced package. For anyone who loves close‑up or macro work, that alone makes the camera worth a serious look.
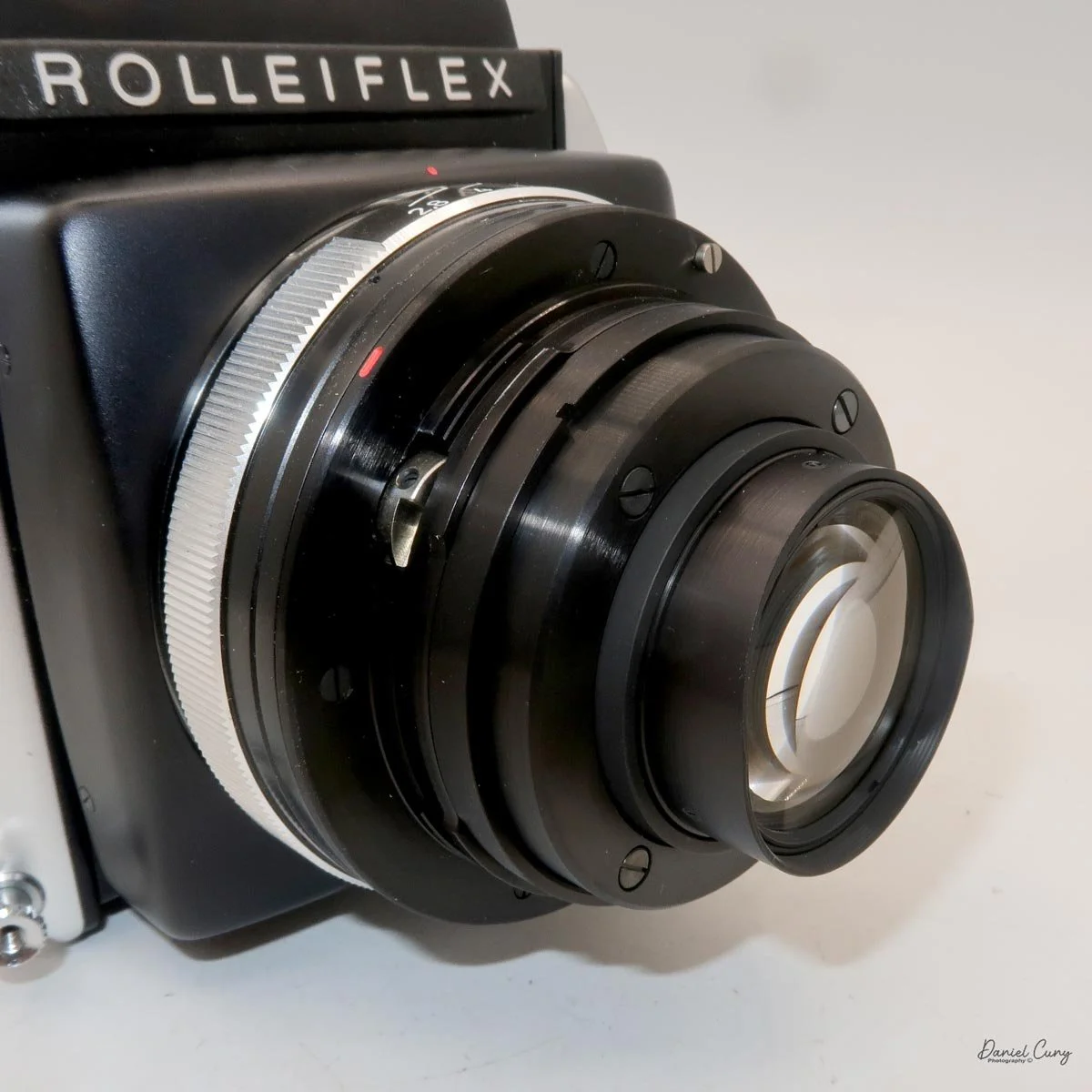
The second signature feature is the double-bayonet lens mount, primarily used with the 50mm, 80mm, and 150mm lenses. The lenses can mount in the normal way, with automatic aperture operation, or be reversed on the body for even greater magnification. In reversed mode, the aperture becomes manual: you open up to focus, then stop down to your chosen aperture for the exposure. It's slower than modern macro setups, but the flexibility it provides is excellent for tabletop and product work.
In addition to bellows and reverse mounting, the SL66 offers up to 8 degrees of lens tilt. That tilt lets you "lay down" the plane of focus, bringing more of a product or subject into sharpness at wider apertures. In practice, it means I can photograph something like a 35mm cassette and its box at close range and keep both on‑axis surfaces acceptably sharp without having to stop down to the smallest apertures.
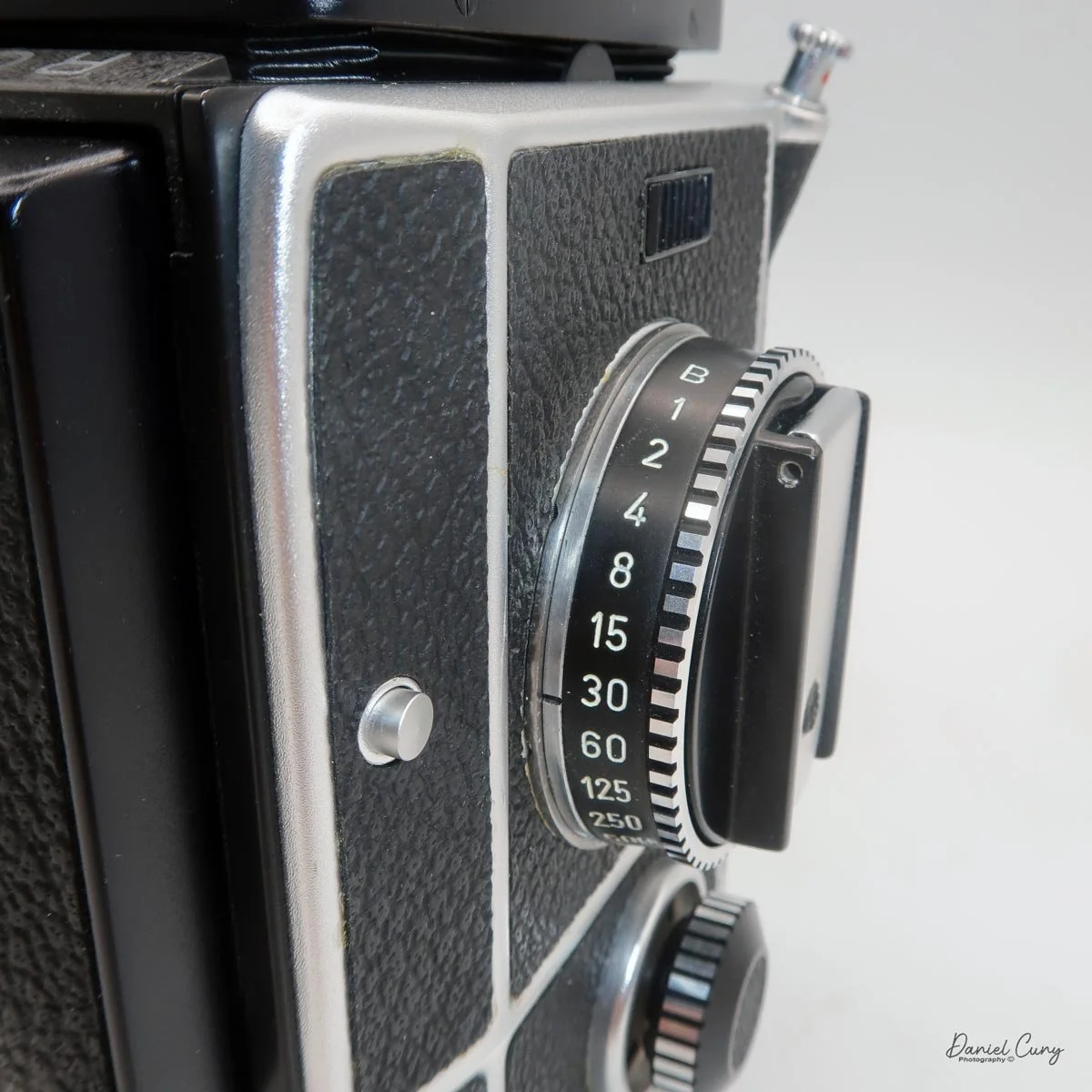
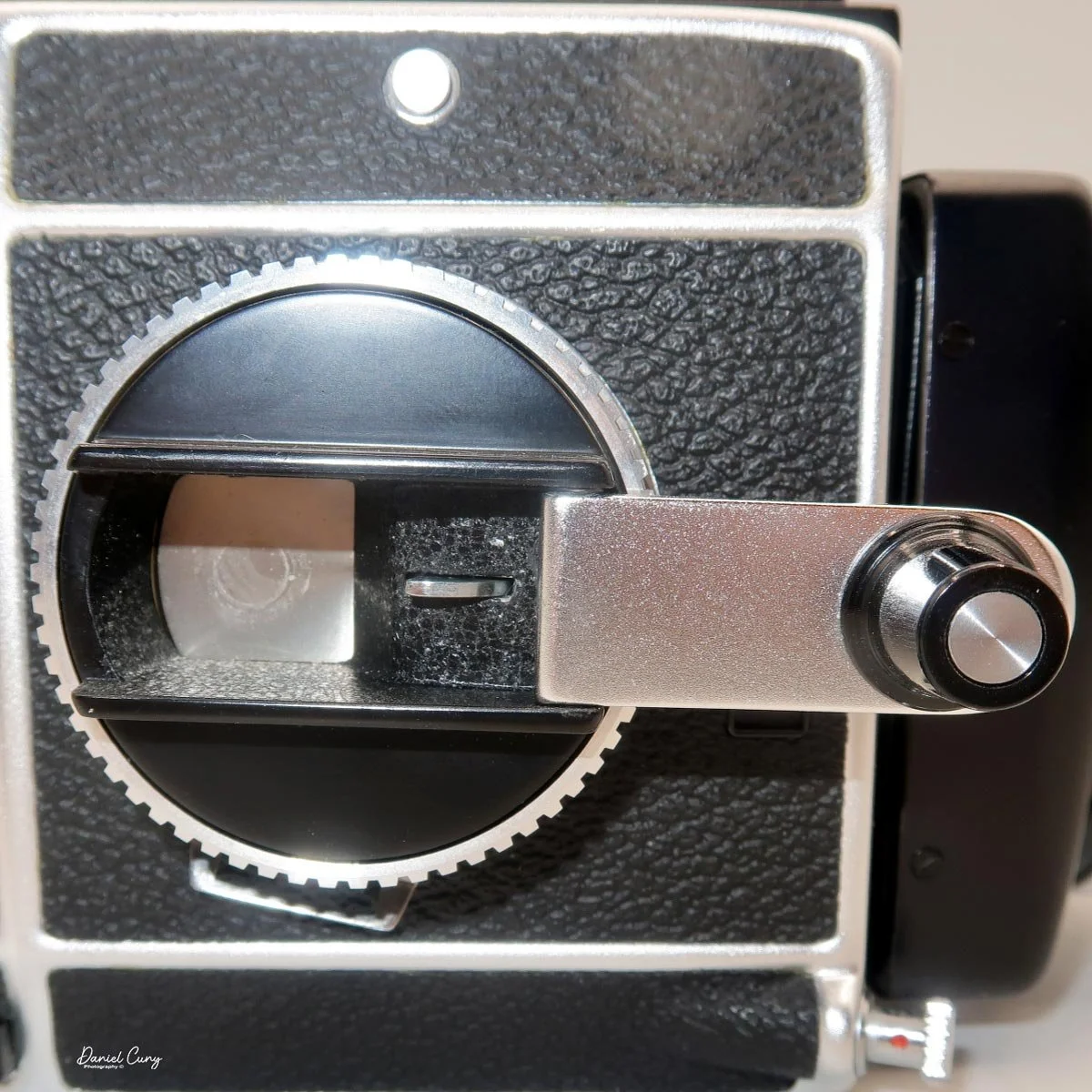
Unlike Hasselblad V‑series cameras, which use leaf shutters in the lenses, the SL66 uses a focal‑plane shutter in the body, with speeds from 1 second to 1/1000 plus "B" for long exposures. Flash sync is limited to 1/30, but for studio or location strobe work, the flash duration actually stops motion, so I haven't found the 1/30 sync speed to be a practical limitation with decent strobes. The shutter speed dial is integrated into the film advance: you pull out the handle, advance clockwise until it stops, then swing it back counterclockwise to cock the shutter for the next frame. Inside the crank is a multiple‑exposure switch, which makes stacking exposures on one frame very straightforward once you know where to find it.
The SL66 lens lineup was designed by Carl Zeiss, and it shows. Optically, the lenses I have are excellent, with contrast and sharpness fully in the "top tier" I expect from Zeiss glass. The system spans from 30mm all the way to 1000mm, and Rollei also offered two leaf‑shutter lenses—an 80mm Distagon and a 150mm Sonnar—with flash sync up to 1/500 for shooters who need higher sync speeds. In my experience so far, the standard lenses deliver exactly the kind of image quality you want from a camera of this size and weight.
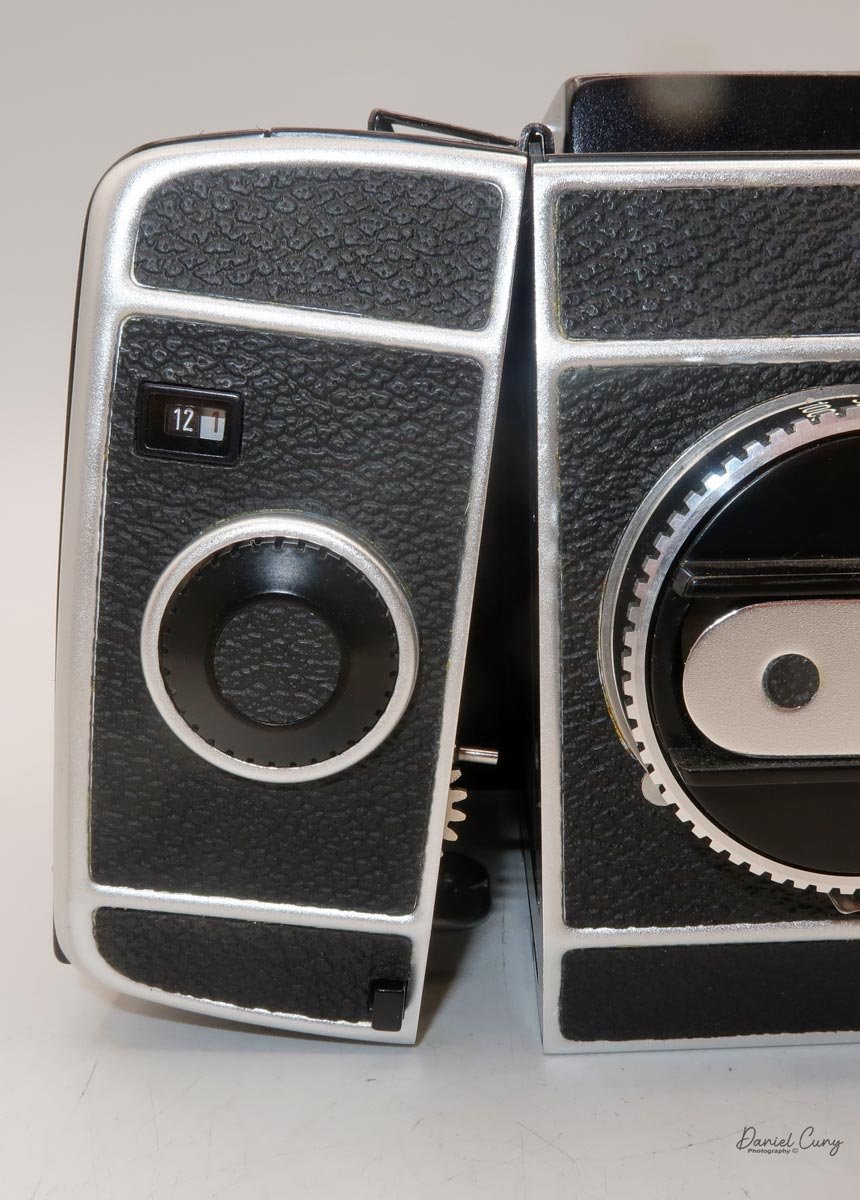
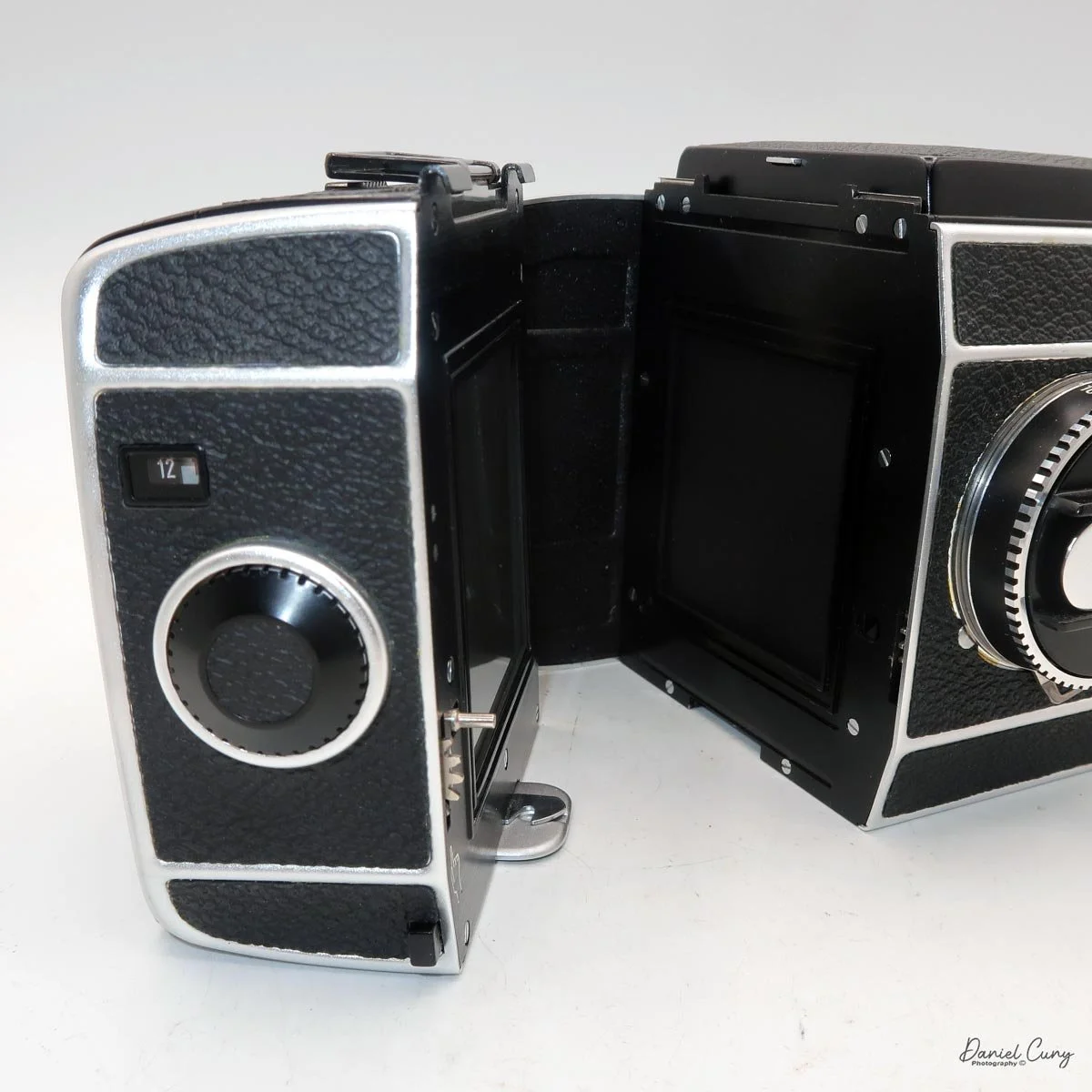
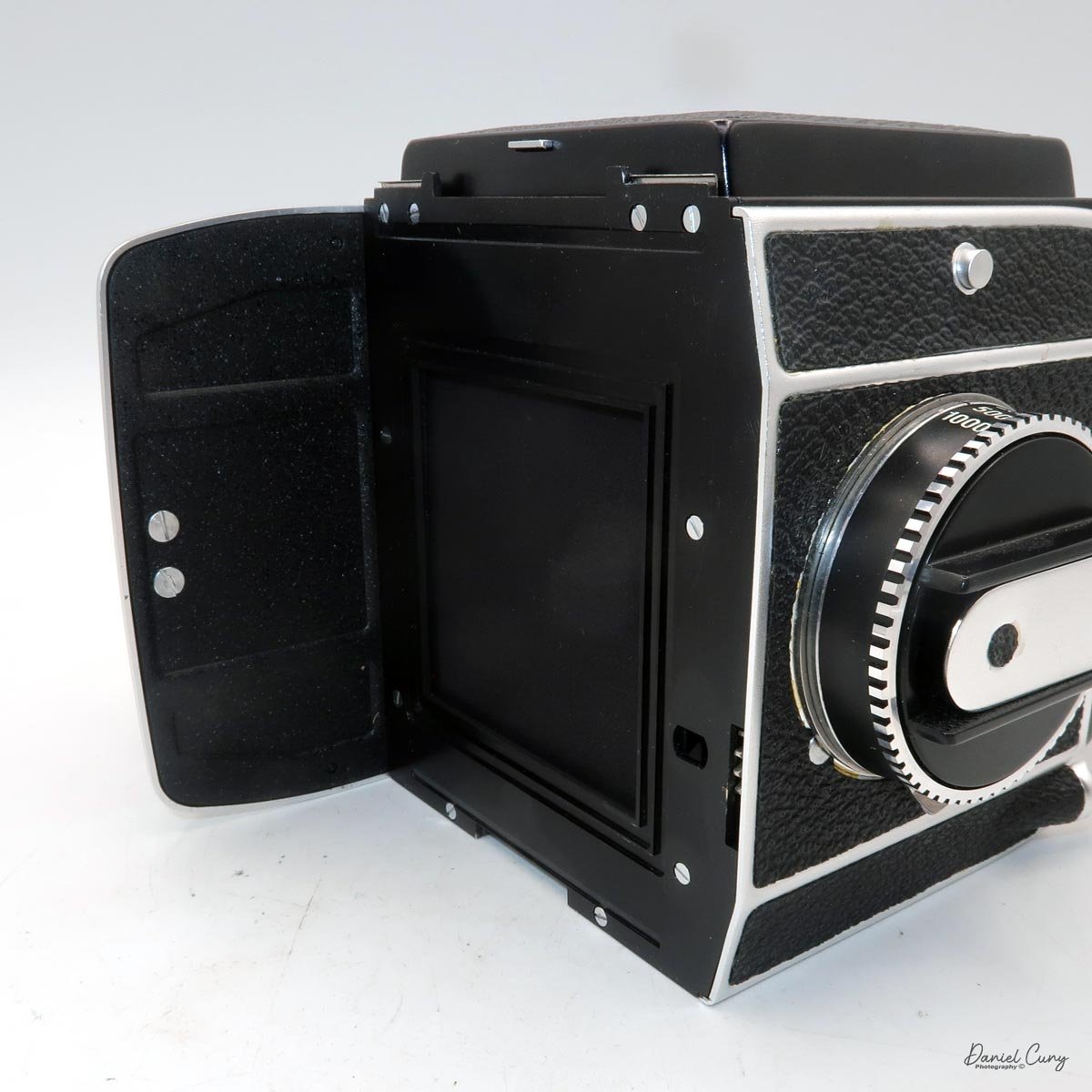
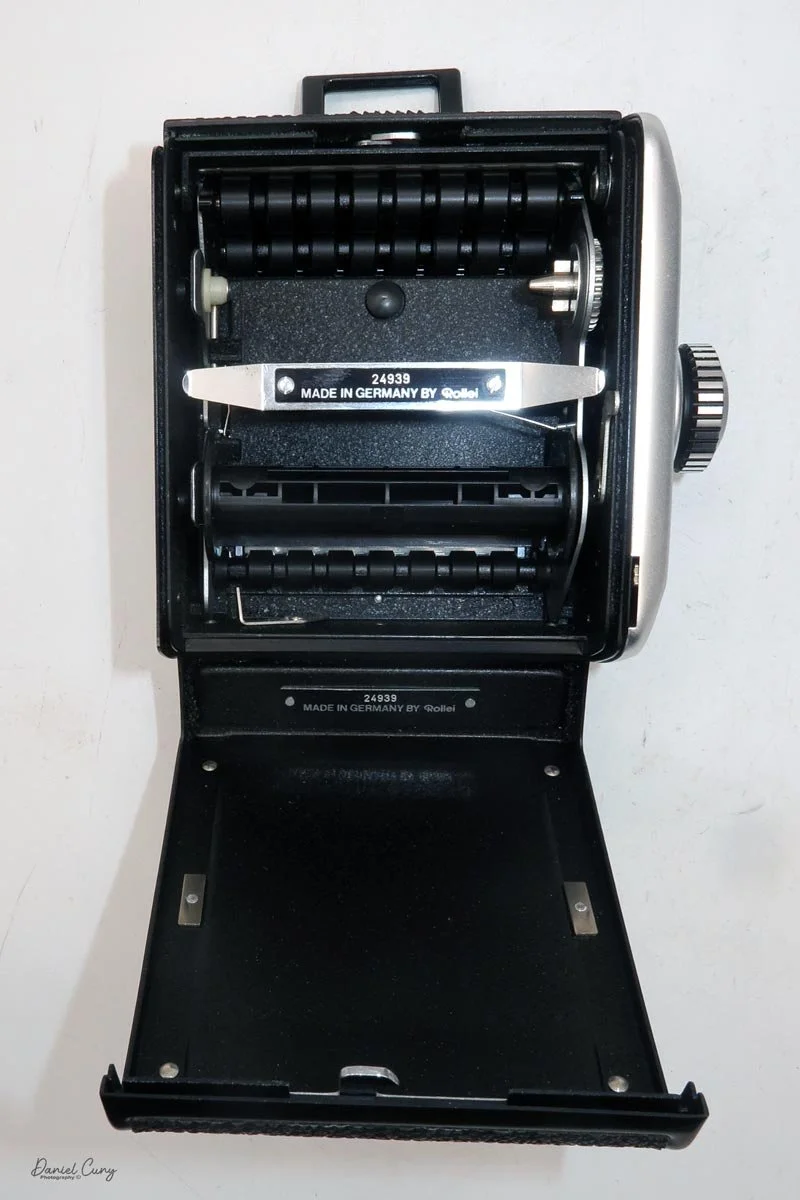
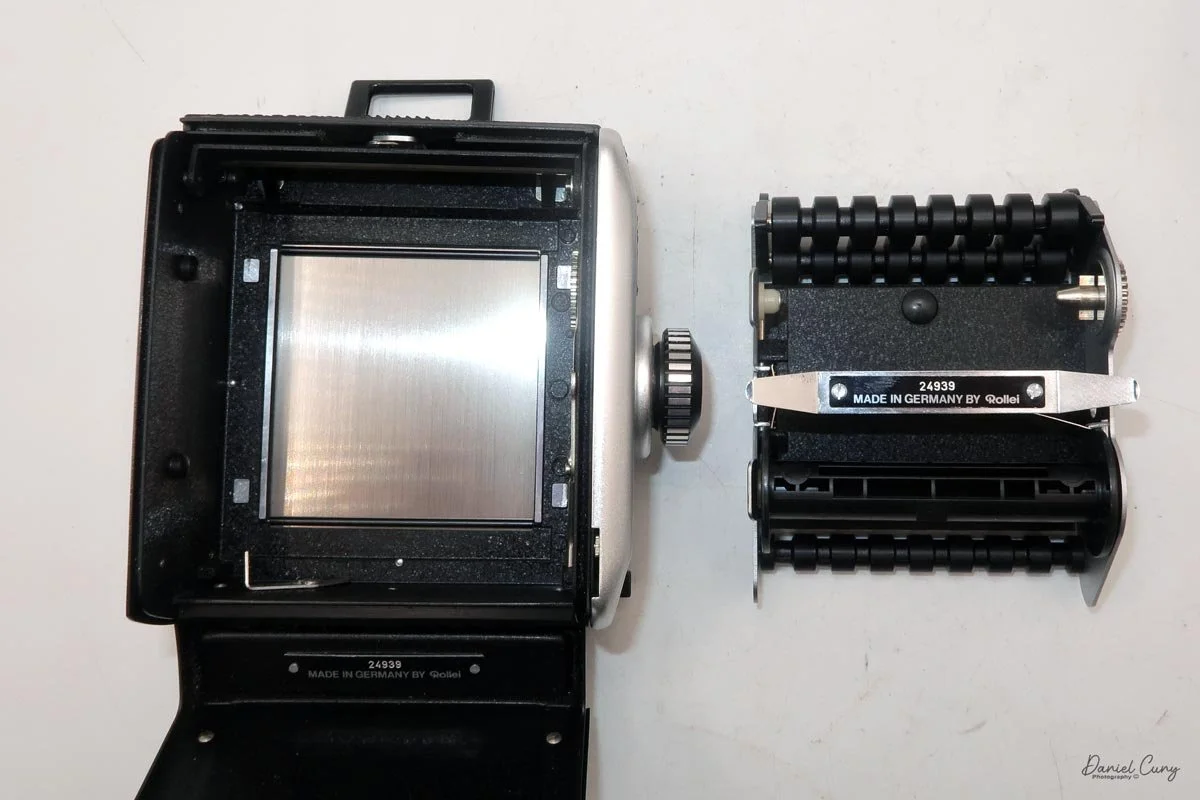
The film back system is well thought out. The standard back takes either 120 or 220 film, and you can get inserts and backs for 6×6 or 6×4.5. The dark slide parks neatly on the back when you're shooting, which means you're not constantly wondering where you set it down. Loading is similar to Mamiya's insert‑based backs: open the door, pull the insert, load the film, reinsert, then wind to the first frame. A pop‑out winding wheel on the side of the back helps tension and advance the film before the main crank takes over. Once you've shot the twelve frames on 120, the wheel pops back out to let you wind the roll off before opening the back.
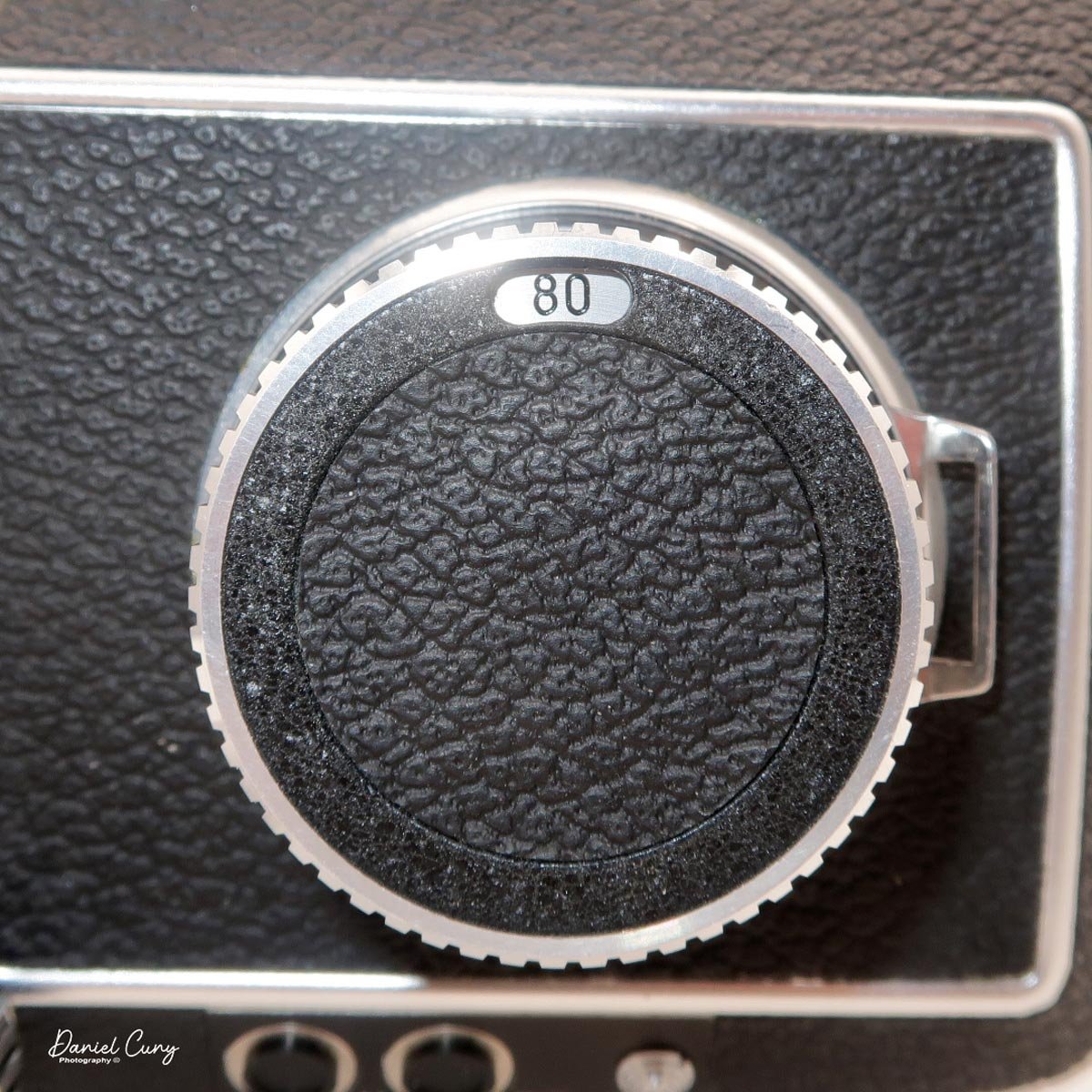
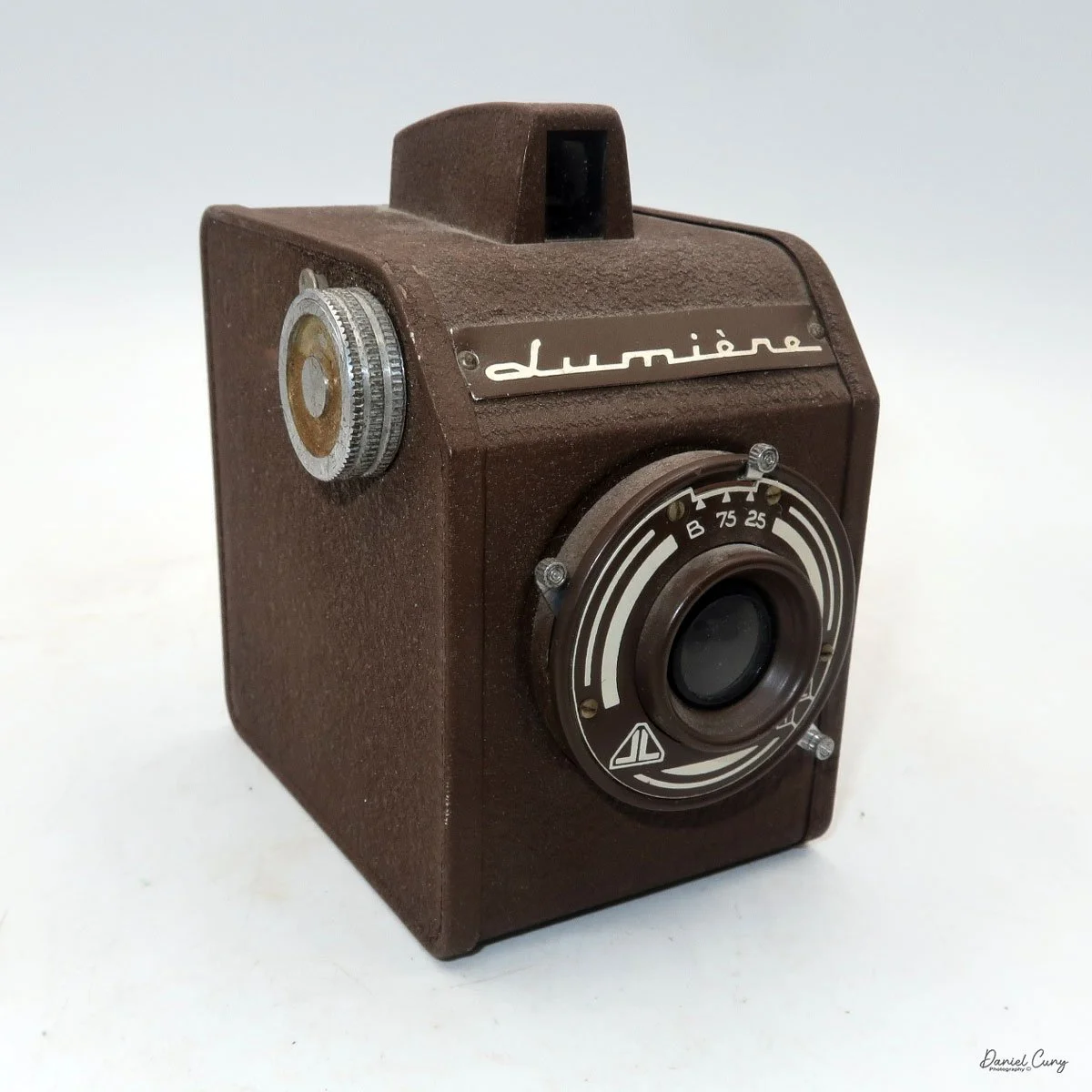
On the camera body's left side is that big focusing knob, which doubles as a reference for the lens in use; you can pull it out and set it for your focal length. The knob turns quite a bit when you're focused in tight, but the throw is smooth and precise. Just ahead of it is the tilt control: a locking lever and wheel for setting and securing the lens tilt angle. The body also carries a cold shoe for accessories and a pair of covered flash sync ports. Up top, pressing the chrome button opens the waist‑level finder, and a second press pops up the magnifier for critical focusing.
I use an L‑grip that mounts into the bottom quick‑mount slot alongside the tripod socket. That grip transforms the camera from a studio brick into something I'm comfortable hand‑holding for a walk, letting my left hand manage focus and support while my right handles shutter release and film advance. It doesn't make the SL66 light, but it does make it surprisingly usable off a tripod.
My Results
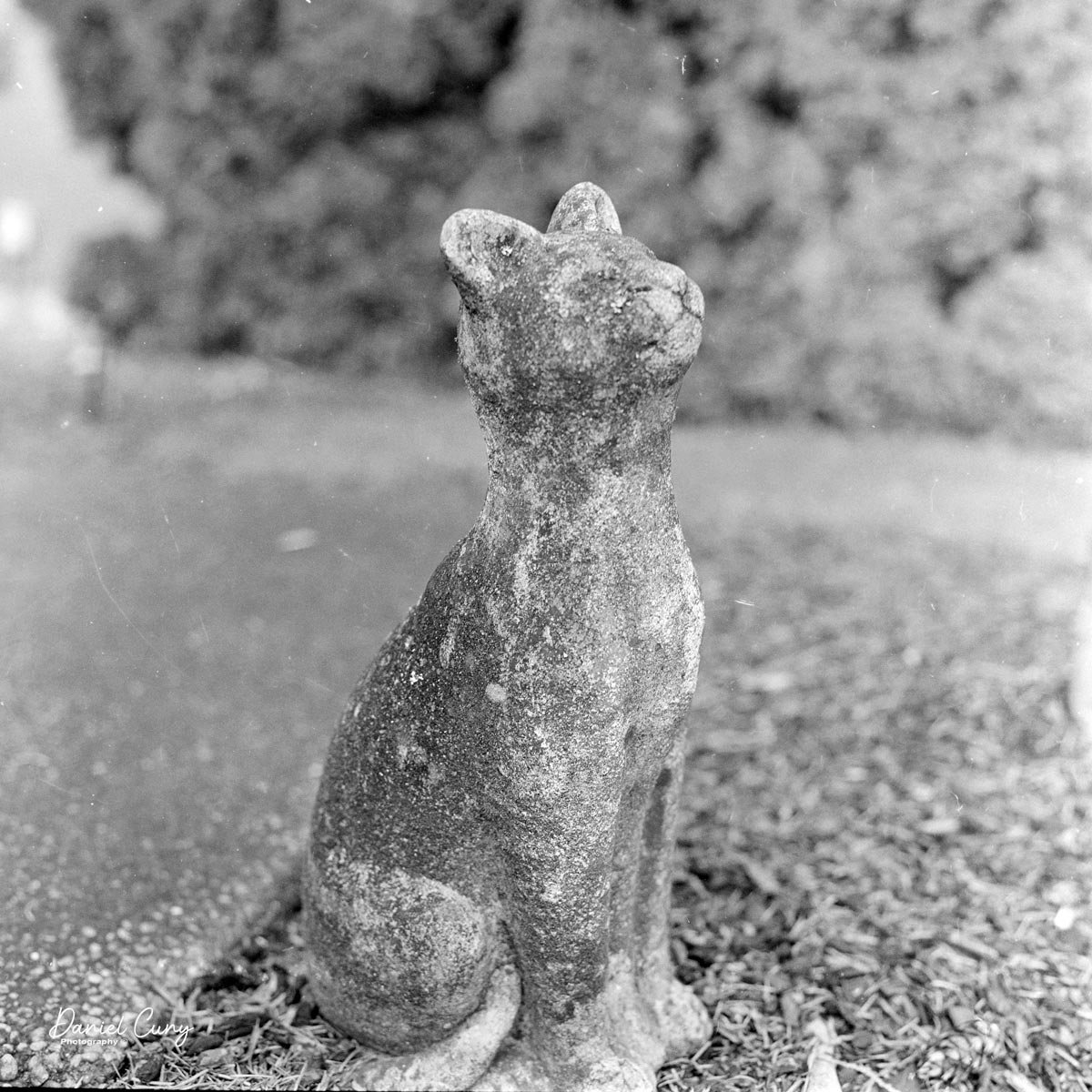
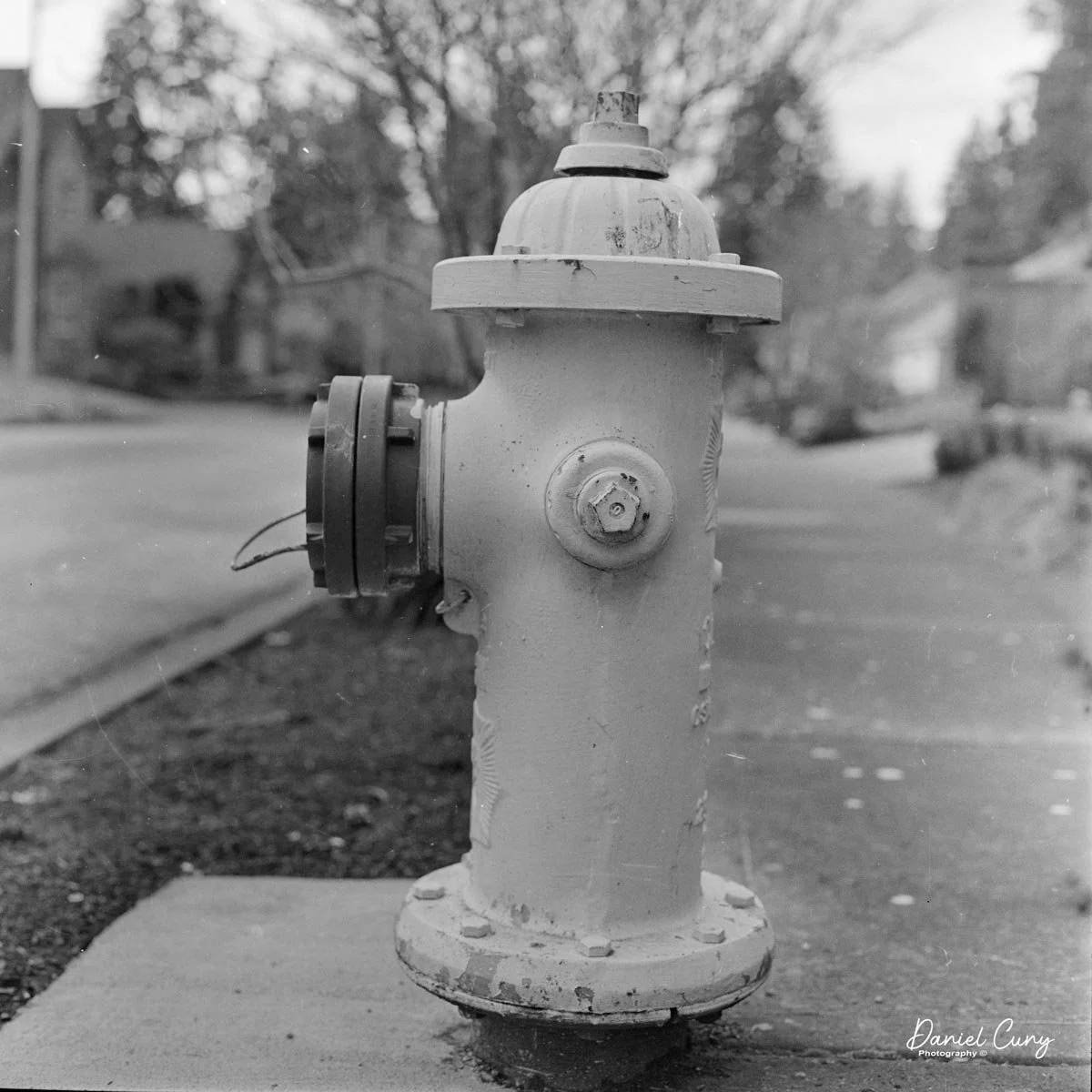
When I finally pulled the SL66 off the shelf this year, I decided not to overthink it. I loaded a roll of film, stepped out into my neighborhood on an uncharacteristically sunny February day in the Pacific Northwest, and treated it like any other camera I'd take for a walk. The first few frames were simple subjects—houses, trees, textures—mainly to get a feel for the shutter sequence, the advance, and how the camera balanced with the L‑grip in hand.
What struck me almost immediately was how deliberate the camera feels. The weight and long focus throw slow you down in a good way; you don't "spray and pray" with an SL66. Composing on the waist‑level finder is a pleasure: the screen is bright, the magnifier makes critical focusing easy, and the big focus knob lets you land focus precisely rather than hunting back and forth. By the time I finished that first roll, the camera felt intuitive in a way only a well‑designed mechanical tool can.
Back at home, I wanted to see what the SL66 could really do in its natural habitat: close‑up work. I set up a small scene with a 35mm film cassette and its box, first focusing as close as I could with the lens in the normal position. Even without reversing the lens, the built‑in bellows let me get in surprisingly tight. Then I flipped the lens around on the double bayonet mount and repeated the setup. The difference in magnification was obvious—the frame filled with the cassette and text on the box —and the tilt function came into its own, letting me hold both the front and top surfaces in focus at a reasonable working aperture.
My apologies for the dusty images.
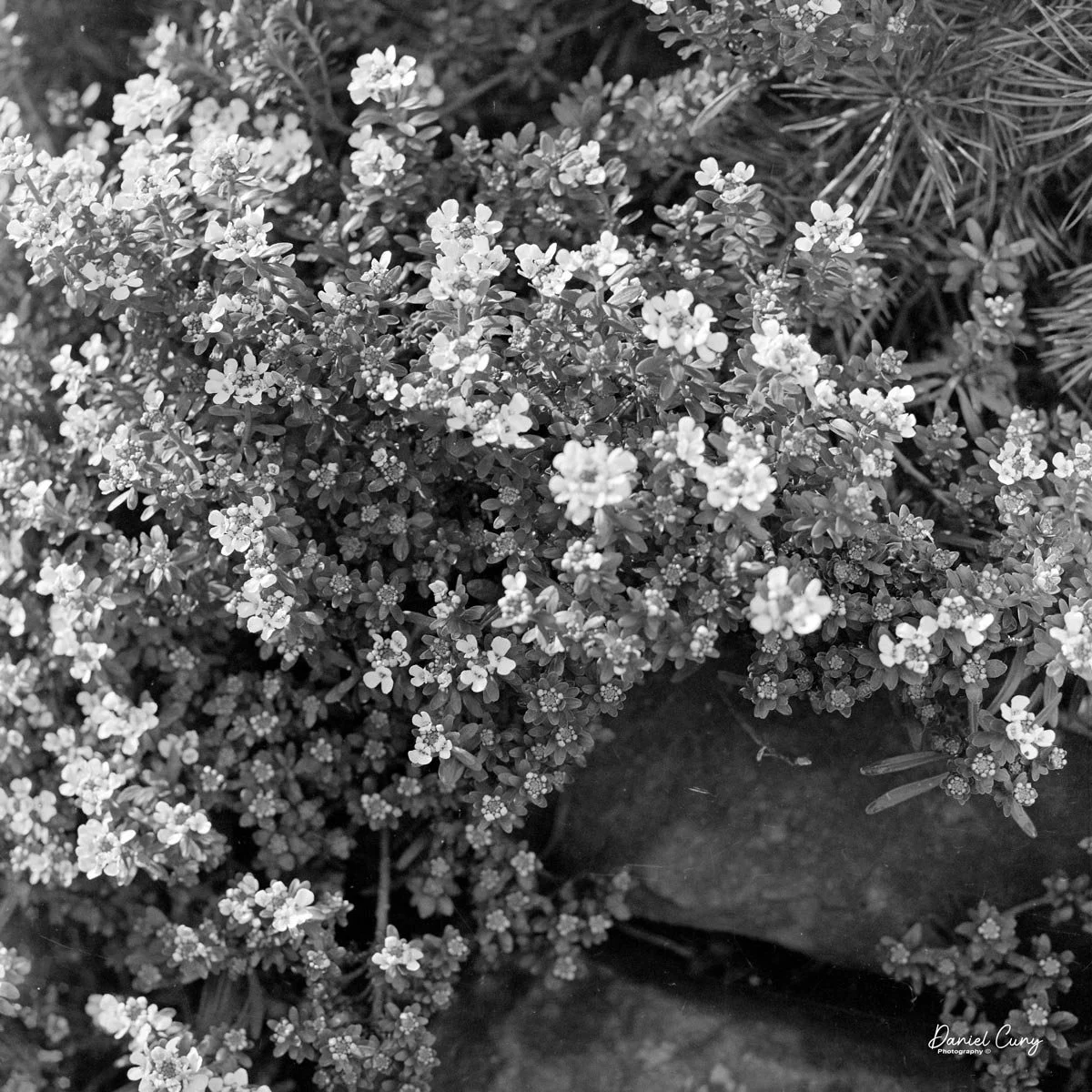
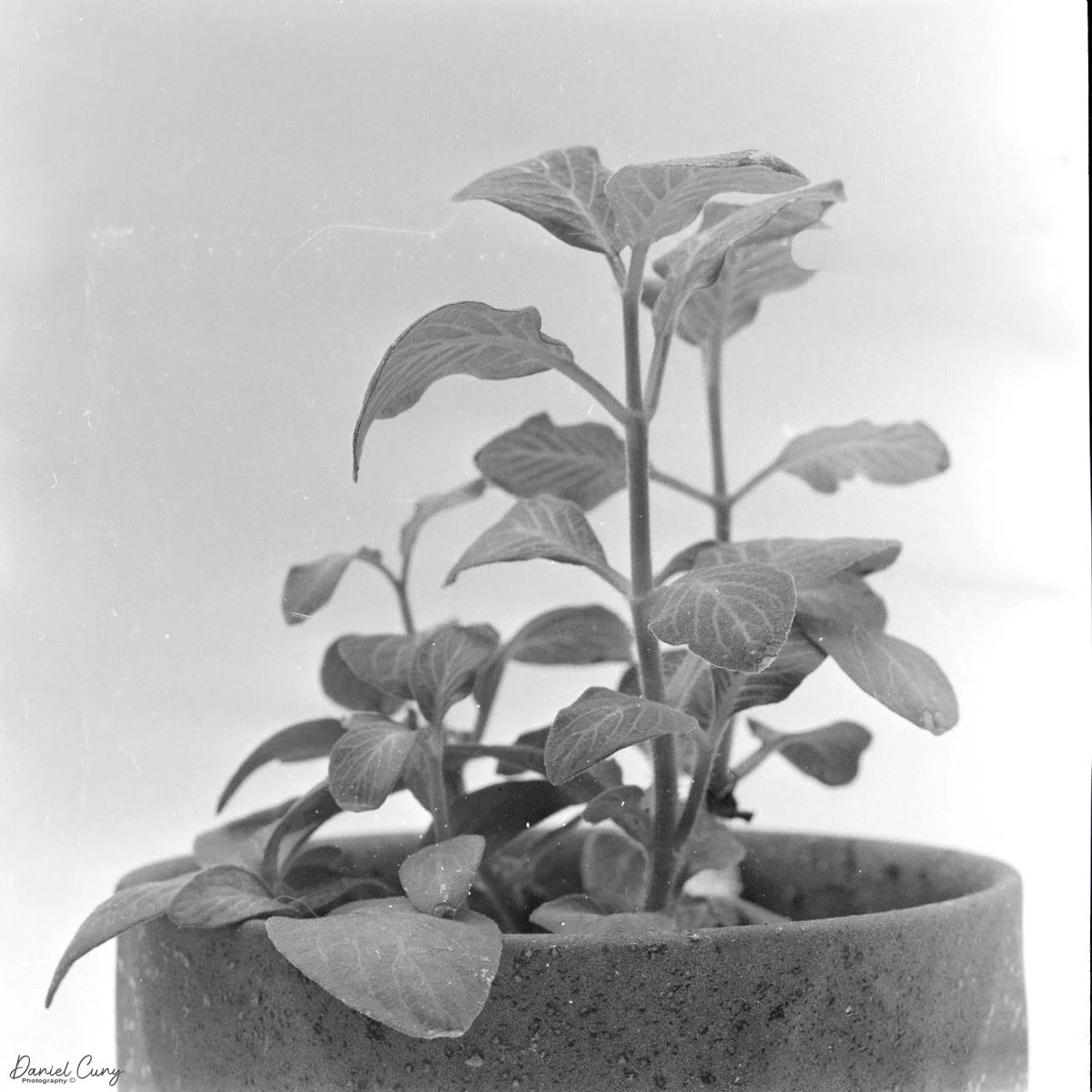
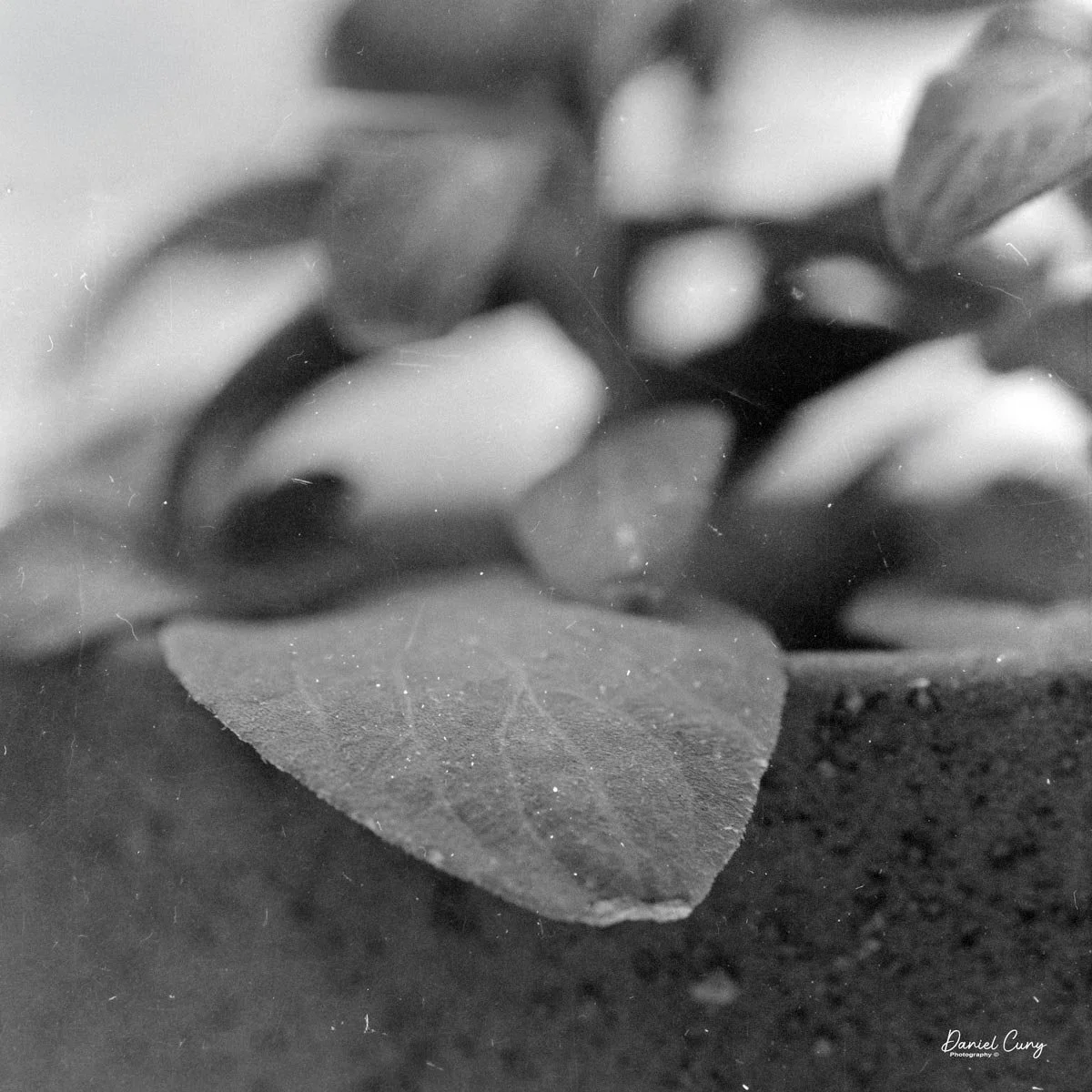
I also pointed the camera at a plant in my office, working closely again. Here, the combination of bellows, tilt, and that Zeiss glass really shone: crisp detail where I wanted it, smooth falloff where I didn't, and a rendering that feels more like a small view camera than a traditional medium‑format SLR. The process is slower than with a modern macro lens and autofocus, but the results—and the experience of making the images—are deeply satisfying.
Conclusion: Is the SL66 the Best Medium‑Format SLR?
In my personal opinion, the Rolleiflex SL66 is the best medium‑format single‑lens reflex camera I've ever used. It isn't the lightest, fastest, or most convenient option, but as a creative tool—especially for close‑up, product, and careful location work—it's truly exceptional.
Why I let it sit so long is beyond me. The camera is a joy to shoot, and the results justify the effort. Small design touches like the dark‑slide holder, the smart film advance on the back, the generous close‑focusing via bellows, and the ability to reverse lenses for even greater magnification all add up to a macro photographer's dream. The overall build quality, leatherwork, and control layout make it feel every bit the premium instrument it was intended to be.
That said, it's important to be honest about the downsides. The SL66 is heavy and bulky compared with many 6×6 systems; accessories and lenses can be harder to find and more expensive than Hasselblad equivalents, and the focal‑plane shutter's 1/30 flash sync may be a deal‑breaker for some styles of studio work. It's also an older, complex mechanical camera, which means a good technician and a healthy maintenance budget are essential.
If you value portability, fast handling, and high sync speeds above all else, there are better choices. But if you're drawn to careful composition, close‑up and tabletop work, and you appreciate a camera that rewards deliberate, thoughtful photography, the Rolleiflex SL66 is tough to beat. It has become one of my favorite medium‑format cameras, and I fully expect it to see regular use.
Thank you for taking the time to learn about my new favorite medium‑format camera. I'd love to hear your experiences with the SL66—or your questions about this or any of my other camera reviews—and if you're curious about owning one yourself, feel free to stop by my eBay store, Cuny's Cameras and Photos, to see what I currently have available.